THE HAGUE, Netherlands (AP) — International Criminal Court prosecutors said Monday that they are “actively monitoring” events in Venezuela, where security forces have launched a crackdown on the opposition in the aftermath of the nation's disputed presidential election.
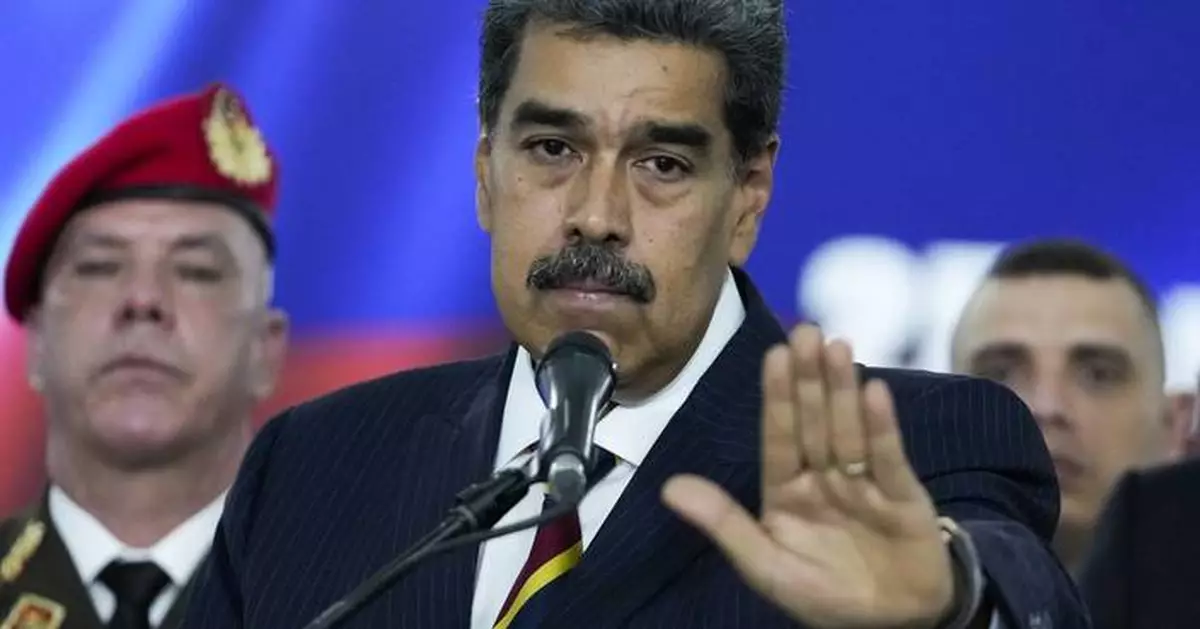
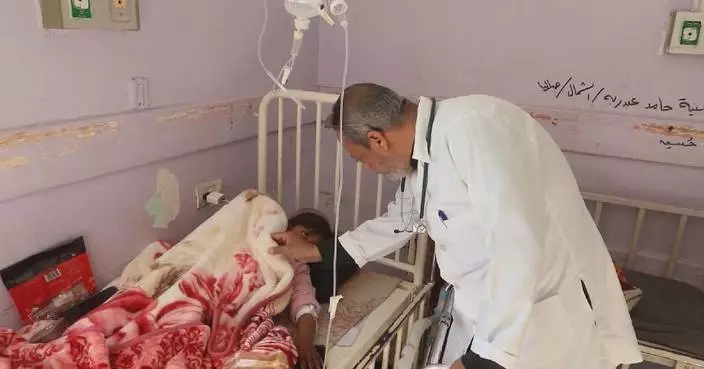
Forces loyal to President Nicolás Maduro have rounded up more than 2,000 people for demonstrating against the president or casting doubt on his claims that he won a third term in the July 28 election despite strong evidence he lost the vote by a more than two-to-one margin.
In a written statement to reporters, the office of ICC Prosecutor Karim Khan said it is “actively monitoring the present events and has received multiple reports of instances of violence and other allegations following the presidential election of 28 July in Venezuela.”
The statement said that Khan's office has “engaged with the Government of Venezuela at the highest-level to underline the importance of ensuring that the rule of law is adhered to in the present moment and emphasize that all persons must be protected from violations that may constitute Rome Statute crimes.”
The Rome Statute is the court's founding treaty and outlines the crimes over which it has jurisdiction.
Maduro has called on Venezuelans to denounce election doubters via a government-run app originally created to report power outages. He also said the government was refurbishing two gang-dominated prisons to accommodate an expected surge in jailing of opponents.
“There will be no mercy,” Maduro said on state TV.
The ICC has an ongoing investigation into violence that followed Venezuela's 2017 election but has so far not sought any arrest warrants.
Khan, announced in late 2021 that he was opening the investigation after a lengthy preliminary probe and an official referral — a request to investigate — in 2018 by Argentina, Canada, Colombia, Chile, Paraguay and Peru.
His office said Monday that “those investigations are continuing with focus.” It highlighted an online portal where potential evidence can be filed.
“Should any individual or organization have information that may be relevant to this ongoing investigation, we would welcome you to submit this,” the prosecution statement said.
Follow AP’s coverage of Venezuela at https://apnews.com/hub/venezuela
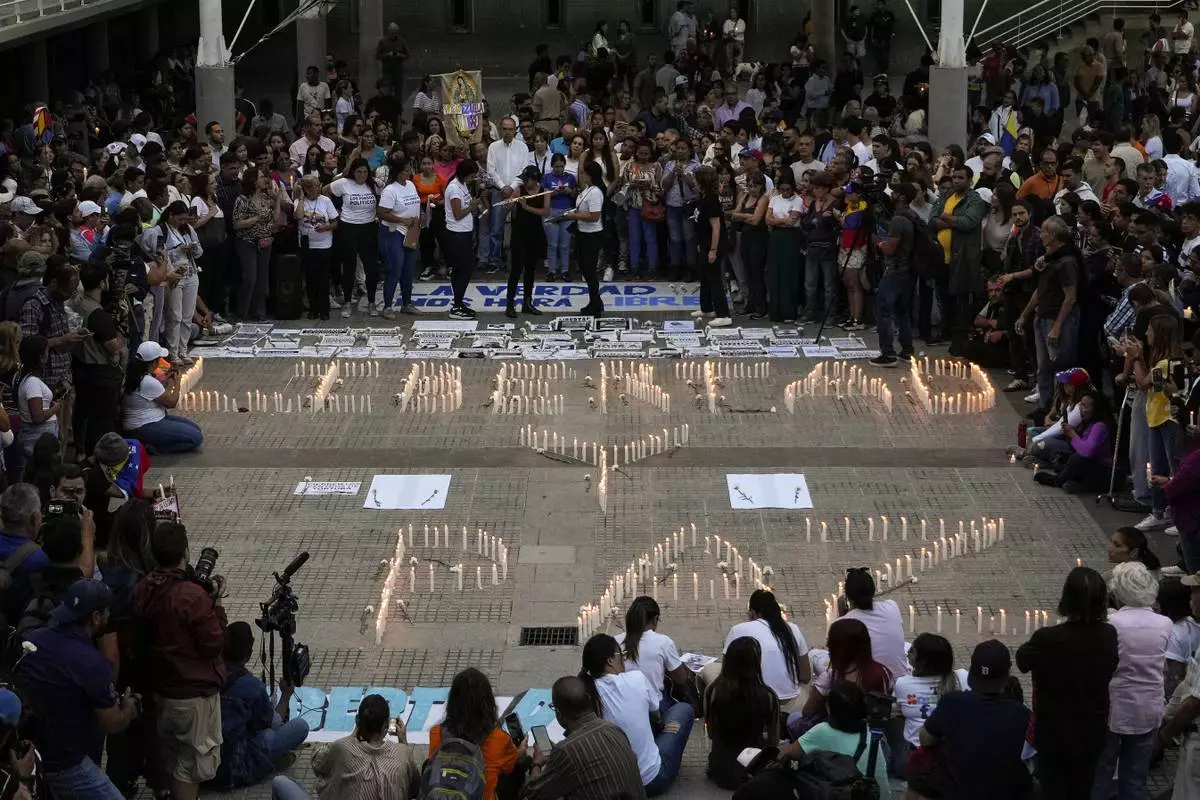

Family members of those detained amid a government crackdown on protestors participate in a vigil in Caracas, Venezuela, Thursday, Aug. 8, 2024. The candles read in Spanish: "Freedom and peace." (AP Photo/Matias Delacroix)

Venezuelan President Nicolas Maduro speaks to the press before leaving the Supreme Court where he arrived for procedures related to the court's audit of presidential election results in Caracas, Venezuela, Friday, Aug. 9, 2024. (AP Photo/Matías Delacroix)
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Donald Trump signed an executive order Monday directing the United States to again withdraw from the landmark Paris climate agreement, dealing a blow to worldwide efforts to combat global warming and once again distancing the U.S. from its closest allies.
Trump's action, hours after he was sworn in to a second term, echoed his directive in 2017, when he announced that the U.S. would abandon the global Paris accord. The pact is aimed at limiting long-term global warming to 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit (1.5 degrees Celsius) above pre-industrial levels or, failing that, keeping temperatures at least well below 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit (2 degrees Celsius) above pre-industrial levels.
Trump also signed a letter to the United Nations indicating his intention to withdraw from the 2015 agreement, which allows nations to provide targets to cut their own emissions of greenhouse gases from the burning of coal, oil and natural gas. Those targets are supposed to become more stringent over time, with countries facing a February 2025 deadline for new individual plans. The outgoing Biden administration last month offered a plan to cut U.S. greenhouse gas emissions by more than 60% by 2035.
Trump's order says the Paris accord is among a number of international agreements that don't reflect U.S. values and “steer American taxpayer dollars to countries that do not require, or merit, financial assistance in the interests of the American people."
Instead of joining a global agreement, “the United States’ successful track record of advancing both economic and environmental objectives should be a model for other countries,'' Trump said.
Laurence Tubiana, CEO of the European Climate Foundation and a key architect of the Paris accord, called the planned U.S. withdrawal unfortunate but said action to slow climate change “is stronger than any single country’s politics and policies."
The global context for Trump's action is “very different to 2017,'' Tubiana said Monday, adding that “there is unstoppable economic momentum behind the global transition, which the U.S has gained from and led but now risks forfeiting."
The International Energy Agency expects the global market for key clean energy technologies to triple to more than $2 trillion by 2035, she said.
“The impacts of the climate crisis are also worsening. The terrible wildfires in Los Angeles are the latest reminder that Americans, like everyone else, are affected by worsening climate change,” Tubiana said.
Gina McCarthy, who served as White House climate adviser under President Joe Biden, a Democrat, said that if Trump, a Republican, “truly wants America to lead the global economy, become energy independent and create good-paying American jobs," then he must “stay focused on growing our clean energy industry. Clean technologies are driving down energy costs for people all across our country."
The world is now long-term 2.3 degrees Fahrenheit (1.3 degrees Celsius) above mid-1800s temperatures. Most but not all climate monitoring agencies said global temperatures last year passed the warming mark of 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit, and all said it was the warmest year on record.
The withdrawal process from the Paris accord takes one year. Trump’s previous withdrawal took effect the day after the 2020 presidential election, which he lost to Biden.
While the first Trump-led withdrawal from the landmark U.N. agreement — adopted by 196 nations — shocked and angered nations across the globe, “not a single country followed the U.S. out the door,” said Alden Meyer, a longtime climate negotiations analyst with the European think tank E3G.
Instead, other nations renewed their commitment to slowing climate change, along with investors, businesses, governors, mayors and others in the U.S., Meyer and other experts said.
Still, they lamented the loss of U.S. leadership in global efforts to slow climate change, even as the world is on track to set yet another record hot year and has been lurching from drought to hurricane to flood to wildfire.
“Clearly America is not going to play the commanding role in helping solve the climate crisis, the greatest dilemma humans have ever encountered,″ said climate activist and writer Bill McKibben. “For the next few years the best we can hope is that Washington won’t manage to wreck the efforts of others.”
About half of Americans “somewhat” or “strongly” oppose U.S. action to withdraw from the climate accord, and even Republicans aren’t overwhelmingly in favor, according according to a poll from The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research. Only about 2 in 10 U.S. adults “somewhat” or “strongly” in favor of withdrawing from the Paris agreement, while about one-quarter are neutral.
Much of the opposition to U.S. withdrawal comes from Democrats, but Republicans display some ambivalence as well. Slightly less than half of Republicans are in favor of withdrawing from the climate accord, while about 2 in 10 are opposed.
China several years ago passed the United States as the world's largest annual carbon dioxide emitting nation. The U.S. — the second biggest annual carbon polluting country — put 4.9 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide in the air in 2023, down 11% from a decade earlier, according to the scientists who track emissions for the Global Carbon Project.
But carbon dioxide lasts in the atmosphere for centuries, so the United States has put more of the heat-trapping gas that is now in the air than any other nation. The U.S. is responsible for nearly 22% of the carbon dioxide put in the atmosphere since 1950, according to Global Carbon Project.
While global efforts to fight climate change continued during Trump's first term, many experts worry that a second Trump term will be more damaging, with the United States withdrawing even further from climate efforts in a way that could cripple future presidents’ efforts. With Trump, who has dismissed climate change, in charge of the world’s leading economy, those experts fear other countries, especially China, could use it as an excuse to ease off their own efforts to curb carbon emissions.
Simon Stiell, the U.N. climate change executive secretary, held out hope that the U.S. would continue to embrace the global clean energy boom.
“Ignoring it only sends all that vast wealth to competitor economies, while climate disasters like droughts, wildfires and superstorms keep getting worse," Stiell said. “The door remains open to the Paris Agreement, and we welcome constructive engagement from any and all countries.”
Associated Press writer Linley Sanders contributed to this report.
The Associated Press’ climate and environmental coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. The AP is solely responsible for all content. Find the AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.
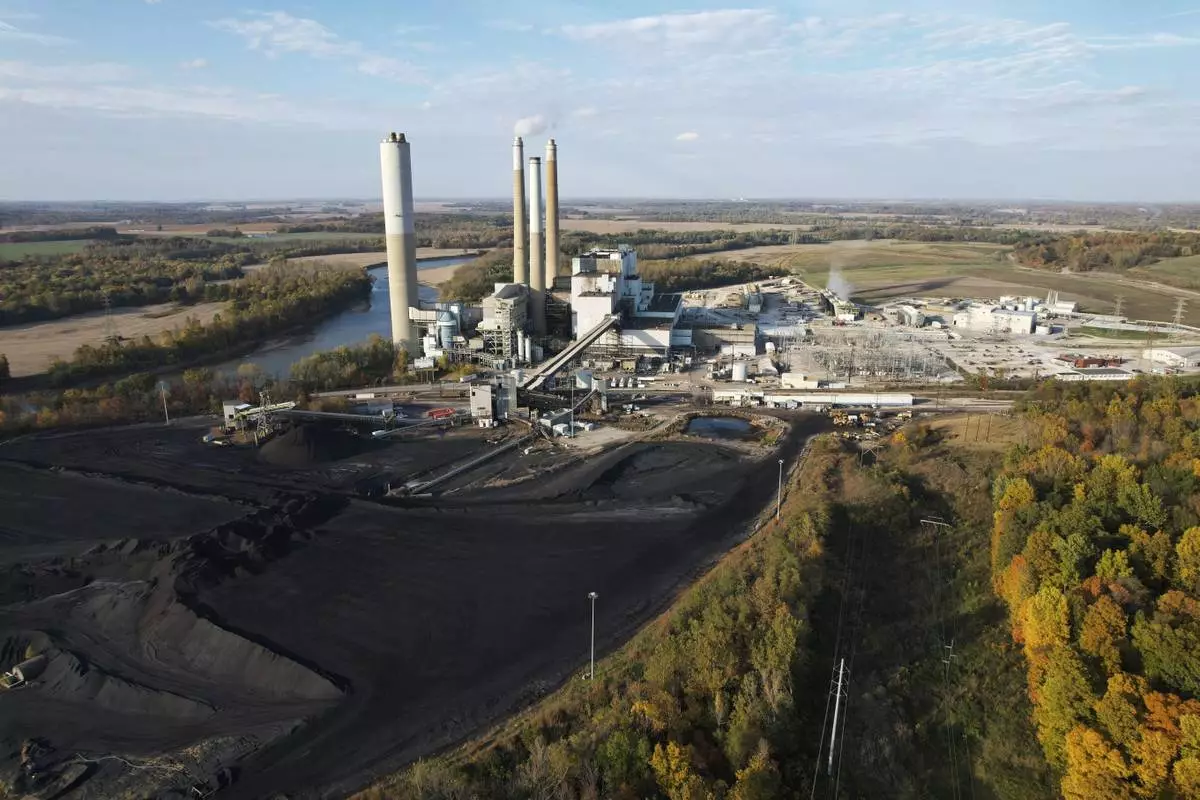

AES Indiana Petersburg Generating Station, a coal-fired power plant, operates in Petersburg, Ind., on Wednesday, Oct. 25, 2023. (AP Photo/Joshua A. Bickel)

FILE - Wind turbines stretch across the horizon at dusk at the Spearville Wind Farm, Sept. 29, 2024, near Spearville, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel, File)

President Donald Trump gestures during the 60th Presidential Inauguration in the Rotunda of the U.S. Capitol in Washington, Monday, Jan. 20, 2025. (AP Photo/Julia Demaree Nikhinson, Pool)