WASHINGTON (AP) — House Republicans on Sunday issued a scathing report on their investigation into the U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan, blaming the disastrous end of America's longest war on President Joe Biden's administration and minimizing the role of former President Donald Trump, who had signed the withdrawal deal with the Taliban.
The partisan review lays out the final months of military and civilian failures, following Trump's February 2020 withdrawal deal, that allowed America's fundamentalist Taliban enemy to sweep through and conquer all of the country even before the last U.S. officials flew out on Aug. 30, 2021. The chaotic exit left behind many American citizens, Afghan battlefield allies, women activists and others at risk from the Taliban.
But House Republicans' report breaks little new ground as the withdrawal has been exhaustively litigated through several independent reviews. Previous investigations and analyses have pointed to a systemic failure spanning the last four presidential administrations and concluded that Biden and Trump share the heaviest blame.
Texas Republican Rep. Michael McCaul, who led the investigation as chairman of the House Foreign Affairs Committee, said the GOP review reveals that the Biden administration “had the information and opportunity to take necessary steps to plan for the inevitable collapse of the Afghan government, so we could safely evacuate U.S. personnel, American citizens, green card holders, and our brave Afghan allies.”
“At each step of the way, however, the administration picked optics over security,” he said in a statement.
McCaul earlier in the day denied that the timing of the report's release ahead of the presidential election was political, or that Republicans ignored Trump's mistakes in the U.S. withdrawal.
A White House spokesperson, Sharon Yang, said the Republican report was based on “cherry-picked facts, inaccurate characterizations, and preexisting biases.”
“Because of the bad deal former President Trump cut with the Taliban to get out of Afghanistan by May of 2021, President Biden inherited an untenable position,” either ramp up the U.S. war against a strengthened Taliban, or end it, Yang said in a statement.
House Democrats in a statement said the report by their Republican colleagues ignored facts about Trump's role.
The more than 18-month investigation by Republicans on the House Foreign Affairs Committee zeroed in on the months leading up to the removal of U.S. troops, saying that Biden and his administration undermined high-ranking officials and ignored warnings as the Taliban seized key cities far faster than most U.S. officials had expected or prepared for.
“I called their advance ‘the Red Blob,’'' retired Col. Seth Krummrich said of the Taliban, telling the committee that at the special operations' central command where he was chief of staff, ”we tracked the Taliban advance daily, looking like a red blob gobbling up terrain."
“I don't think we ever thought — you know, nobody ever talked about, ‘Well, what’s going to happen when the Taliban come over the wall?''' Carol Perez, the State Department's acting undersecretary for management at the time of the withdrawal, said of what House Republicans said was minimal State Department planning before abandoning the embassy in mid-August 2021 when the Taliban swept into Kabul, Afghanistan's capital.
The withdrawal ended a nearly two-decade occupation by U.S. and allied forces begun to rout out the al-Qaida militants responsible for the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks on the United States. The Taliban had allowed al-Qaida's leader, Osama bin Laden, to shelter in Afghanistan. Committee staffers noted reports since the U.S. withdrawal of the group rebuilding in Afghanistan, such as a U.N. report of up to eight al-Qaida training camps there.
The Taliban overthrew an Afghan government and military that the U.S. had spent nearly 20 years and trillions of dollars building in hopes of keeping the country from again becoming a base for anti-Western extremists.
A 2023 report by the U.S. government watchdog for the U.S. in Afghanistan singles out Trump’s February 2020 deal with the Taliban agreeing to withdraw all American forces and military contractors by the spring of the next year, and both Trump’s and Biden’s determination to keep pulling out U.S. forces despite the Taliban breaking key commitments in the withdrawal deal.
House Republicans' more than 350-page document is the product of hours of testimony — including with former Joint Chiefs Chairman Gen. Mark Milley, U.S. Central Command retired Gen. Frank McKenzie and others who were senior officials at the time — seven public hearings and round-tables as well as more than 20,000 pages of State Department documents reviewed by the committees.
With Biden no longer running for reelection, Trump and his GOP allies have tried to elevate the withdrawal as a campaign issue against Vice President Kamala Harris, who is now Trump's Democratic opponent in the presidential race.
The report by House Republican cites Harris' overall responsibility as an adviser to Biden, but doesn't point to specific counsel or action by Harris that contributed to the many failures.
Some highlights of the report:
Republicans point to testimony and records that claim the Biden administration's reliance on input from military and civilian leaders on the ground in Afghanistan in the months before the withdrawal was “severely limited,” with most of the decision-making taking place by National Security Adviser Jake Sullivan without consultation with key stakeholders.
Yang, the White House spokesperson, denied that, saying the administration had sought input from officials in Kabul and others across the U.S. government.
The report says Biden proceeded with the withdrawal even though the Taliban was failing to keep some of its agreements under the deal, including breaking its promise to enter talks with the then-U.S.- backed Afghan government.
Former State Department spokesperson Ned Price testified to the committee that adherence to the Doha Agreement was “immaterial” to Biden's decision to withdraw, according to the report.
Earlier reviews have said Trump also carried out his early steps of the withdrawal deal, cutting the U.S. troop presence from about 13,000 to an eventual 2,500 despite early Taliban noncompliance with some parts of the deal, and despite the Taliban escalating attacks on Afghan forces.
The House report faults a longtime U.S. diplomat for Afghanistan, former Ambassador Zalmay Khalilzad, not Trump, for Trump administration actions in its negotiations with the Taliban. The new report says that Trump was following recommendations of American military leaders in making sharp cuts in U.S. troop numbers in Afghanistan after the signing.
The report also goes into the vulnerability of U.S. embassy staff in Kabul as the Biden administration planned its exit. Republicans claim there was a “dogmatic insistence” by the Biden administration to maintain a large diplomatic footprint despite concerns about the lack of security afforded to personnel once U.S. forces left.
McKenzie, who was one of the two U.S. generals who oversaw the evacuation, told lawmakers that the administration’s insistence at keeping the embassy open and fully operational was the “fatal flaw that created what happened in August," according to the report.
The committee report claims that State Department officials went as far as watering down or “even completely rewriting reports” from heads of diplomatic security and the Department of Defense that had warned of the threats to U.S. personnel as the withdrawal date got closer.
“We were still in planning" when Kabul fell, Perez, the senior U.S. diplomat, testified to the committee.
Associated Press writer Rebecca Santana contributed to this report.
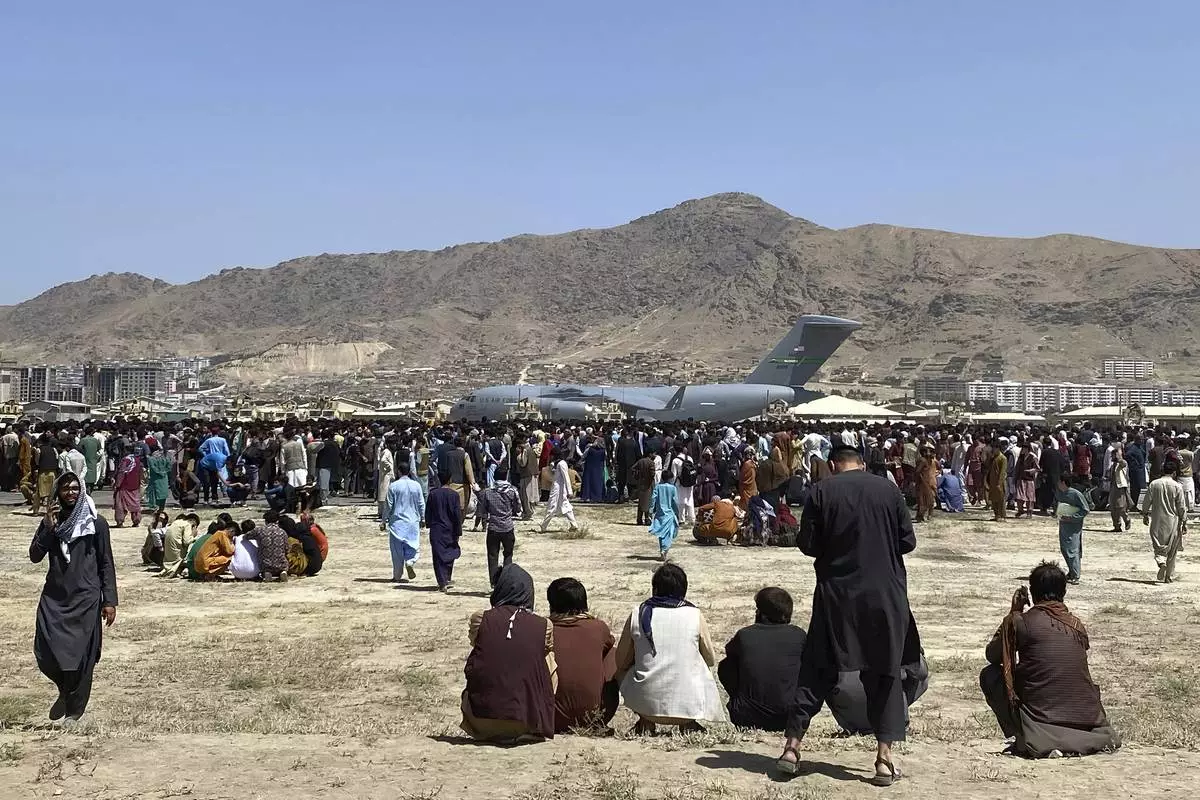

FILE - Hundreds of people gather near a U.S. Air Force C-17 transport plane at the perimeter of the international airport in Kabul, Afghanistan, on Aug. 16, 2021. (AP Photo/Shekib Rahmani, File)
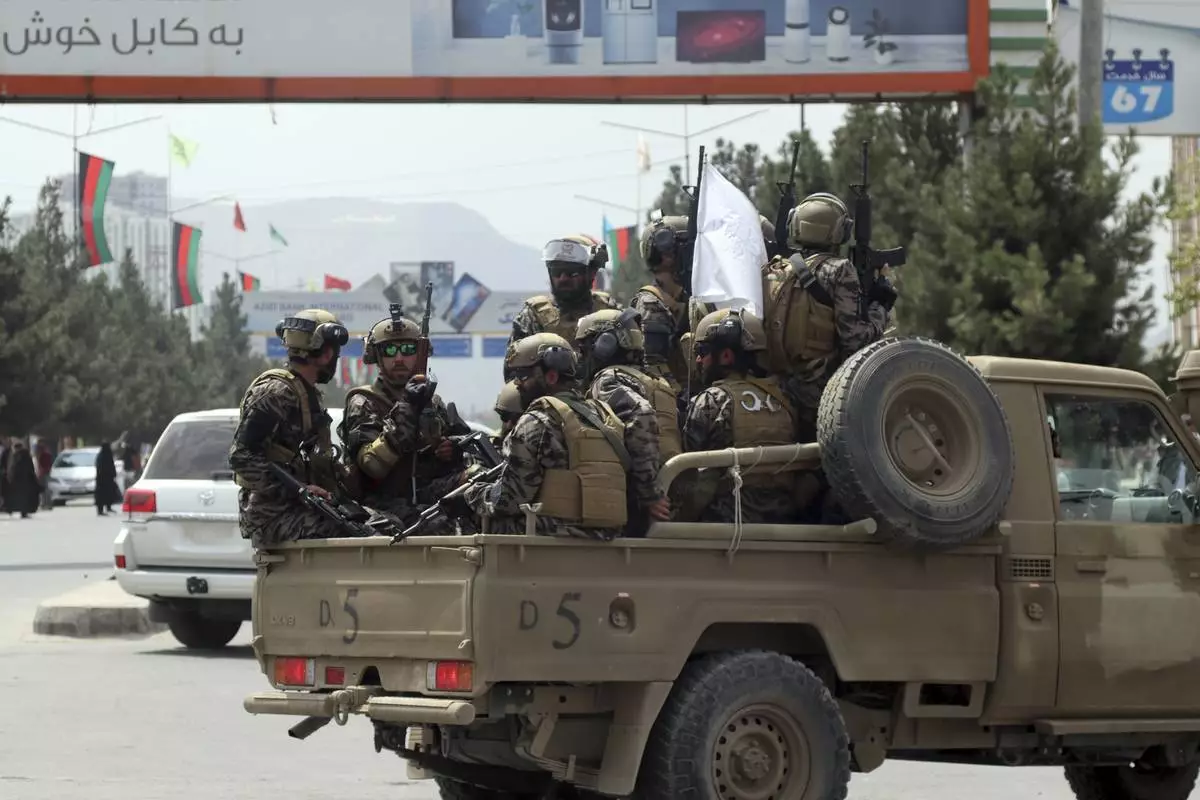

FILE - Taliban special force fighters arrive inside the Hamid Karzai International Airport after the U.S. military's withdrawal, in Kabul, Afghanistan, Aug. 31, 2021. (AP Photo/Khwaja Tawfiq Sediqi, File)
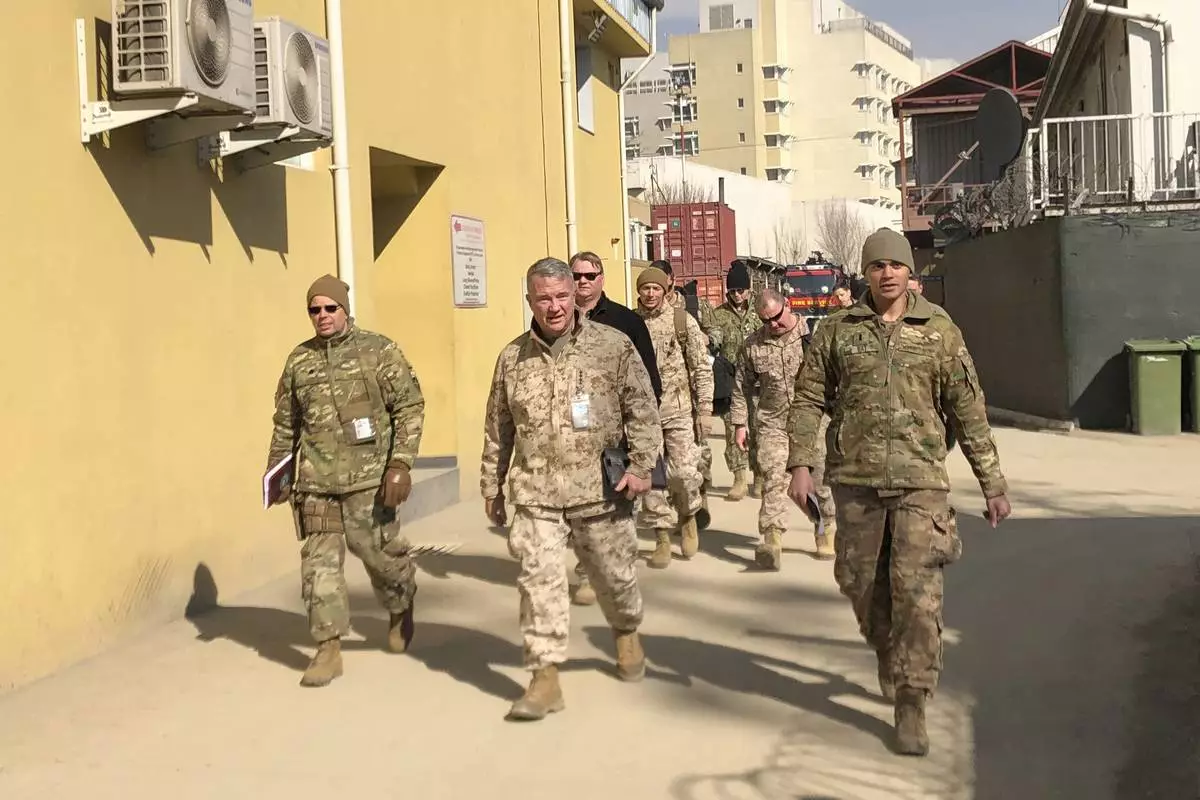

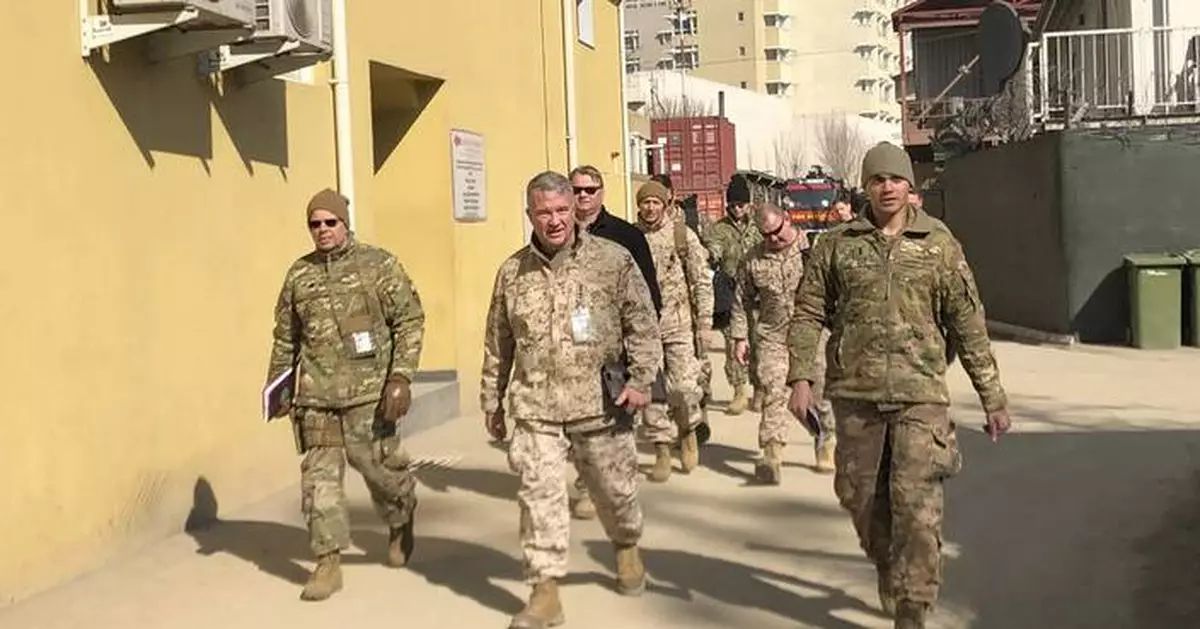
FILE - Marine Gen. Frank McKenzie, center, top U.S. commander for the Middle East, makes an unannounced visit in Kabul, Afghanistan, Jan. 31, 2020. (AP Photos/Lolita Baldor, File)