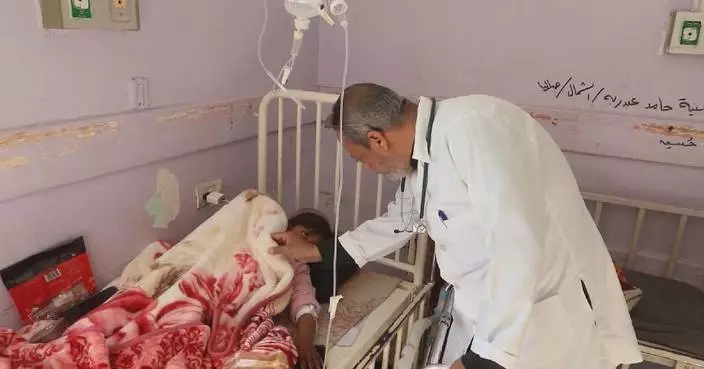
HANOI, Vietnam (AP) — The death toll from Typhoon Yagi and its subsequent rain that triggered floods and landslides climbed to 87 on Tuesday as 70 others remain missing and hundreds were injured, state media said.
Yagi was the strongest typhoon to hit the Southeast Asian country in decades. It made landfall Saturday with winds of up to 149 kph (92 mph) and despite weakening on Sunday, downpours continued.
Click to Gallery
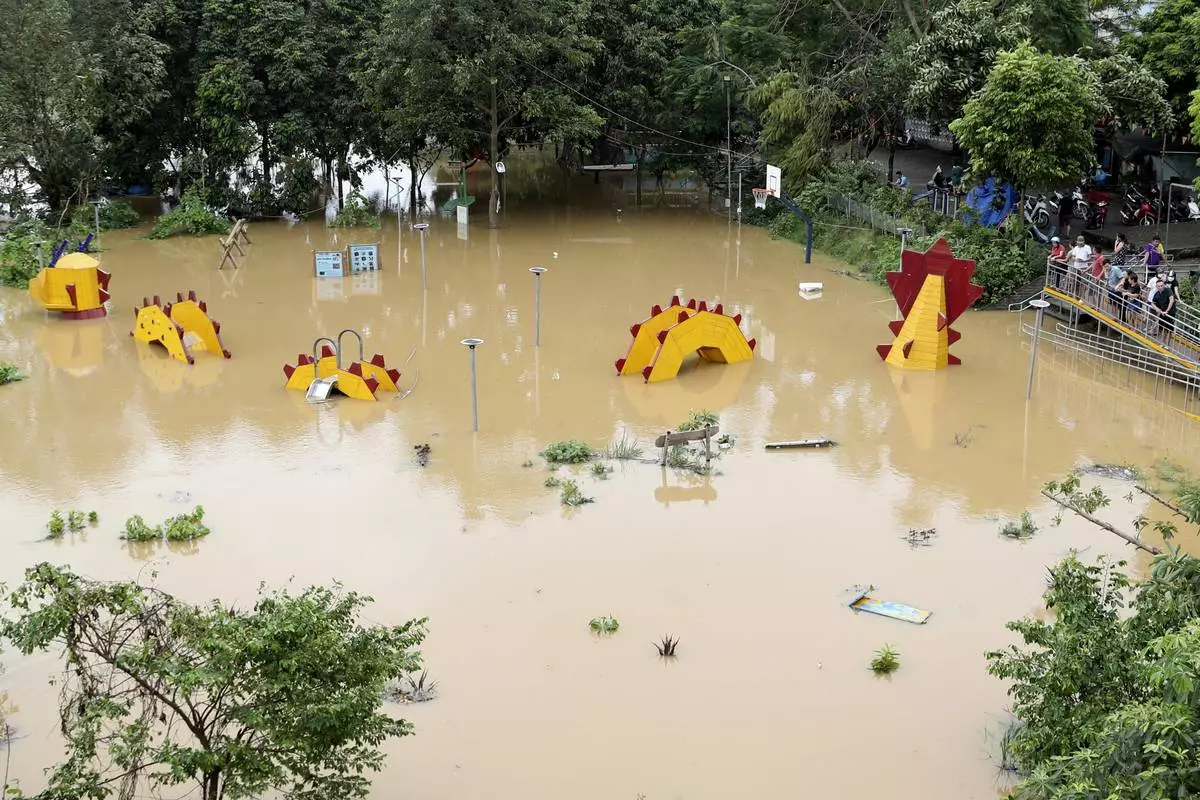
People look on a submerged dragon structure in a playground, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
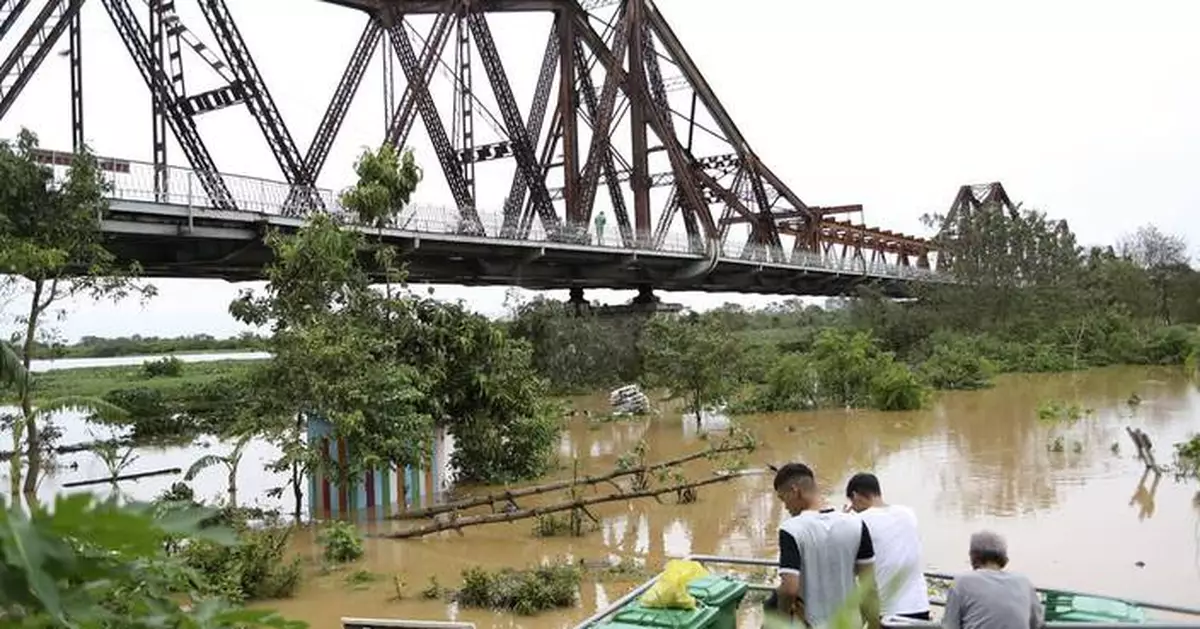
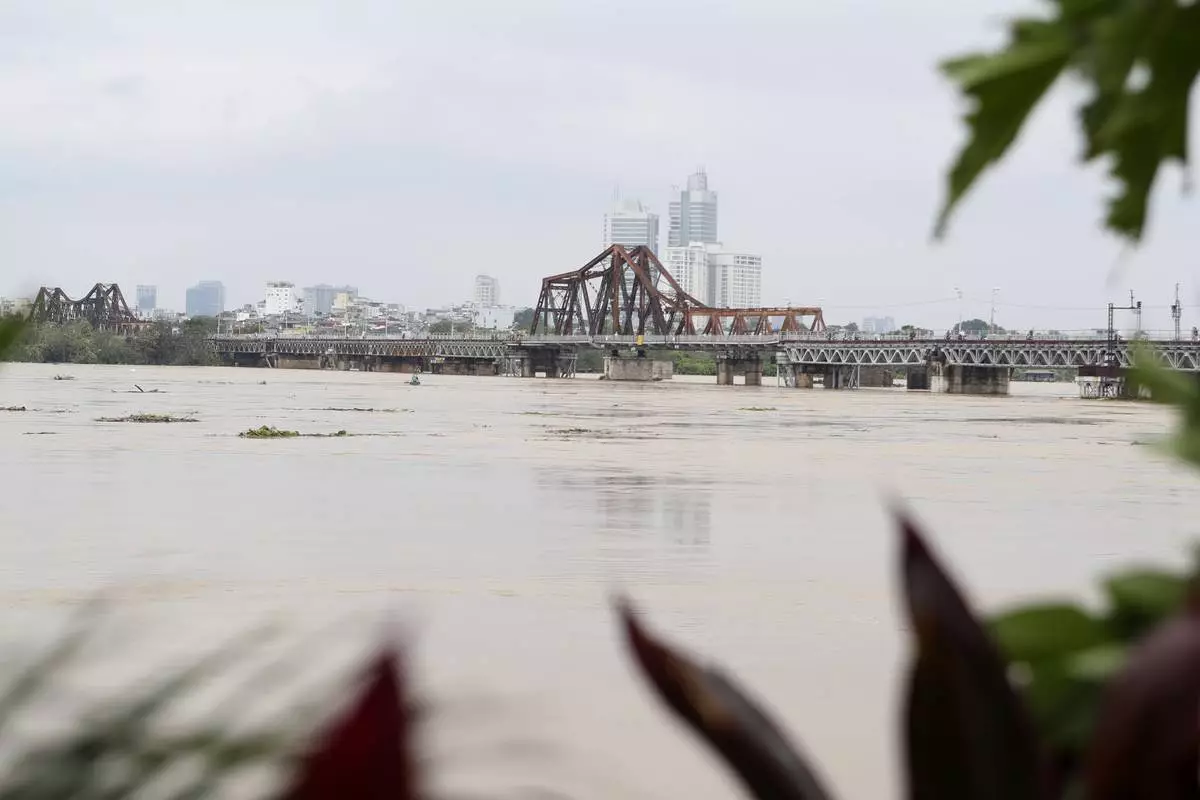
The iconic Long Bien bridge is seen on flooded Red river, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
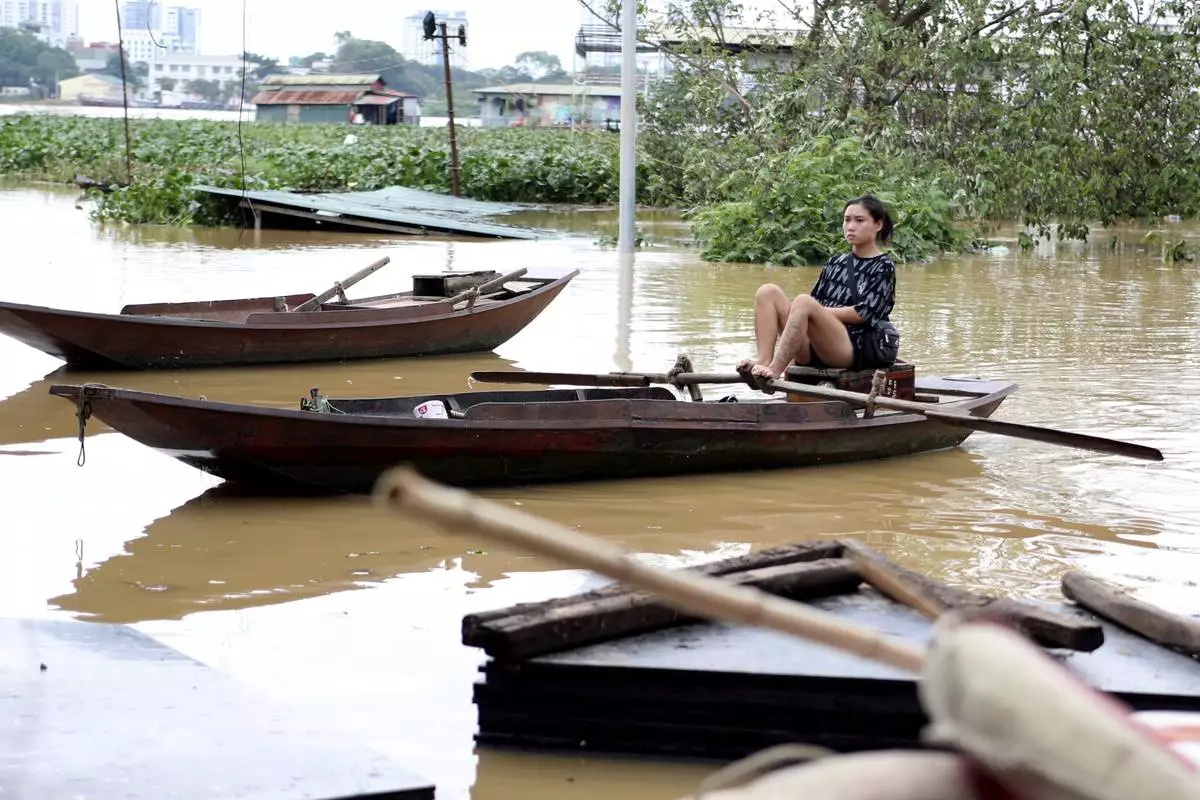
A woman paddles a boat on a flooded street, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
A banana garden is submerged in flood, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
People watch a submerged dragon structure in a playground, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
A man pushes a stack of plyboards in flood following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
People fish next to a submerged playground due to flood , following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
People watch the flooded Red river next to iconic Long Bien bridge, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
Vietnamese state broadcaster VTV said floods and landslides caused most of the deaths.
Water levels in several rivers, including the Red River that flows through the capital, Hanoi, were dangerously high, forcing authorities to evacuate people living close by. State media cited local officials saying Hanoi, Vietnam’s second-most populated city and home to 8.5 million people, experienced floods not seen since 2008.
Heavy rainfall and landslides killed 19 people in northwestern Lao Cai province bordering China. Video obtained by The Associated Press on Tuesday showed soil sliding down a hill onto houses and a road while people fled for safety. Meanwhile, authorities said three people were rescued after a steel bridge crumpled the day before into the Red River in the province, while 13 others remain missing, according to state media.
Thousands of people were also evacuated in the mountainous province of Yen Bai because of rising floods, local media said, adding that at least 32 people had died and seven were missing. Authorities said over 10,000 homes in the province's eponymous main city were completely inundated with floodwaters.
Blue Dragon Children’s Foundation said in a statement hundreds were displaced and isolated in the rocky provinces of Ha Giang and Dien Bien. It also said debris from landslides blocked the roads in Ha Giang while schools near rivers were shut because of flooding risk.
The nonprofit’s co-CEO, Skye Maconachie, said Vietnamese communities who were already vulnerable were the most impacted “as it often happens in disasters like this."
One of the hardest-hit Vietnamese provinces is Cao Bang, where 19 people died and 36 others are missing because of landslides in the hilly area, and where a bridge collapsed and a bus was swept away, carrying about 20 people into a flooded stream on Monday.
Yagi and its heavy rain also damaged factories in northern provinces like Haiphong.
Storms like Typhoon Yagi are “getting stronger due to climate change, primarily because warmer ocean waters provide more energy to fuel the storms, leading to increased wind speeds and heavier rainfall,” said Benjamin Horton, director of the Earth Observatory of Singapore.

People look on a submerged dragon structure in a playground, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)

The iconic Long Bien bridge is seen on flooded Red river, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)

A woman paddles a boat on a flooded street, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
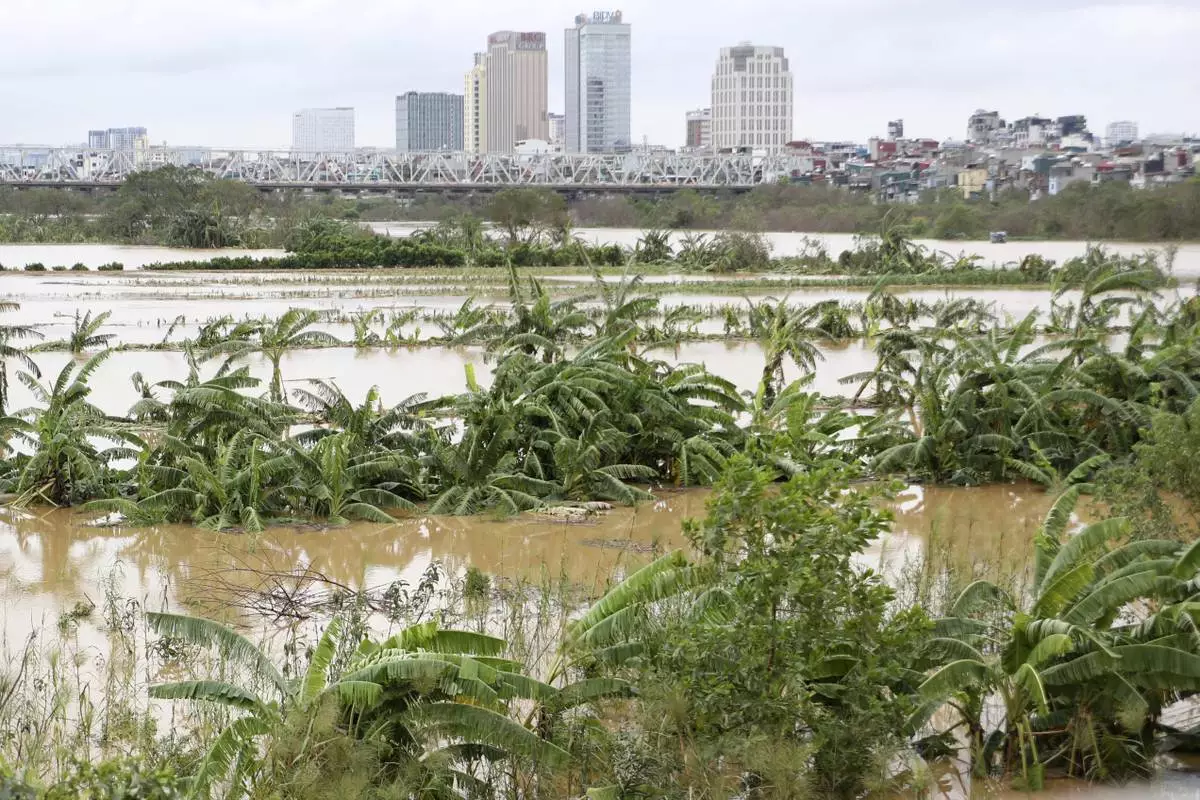

A banana garden is submerged in flood, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
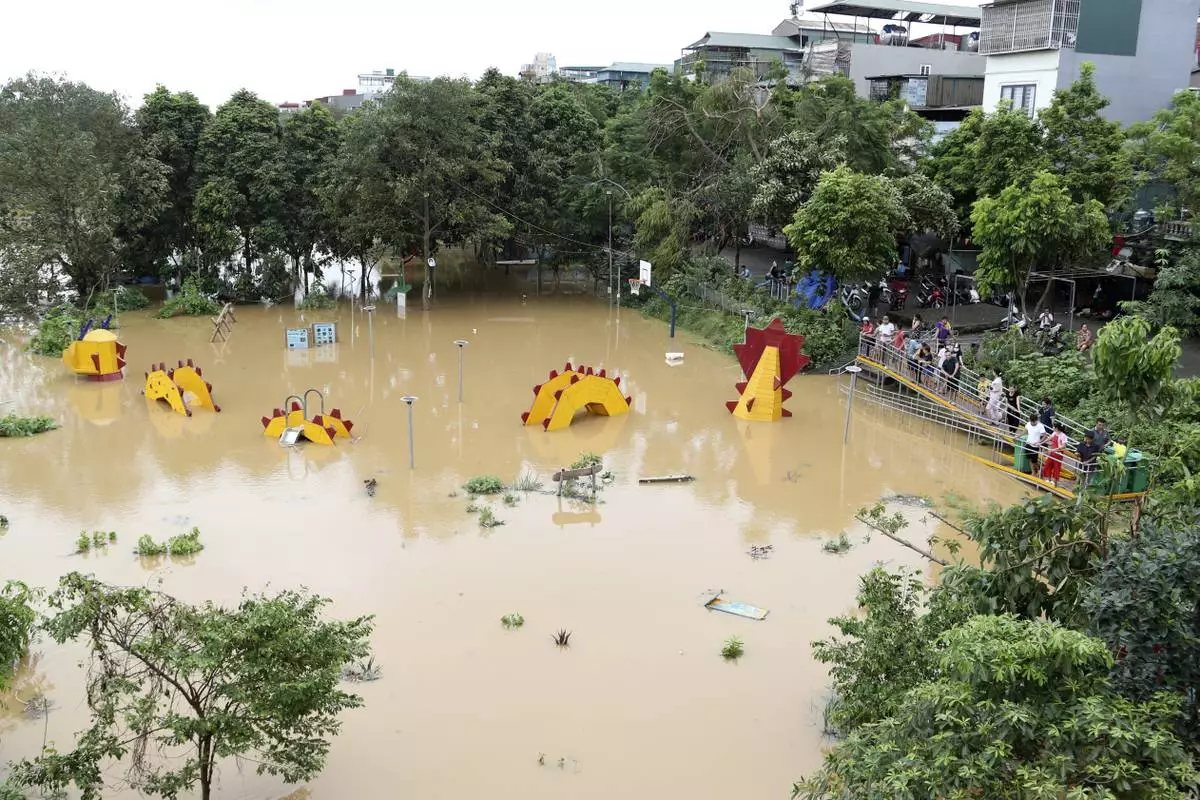

People watch a submerged dragon structure in a playground, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
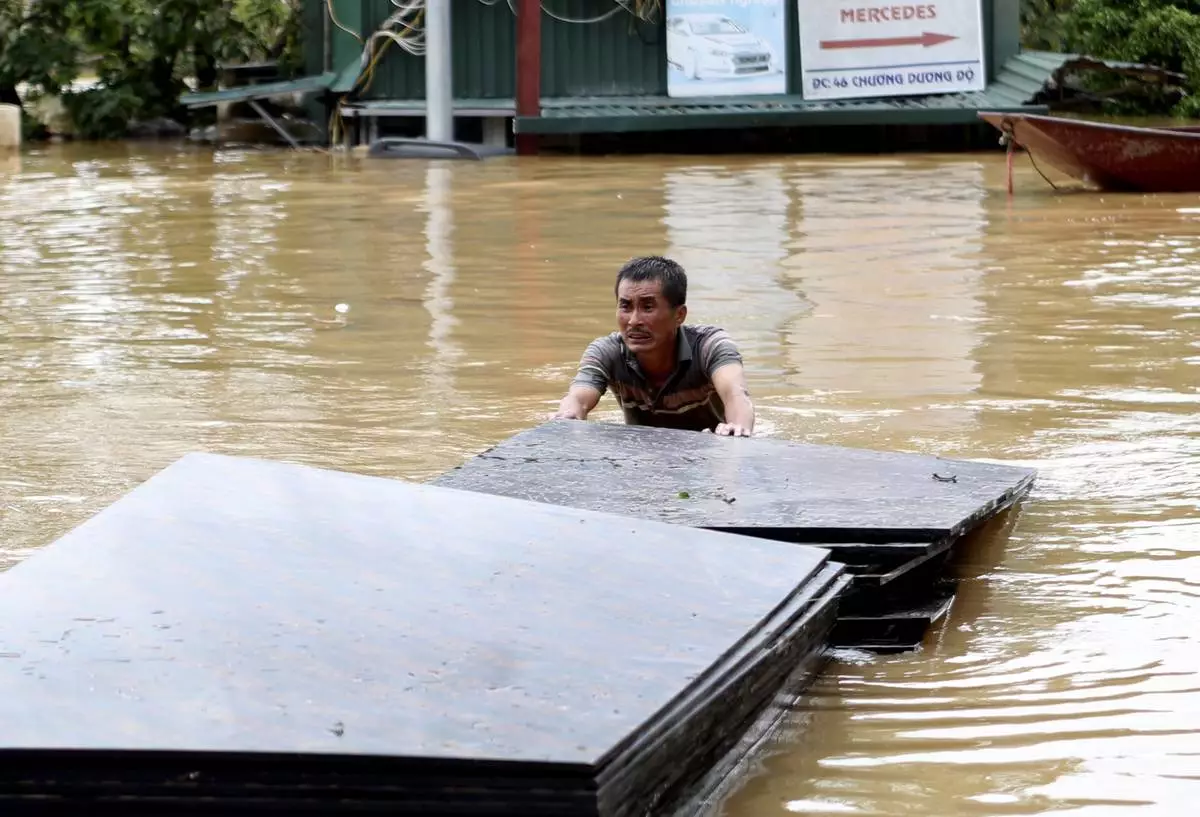

A man pushes a stack of plyboards in flood following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
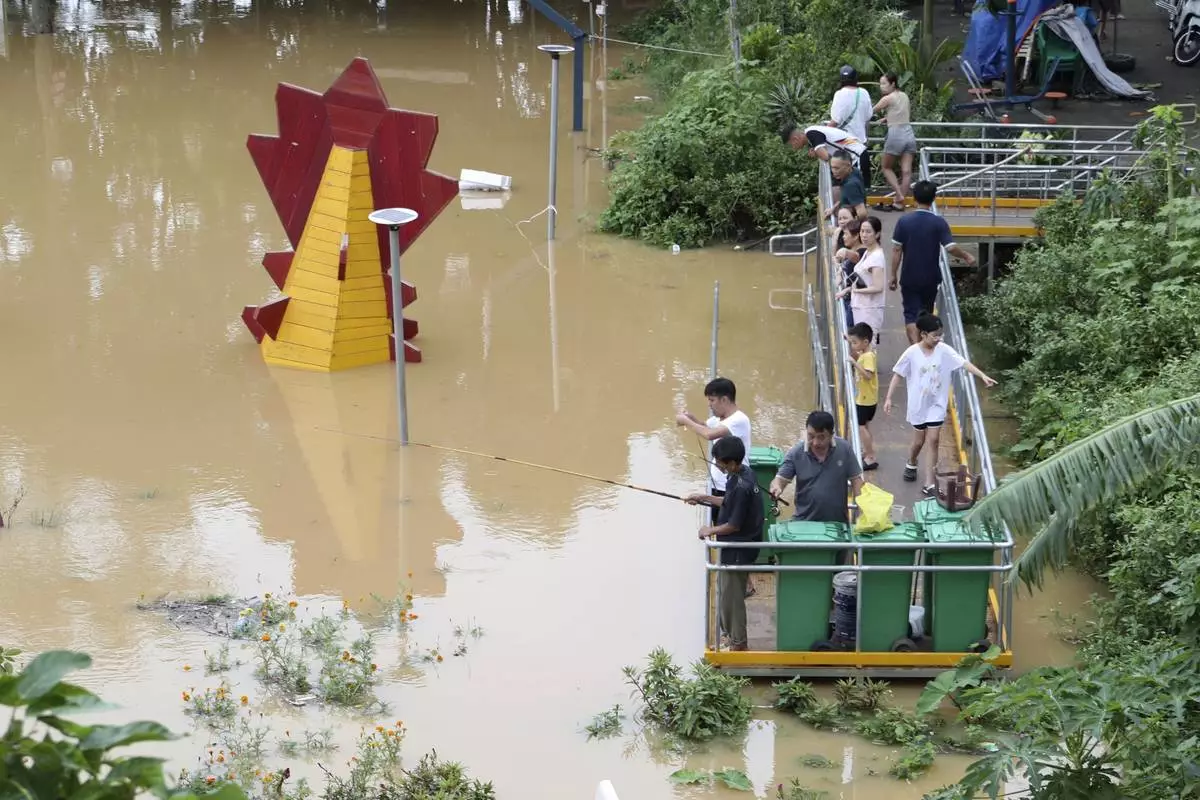

People fish next to a submerged playground due to flood , following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
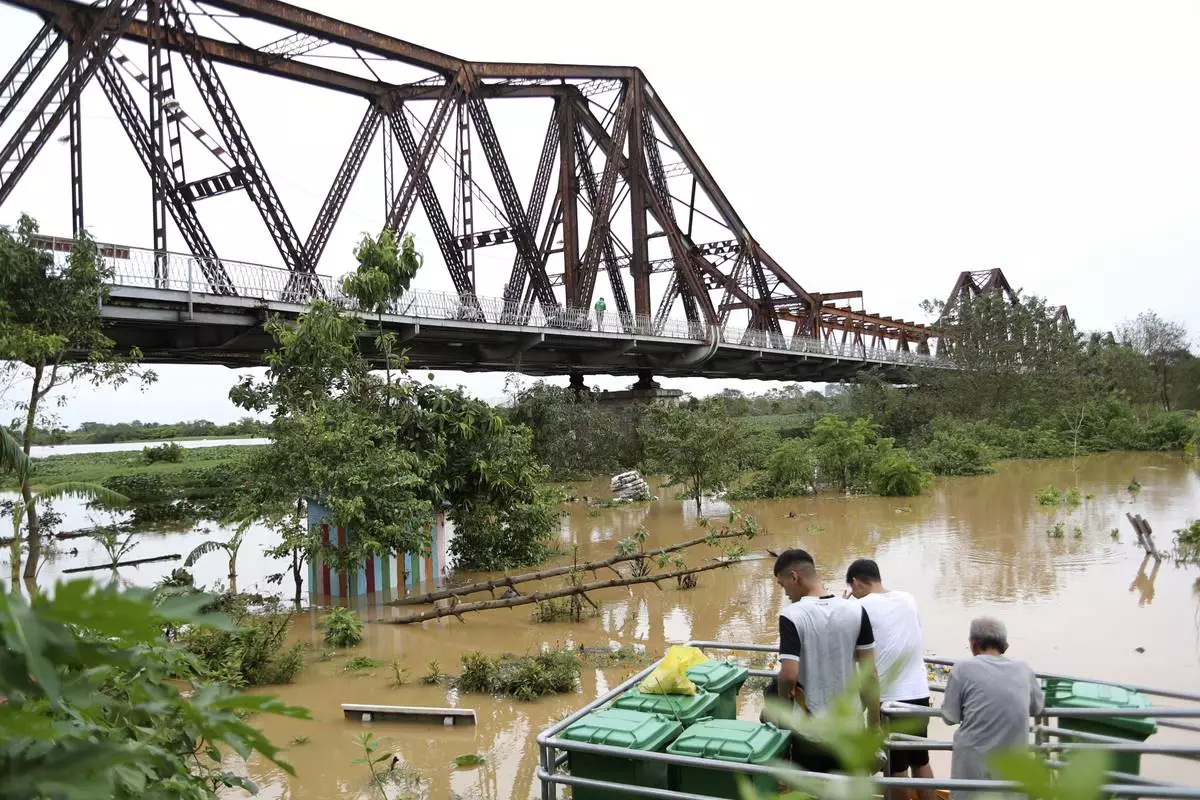

People watch the flooded Red river next to iconic Long Bien bridge, following Typhoon Yagi in Hanoi, Vietnam on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Huy Han)
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Donald Trump signed an executive order Monday directing the United States to again withdraw from the landmark Paris climate agreement, dealing a blow to worldwide efforts to combat global warming and once again distancing the U.S. from its closest allies.
Trump's action, hours after he was sworn in to a second term, echoed his directive in 2017, when he announced that the U.S. would abandon the global Paris accord. The pact is aimed at limiting long-term global warming to 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit (1.5 degrees Celsius) above pre-industrial levels or, failing that, keeping temperatures at least well below 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit (2 degrees Celsius) above pre-industrial levels.
Trump also signed a letter to the United Nations indicating his intention to withdraw from the 2015 agreement, which allows nations to provide targets to cut their own emissions of greenhouse gases from the burning of coal, oil and natural gas. Those targets are supposed to become more stringent over time, with countries facing a February 2025 deadline for new individual plans. The outgoing Biden administration last month offered a plan to cut U.S. greenhouse gas emissions by more than 60% by 2035.
Trump's order says the Paris accord is among a number of international agreements that don't reflect U.S. values and “steer American taxpayer dollars to countries that do not require, or merit, financial assistance in the interests of the American people."
Instead of joining a global agreement, “the United States’ successful track record of advancing both economic and environmental objectives should be a model for other countries,'' Trump said.
Laurence Tubiana, CEO of the European Climate Foundation and a key architect of the Paris accord, called the planned U.S. withdrawal unfortunate but said action to slow climate change “is stronger than any single country’s politics and policies."
The global context for Trump's action is “very different to 2017,'' Tubiana said Monday, adding that “there is unstoppable economic momentum behind the global transition, which the U.S has gained from and led but now risks forfeiting."
The International Energy Agency expects the global market for key clean energy technologies to triple to more than $2 trillion by 2035, she said.
“The impacts of the climate crisis are also worsening. The terrible wildfires in Los Angeles are the latest reminder that Americans, like everyone else, are affected by worsening climate change,” Tubiana said.
Gina McCarthy, who served as White House climate adviser under President Joe Biden, a Democrat, said that if Trump, a Republican, “truly wants America to lead the global economy, become energy independent and create good-paying American jobs," then he must “stay focused on growing our clean energy industry. Clean technologies are driving down energy costs for people all across our country."
The world is now long-term 2.3 degrees Fahrenheit (1.3 degrees Celsius) above mid-1800s temperatures. Most but not all climate monitoring agencies said global temperatures last year passed the warming mark of 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit, and all said it was the warmest year on record.
The withdrawal process from the Paris accord takes one year. Trump’s previous withdrawal took effect the day after the 2020 presidential election, which he lost to Biden.
While the first Trump-led withdrawal from the landmark U.N. agreement — adopted by 196 nations — shocked and angered nations across the globe, “not a single country followed the U.S. out the door,” said Alden Meyer, a longtime climate negotiations analyst with the European think tank E3G.
Instead, other nations renewed their commitment to slowing climate change, along with investors, businesses, governors, mayors and others in the U.S., Meyer and other experts said.
Still, they lamented the loss of U.S. leadership in global efforts to slow climate change, even as the world is on track to set yet another record hot year and has been lurching from drought to hurricane to flood to wildfire.
“Clearly America is not going to play the commanding role in helping solve the climate crisis, the greatest dilemma humans have ever encountered,″ said climate activist and writer Bill McKibben. “For the next few years the best we can hope is that Washington won’t manage to wreck the efforts of others.”
About half of Americans “somewhat” or “strongly” oppose U.S. action to withdraw from the climate accord, and even Republicans aren’t overwhelmingly in favor, according according to a poll from The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research. Only about 2 in 10 U.S. adults “somewhat” or “strongly” in favor of withdrawing from the Paris agreement, while about one-quarter are neutral.
Much of the opposition to U.S. withdrawal comes from Democrats, but Republicans display some ambivalence as well. Slightly less than half of Republicans are in favor of withdrawing from the climate accord, while about 2 in 10 are opposed.
China several years ago passed the United States as the world's largest annual carbon dioxide emitting nation. The U.S. — the second biggest annual carbon polluting country — put 4.9 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide in the air in 2023, down 11% from a decade earlier, according to the scientists who track emissions for the Global Carbon Project.
But carbon dioxide lasts in the atmosphere for centuries, so the United States has put more of the heat-trapping gas that is now in the air than any other nation. The U.S. is responsible for nearly 22% of the carbon dioxide put in the atmosphere since 1950, according to Global Carbon Project.
While global efforts to fight climate change continued during Trump's first term, many experts worry that a second Trump term will be more damaging, with the United States withdrawing even further from climate efforts in a way that could cripple future presidents’ efforts. With Trump, who has dismissed climate change, in charge of the world’s leading economy, those experts fear other countries, especially China, could use it as an excuse to ease off their own efforts to curb carbon emissions.
Simon Stiell, the U.N. climate change executive secretary, held out hope that the U.S. would continue to embrace the global clean energy boom.
“Ignoring it only sends all that vast wealth to competitor economies, while climate disasters like droughts, wildfires and superstorms keep getting worse," Stiell said. “The door remains open to the Paris Agreement, and we welcome constructive engagement from any and all countries.”
Associated Press writer Linley Sanders contributed to this report.
The Associated Press’ climate and environmental coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. The AP is solely responsible for all content. Find the AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.
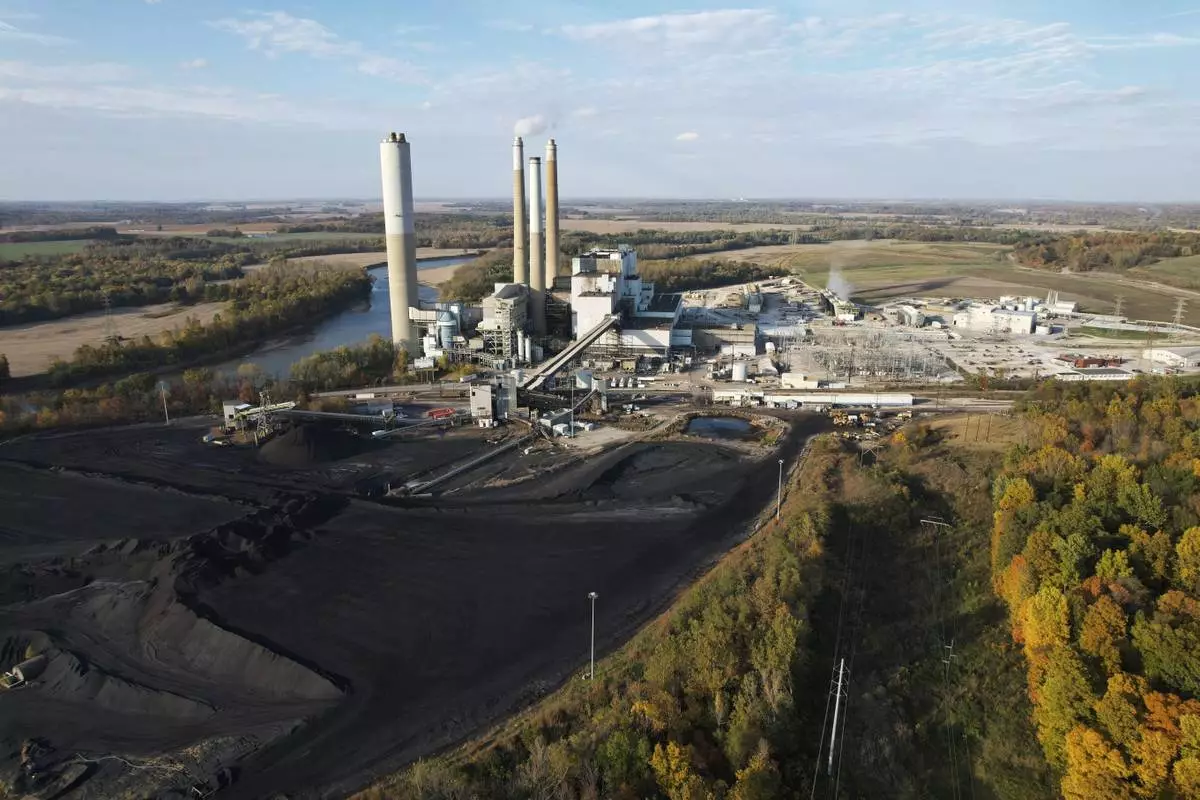

AES Indiana Petersburg Generating Station, a coal-fired power plant, operates in Petersburg, Ind., on Wednesday, Oct. 25, 2023. (AP Photo/Joshua A. Bickel)
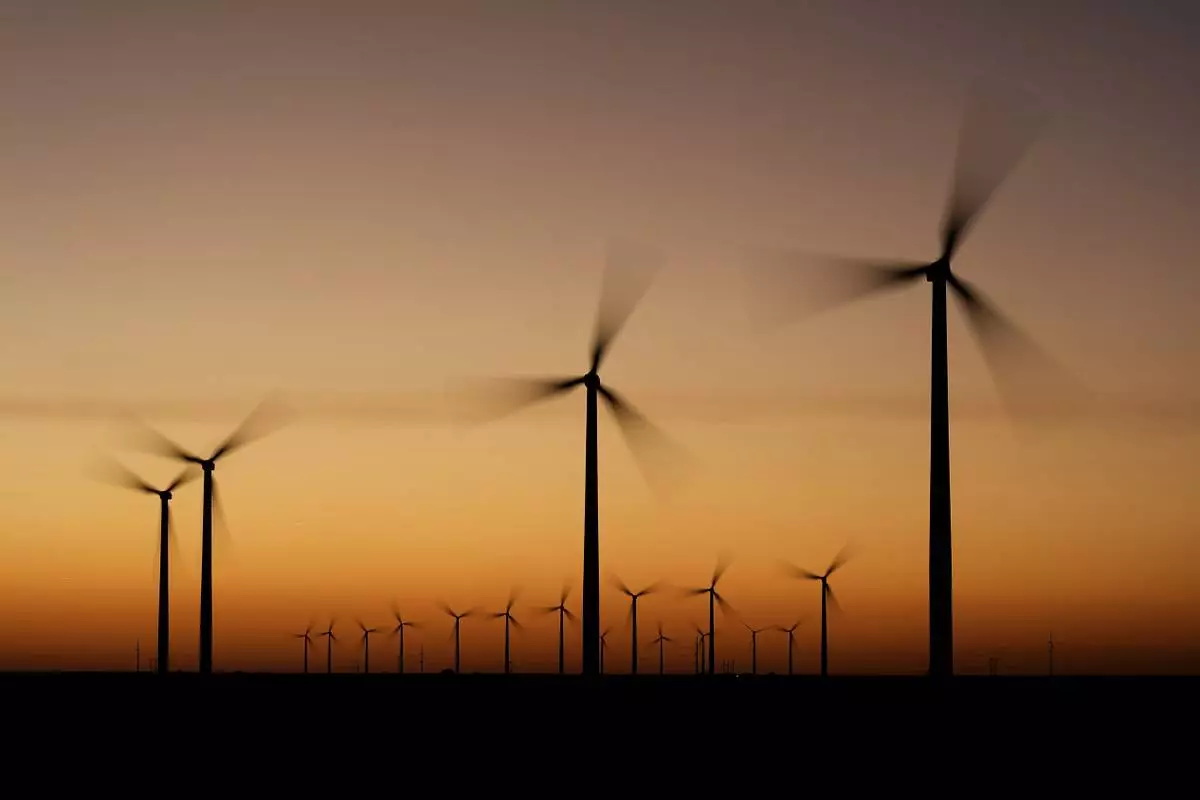

FILE - Wind turbines stretch across the horizon at dusk at the Spearville Wind Farm, Sept. 29, 2024, near Spearville, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel, File)

President Donald Trump gestures during the 60th Presidential Inauguration in the Rotunda of the U.S. Capitol in Washington, Monday, Jan. 20, 2025. (AP Photo/Julia Demaree Nikhinson, Pool)