WASHINGTON (AP) — It's a scenario that terrifies America's auto industry.
Chinese carmakers set up shop in Mexico to exploit North American trade rules. Once in place, they send ultra-low-priced electric vehicles streaming into the United States.
As the Chinese EVs go on sale across the country, America’s homegrown EVs — costing an average of $55,000, roughly double the price of their Chinese counterparts — struggle to compete. Factories close. Workers lose jobs across America's industrial heartland.
Ultimately, it could all become a painful replay of how government-subsidized Chinese competition devastated American industries from steel to solar equipment over the past quarter-century. This time, it would be electric vehicles, which America's automakers envision as the core of their business in the coming decades.
“Time and again, we have seen the Chinese government dump highly subsidized goods into markets for the purpose of undermining domestic manufacturing,’’ Sen. Sherrod Brown, an Ohio Democrat, wrote in an April letter to President Joe Biden that called for an outright ban on Chinese electric vehicles in the U.S. “We cannot let the same occur when it comes to EVs.’’
Low-priced Chinese EVs pose a potentially “extinction-level event’’ for America's auto industry, the Alliance for American Manufacturing has warned.
The trade deal that Beijing could potentially exploit — the U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement — was negotiated by the Trump administration and enacted in 2020. Its rules could let Chinese autos assembled in Mexico enter the United States, either duty-free or at a nominal 2.5% tariff rate. Either way, China could sell its EVs well below typical U.S. prices.
To defuse the threat, the U.S. does have options. Customs officials could rule that Chinese EVs don't qualify for the low-duty or duty-free benefits of being assembled in Mexico. U.S. policymakers could also pressure Mexico to keep Chinese vehicles out of that country. Or they could bar Chinese EVs from the U.S. on the grounds that they would threaten America's national security.
For his part, Donald Trump told Time magazine in April: “I will tariff them at 100%. Because I’m not going to allow them to steal the rest of our business.’’
Whatever steps the U.S. government might take, though, would likely face legal challenges from companies that want to import the Chinese EVs.
The threat from Beijing is emerging just as U.S. automakers face slowing EV sales even while investing billions to produce them in a high-priced bet that Americans will embrace battery-powered autos in the coming decades. Comparatively high prices, despite federal tax incentives for buyers, have weakened EV sales in the United States. So has public anxiety about a scarcity of charging stations, potentially made worse by rising thefts of cables at charging stations.
Optimists suggest that an influx of ultra-low-priced Chinese EVs could accelerate U.S. electric vehicle purchases, speed up investment in charging stations and force down prices.
“It would be cheaper just to let the Chinese cars come in, forget all the tariffs and subsidies, let the market figure it out,’’ said Christine McDaniel, a senior research fellow at George Mason University’s Mercatus Center who was a trade official in the George W. Bush administration. “Yes, it would be disruptive. But EVs would get on the road in the U.S. a lot faster."
At stake is an enormously consequential question: Who stands to dominate the manufacture and sale of zero-emissions electric vehicles?
China has so far taken a daunting lead. It accounted for nearly 62% of the 10.4 million battery-powered EVs that were produced worldwide last year. The United States, at No. 2, made about 1 million — less than 10% of the total, according to the consulting and analysis firm GlobalData.
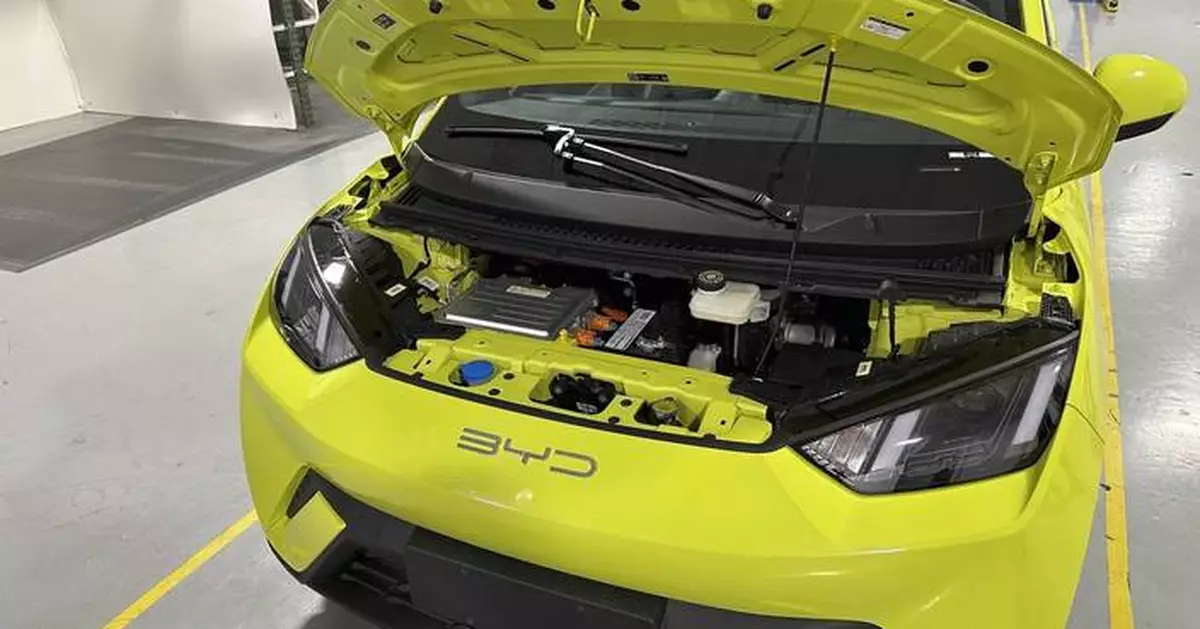
In achieving technological breakthroughs while holding down costs, Chinese automakers have made remarkable strides. China’s BYD last year introduced a small EV called the Seagull that sells for just $12,000 in China ($21,000 for a version sold in some Latin American countries). Considered a marvel of engineering efficiency, its lightweight design allows the Seagull to go farther per charge on a smaller battery. BYD has said it's considering building a factory in Mexico — but only for the Mexican market.
U.S. policymakers and auto companies are less than reassured.
“Just look at China — look at how big their market share is in EVs,’’ John Lawler, Ford Motor’s chief financial officer, said at this month's Deutsche Bank Global Auto Industry Conference. “Those are significant competitive threats we need to deal with. They have a development process that is much faster — 24 months.’’ (By contrast, U.S. vehicles have typically undergone development for four to five years, though that’s been reduced to three years or less for EVs.)
Critics note that BYD and other Chinese EV makers have achieved their cost efficiencies thanks to heavy government subsidies. Beijing spent 953 billion Chinese renminbi (more than $130 billion at current exchange rates) on EVs and other green vehicles from 2009 through 2021, according to researchers at the Center for Strategic and International Studies.
“It’s not competition,’’ Biden asserted last month. “It’s cheating.’’
Last month, Biden drastically raised the tariff on Chinese EVs, from the 27.5% established under Trump to 102.5%. It's meant to price even the bargain-priced BYD Seagull out of the U.S. market. (Europeans are worried, too: The European Union says it plans to impose tariffs of up to 38.1% on Chinese EVs for four months starting in July.)
The U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement, though, potentially lets vehicles assembled in Mexico — even if made by European or Asian automakers — enter the U.S. at a much lower tariff or none at all. If made-in-Mexico cars met the USMCA's requirements, they could enter the United States duty-free. At least 75% of a car and its parts would have to come from North America. And at least 40% of it must originate in places where workers earn at least $16 an hour.
Still, for a Chinese EV maker like BYD, qualifying for duty-free treatment under the USMCA might be difficult even if it tried to source parts in North America.
“Even North American automakers have a challenging time reaching those thresholds," said Daniel Ujczo, senior counsel at the Thompson Hine law firm in Columbus, Ohio.
But there’s an easier way that Chinese EV makers could use Mexico to try to dodge Biden’s killer 102.5% import tax: They would have to pay only 2.5% — the tax imposed on most cars imported to the United States — if they could show that assembling their EVs in Mexico involved a “substantial transformation’’ that essentially turned them from Chinese into Mexican cars.
U.S. officials could reject the notion that a substantial transformation occurred during the assembly process. But the U.S. would struggle to prevail if that decision were challenged in the U.S. Court of International Trade, “given the substantial changes that typically take place in automotive assembly factories,’’ David Gantz, a trade lawyer and a fellow at Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy, has written.
Still, Gantz said by email: “My takeaway is that using one or more of the available trade and national security mechanisms available to the U.S. government, the U.S. will be successful in excluding Mexican/Chinese EVs.’’
The “most effective and quickest’’ way to keep out Chinese EVs, Gantz argues, would be to block them on national security grounds. Today’s EVs, after all, are loaded with cameras, sensors and other technological gizmos that could collect images from the autos’ surroundings and sensitive personal information from drivers. And China isn't merely an economic competitor. It’s a geopolitical adversary — and potentially a military one, too.
“U.S. fears regarding possible use of connected vehicles to spy on military installations or powerplants are not irrational,’’ Gantz wrote.
Biden has even warned that the EVs “could be remotely accessed or disabled.’’ In February, he ordered his Commerce Department to investigate the technology in Chinese "smart cars,' ' a potential prelude to blocking Chinese EVs on national security grounds.
McDaniel of the Mercatus Center argues that the United States has significant leeway to do what it wants — especially given Mexico’s dependence on the U.S., its No. 1 export market.
“You could imagine a scenario where the U.S. tells Mexico: ‘Don’t even think about allowing this (Chinese EV) investment into Mexico,' " she said. ” 'We will not allow those cars into the U.S.’ ’’
“What’s stopping the White House," McDaniel said, "whether it’s right now or the next administration, from just releasing a new document, an executive order, saying, ‘We will no longer recognize products from our USMCA partners if they have more than X percent content from foreign entities of concern, including China' "?
The U.S. has additional leverage because the USMCA comes up for review in 2026. If it seeks to alter the agreement — perhaps adding a provision to ban or limit Chinese EVs from Mexico — but fails to prevail after negotiating with Canada and Mexico, it could let the USMCA expire.
McDaniel noted that the World Trade Organization, which was established to enforce global trade rules, has become largely toothless. The WTO's Appellate Body — its supreme court — effectively stopped functioning in December 2019 because the U.S. blocked the appointment of new judges to the panel. Trade cases now go unresolved indefinitely.
“We’re not in a WTO world anymore,’’ McDaniel said. “It’s ‘might makes right’ — that’s the sort of world we’re in.’’
AP Auto Writer Tom Krisher in Detroit contributed to this report.
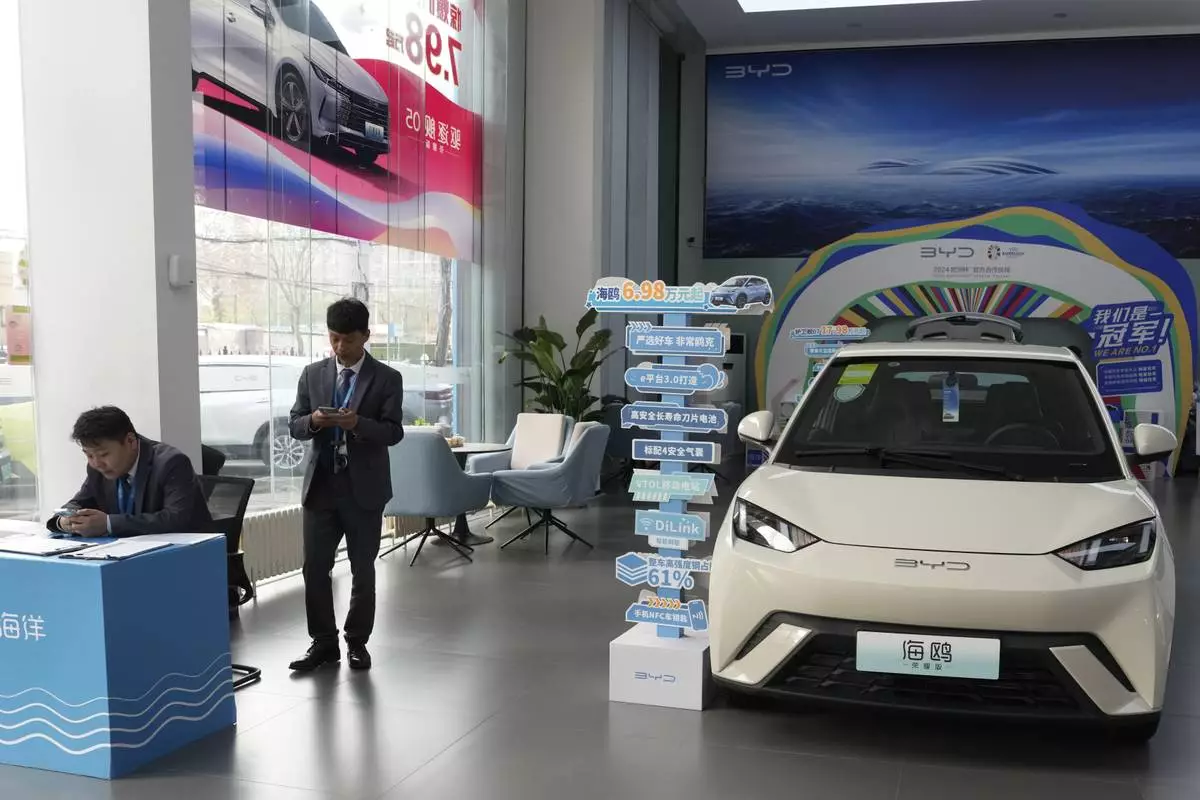

FILE - Sales staff stand near the Seagull electric vehicle from Chinese automaker BYD at a showroom in Beijing on April 10, 2024. Considered a marvel of engineering efficiency, its lightweight design allows the Seagull to go farther per charge on a smaller battery. (AP Photo/Ng Han Guan, File)
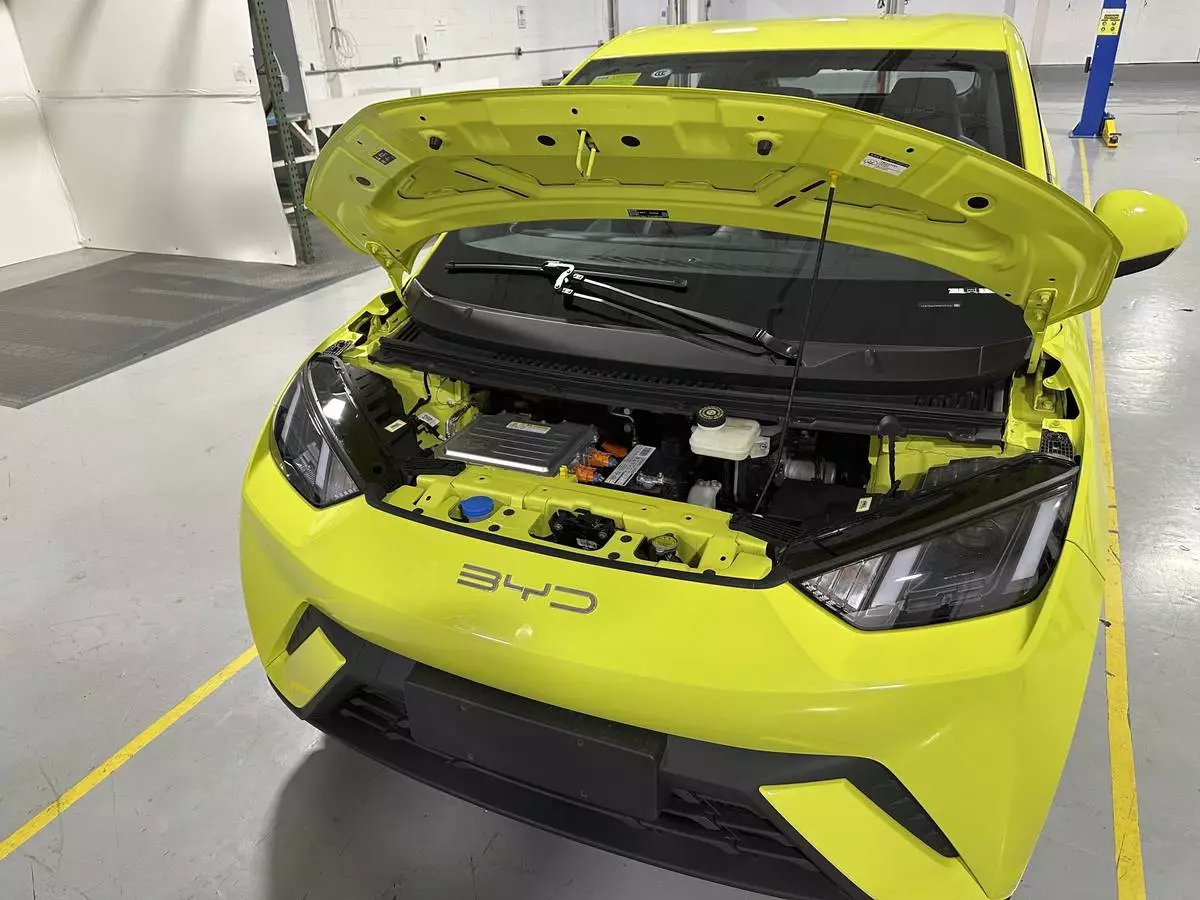

FILE - A BYD Seagull electric vehicle, with its hood open, is shown at the Caresoft Global facility April 3, 2024, in Livonia, Mich. China's BYD last year introduced the Seagull, a small EV that sells for just $12,000 in China. (AP Photo/Mike Householder, File)