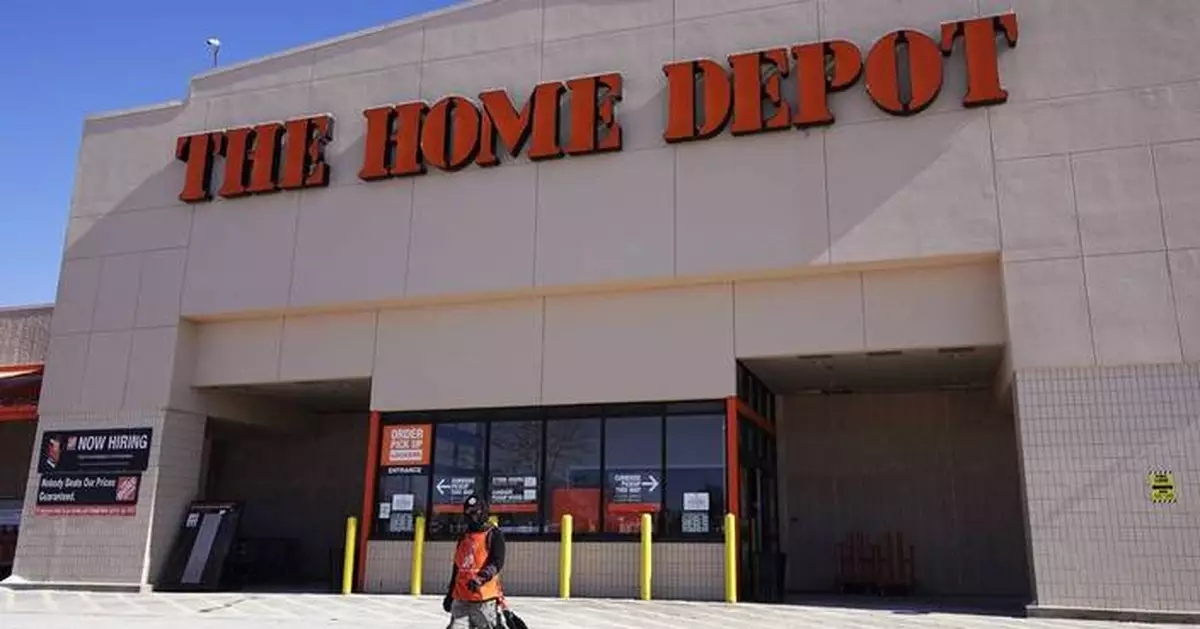
Home Depot's second-quarter sales rose slightly as the nation's biggest home improvement retailer benefitted from an $18 billion acquisition this spring, but customers continued to rein in spending because of broadly higher costs and elevated interest rates.
Sales edged up to $43.18 billion, from $42.92 billion, beating the $42.57 billion that Wall Street had expected, according to a poll by Zacks Investment Research.
The quarterly performance was an improvement thanks in part to the acquisition of contract supplier SRS Distribution, which contributed $1.3 billion to Home Depot’s sales for the quarter. SRS provides materials for professionals like roofers, landscapers and pool contractors.
“The decision of Home Depot to deepen its expertise in specialist categories via the SRS Distribution acquisition is to be welcomed as this adds a new base of customers,” Neil Saunders, managing director of GlobalData, said. “We believe the integration of SRS will bring sales and bottom-line benefits over time, as well as providing a major point of differentiation against rivals like Lowe’s which are trying to cash in on the pro space.”
The performance helped Home Depot snap a sales slump. In the first quarter, Home Depot ’s sales dipped 2.3% to $36.42 billion as the Atlanta company dealt with high mortgage rates, inflation and a delayed start to spring. It was the third consecutive quarter of declining sales for the retailer, which saw sales skyrocket during the pandemic as millions spent more on their homes.
Customer transactions slipped 1.8% in the quarter and they also spent less, with the average ticket totaling $88.90 compared with $90.07 in the same three months last year.
Chairman and CEO Ted Decker said during the company's conference call that Home Depot experienced ongoing softness in spring projects, which was hurt by extreme weather changes during the quarter.
In addition, sales at store open at least a year, a key metric of a retailer’s health, declined 3.3% in the quarter. In the U.S., the figure fell 3.6%.
The company is now expecting 2024 sales at stores open at least a year to decline between 3% and 4%. Its previous outlook was for a decline of approximately 1%. Home Depot expects full-year earnings per share to fall between 2% and 4%. Previously, the company predicted earnings per share growth of about 1%. Total sales for the year, the company said, are expected to be up 2.5% to 3.5%. Its prior guidance was for an increase of about 1%.
Saunders said that Home Depot's revised outlook “suggests more negative sentiment around the consumer economy from management and reflects a more cautious rate cutting stance from the Fed than was expected earlier in the year.”
Shares of Home Depot rose slightly in morning trading on Tuesday.
"The underlying long-term fundamentals supporting home improvement demand are strong,” Decker said in a prepared statement on Tuesday. “During the quarter, higher interest rates and greater macro-economic uncertainty pressured consumer demand more broadly, resulting in weaker spend across home improvement projects."
Home improvement retailers like Home Depot have been dealing with homeowners putting off bigger projects due to higher rates and lingering concerns about inflation.
Elevated mortgage rates, which can add hundreds of dollars a month in costs for borrowers, have discouraged home shoppers for a while, extending the nation’s housing slump into its third year.
Sales of previously occupied U.S. homes fell in June for the fourth month in a row. And sales of new single-family homes fell last month to the slowest annual pace since November.
“Interest rate decisions matter more to Home Depot than they do to an average retailer, if only because a large chunk of home improvement demand is tied to the housing market,” Saunders said. “High interest rates have, and still are, acting as a brake on house moves.”
For the three months ended July 28, Home Depot Inc. earned $4.56 billion, or $4.60 per share. A year ago it earned $4.66 billion, or $4.65 per share.
Removing certain items, earnings were $4.67 per share. Wall Street was calling for $4.54 per share.
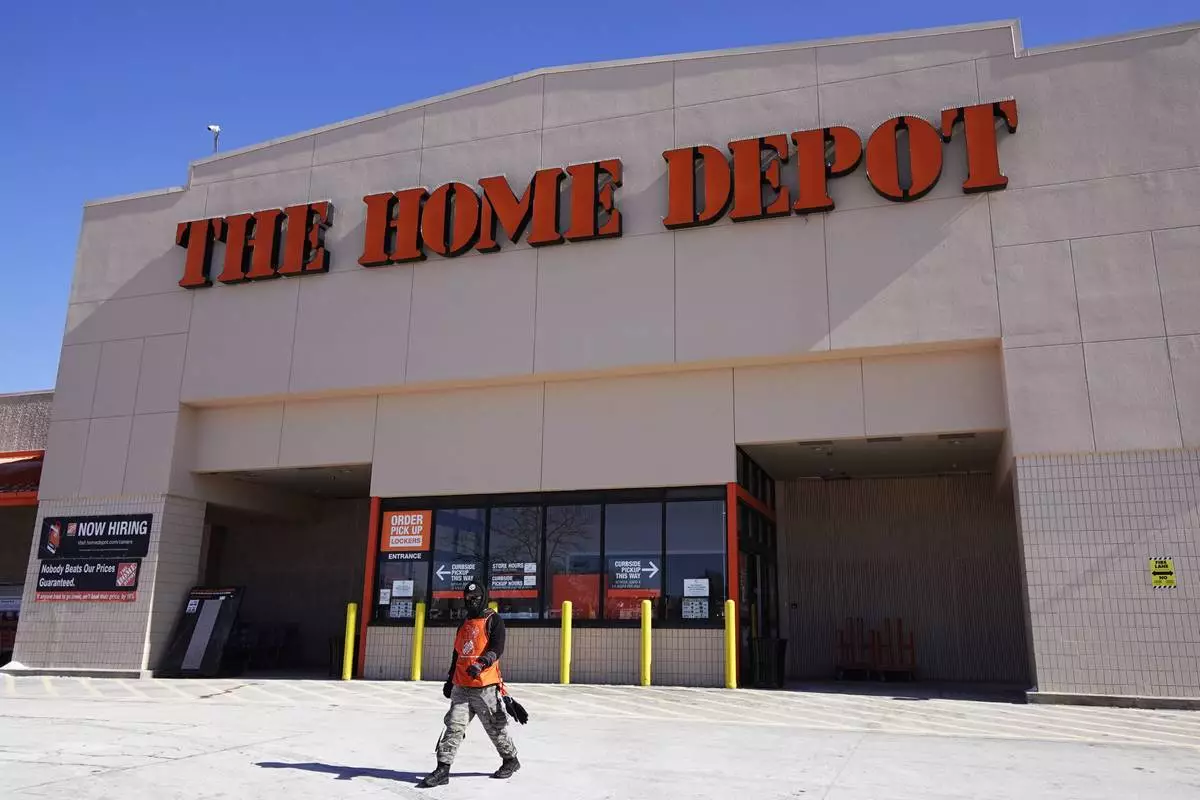

FILE - A view of the exterior of the Home Depot improvement store, in Niles, Ill., on Feb. 19, 2022. Home Depot reports earnings on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023. Home Depot's sales rose slightly in its fiscal second quarter as the country's biggest home improvement retailer saw gains from a recent acquisition, but it continues to be squeezed by customers watching their spending due to prolonged high interest rates. (AP Photo/Nam Y. Huh, File)
What's in a name change, after all?
The water bordered by the Southern United States, Mexico and Cuba will be critical to shipping lanes and vacationers whether it’s called the Gulf of Mexico, as it has been for four centuries, or the Gulf of America, as President Donald Trump ordered this week. North America’s highest mountain peak will still loom above Alaska whether it’s called Mt. Denali, as ordered by former President Barack Obama in 2015, or changed back to Mt. McKinley as Trump also decreed.
But Trump's territorial assertions, in line with his “America First” worldview, sparked a round of rethinking by mapmakers and teachers, snark on social media and sarcasm by at least one other world leader. And though Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis put the Trumpian “Gulf of America” on an official document and some other gulf-adjacent states were considering doing the same, it was not clear how many others would follow Trump's lead.
Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum joked that if Trump went ahead with the renaming, her country would rename North America “Mexican America.” On Tuesday, she toned it down: “For us and for the entire world it will continue to be called the Gulf of Mexico.”
Map lines are inherently political. After all, they're representations of the places that are important to human beings — and those priorities can be delicate and contentious, even more so in a globalized world.
There’s no agreed-upon scheme to name boundaries and features across the Earth.
“Denali” is the mountain's preferred name for Alaska Natives, while “McKinley" is a tribute to President William McKinley, designated in the late 19th century by a gold prospector. China sees Taiwan as its own territory, and the countries surrounding what the United States calls the South China Sea have multiple names for the same body of water.
The Persian Gulf has been widely known by that name since the 16th century, although usage of “Gulf” and “Arabian Gulf” is dominant in many countries in the Middle East. The government of Iran — formerly Persia — threatened to sue Google in 2012 over the company’s decision not to label the body of water at all on its maps. Many Arab countries don’t recognize Israel and instead call it Palestine. And in many official releases, Israel calls the occupied West Bank by its biblical name, “Judea and Samaria.”
Americans and Mexicans diverge on what to call another key body of water, the river that forms the border between Texas and the Mexican states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo Leon and Tamaulipas. Americans call it the Rio Grande; Mexicans call it the Rio Bravo.
Trump's executive order — titled “Restoring Names That Honor American Greatness” — concludes thusly: “It is in the national interest to promote the extraordinary heritage of our Nation and ensure future generations of American citizens celebrate the legacy of our American heroes. The naming of our national treasures, including breathtaking natural wonders and historic works of art, should honor the contributions of visionary and patriotic Americans in our Nation’s rich past.”
But what to call the gulf with the 3,700-mile coastline?
“It is, I suppose, an internationally recognized sea, but (to be honest), a situation like this has never come up before so I need to confirm the appropriate convention,” said Peter Bellerby, who said he was talking over the issue with the cartographers at his London company, Bellerby & Co. Globemakers. “If, for instance, he wanted to change the Atlantic Ocean to the American Ocean, we would probably just ignore it."
As of Wednesday night, map applications for Google and Apple still called the mountain and the gulf by their old names. Spokespersons for those platforms did not immediately respond to emailed questions.
A spokesperson for National Geographic, one of the most prominent map makers in the U.S., said this week that the company does not comment on individual cases and referred questions to a statement on its web site, which reads in part that it "strives to be apolitical, to consult multiple authoritative sources, and to make independent decisions based on extensive research.” National Geographic also has a policy of including explanatory notes for place names in dispute, citing as an example a body of water between Japan and the Korean peninsula, referred to as the Sea of Japan by the Japanese and the East Sea by Koreans.
In discussion on social media, one thread noted that the Sears Tower in Chicago was renamed the Willis Tower in 2009, though it's still commonly known by its original moniker. Pennsylvania's capital, Harrisburg, renamed its Market Street to Martin Luther King Boulevard and then switched back to Market Street several years later — with loud complaints both times. In 2017, New York's Tappan Zee Bridge was renamed for the late Gov. Mario Cuomo to great controversy. The new name appears on maps, but “no one calls it that,” noted another user.
“Are we going to start teaching this as the name of the body of water?” asked one Reddit poster on Tuesday.
“I guess you can tell students that SOME PEOPLE want to rename this body of water the Gulf of America, but everyone else in the world calls it the Gulf of Mexico,” came one answer. “Cover all your bases — they know the reality-based name, but also the wannabe name as well.”
Wrote another user: “I'll call it the Gulf of America when I'm forced to call the Tappan Zee the Mario Cuomo Bridge, which is to say never.”

FILE - President Donald Trump speaks in the Roosevelt Room of the White House, Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025, in Washington. (AP Photo/Julia Demaree Nikhinson, File)

FILE - Peter Bellerby, the founder of Bellerby & Co. Globemakers, holds a globe at a studio in London, Tuesday, Feb. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Kin Cheung, File)

FILE - A boat is seen on the Susitna River near Talkeetna, Alaska, on Sunday, June 13, 2021, with Denali in the background. Denali, the tallest mountain on the North American continent, is located about 60 miles northwest of Talkeetna. (AP Photo/Mark Thiessen, File)

FILE - The water in the Gulf of Mexico appears bluer than usual off of East Beach, Saturday, June 24, 2023, in Galveston, Texas. (Jill Karnicki/Houston Chronicle via AP, File)