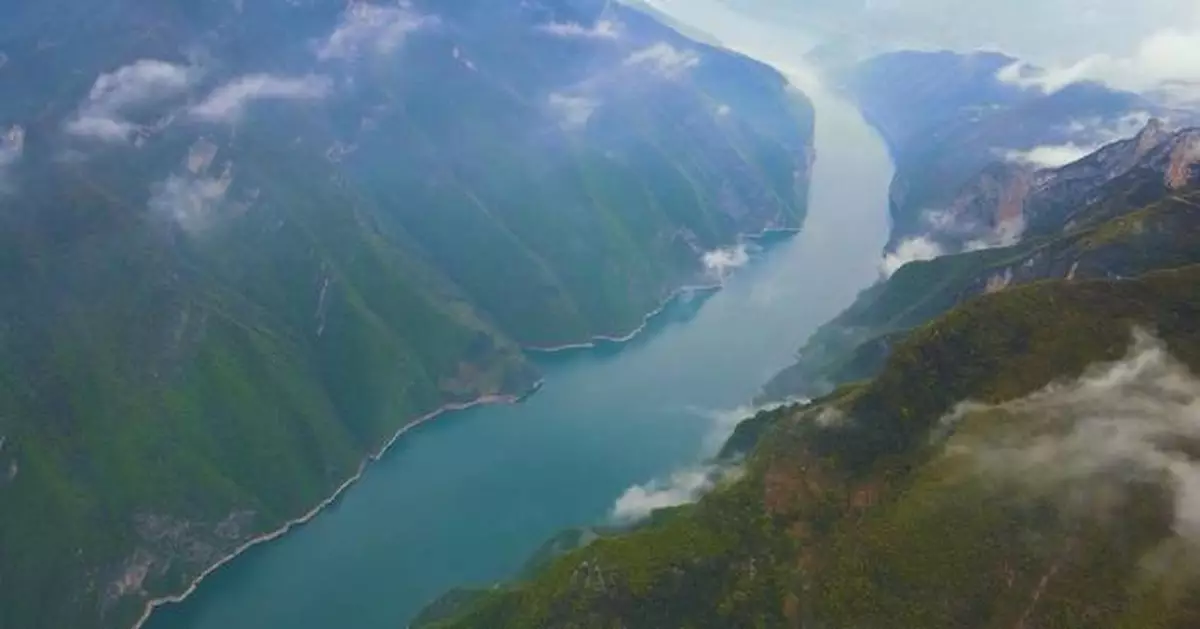
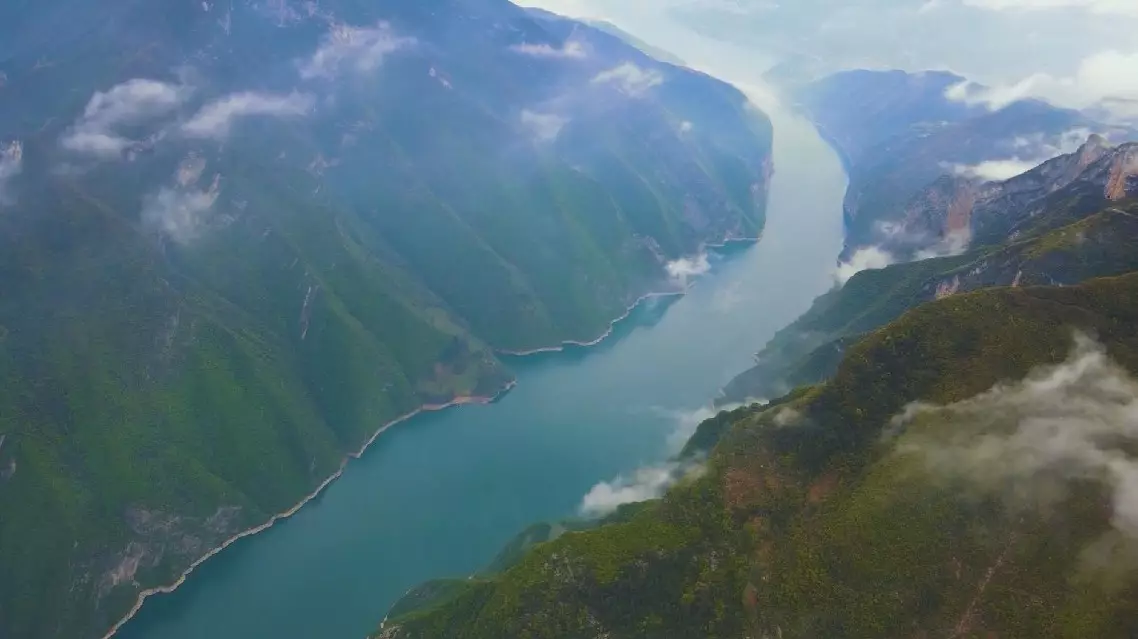
The aquatic resources and biodiversity in Yangtze River have significantly recovered since the implementation of a decade-long fishing ban, with improvements observed in resource density, water quality, and the aquatic biological integrity index across key water bodies.
The resource density per unit area in the Yangtze River's mainstream increased by 16.7 percent year-on-year in 2023, while important tributaries saw a 64.3 percent rise in resource density, according to the "Yangtze River Basin Aquatic Biological Resources and Habitat Status Bulletin (2023)" released by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, the Ministry of Water Resources, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, and the Ministry of Transport on Monday.
China implemented the fishing ban in the Yangtze River Basin in 2021 to accelerate the ecological restoration of its aquatic biodiversity and water environment.
In Jianli city, located in central Hubei province, a monitoring site in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River recorded 5.98 billion fish larvae from four major species -- black carp, grass carp, silver carp, and bighead carp -- an increase of 4.4 times compared to before the fishing ban.
In the lower reaches, the resource density of coilia nasus was 7.3 times higher than before the ban.
Since the implementation of the fishing ban, aquatic biodiversity in the Yangtze River has shown steady improvement.
In 2023, 227 species of indigenous fish were monitored in the Yangtze River Basin, an increase of 34 species year-on-year. Additionally, 14 species of nationally protected aquatic wildlife were recorded, 3 species more than that of the previous year.
The aquatic habitats in the Yangtze River have also remained generally stable.
In 2023, the overall water quality of the Yangtze River's main and tributary streams was rated as excellent, with 98.5 percent of the water sections classified as Class I to III, indicating that the water is suitable for drinking, swimming, and supporting aquatic life.
The intensity of new development projects affecting fisheries, such as sand mining and waterway regulation, has decreased. Meanwhile, the Aquatic Biological Integrity Index for the Yangtze River showed steady improvement.
"The Yangtze River's aquatic biological integrity index is categorized into six levels. In 2023, key water bodies, including the Yangtze River's mainstream, Dongting Lake, and Poyang Lake, maintained a Level 4 rating. This marks a significant improvement from the lowest Level 6 before the fishing ban, reflecting a two-level advancement," said Zhuang Ping, deputy director of Yangtze River Aquatic Biological Science Committee, which is under the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs.

Fishing ban leads to significant recovery in aquatic resources and biodiversity in Yangtze River

Fishing ban leads to significant recovery in aquatic resources and biodiversity in Yangtze River

Fishing ban leads to significant recovery in aquatic resources and biodiversity in Yangtze River