BOSTON (AP) — The latest flooding in Vermont has added fresh urgency to concerns about the hundreds of dams in the state, a third of which are more than a century old.
This week’s deluge from the remnants of Hurricane Beryl wasn’t as bad for the hundreds of dams compared to last year’s floods, when five failed and nearly 60 overtopped. But the second bad flood in a year raises concerns about the viability of these structures as climate change brings heavier rains and more powerful storms.
“The many thousands of obsolete dams that remain in our rivers do not provide protection from flooding, despite what many may think,” Andrew Fisk, the northeast regional director for the environmental advocacy group American Rivers, said. "Dams not created specifically for flood protection are regularly full and do not provide storage capacity. And they also frequently direct water outside of the main channel at high velocities which causes bank erosion and impacts to communities."
The challenge facing dams in Vermont is playing out across the country as more dams overtop or fail during heavy rains. The Rapidan Dam, a 1910 hydroelectric dam in Minnesota, was badly damaged last month by the second-worst flood in its history. And in Texas, flooding damaged the Lake Livingston Dam’s spillway about 65 miles (105 kilometers) northeast of Houston.
There are roughly 90,000 significant dams in the U.S. At least 4,000 are in poor or unsatisfactory condition and could kill people or only harm the environment if they failed, according to data from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. They need inspections, upgrades and even emergency repairs.
Like the rest of New England, Vermont has mostly older, small dams built to power textile mills, store water or supply irrigation to farms. The concern is they have outlived their usefulness and climate change could bring storms they were never built to withstand.
The floods last year in Vermont drew outsized attention to dams mostly due to the failures and near failures. In the capital Montpelier, a dam was at risk of sending water over the emergency spillway and through parts of the town. The National Inventor of Dams, a database regulated by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, lists 372 dams in the state, with 62 rated as high hazard, which means lives could be lost if the dam fails. Ten of those were rated in poor condition, which means remedial action is necessary.
State officials say they actually regulate 417 dams and that there are hundreds more too small and of minimal hazard to be regulated.
The storms last year led to a rapid inspection of all the state's dams, with more than $1.5 million spent to stabilize and repair storm damage.
“The team had never been faced with a situation of, you know, 8 inches of widespread rain across essentially the entire state of Vermont,” Neil Kamman, the director of the Water Investment Division in the Vermont Department of Environmental Conservation, said. “It stressed all of the facilities that the state of Vermont owns and that the dam safety team manages but filled up hundreds of dams, caused the failures that you know about and created a whole bunch of unknown uncertainties out there on the landscape in terms of downstream risk due to, you know, prospective dams having been destabilized.”
In response, the legislature approved the hiring of four staffers in the dam safety program, bringing the total to nine, and allocated an additional $4 million to a dam safety program, up from $200,000. That money can be used for emergency risk reduction, restoration or removal of dams.
This time around, dam safety officials said the damage has been minimal. No dams are believed to have failed and only one dam — Harvey’s Lake in Barnet, which is classified as a low hazard structure — overtopped. But even in that case, there was not likely to be any significant impact to property nor the nearby roadways, officials said.
Julie Moore, secretary of the Vermont Agency of Natural Resources, said during a news conference Friday that inspections found that Winooski River Valley flood control reservoir “continue to do their job well” and that levels at the Waterbury Reservoir “are stabilizing with plenty of storage remaining.” Those dams and the East Barre Dam are critical to flood control in an area that stretches from Barre to Essex.
She also said that officials had completed inspections at “seven particularly at risk” dams in the northern part of the state and that “no damage was identified.”
The floods this year came too soon for the additional money and staffing to have an impact. But Kamman said the experience of responding to last year's flood helped shaped a more robust response from the team this time around.
“The biggest difference between the response this year and last year is the fact that we had the game plan worked out for a widespread event that would stress a large number of facilities all at once," he said.
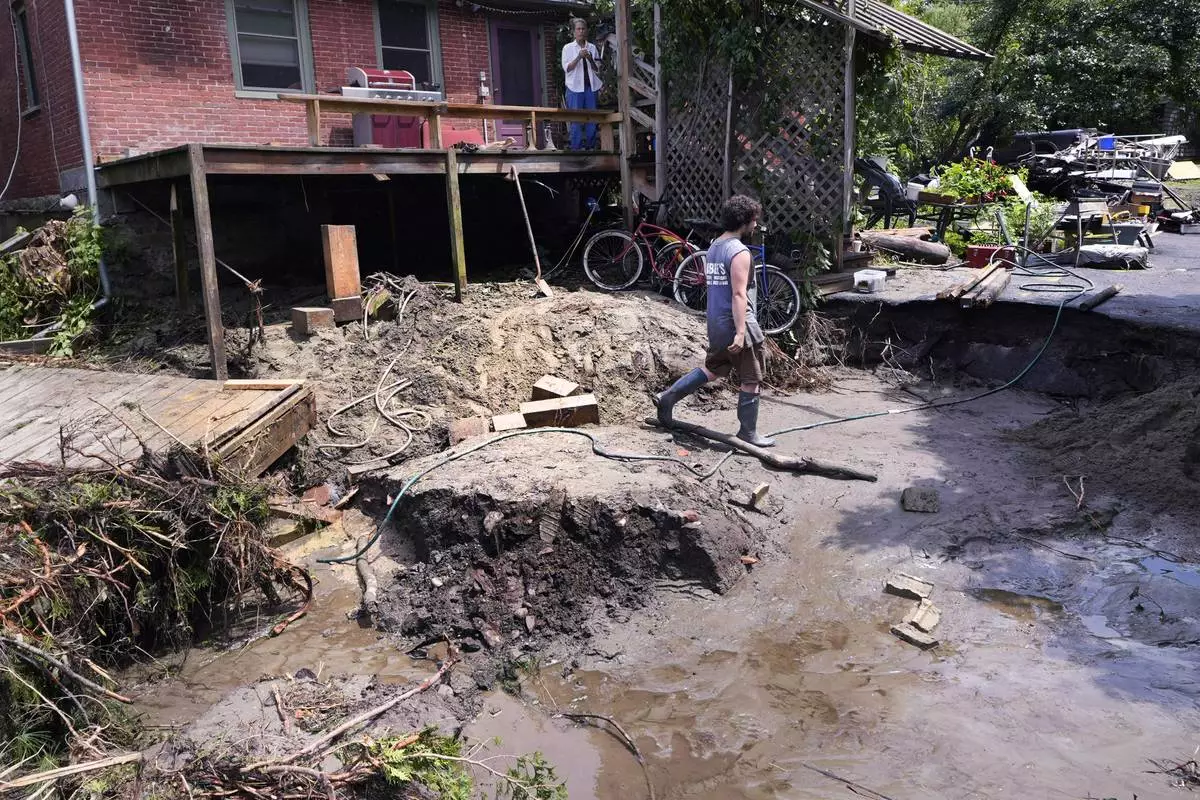

August Thompson walks over the washed out remains of the road in front of his grandfather's home after remnants of Hurricane Beryl caused flooding and destruction, Friday, July 12, 2024, in Plainfield, Vt. (AP Photo/Charles Krupa)
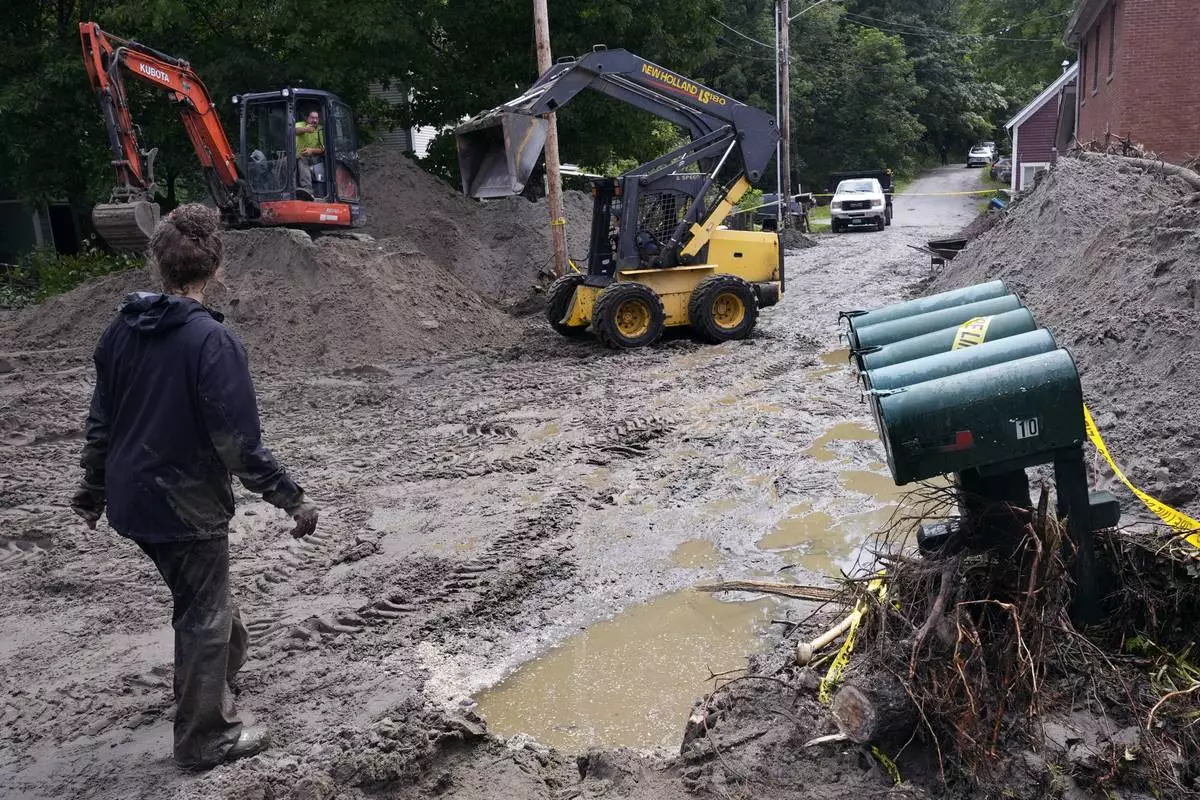

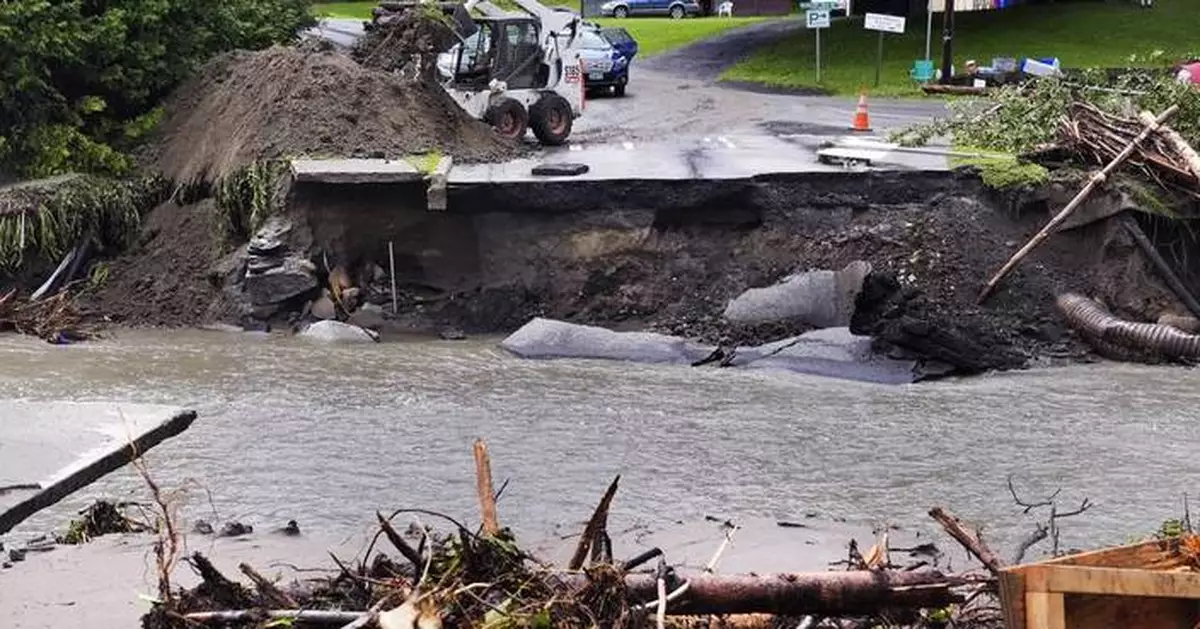
An excavator and loader clear Hudson Avenue of mud after remnants of Hurricane Beryl caused flooding and destruction, Friday, July 12, 2024, in Plainfield, Vt. (AP Photo/Charles Krupa)
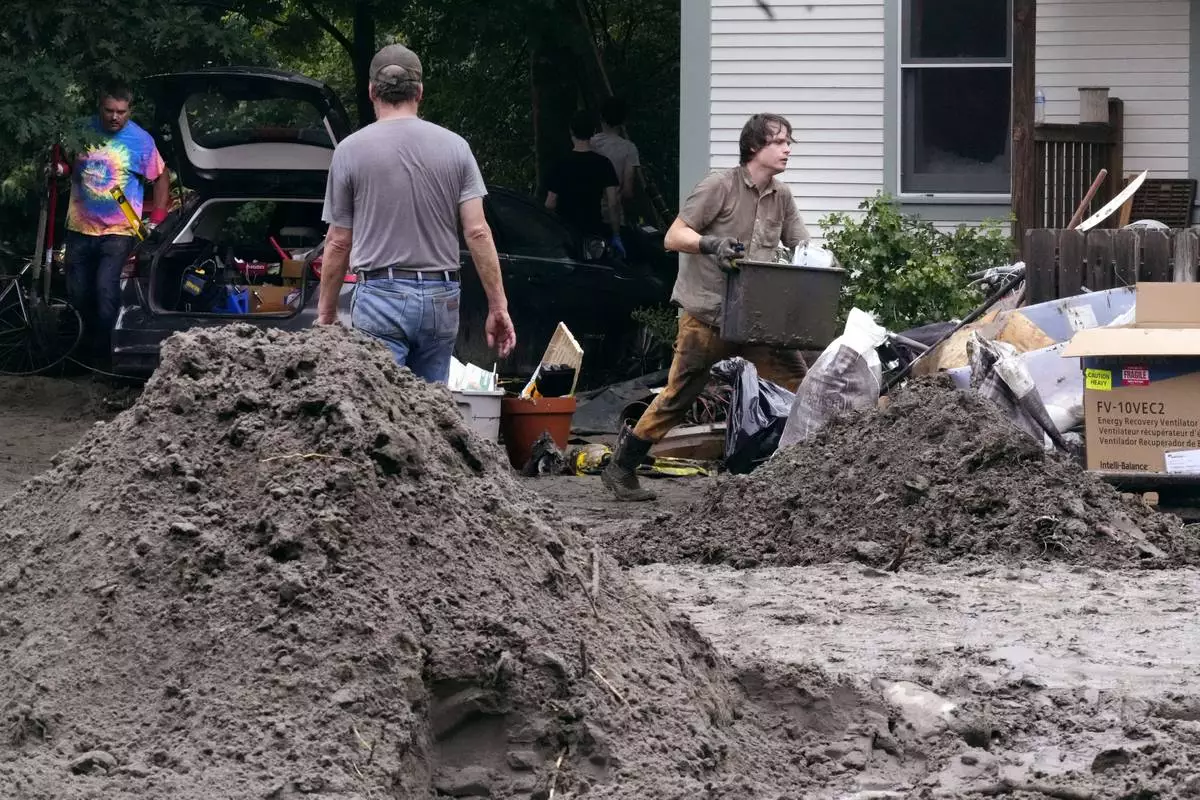

Walker Blackwell, right, cleans up the damage to his home after remnants of Hurricane Beryl caused flooding and destruction, Friday, July 12, 2024, in Plainfield, Vt. (AP Photo/Charles Krupa)
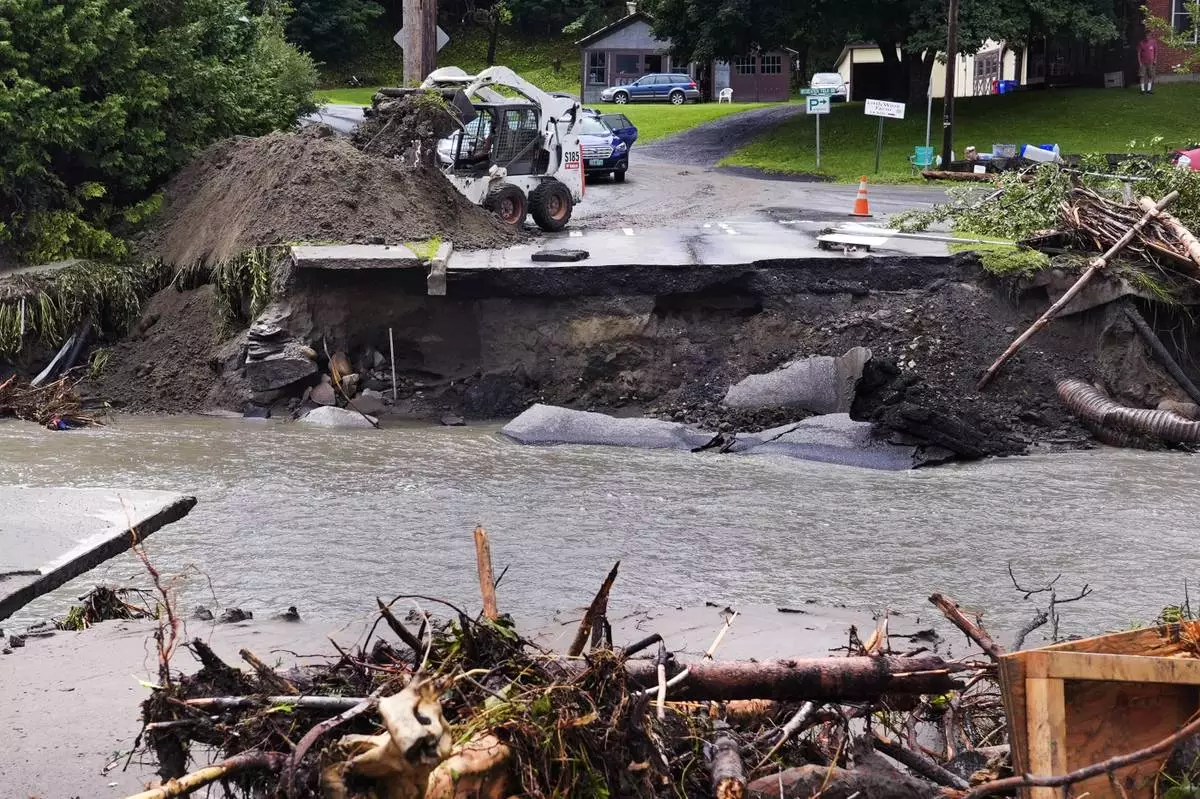

A loader dumps dirt along a washed out portion of Mill Street after remnants of Hurricane Beryl caused flooding and destruction, Friday, July 12, 2024, in Plainfield, Vt. (AP Photo/Charles Krupa)