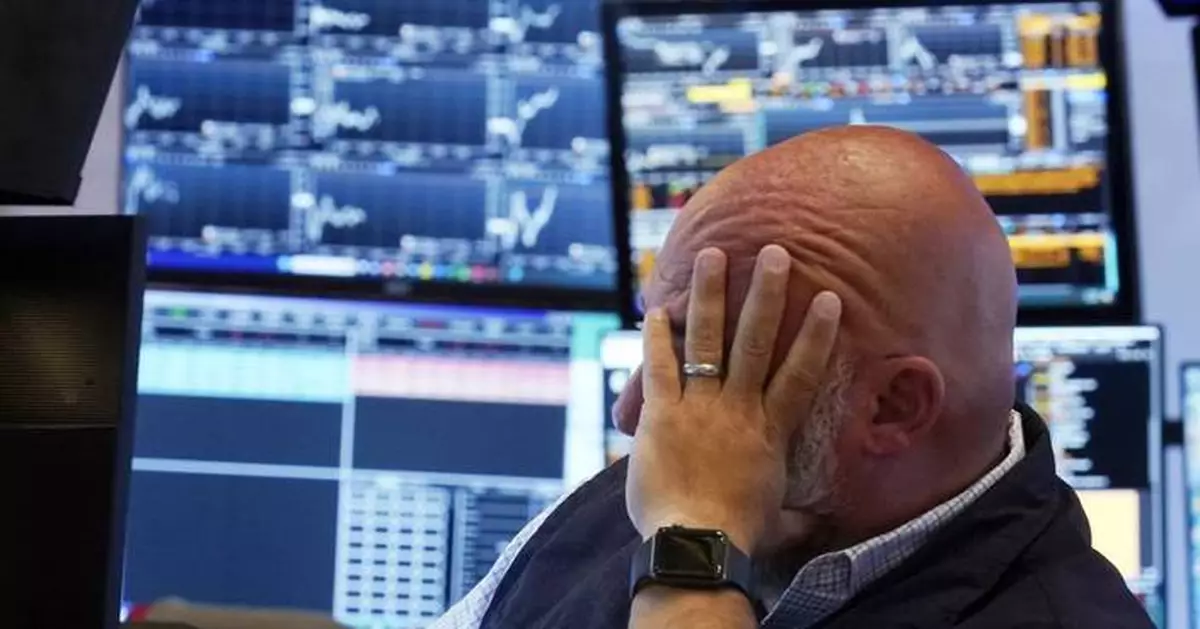
NEW YORK (AP) — Markets on Wall Street and around the world are in a mini-panic. Worried about a slowing U.S. economy, investors sent the market in Japan to its worst day in decades and have sliced billions in market value off some of the world’s biggest technology companies. They’ve turned a relatively calm year in markets on its head.
For most of the year, investors worldwide drove stock markets higher, convinced that central banks were successfully, if haltingly, getting inflation under control, and buoyed by a healthy U.S. economy and the promise of artificial intelligence.
That confidence has taken a hit the past few days. Weak readings on the job market, manufacturing and construction last week sparked worries about a U.S. economic slowdown and criticism that the Federal Reserve waited too long to cut rates. Meanwhile, the Bank of Japan raised rates, causing turmoil in Japan’s markets. On Monday, the Nikkei plunged more than 12%, its worst drop since 1987.
Investors are now listening to warnings that Apple, Nvidia and other Big Tech stocks have gotten too expensive. On Friday, the tech-heavy Nasdaq composite went into a correction, which is a 10% decline from its most recent high. It dropped an additional 3,4% Monday.
Traders in the U.S. are betting the Federal Reserve will lower rates by half a percentage point in September instead of the usual quarter point. Some are calling for an emergency rate cut. The heaviest selling has been in small companies that make most if not all their sales and profits in the U.S. Prices for oil and other commodities fell because of the economic worries.
However, there are opposing voices saying the sell-off is a good thing because stock prices had risen too high. For individual investors, it’s not time for rash decisions, but a moment to make sure their investments are properly diversified, experts say.
Here’s a look at what’s driving the turbulence in markets:
Starting in 2022, the Fed rapidly raised interest rates to combat a spike in inflation. It’s maintained its key rate at 5.4% for about a year. As part of its inflation fight, the Fed also aimed to cool down a red-hot labor market.
Investors thought the Fed and other central banks were on track, even though inflation remained somewhat above their targets — in the Fed’s case, 2%. The European Central Bank and the Bank of England cut rates once and the Fed signaled it was prepared to start cutting rates in September.
Despite some signs of cooling, the U.S. economy kept chugging along even with higher rates, outpacing Europe and Asia. Then came last week’s economic reports.
Weak reports on manufacturing and construction were followed by the government’s monthly report on the job market, which showed a significant slowdown in hiring by U.S. employers. Worries that the Fed may have kept the brakes on the economy too long spread through the markets.
A handful of Big Tech stocks drove the market’s double-digit gains into July. But their momentum turned last month on worries investors had taken their prices too high and expectations for their profit gains had grown too difficult to meet -- a notion that gained credence when the group’s latest earnings reports were mostly underwhelming.
Apple fell more than 5% Monday after Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway disclosed that it had slashed its ownership stake in the iPhone maker. Nvidia lost more than $420 billion in market value Thursday through Monday. Overall, the tech sector of the S&P 500 was the biggest drag on the market Monday.
The Nikkei suffered its worst two-day decline ever, dropping 18.2% on Friday and Monday combined. One catalyst for the outsized move has been an interest rate hike by the Bank of Japan last week.
The BoJ’s rate increase affected what are known as carry trades. That's when investors borrow money from a country with low interest rates and a relatively weak currency, like Japan, and invest those funds in places that will yield a high return. The higher interest rates, plus a stronger Japanese yen, may have forced investors to sell stocks to repay those loans.
The prevailing wisdom is: Hold steady.
Experts and analysts encourage taking a long view, especially for investors concerned about retirement savings,.
“More often than not, panic selling on a red day is generally a great way to lose more money than you save,” said Jacob Channel, senior economist for LendingTree, who reminds investors that markets have recovered from worse sell-offs than the current one.
As of 4 p.m. Monday, the price of the world’s largest cryptocurrency was just above $54,000 — down from nearly $68,000 one week ago, per data from CoinMarketCap.
While bitcoin did serve as a safe haven of sorts during the worst of the pandemic, it mostly acts like any another risky asset that investors steer clear from during market downturns.
Greg McBride, financial analyst for Bankrate, points out that a 10% pullback in markets happens on average once every 12 months. The S&P 500 is down about 8.5% from its recent high.
Chris Zaccarelli, chief investment officer for Independent Advisor Alliance, says investors should wait to see how the recent turbulence plays out.
“It remains to be seen whether this recent weakness in the labor market is the canary in the coal mine (in which case the selling is justified) or if it is just a temporary cooling of the job market (in which case this will prove to be another buying opportunity),” he wrote in a note to clients Monday.
__
Cora Lewis and Wyatte Grantham-Philips in New York contributed to this report.
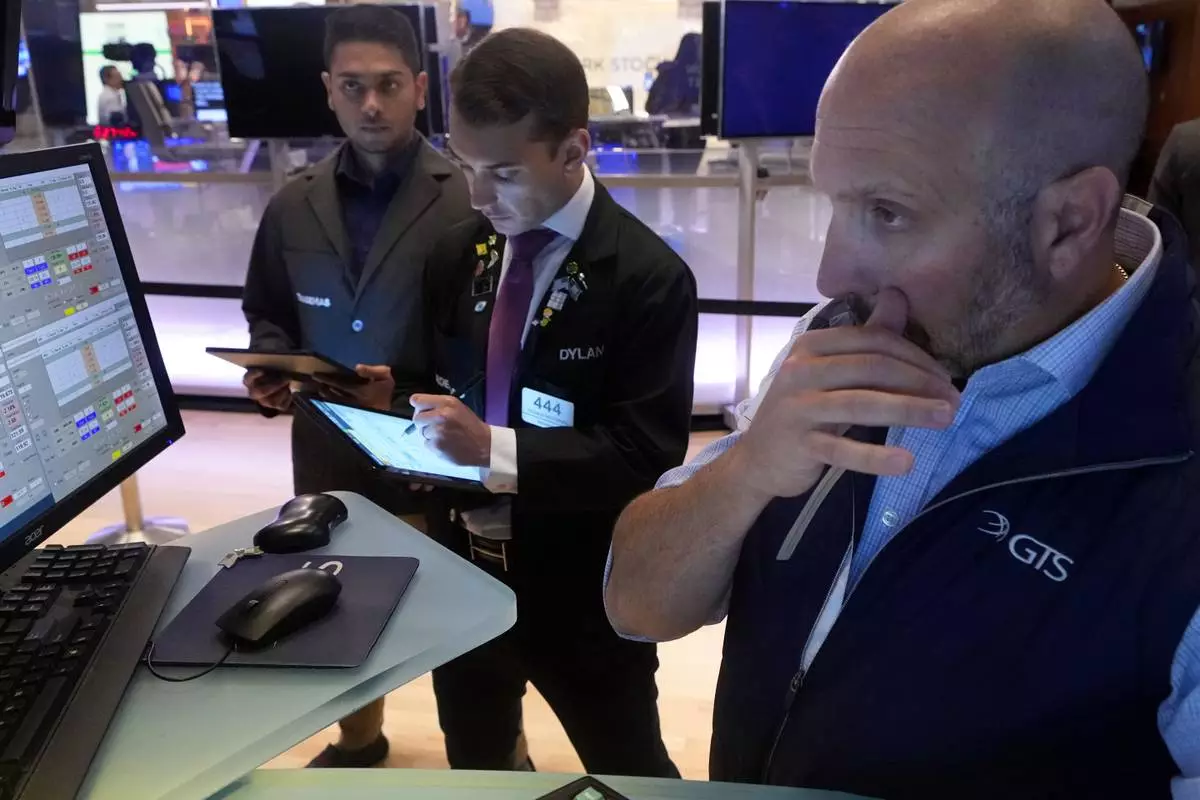

Specialist James Denaro, right, works at his post on the floor of the New York Stock Exchange, Monday, Aug. 5, 2024. Nearly everything on Wall Street is tumbling as fear about a slowing U.S. economy worsens and sets off another sell-off for financial markets around the world. (AP Photo/Richard Drew)
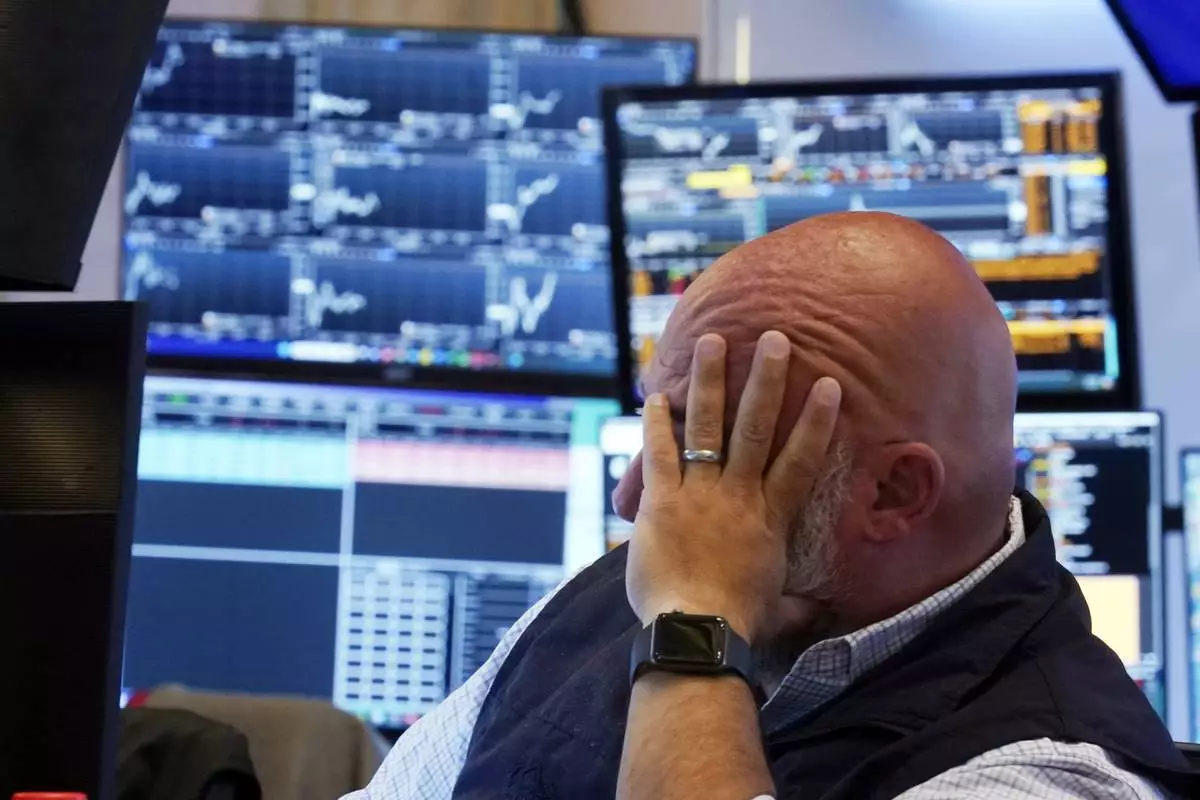

Trader Vincent Napolitano works on the floor of the New York Stock Exchange, Monday, Aug. 5, 2024. (AP Photo/Richard Drew)