NEW YORK (AP) — Stocks closed higher on Wall Street, ending a four-day losing streak. The S&P 500 added 1.2% Monday. The benchmark index is coming off its worst week in nearly a year and a half. The Dow Jones Industrial Average and the Nasdaq composite also rose 1.2%. Boeing helped lead the market after reaching a tentative deal with its largest union on a new contract. Palantir Technologies and Dell Technologies rose after being named to join the S&P 500. Yields held relatively steady in the bond market ahead of reports coming this week on inflation at both the wholesale and consumer levels.
THIS IS A BREAKING NEWS UPDATE. AP’s earlier story follows below.
Click to Gallery
FILE - People pass the New York Stock Exchange on Aug. 27, 2024, in New York. (AP Photo/Peter Morgan, File)
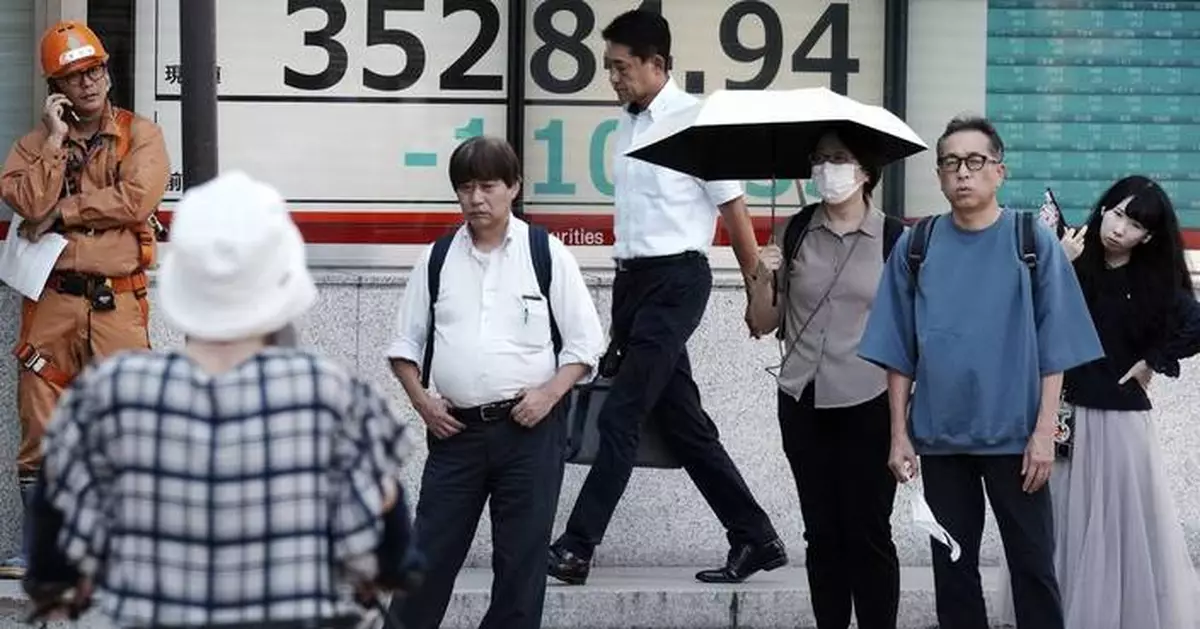
A person walks near an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
A person stands in front of an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
A person looks at an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
A person looks at an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
A person looks at an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
People stand near an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
NEW YORK (AP) — U.S. stocks are rising Monday and clawing back some of the losses from their worst week in nearly a year and a half.
The S&P 500 was 0.9% higher in afternoon trading and on track to break a four-day losing streak. The Dow Jones Industrial Average was up 453 points, or 1.1%, as of 2:17 p.m. Eastern time, and the Nasdaq composite was 0.7% higher.
Boeing climbed 3.6% after reaching a tentative deal with its largest union on a new contract that, if ratified, will avoid a strike that threatened to shut down aircraft production by the end of the week. Boeing said 33,000 workers represented by the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers would get pay raises of 25% over the four-year contract.
After likewise climbing a bit in the morning, Treasury yields later pared their gains in the bond market. That followed sharp swings last week, when a highly anticipated update on the U.S. job market came in weak enough to worsen worries about the slowing U.S. economy.
The Federal Reserve has been intentionally pressing the brakes on the economy through high interest rates in order to stifle high inflation. It’s set to start lowering rates later this month, which would ease the pressure on the economy, as it turns its focus toward protecting the job market and avoiding a recession. The question on Wall Street is if the Fed's shift in focus will prove to be too late.
Cuts to interest rates give stock prices a boost, but if an economic downturn does hit, it could more than offset such a benefit by dragging down profits for companies. That's what happened in 2007, for example, when the Great Recession wrecked the global economy and financial markets.
“Today, the absence of glaring household or corporate balance sheet vulnerabilities means Fed easing should be enough to prevent recession, and should provide investors some optimism for the future of the market,” suggests Seema Shah, chief global strategist at Principal Asset Management.
On Wall Street, Apple’s stock fell 1.3% as the company held an event unveiling its latest iPhone model, the 16. It’s the first model to be tailored specifically for artificial intelligence, with expected improvements to its often dim-witted virtual assistant, Siri.
Palantir Technologies jumped 12.8% in its first trading after S&P Dow Jones Indices said it would add the company to its widely followed S&P 500 index. Dell Technologies rose 3.6%, and Erie Indemnity gained 1.3% after they likewise got a notice of promotion to the index.
Trading in Big Lots was halted after the discount retailer filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection and said it plans to sell its assets and ongoing business operations to private equity firm Nexus Capital Management.
In the bond market, the 10-year Treasury yield edged down to 3.71% from 3.72% late Friday.
This upcoming week will feature the latest monthly updates on inflation at the consumer and wholesale levels. Such reports used to be the most anticipated economic data of each month, but market watchers say they’re now taking the back seat to updates on the job market because of the worries about a possible recession.
Of course, if the inflation reports show an unexpected spike higher in inflation, that could put the Federal Reserve in its worst-case scenario. Lower interest rates could help boost the economy, but they could also give inflation more fuel.
In stock markets abroad, indexes rose in much of Europe after falling in Asia. Japan’s Nikkei 225 slipped 0.5% after the country’s economic growth for the second quarter was revised below expectations.
Chinese stocks racked up losses after worse-than-expected inflation data disappointed investors. Indexes fell 1.4% in Hong Kong and 1.1% in Shanghai.
AP Writers Matt Ott and Zimo Zhong contributed.

FILE - People pass the New York Stock Exchange on Aug. 27, 2024, in New York. (AP Photo/Peter Morgan, File)

A person walks near an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)

A person stands in front of an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
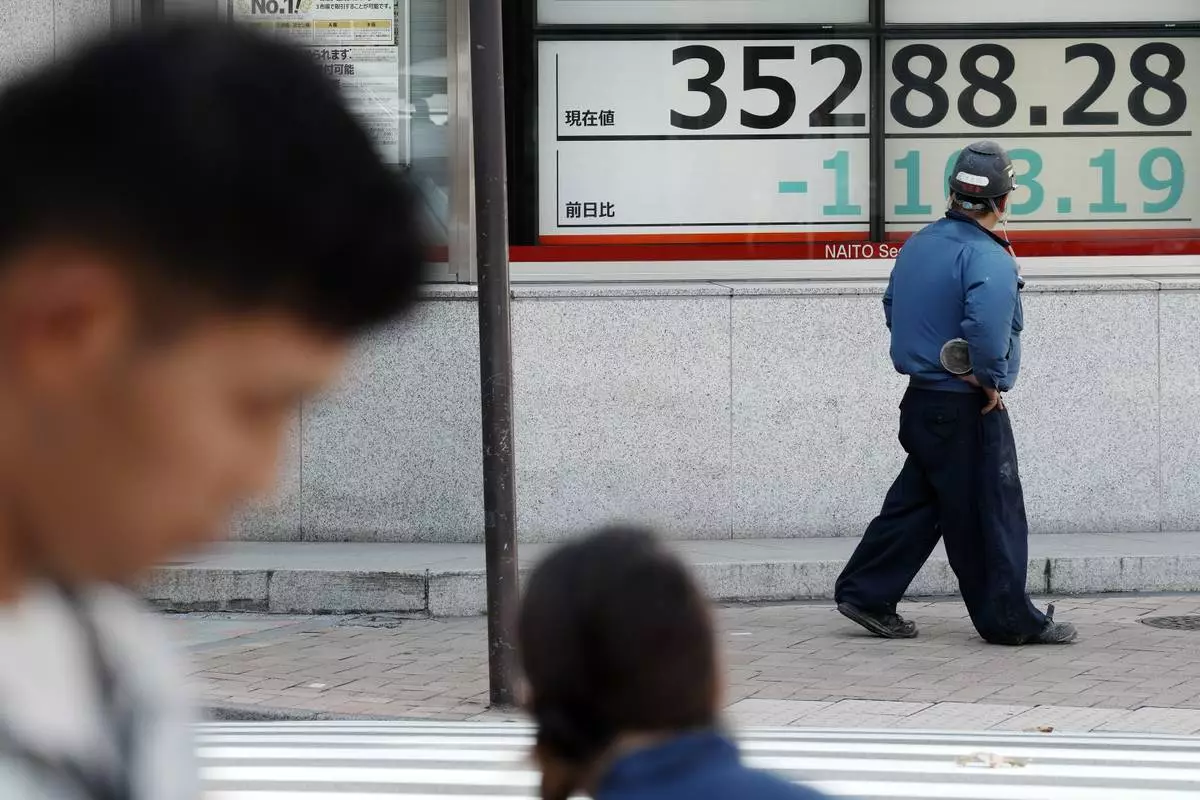

A person looks at an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
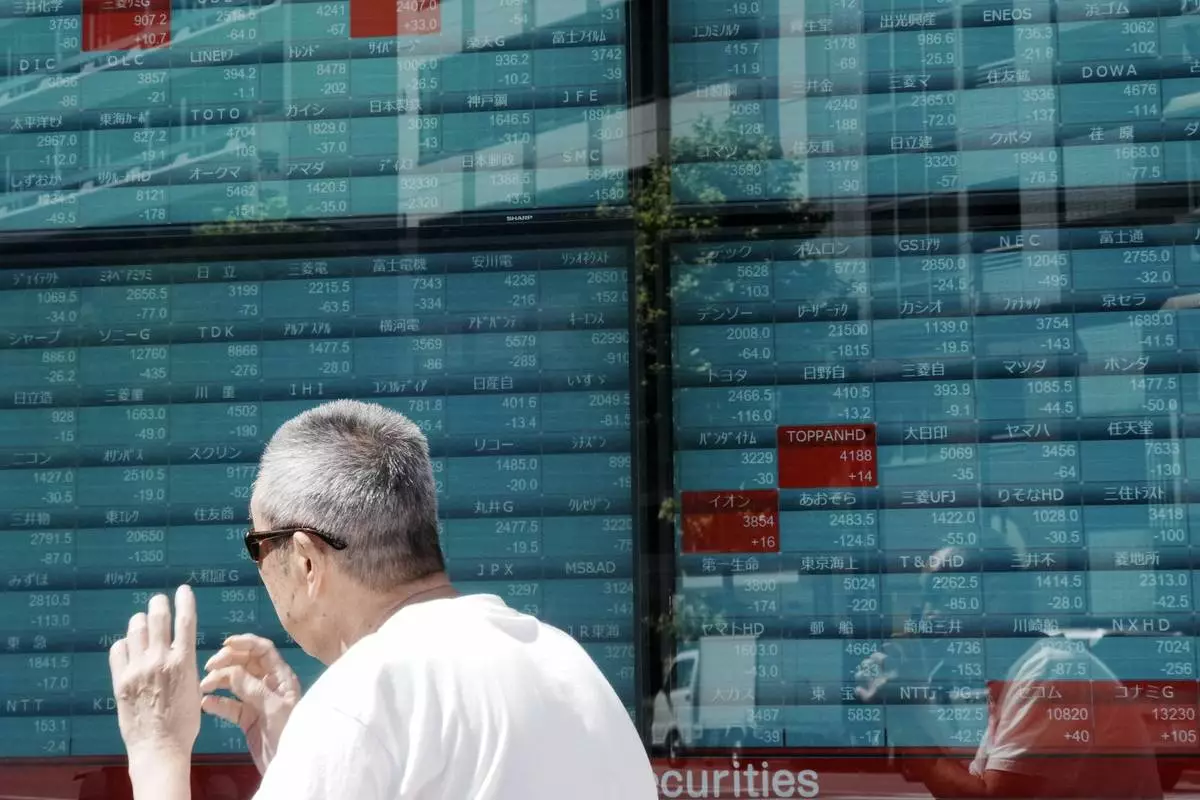

A person looks at an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)

A person looks at an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
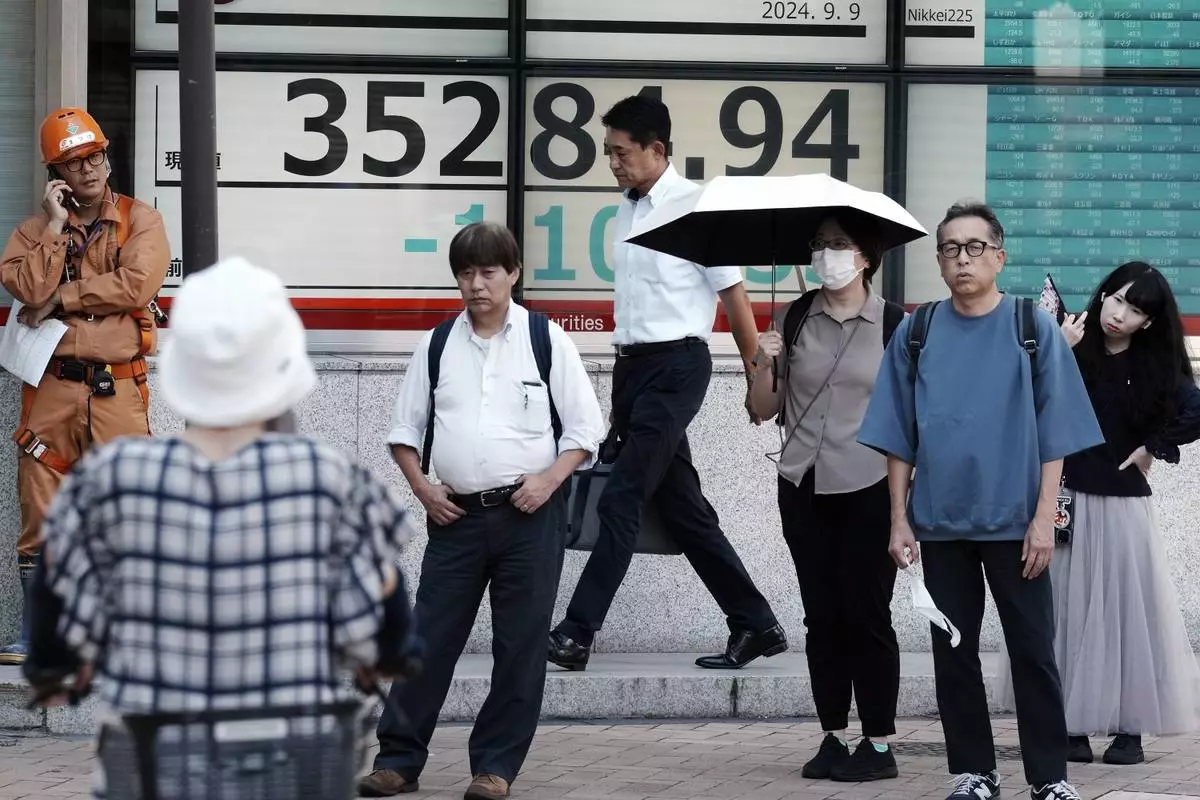

People stand near an electronic stock board showing Japan's Nikkei index at a securities firm Monday, Sept. 9, 2024, in Tokyo. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Donald Trump signed an executive order Monday directing the United States to again withdraw from the landmark Paris climate agreement, dealing a blow to worldwide efforts to combat global warming and once again distancing the U.S. from its closest allies.
Trump's action, hours after he was sworn in to a second term, echoed his directive in 2017, when he announced that the U.S. would abandon the global Paris accord. The pact is aimed at limiting long-term global warming to 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit (1.5 degrees Celsius) above pre-industrial levels or, failing that, keeping temperatures at least well below 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit (2 degrees Celsius) above pre-industrial levels.
Trump also signed a letter to the United Nations indicating his intention to withdraw from the 2015 agreement, which allows nations to provide targets to cut their own emissions of greenhouse gases from the burning of coal, oil and natural gas. Those targets are supposed to become more stringent over time, with countries facing a February 2025 deadline for new individual plans. The outgoing Biden administration last month offered a plan to cut U.S. greenhouse gas emissions by more than 60% by 2035.
Trump's order says the Paris accord is among a number of international agreements that don't reflect U.S. values and “steer American taxpayer dollars to countries that do not require, or merit, financial assistance in the interests of the American people."
Instead of joining a global agreement, “the United States’ successful track record of advancing both economic and environmental objectives should be a model for other countries,'' Trump said.
Laurence Tubiana, CEO of the European Climate Foundation and a key architect of the Paris accord, called the planned U.S. withdrawal unfortunate but said action to slow climate change “is stronger than any single country’s politics and policies."
The global context for Trump's action is “very different to 2017,'' Tubiana said Monday, adding that “there is unstoppable economic momentum behind the global transition, which the U.S has gained from and led but now risks forfeiting."
The International Energy Agency expects the global market for key clean energy technologies to triple to more than $2 trillion by 2035, she said.
“The impacts of the climate crisis are also worsening. The terrible wildfires in Los Angeles are the latest reminder that Americans, like everyone else, are affected by worsening climate change,” Tubiana said.
Gina McCarthy, who served as White House climate adviser under President Joe Biden, a Democrat, said that if Trump, a Republican, “truly wants America to lead the global economy, become energy independent and create good-paying American jobs," then he must “stay focused on growing our clean energy industry. Clean technologies are driving down energy costs for people all across our country."
The world is now long-term 2.3 degrees Fahrenheit (1.3 degrees Celsius) above mid-1800s temperatures. Most but not all climate monitoring agencies said global temperatures last year passed the warming mark of 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit, and all said it was the warmest year on record.
The withdrawal process from the Paris accord takes one year. Trump’s previous withdrawal took effect the day after the 2020 presidential election, which he lost to Biden.
While the first Trump-led withdrawal from the landmark U.N. agreement — adopted by 196 nations — shocked and angered nations across the globe, “not a single country followed the U.S. out the door,” said Alden Meyer, a longtime climate negotiations analyst with the European think tank E3G.
Instead, other nations renewed their commitment to slowing climate change, along with investors, businesses, governors, mayors and others in the U.S., Meyer and other experts said.
Still, they lamented the loss of U.S. leadership in global efforts to slow climate change, even as the world is on track to set yet another record hot year and has been lurching from drought to hurricane to flood to wildfire.
“Clearly America is not going to play the commanding role in helping solve the climate crisis, the greatest dilemma humans have ever encountered,″ said climate activist and writer Bill McKibben. “For the next few years the best we can hope is that Washington won’t manage to wreck the efforts of others.”
About half of Americans “somewhat” or “strongly” oppose U.S. action to withdraw from the climate accord, and even Republicans aren’t overwhelmingly in favor, according according to a poll from The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research. Only about 2 in 10 U.S. adults “somewhat” or “strongly” in favor of withdrawing from the Paris agreement, while about one-quarter are neutral.
Much of the opposition to U.S. withdrawal comes from Democrats, but Republicans display some ambivalence as well. Slightly less than half of Republicans are in favor of withdrawing from the climate accord, while about 2 in 10 are opposed.
China several years ago passed the United States as the world's largest annual carbon dioxide emitting nation. The U.S. — the second biggest annual carbon polluting country — put 4.9 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide in the air in 2023, down 11% from a decade earlier, according to the scientists who track emissions for the Global Carbon Project.
But carbon dioxide lasts in the atmosphere for centuries, so the United States has put more of the heat-trapping gas that is now in the air than any other nation. The U.S. is responsible for nearly 22% of the carbon dioxide put in the atmosphere since 1950, according to Global Carbon Project.
While global efforts to fight climate change continued during Trump's first term, many experts worry that a second Trump term will be more damaging, with the United States withdrawing even further from climate efforts in a way that could cripple future presidents’ efforts. With Trump, who has dismissed climate change, in charge of the world’s leading economy, those experts fear other countries, especially China, could use it as an excuse to ease off their own efforts to curb carbon emissions.
Simon Stiell, the U.N. climate change executive secretary, held out hope that the U.S. would continue to embrace the global clean energy boom.
“Ignoring it only sends all that vast wealth to competitor economies, while climate disasters like droughts, wildfires and superstorms keep getting worse," Stiell said. “The door remains open to the Paris Agreement, and we welcome constructive engagement from any and all countries.”
Associated Press writer Linley Sanders contributed to this report.
The Associated Press’ climate and environmental coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. The AP is solely responsible for all content. Find the AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.
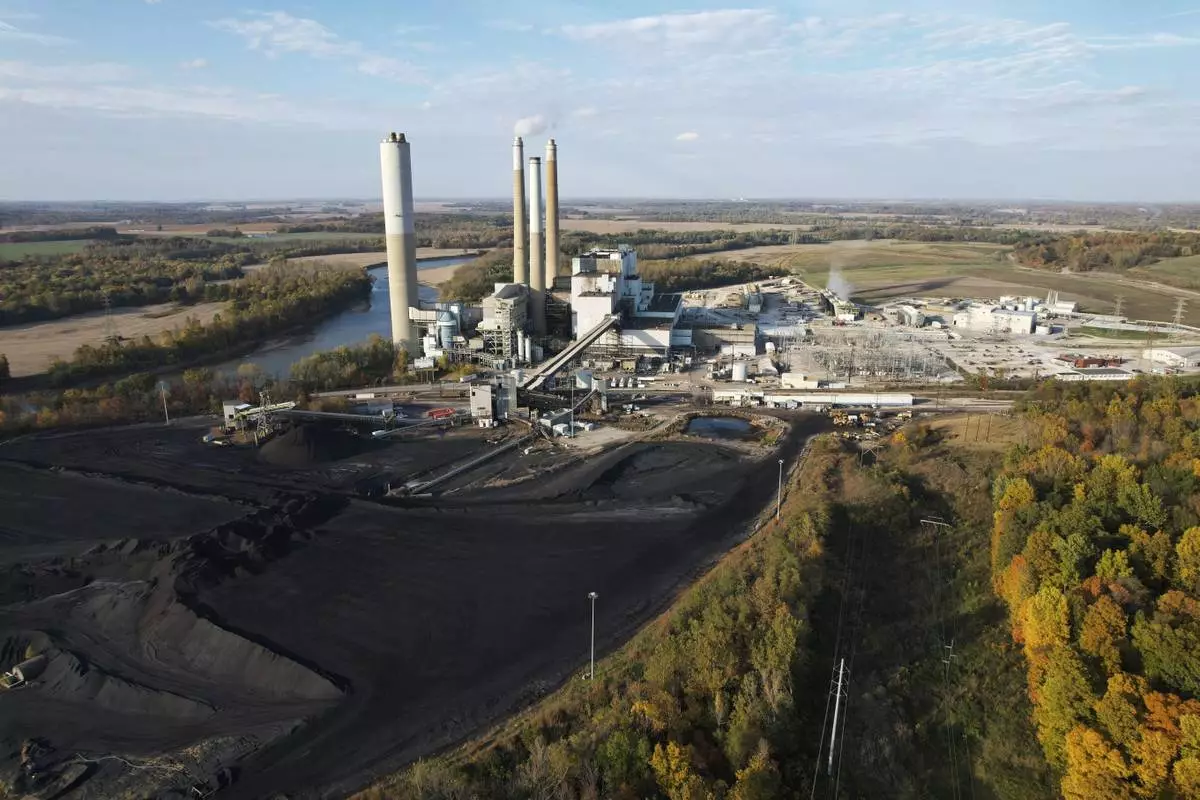

AES Indiana Petersburg Generating Station, a coal-fired power plant, operates in Petersburg, Ind., on Wednesday, Oct. 25, 2023. (AP Photo/Joshua A. Bickel)
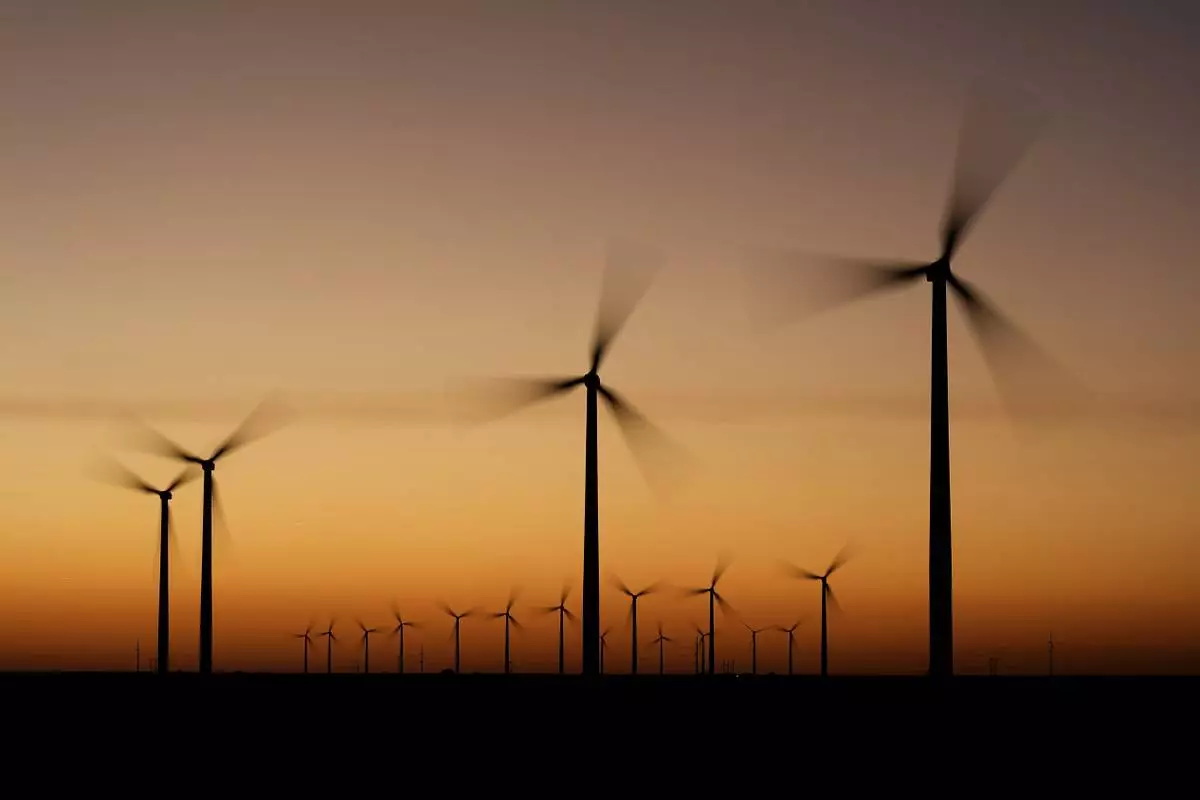

FILE - Wind turbines stretch across the horizon at dusk at the Spearville Wind Farm, Sept. 29, 2024, near Spearville, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel, File)
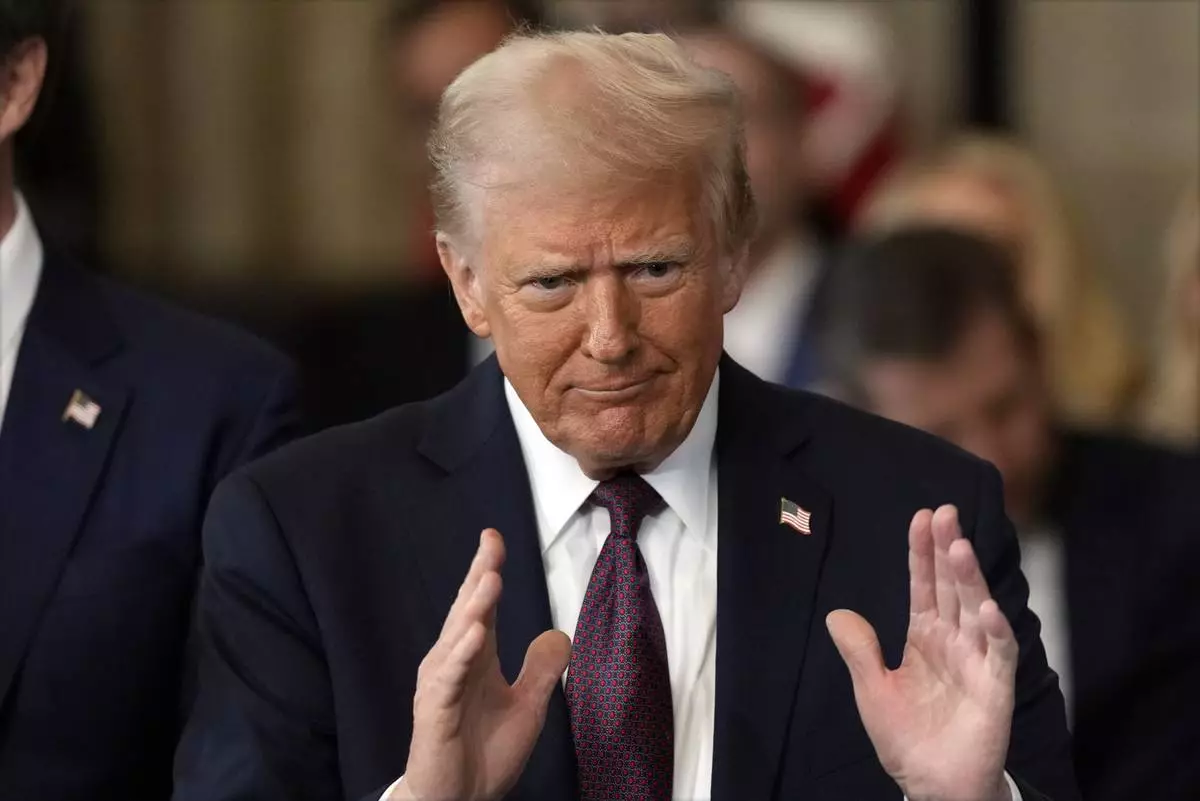

President Donald Trump gestures during the 60th Presidential Inauguration in the Rotunda of the U.S. Capitol in Washington, Monday, Jan. 20, 2025. (AP Photo/Julia Demaree Nikhinson, Pool)