UNITED NATIONS (AP) — Nearly 40 million people were living with the HIV virus that causes AIDS last year, over 9 million weren’t getting any treatment, and the result was that every minute someone died of AIDS-related causes, the U.N. said in a new report launched Monday.
While advances are being made to end the global AIDS pandemic, the report said progress has slowed, funding is shrinking, and new infections are rising in three regions: the Middle East and North Africa, Eastern Europe and Central Asia, and Latin America.
In 2023, around 630,000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses, a significant decline from the 2.1 million deaths in 2004. But the latest figure is more than double the target for 2025 of fewer than 250,000 deaths, according to the report by UNAIDS, the U.N. agency leading the global effort to end the pandemic.
Gender inequality is exacerbating the risks for girls and women, the report said, citing the extraordinarily high incidence of HIV among adolescents and young women in parts of Africa.
The proportion of new infections globally among marginalized communities that face stigma and discrimination – sex workers, men who have sex with men, and people who inject drugs also increased to 55% in 2023 from 45% in 2010, it said.
UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima said: “World leaders pledged to end the AIDS pandemic as a public health threat by 2030, and they can uphold their promise, but only if they ensure that the HIV response has the resources it needs, and that the human rights of everyone are protected.”
As part of that pledge, leaders vowed to reduce annual new HIV infections to below 370,000 by 2025, but the report said in 2023 new infections were more than three times higher at 1.3 million.
Last year, among the 39.9 million people globally living with HIV, 86% knew they were infected, 77% were accessing treatment, and for 72% the virus was suppressed, the report said
César Núñez, director of the UNAIDS New York office, told a news conference there has been progress in HIV treatments — injections that can stay in the body for six months, but the two doses cost $40,000 yearly, out of reach for all but the richest people with the virus.
He said UNAIDS has been asking the manufacturer to make it available at lower cost to low and middle-income countries.
Núñez said there have also been seven cases where people with HIV who were treated for leukemia emerged with no sign of the HIV virus in their system.
He said injections and the seven cases will be discussed at the 25th International AIDS Conference which began Monday in Munich.
At present, he said, daily treatment with pills costs about $75 per person per year. It has allowed many countries to increase the number of people with HIV to receive treatment.
Núñez said UNAIDS will continue advocating for a vaccine to prevent AIDS.
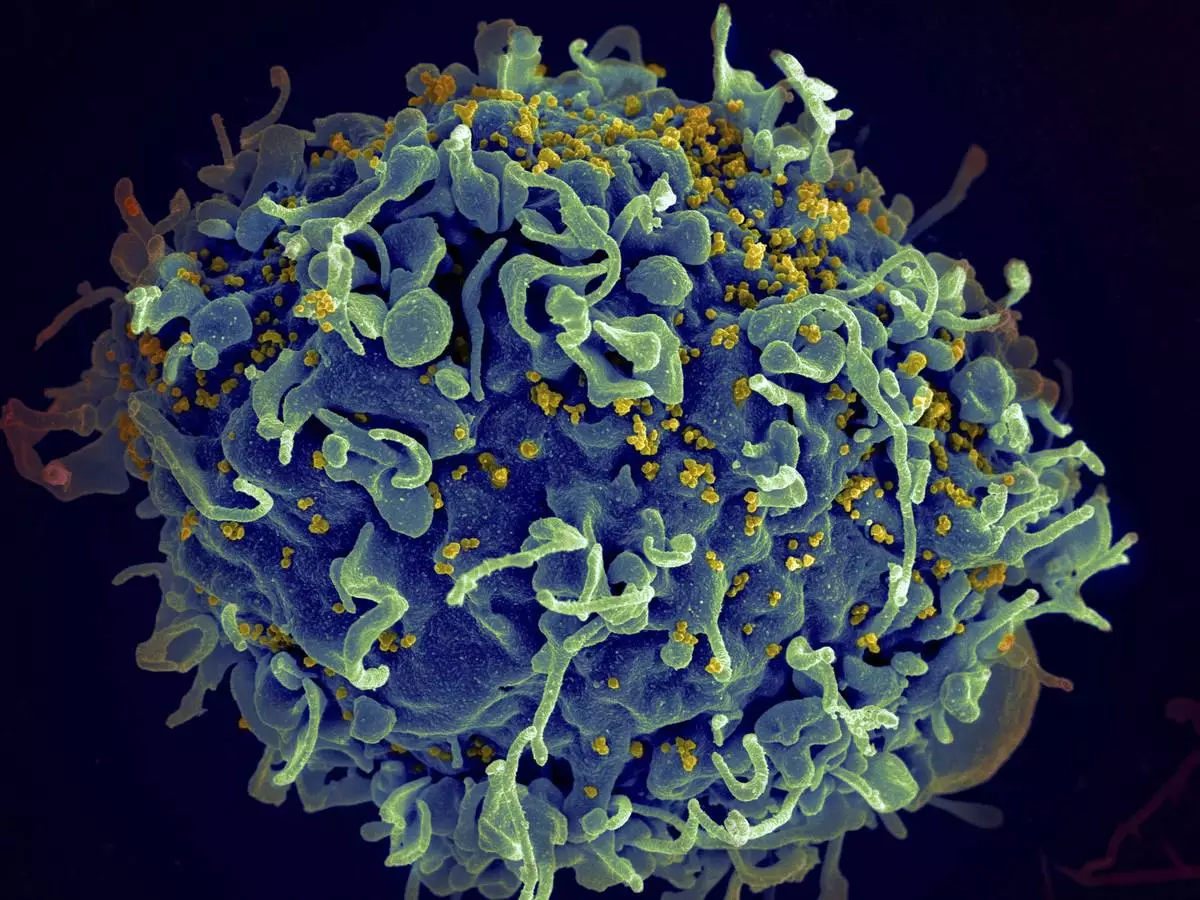
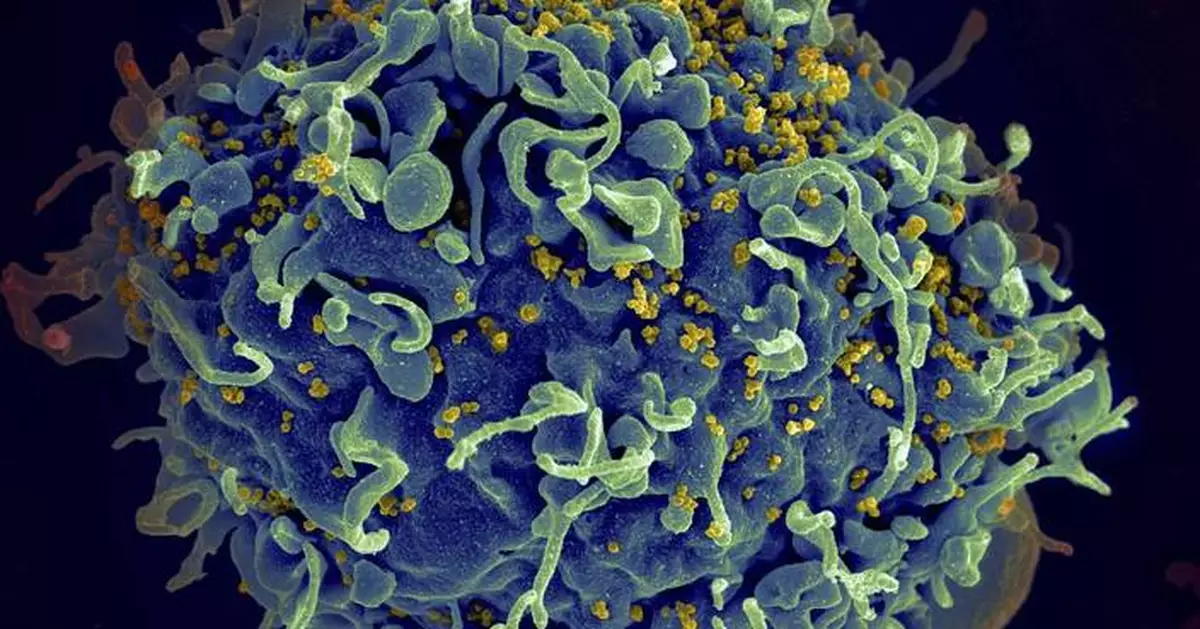
FILE - This electron microscope image made available by the U.S. National Institutes of Health shows a human T cell, in blue, under attack by HIV, in yellow, the virus that causes AIDS. (Seth Pincus, Elizabeth Fischer, Austin Athman/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/NIH via AP, File)
TEL AVIV, Israel (AP) — Israeli aircraft struck Hezbollah weapons smuggling sites along Syria's border with Lebanon, the Israeli military said Saturday, testing a fragile, days-old ceasefire that halted months of fighting between the sides but has seen continued sporadic fire.
The military said it struck sites that had been used to smuggle weapons from Syria to Lebanon after the ceasefire took effect, which the military said was a violation of its terms. There was no immediate comment from Syrian authorities or activists monitoring the conflict in that country. Hezbollah also did not immediately comment.
The Israeli strike, the latest of several since the ceasefire began on Wednesday, came as unrest spread to other areas of the Middle East, with Syrian insurgents breaching the country's largest city, Aleppo, in a shock offensive that added fresh uncertainty to a region reeling from multiple wars.
The truce between Israel and the Iran-backed Hezbollah, brokered by the United States and France, calls for an initial two-month ceasefire in which the militants are to withdraw north of Lebanon's Litani River and Israeli forces are to return to their side of the border.
The repeated bursts of violence — with no reports of serious casualties — reflected the uneasy nature of the ceasefire that otherwise appeared to hold. While Israel has accused Hezbollah of violating the ceasefire, Lebanon has also accused Israel of the same in the days since it took effect.
Many Lebanese, some of the 1.2 million displaced in the conflict, were streaming south to their homes, despite warnings by the Israeli and Lebanese militaries to stay away from certain areas.
Lebanon’s state-run National News Agency reported that an Israeli drone attacked a car in the southern village of Majdal Zoun. The agency said there had been casualties but gave no further details. Majdal Zoun, near the Mediterranean Sea, is close to where Israeli troops still have a presence.
The military said earlier Saturday that its forces, who remain in southern Lebanon until they withdraw gradually over the 60-day period, had been operating to distance “suspects” in the region, without elaborating, and said troops had located and seized weapons found hidden in a mosque.
Israel says it reserves the right under the ceasefire to strike against any perceived violations. Israel has made returning the tens of thousands of displaced Israelis home the goal of the war with Hezbollah but Israelis, concerned Hezbollah was not deterred and could still attack northern communities, have been apprehensive about returning home.
Hezbollah began attacking Israel on Oct. 8, 2023, in solidarity with the Palestinian militant group Hamas and its assault on southern Israel the day before. Israel and Hezbollah kept up a low-level conflict of cross-border fire for nearly a year, until Israel escalated its fight with a sophisticated attack that detonated hundreds of pagers and walkie-talkies used by Hezbollah fighters. It followed that up with an intense aerial bombardment campaign against Hezbollah assets, killing many of its top leaders including longtime chief Hassan Nasrallah, and it launched a ground invasion in early October.
More than 3,760 people have been killed by Israeli fire in Lebanon during the conflict, many of them civilians, according to Lebanese health officials. The fighting killed more than 70 people in Israel — over half of them civilians — as well as dozens of Israeli soldiers fighting in southern Lebanon.
Mroue reported from Beirut.
Follow AP’s war coverage at https://apnews.com/hub/israel-hamas-war
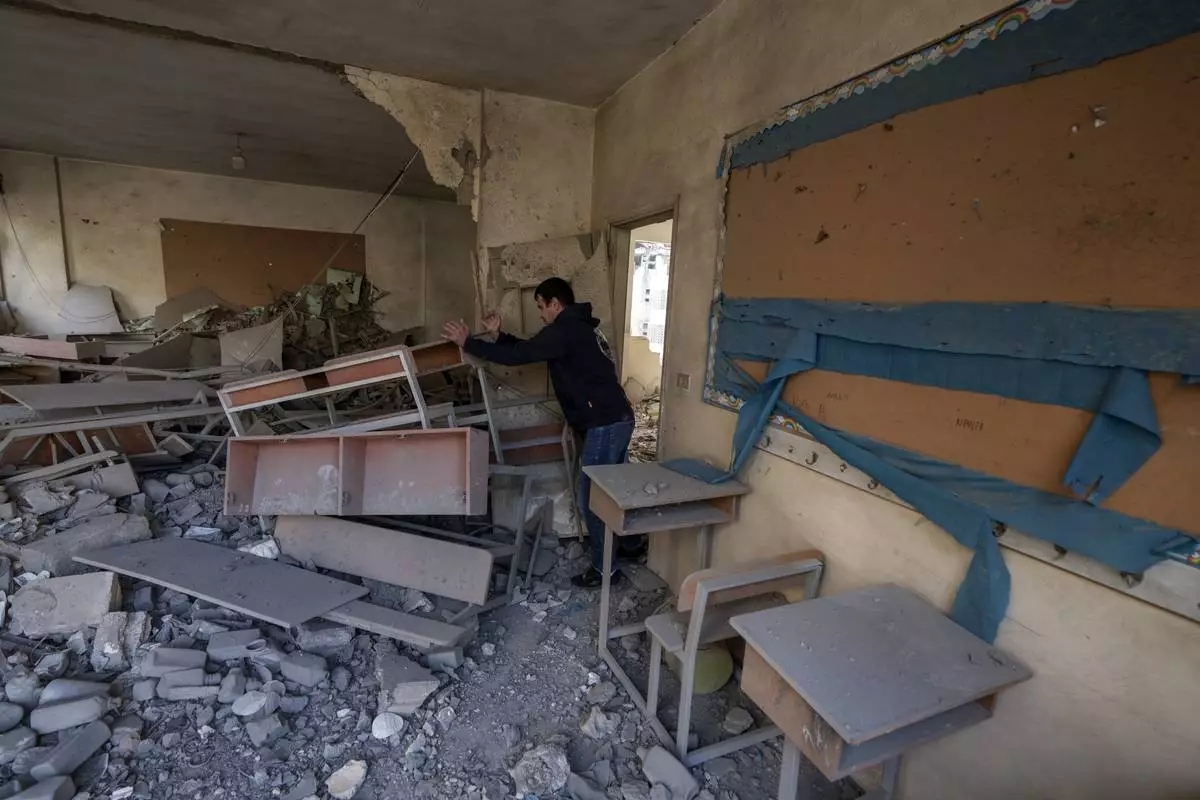

Teacher Ahmed Awada inspects his school that was damaged by an Israeli airstrike in Dahiyeh, Beirut, Lebanon, Friday, Nov. 29, 2024. (AP Photo/Bilal Hussein)
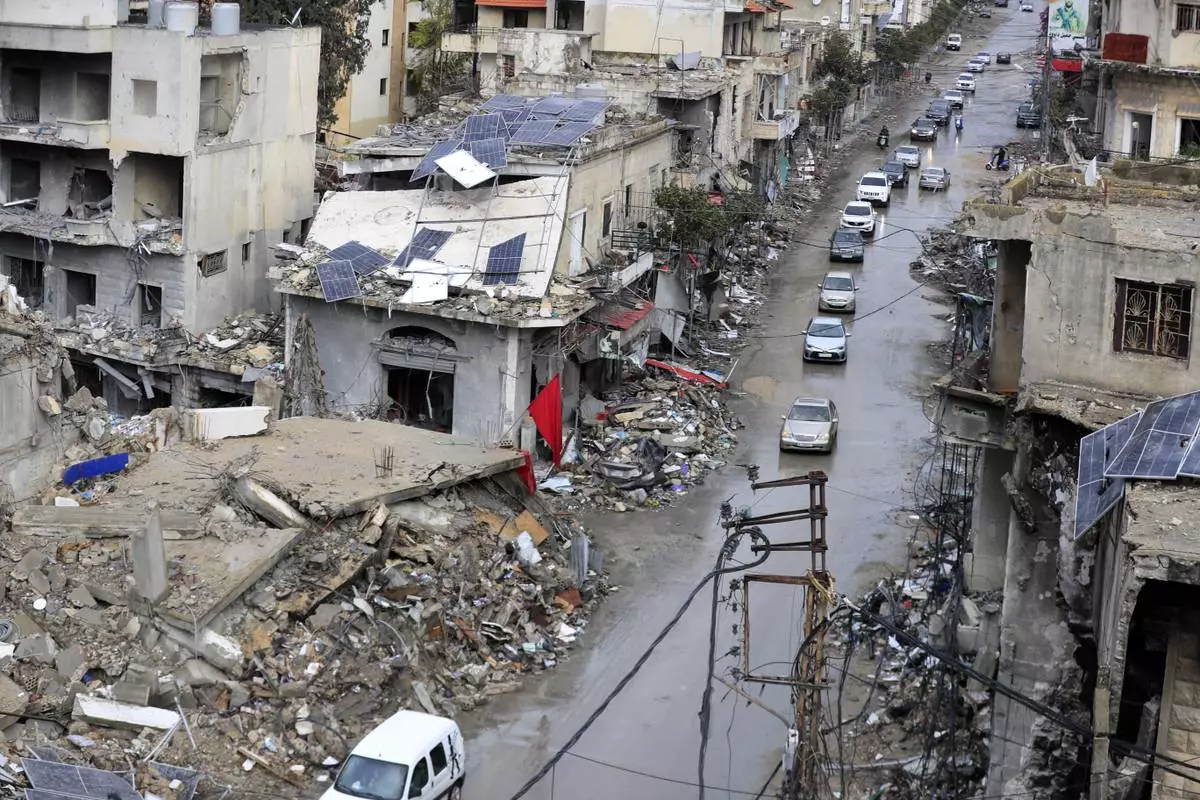

Displaced residents drive past destroyed buildings as they return to Nabatiyeh, Lebanon, after a ceasefire between Israel and Hezbollah went into effect on Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Mohammed Zaatari)
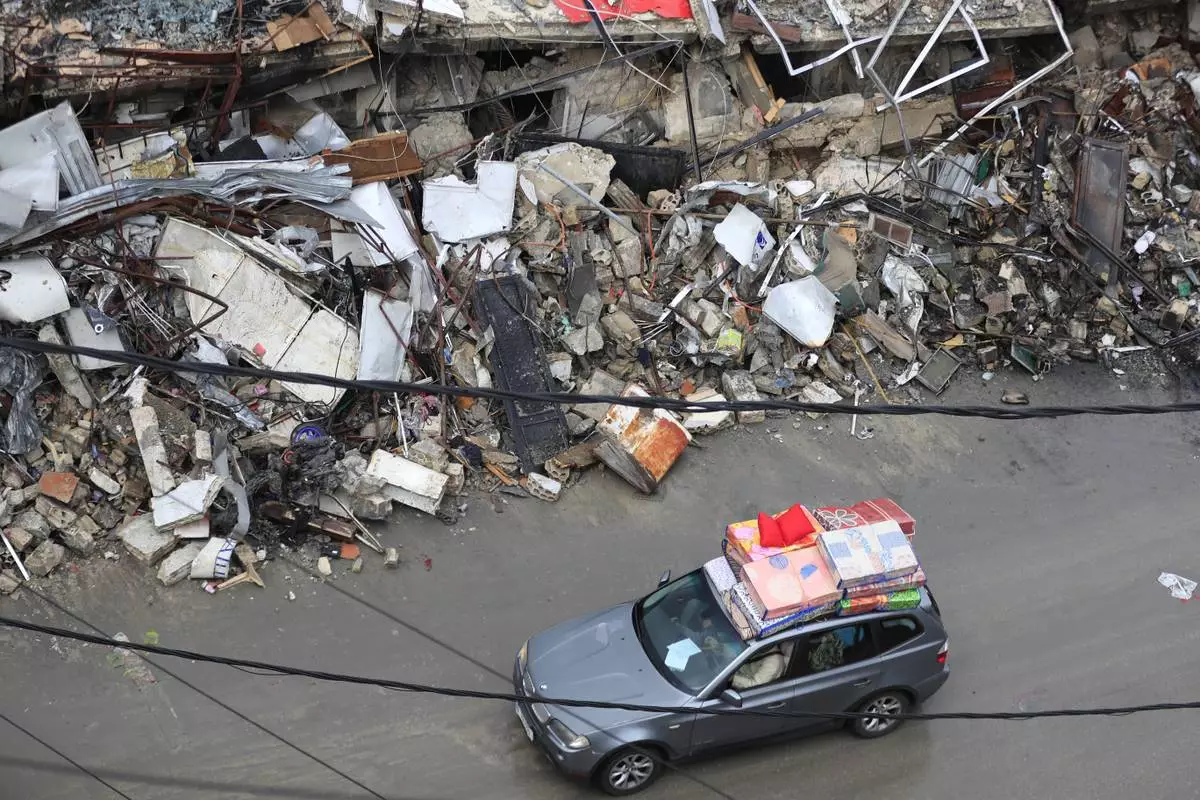

Displaced residents drive past destroyed buildings as they return to Nabatiyeh, Lebanon, after a ceasefire between Israel and Hezbollah went into effect on Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Mohammed Zaatari)
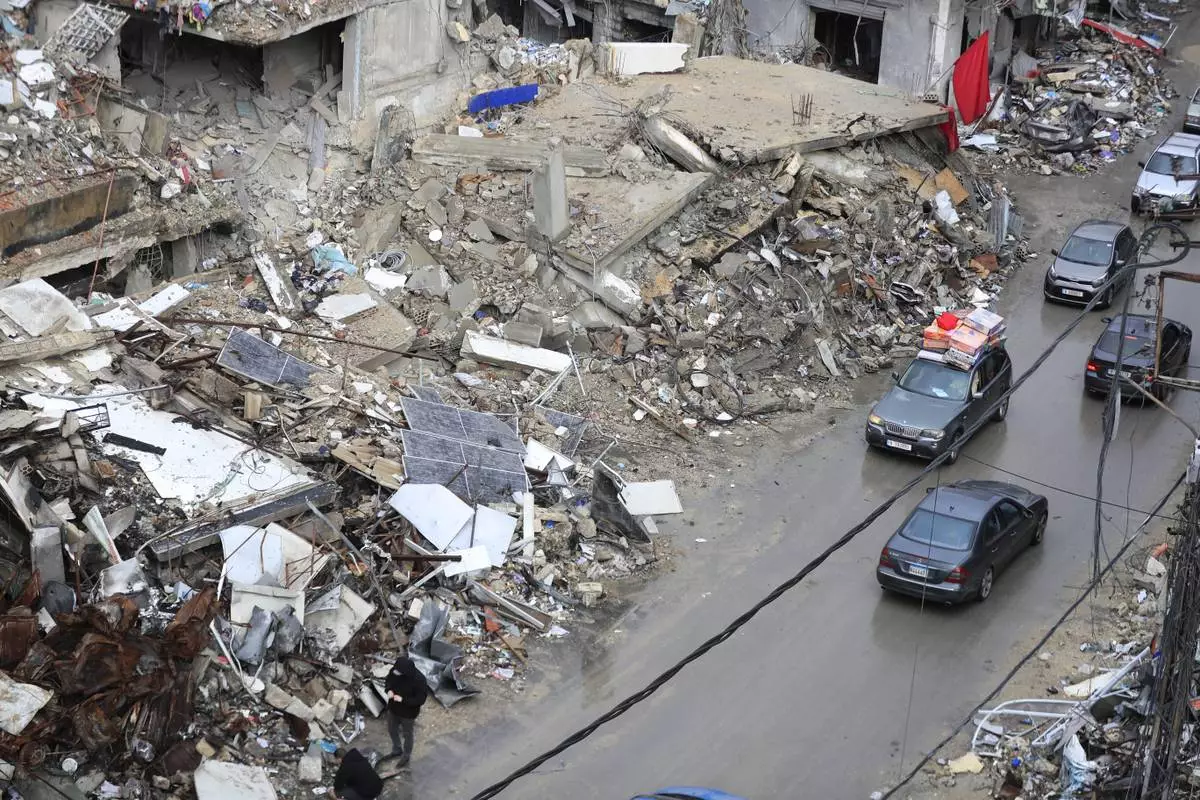

Displaced residents drive past destroyed buildings as they return to Nabatiyeh, Lebanon, after a ceasefire between Israel and Hezbollah went into effect on Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Mohammed Zaatari)
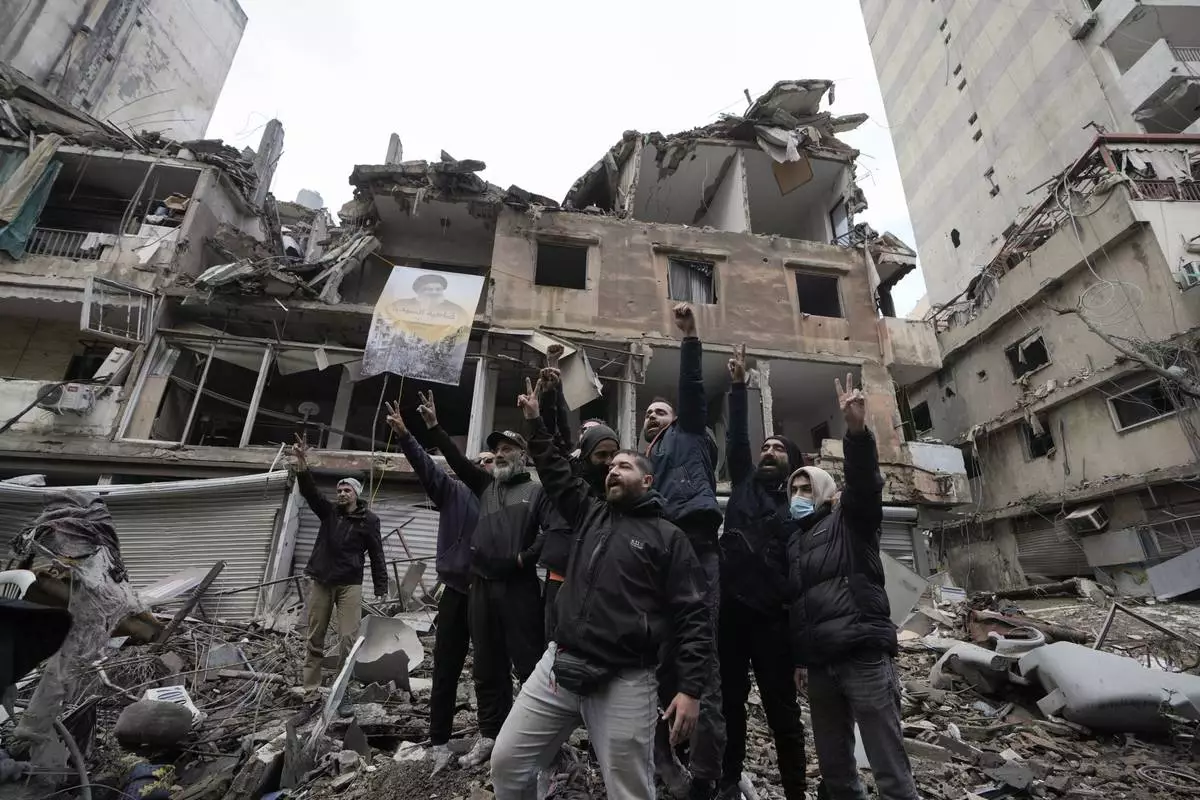

Hezbollah supporters cheer as they return to Dahiyeh, in Beirut, Lebanon, following a ceasefire between Israel and Hezbollah that went into effect on Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Bilal Hussein)
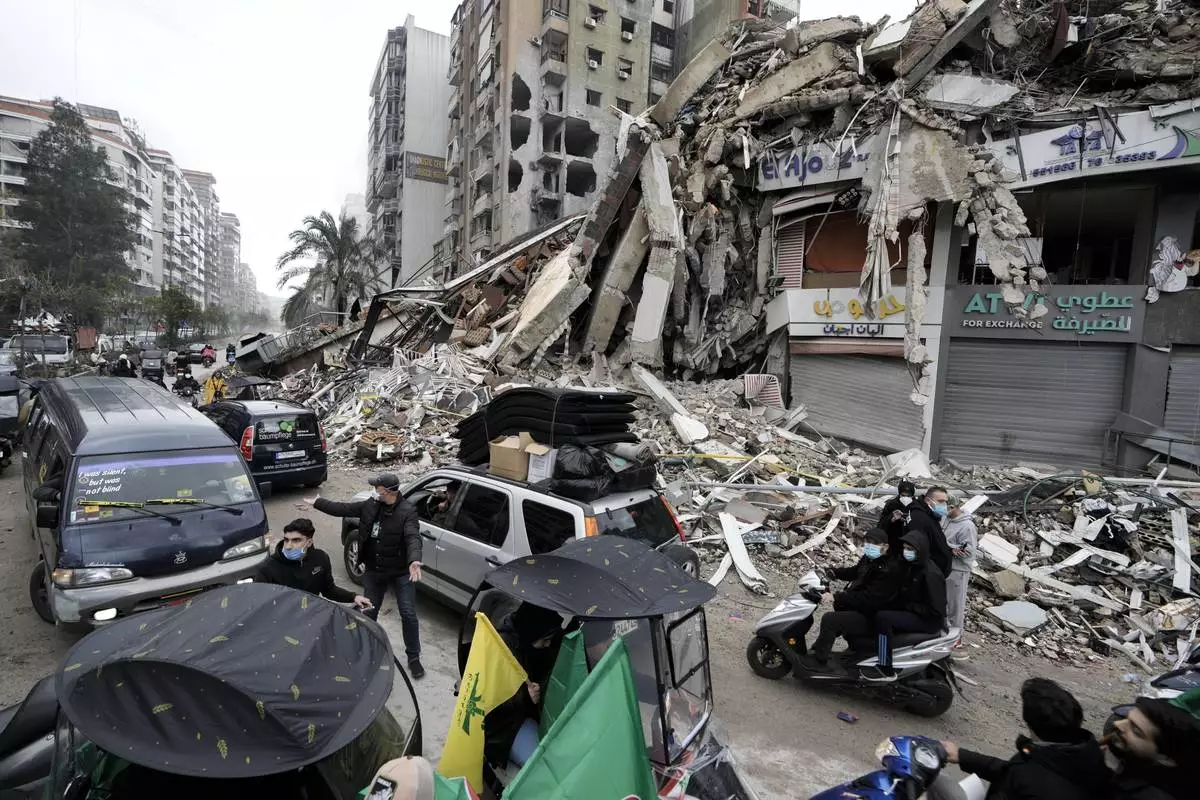

Displaced residents return to Dahiyeh, in Beirut, Lebanon, following a ceasefire between Israel and Hezbollah that went into effect on Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Bilal Hussein)
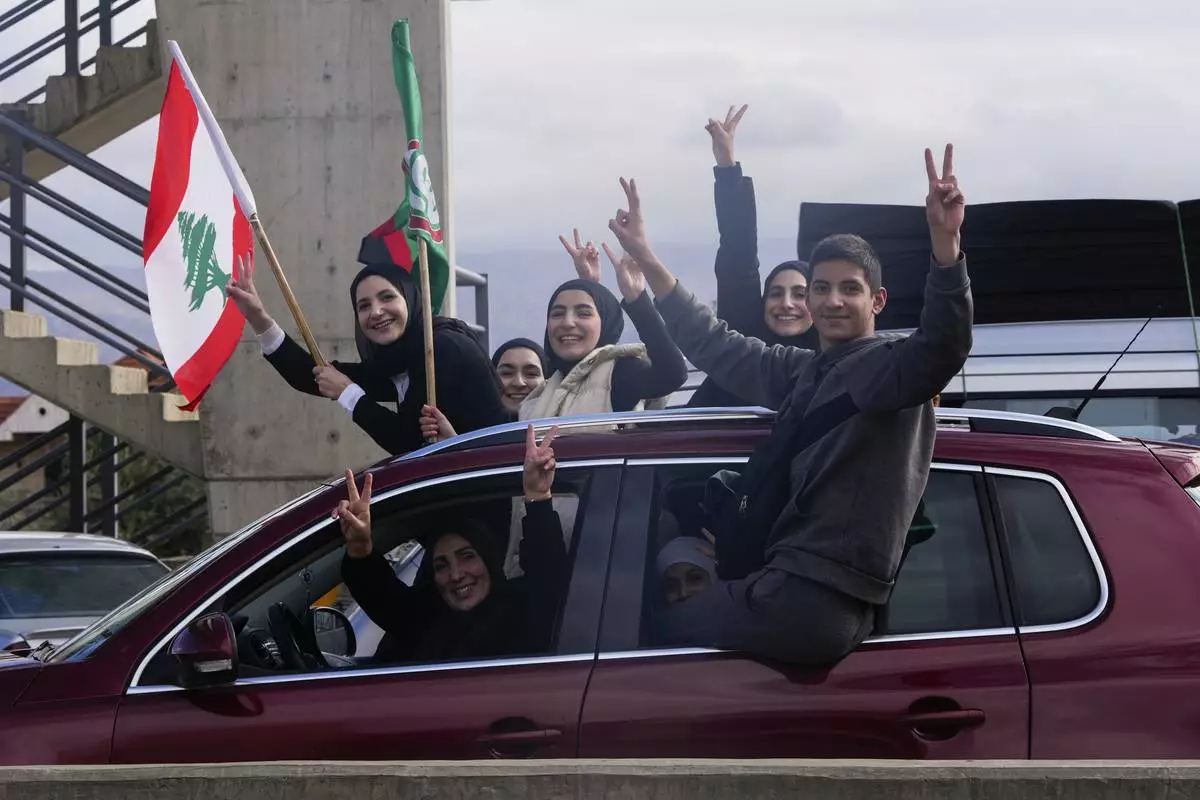

Displaced residents celebrate as they return to their villages following a ceasefire between Israel and Hezbollah that went into effect on Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024, in Ablah, eastern Lebanon. (AP Photo/Hassan Ammar)