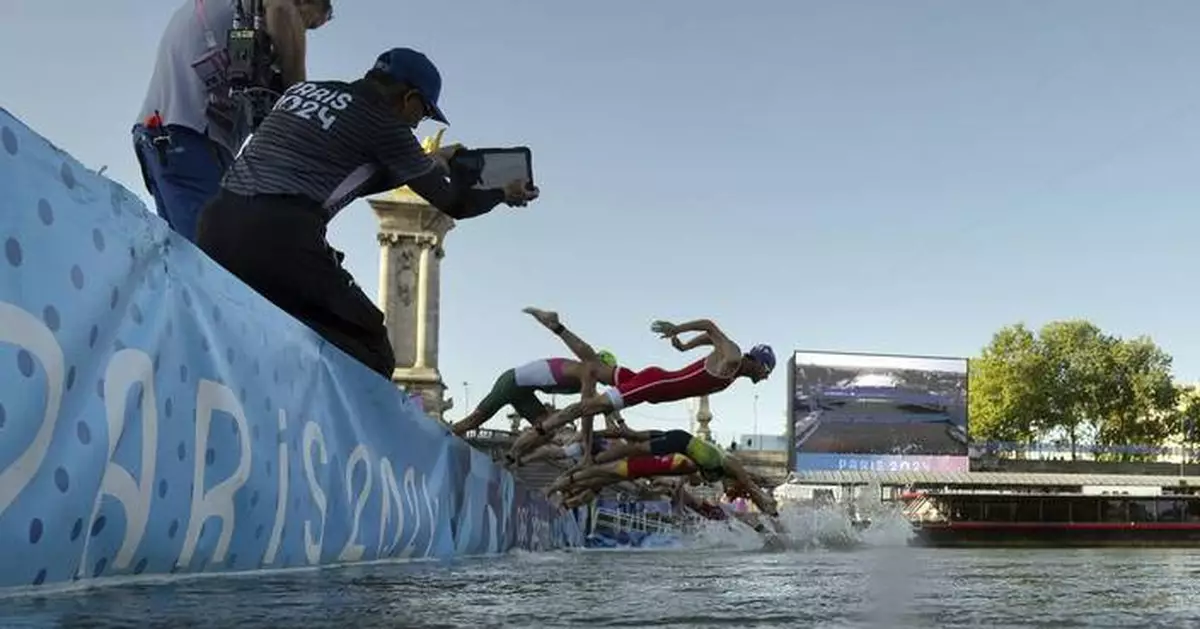
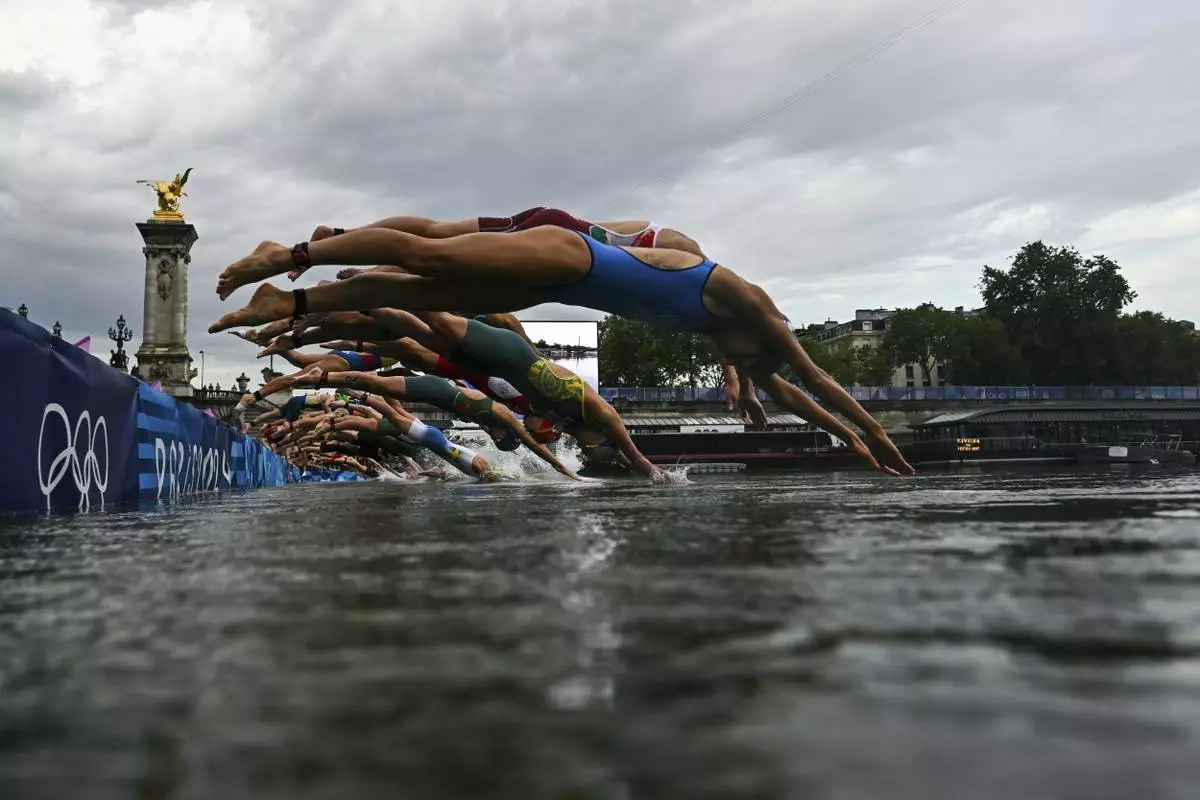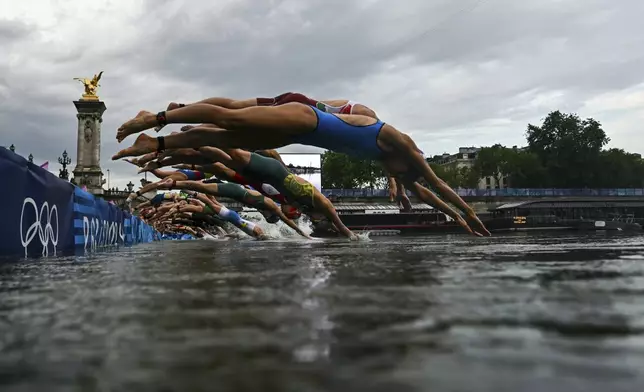PARIS (AP) — Olympic open water swimmers trained in the long-polluted Seine River on Wednesday after Paris organizers determined it was safe to dive in.
A two-hour training session was held on a cool, cloudy morning, providing the only chance for swimmers to familiarize themselves with the picturesque course through the middle of the French capital.
Click to Gallery
FILE - Claire Michel, of Belgium, is assisted by Lotte Miller of Norway after the finish of the women's individual triathlon competition at the 2020 Summer Olympics, in Tokyo, Japan, July 27, 2021. Belgium's Olympic committee announced Sunday Aug.4, 2024 that it would withdraw its team from the mixed relay triathlon at the Paris Olympics after one of its competitors who swam in the Seine River fell ill. Claire Michel, who competed in the women's triathlon Wednesday, "is unfortunately ill and will have to withdraw from the competition," the Belgian Olympic and Interfederal Committee said in a statement. (AP Photo/David Goldman, File)
FILE - Australia's Natalie Van Coevorden (15), Belgium's Claire Michel (5) and Ekaterina Shabalina, of Kazakhstan (32) compete in the swim leg of the women's individual triathlon competition at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Wednesday, July 31, 2024, in Paris, France. Belgium's Olympic committee announced Sunday Aug.4, 2024 that it would withdraw its team from the mixed relay triathlon at the Paris Olympics after one of its competitors who swam in the Seine River fell ill. Claire Michel, who competed in the women's triathlon Wednesday, "is unfortunately ill and will have to withdraw from the competition," the Belgian Olympic and Interfederal Committee said in a statement. (AP Photo/David Goldman, File)
FILE - Claire Michel, of Belgium, is assisted by Lotte Miller of Norway after the finish of the women's individual triathlon competition at the 2020 Summer Olympics, in Tokyo, Japan, July 27, 2021. Belgium's Olympic committee announced Sunday Aug.4, 2024 that it would withdraw its team from the mixed relay triathlon at the Paris Olympics after one of its competitors who swam in the Seine River fell ill. Claire Michel, who competed in the women's triathlon Wednesday, "is unfortunately ill and will have to withdraw from the competition," the Belgian Olympic and Interfederal Committee said in a statement. (AP Photo/David Goldman, File)
FILE - Australia's Natalie Van Coevorden (15), Belgium's Claire Michel (5) and Ekaterina Shabalina, of Kazakhstan (32) compete in the swim leg of the women's individual triathlon competition at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Wednesday, July 31, 2024, in Paris, France. Belgium's Olympic committee announced Sunday Aug.4, 2024 that it would withdraw its team from the mixed relay triathlon at the Paris Olympics after one of its competitors who swam in the Seine River fell ill. Claire Michel, who competed in the women's triathlon Wednesday, "is unfortunately ill and will have to withdraw from the competition," the Belgian Olympic and Interfederal Committee said in a statement. (AP Photo/David Goldman, File)
Athletes jump into the water to compete in the swimming race in the Seine river, during the mixed relay triathlon, at the 2024 Olympic Games, in Paris, France, Monday, Aug. 5, 2024. (Martin Bureau/Pool Photo via AP)
Athletes compete in the swimming race in the Seine during the women's individual triathlon at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Wednesday, July 31, 2024 in Paris, France. (Martin Bureau/Pool Photo via AP)
A view of the Seine River is pictured at sunset during the 2024 Summer Olympics, Monday, Aug. 5, 2024, in Paris, France. (AP Photo/Natacha Pisarenko)
Athletes jump into the water to compete in the swimming race in the Seine river, during the mixed relay triathlon, at the 2024 Olympic Games, in Paris, France, Monday, Aug. 5, 2024. (Martin Bureau/Pool Photo via AP)
Dozens of swimmers — from 2016 Olympic champion Sharon van Rouwendaal to Ireland's Daniel Wiffen, competing in open water for the first time — dove into the Seine one day before the women’s 10-kilometer marathon event. The men’s race is set for Friday.
Before diving in, several swimmers checked out the conditions from the famed Pont Alexandre III, adorned with golden statues and overlooking the starting buoy and finishing chute.
“I think if anyone’s saying they’re not concerned at all, they’re probably lying,” Austrian swimmer Felix Auboeck said. “I am concerned. I just hope and trust the organization in the sense that they let us in when it’s safe enough to do so. But, of course, you’re concerned because no one wants to get ill or sick.”
Then again, Auboeck can see the appeal of swimming in the Seine at the course that has the Eiffel Tower, the gold-domed Invalides, and other stunning Paris landmarks for a backdrop.
“It is super exciting that this is scenery where we are racing,” he said. “That’s probably like the best thing we can do for the sport.”
World Aquatics canceled a test run Tuesday because of concerns over fluctuating bacteria levels in the waterway. Despite massive efforts to clear the Seine, water quality has been a constant concern throughout the Games.
But officials expressed confidence that both races will be held without any issues, especially with a favorable forecast that calls for sunny skies in the afternoon and little chance of rain.
Open water swimmers do most of their training in the controlled conditions of a pool. While concerns about bacteria levels in the Seine might have prompted some to skip the training session and limit their time in the river to the actual event, it appeared that a majority took advantage of the training session — especially to check out the strong current that has also raised concerns.
The current has been measured at 2-3 mph, a significant challenge when going upstream on the six-lap course.
“The current is just going to be another challenge,” Auboeck said. “It’s going to be very, very different to what we have seen before. I wish there would have been more practice races with a current like this. That would have been good.”
Triathlon events have already been held in the river, though the schedule was upended by the readings that are taken daily of the water quality.
Now, it’s time for open water, which at least has a backup plan in place if the Seine is determined to be unsafe. The races would be shifted to Vaires-sur-Marne Nautical Stadium, site of the rowing and canoeing events.
The triathlon mixed relay event was held Monday. World Triathlon released data Tuesday showing the levels of fecal bacteria E. coli and enterococci were within acceptable levels for the length of the triathlon relay course during those swims.
The marathon swims take place on longer portions of the river and will start and finish at the Pont Alexandre III. Marathon swimmers do six laps on the 1.67-kilometer (1 mile) course for a total of 10 kilometers (6.2 miles.)
Paris Mayor Anne Hidalgo, who took a highly publicized swim in the Seine in July to allay fears about water quality ahead of the Olympics, expressed confidence in the preparations.
“There’s been a clear improvement of the weather these past few days,” she said. “So I’m really proud and happy and to all those who want to continue saying it’s impossible to depollute a river, I tell them, ’Yes it’s possible, we did it.’”
With a few exceptions, swimming in the Seine has been prohibited since 1923 because the water has been too toxic.
Paris undertook an ambitious plan, including 1.4 billion euros ($1.5 billion) in infrastructure improvements to ensure that some swimming events could be held in the river. That included the construction of a giant basin to capture excess rainwater and keep wastewater from flowing into the river, renovating sewer infrastructure and upgrading wastewater treatment plants.
Four triathletes — of the more than 100 who competed in the men’s and women’s individual races last week — became sick in the following days, though it’s unclear whether the water was to blame.
Most strains of E. coli and enterococci are harmless, and some live in the intestines of healthy people and animals. But others are dangerous and even a mouthful of contaminated water can cause infections in the urinary tract or intestines.
AP Summer Olympics: https://apnews.com/hub/2024-paris-olympic-games
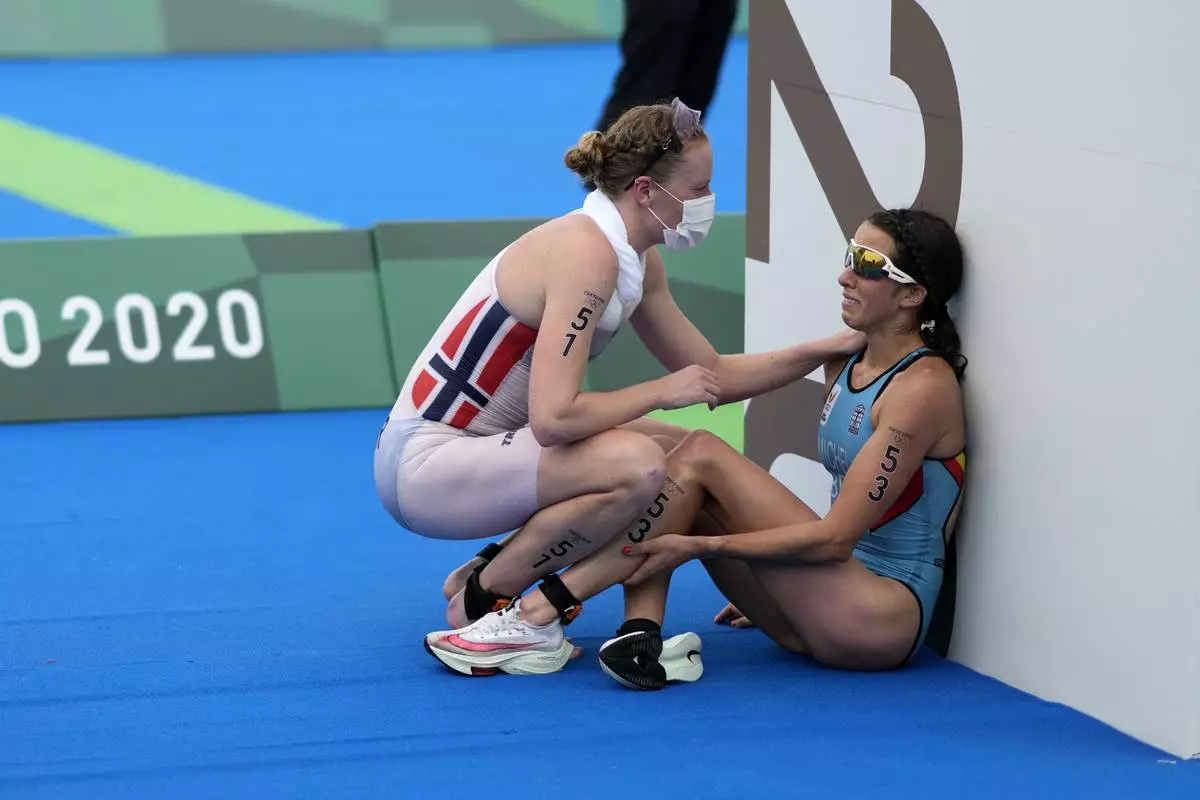

FILE - Claire Michel, of Belgium, is assisted by Lotte Miller of Norway after the finish of the women's individual triathlon competition at the 2020 Summer Olympics, in Tokyo, Japan, July 27, 2021. Belgium's Olympic committee announced Sunday Aug.4, 2024 that it would withdraw its team from the mixed relay triathlon at the Paris Olympics after one of its competitors who swam in the Seine River fell ill. Claire Michel, who competed in the women's triathlon Wednesday, "is unfortunately ill and will have to withdraw from the competition," the Belgian Olympic and Interfederal Committee said in a statement. (AP Photo/David Goldman, File)
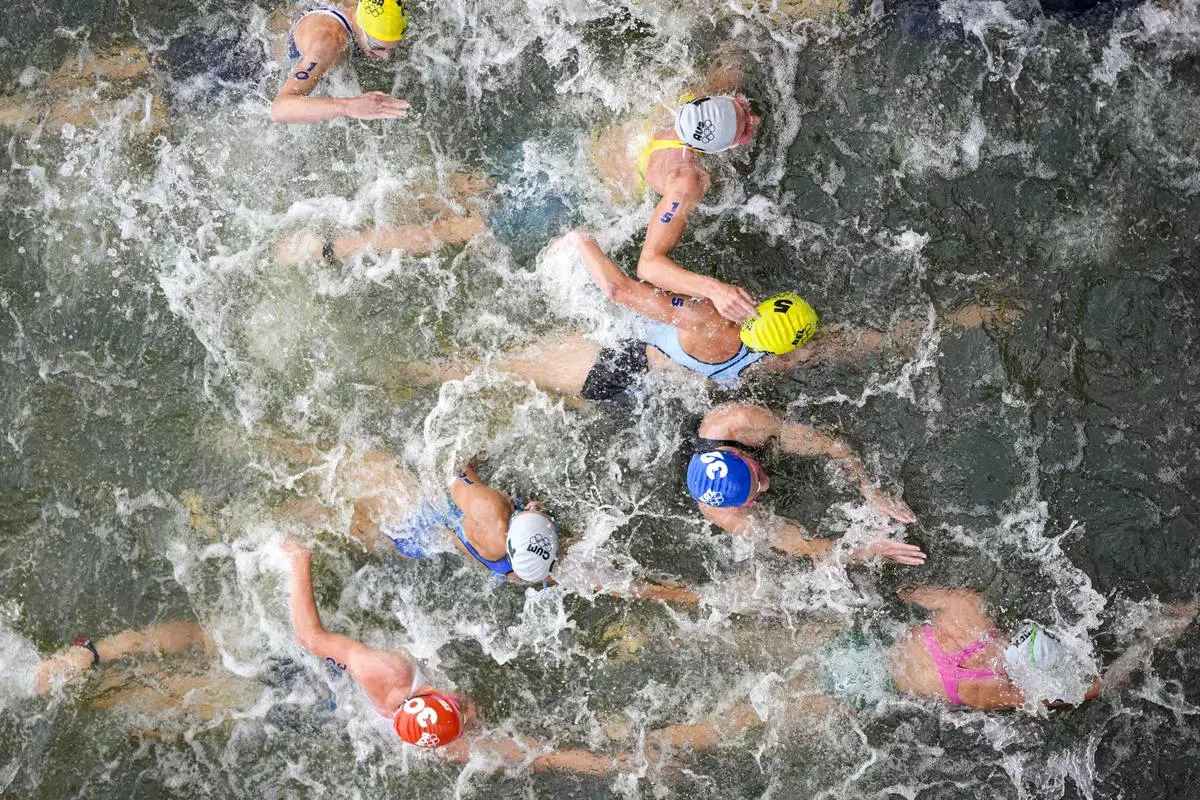

FILE - Australia's Natalie Van Coevorden (15), Belgium's Claire Michel (5) and Ekaterina Shabalina, of Kazakhstan (32) compete in the swim leg of the women's individual triathlon competition at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Wednesday, July 31, 2024, in Paris, France. Belgium's Olympic committee announced Sunday Aug.4, 2024 that it would withdraw its team from the mixed relay triathlon at the Paris Olympics after one of its competitors who swam in the Seine River fell ill. Claire Michel, who competed in the women's triathlon Wednesday, "is unfortunately ill and will have to withdraw from the competition," the Belgian Olympic and Interfederal Committee said in a statement. (AP Photo/David Goldman, File)
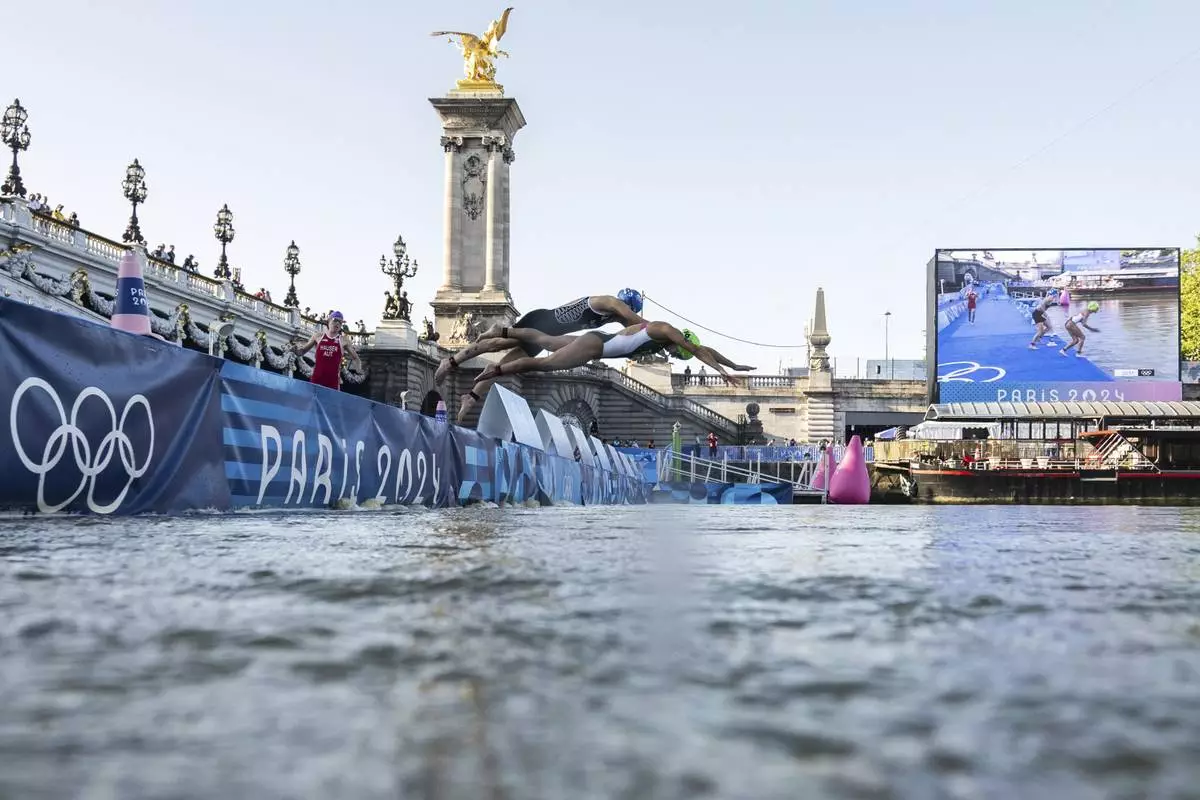

Athletes jump into the water to compete in the swimming race in the Seine river, during the mixed relay triathlon, at the 2024 Olympic Games, in Paris, France, Monday, Aug. 5, 2024. (Martin Bureau/Pool Photo via AP)
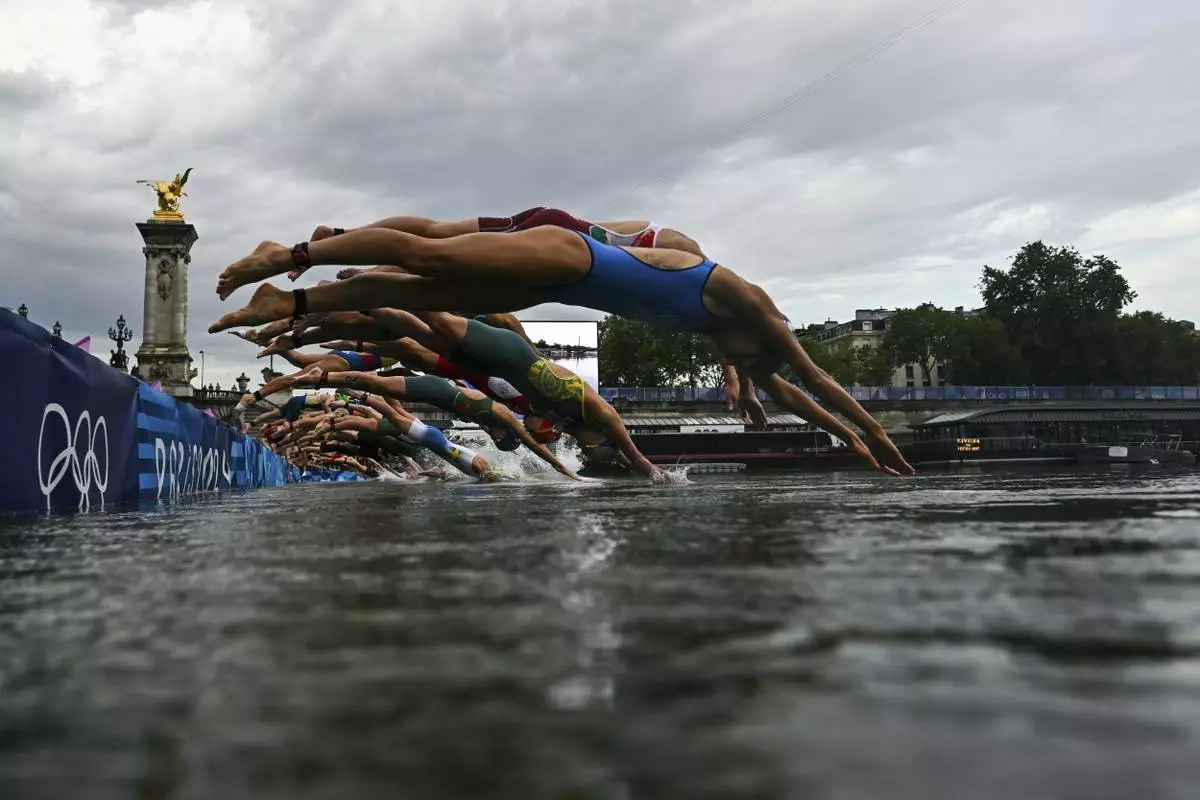
Athletes compete in the swimming race in the Seine during the women's individual triathlon at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Wednesday, July 31, 2024 in Paris, France. (Martin Bureau/Pool Photo via AP)

A view of the Seine River is pictured at sunset during the 2024 Summer Olympics, Monday, Aug. 5, 2024, in Paris, France. (AP Photo/Natacha Pisarenko)
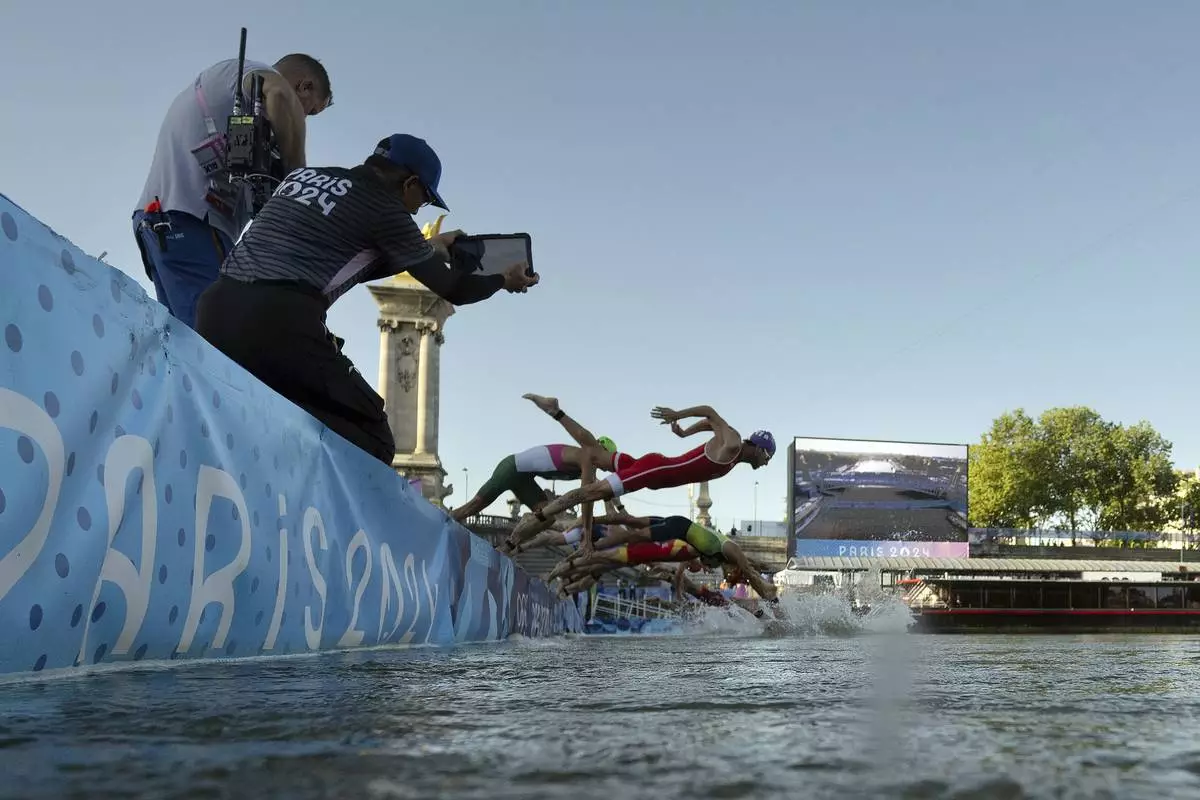

Athletes jump into the water to compete in the swimming race in the Seine river, during the mixed relay triathlon, at the 2024 Olympic Games, in Paris, France, Monday, Aug. 5, 2024. (Martin Bureau/Pool Photo via AP)
What's in a name change, after all?
The water bordered by the Southern United States, Mexico and Cuba will be critical to shipping lanes and vacationers whether it’s called the Gulf of Mexico, as it has been for four centuries, or the Gulf of America, as President Donald Trump ordered this week. North America’s highest mountain peak will still loom above Alaska whether it’s called Mt. Denali, as ordered by former President Barack Obama in 2015, or changed back to Mt. McKinley as Trump also decreed.
But Trump's territorial assertions, in line with his “America First” worldview, sparked a round of rethinking by mapmakers and teachers, snark on social media and sarcasm by at least one other world leader. And though Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis put the Trumpian “Gulf of America” on an official document and some other gulf-adjacent states were considering doing the same, it was not clear how many others would follow Trump's lead.
Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum joked that if Trump went ahead with the renaming, her country would rename North America “Mexican America.” On Tuesday, she toned it down: “For us and for the entire world it will continue to be called the Gulf of Mexico.”
Map lines are inherently political. After all, they're representations of the places that are important to human beings — and those priorities can be delicate and contentious, even more so in a globalized world.
There’s no agreed-upon scheme to name boundaries and features across the Earth.
“Denali” is the mountain's preferred name for Alaska Natives, while “McKinley" is a tribute to President William McKinley, designated in the late 19th century by a gold prospector. China sees Taiwan as its own territory, and the countries surrounding what the United States calls the South China Sea have multiple names for the same body of water.
The Persian Gulf has been widely known by that name since the 16th century, although usage of “Gulf” and “Arabian Gulf” is dominant in many countries in the Middle East. The government of Iran — formerly Persia — threatened to sue Google in 2012 over the company’s decision not to label the body of water at all on its maps. Many Arab countries don’t recognize Israel and instead call it Palestine. And in many official releases, Israel calls the occupied West Bank by its biblical name, “Judea and Samaria.”
Americans and Mexicans diverge on what to call another key body of water, the river that forms the border between Texas and the Mexican states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo Leon and Tamaulipas. Americans call it the Rio Grande; Mexicans call it the Rio Bravo.
Trump's executive order — titled “Restoring Names That Honor American Greatness” — concludes thusly: “It is in the national interest to promote the extraordinary heritage of our Nation and ensure future generations of American citizens celebrate the legacy of our American heroes. The naming of our national treasures, including breathtaking natural wonders and historic works of art, should honor the contributions of visionary and patriotic Americans in our Nation’s rich past.”
But what to call the gulf with the 3,700-mile coastline?
“It is, I suppose, an internationally recognized sea, but (to be honest), a situation like this has never come up before so I need to confirm the appropriate convention,” said Peter Bellerby, who said he was talking over the issue with the cartographers at his London company, Bellerby & Co. Globemakers. “If, for instance, he wanted to change the Atlantic Ocean to the American Ocean, we would probably just ignore it."
As of Wednesday night, map applications for Google and Apple still called the mountain and the gulf by their old names. Spokespersons for those platforms did not immediately respond to emailed questions.
A spokesperson for National Geographic, one of the most prominent map makers in the U.S., said this week that the company does not comment on individual cases and referred questions to a statement on its web site, which reads in part that it "strives to be apolitical, to consult multiple authoritative sources, and to make independent decisions based on extensive research.” National Geographic also has a policy of including explanatory notes for place names in dispute, citing as an example a body of water between Japan and the Korean peninsula, referred to as the Sea of Japan by the Japanese and the East Sea by Koreans.
In discussion on social media, one thread noted that the Sears Tower in Chicago was renamed the Willis Tower in 2009, though it's still commonly known by its original moniker. Pennsylvania's capital, Harrisburg, renamed its Market Street to Martin Luther King Boulevard and then switched back to Market Street several years later — with loud complaints both times. In 2017, New York's Tappan Zee Bridge was renamed for the late Gov. Mario Cuomo to great controversy. The new name appears on maps, but “no one calls it that,” noted another user.
“Are we going to start teaching this as the name of the body of water?” asked one Reddit poster on Tuesday.
“I guess you can tell students that SOME PEOPLE want to rename this body of water the Gulf of America, but everyone else in the world calls it the Gulf of Mexico,” came one answer. “Cover all your bases — they know the reality-based name, but also the wannabe name as well.”
Wrote another user: “I'll call it the Gulf of America when I'm forced to call the Tappan Zee the Mario Cuomo Bridge, which is to say never.”
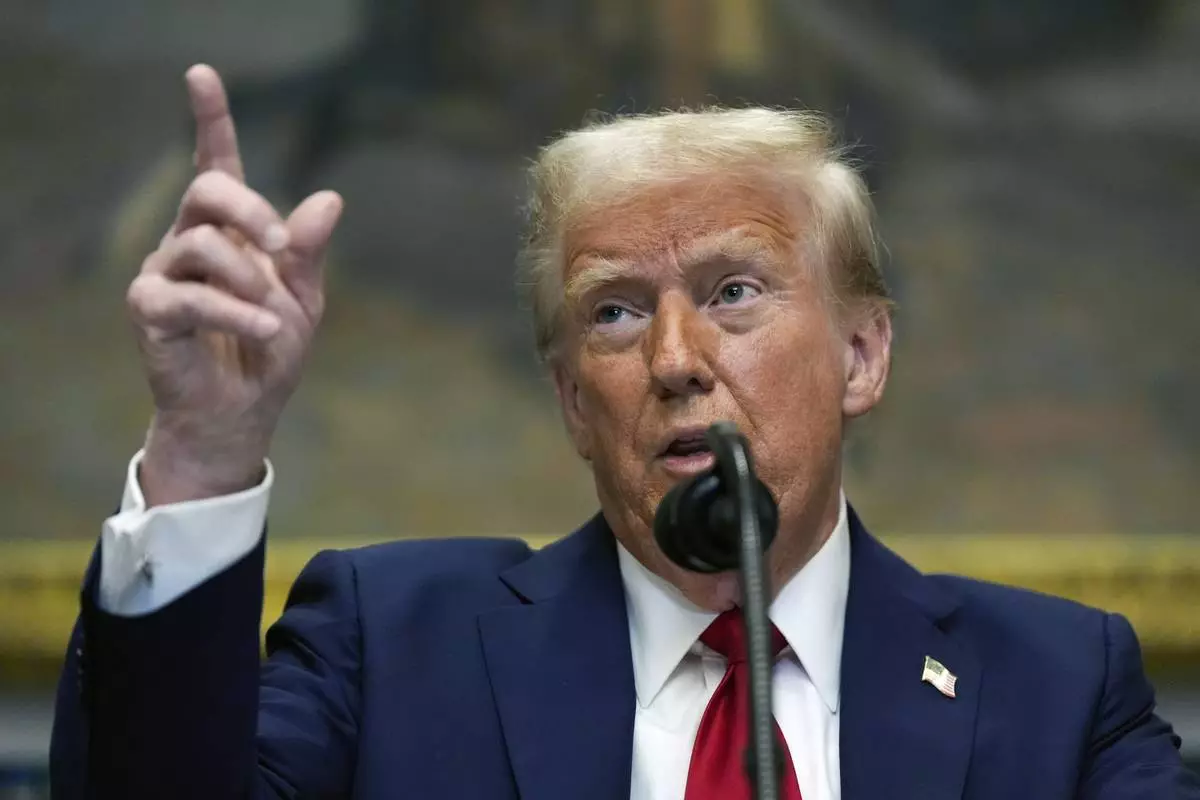

FILE - President Donald Trump speaks in the Roosevelt Room of the White House, Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025, in Washington. (AP Photo/Julia Demaree Nikhinson, File)
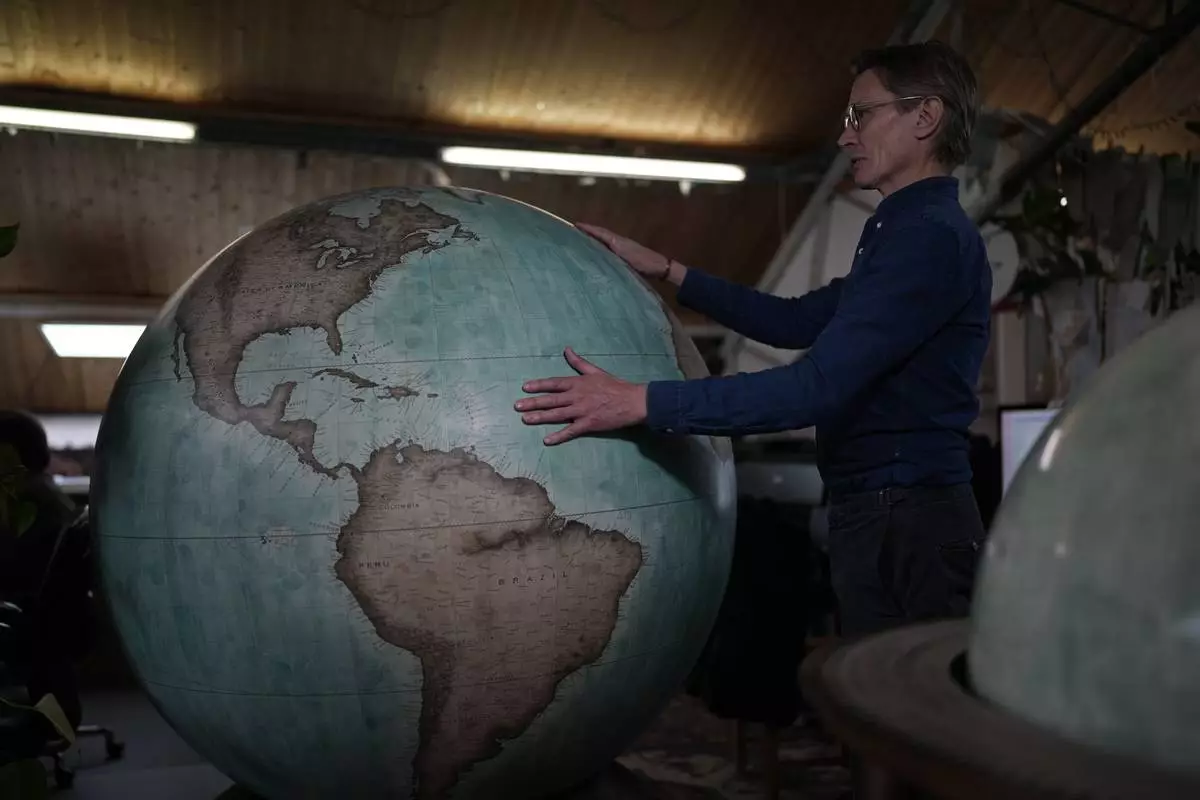

FILE - Peter Bellerby, the founder of Bellerby & Co. Globemakers, holds a globe at a studio in London, Tuesday, Feb. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Kin Cheung, File)
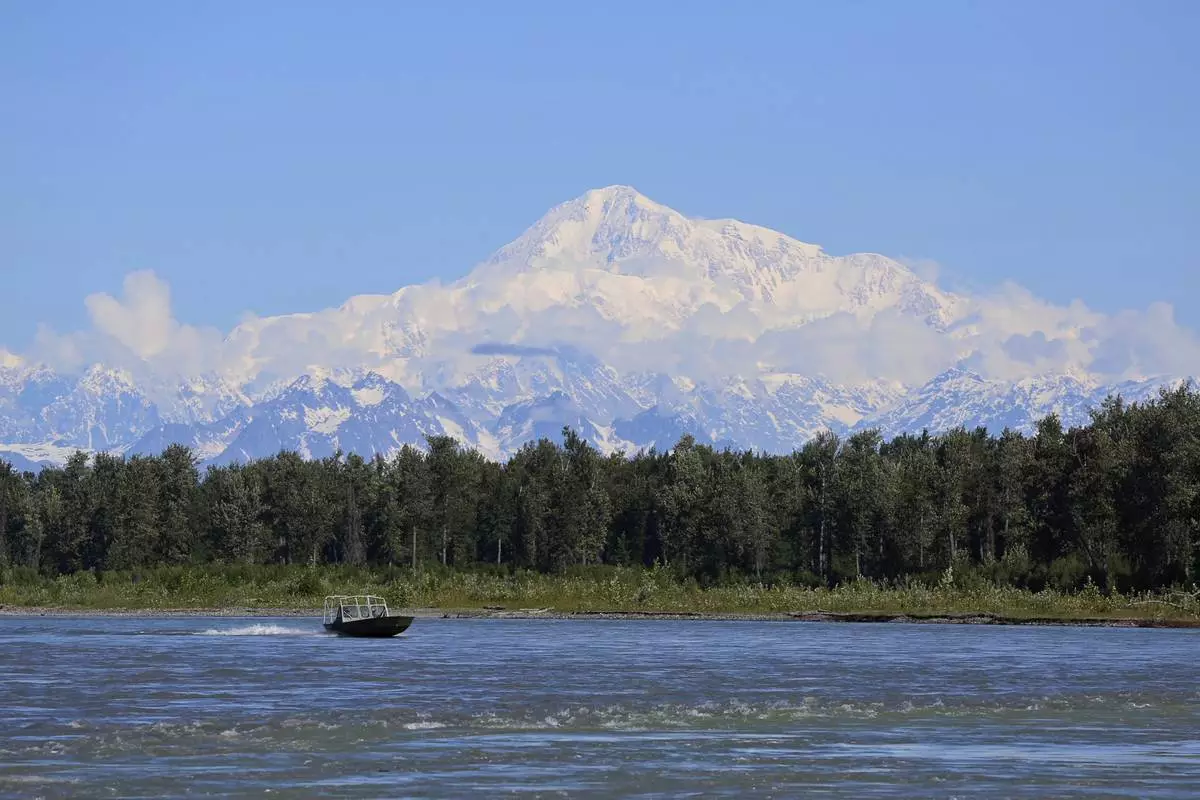

FILE - A boat is seen on the Susitna River near Talkeetna, Alaska, on Sunday, June 13, 2021, with Denali in the background. Denali, the tallest mountain on the North American continent, is located about 60 miles northwest of Talkeetna. (AP Photo/Mark Thiessen, File)
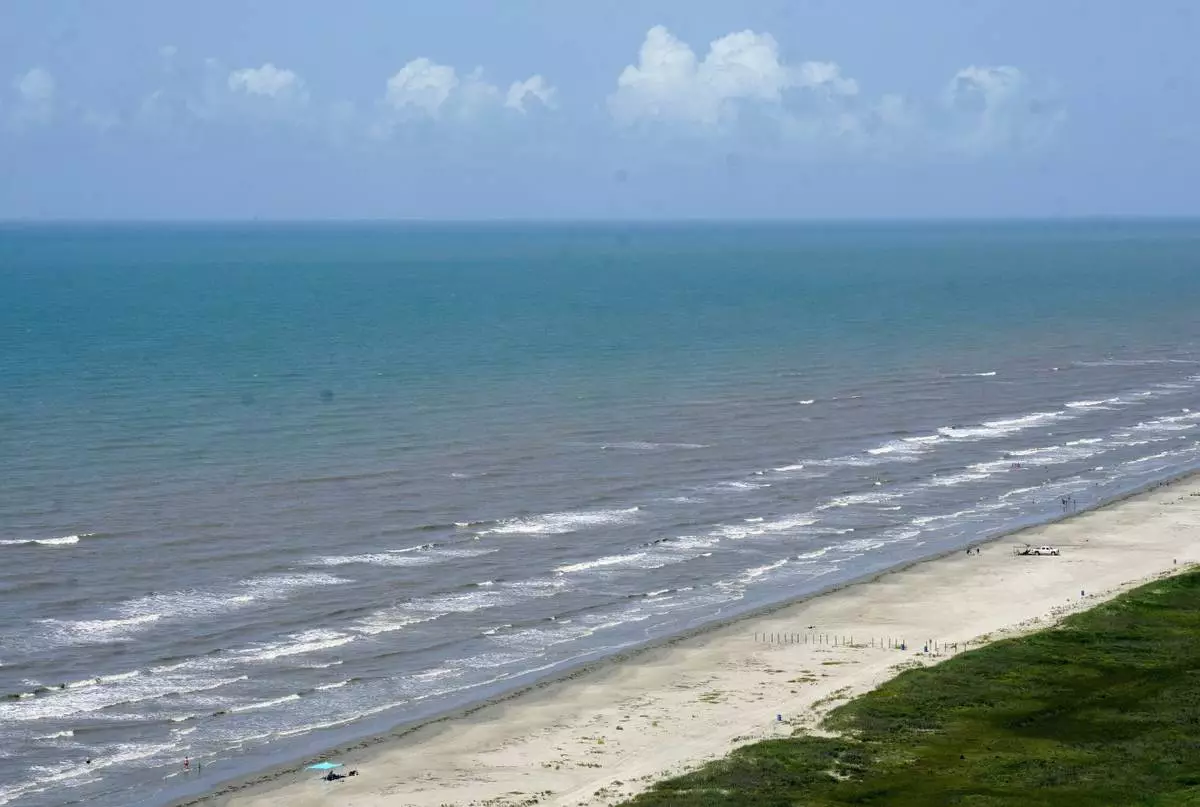

FILE - The water in the Gulf of Mexico appears bluer than usual off of East Beach, Saturday, June 24, 2023, in Galveston, Texas. (Jill Karnicki/Houston Chronicle via AP, File)