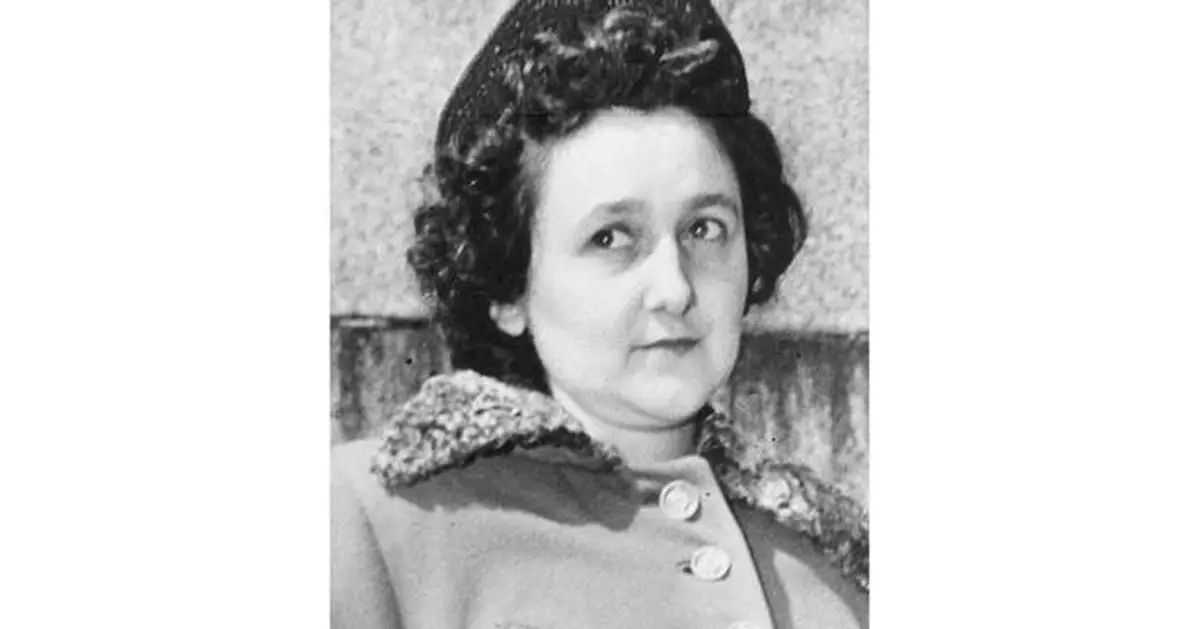
WASHINGTON (AP) — A top U.S. government codebreaker who decrypted secret Soviet communications during the Cold War concluded that Ethel Rosenberg knew about her husband's activities but “did not engage in the work herself,” according to a recently declassified memo that her sons say proves their mother was not a spy and should lead to her exoneration in the sensational 1950s atomic espionage case.
The previously unreported assessment written days after Rosenberg's arrest and shown to The Associated Press adds to the questions about the criminal case against Rosenberg, who along with her husband, Julius, was put to death in 1953 after being convicted of conspiring to steal secrets about the atomic bomb for the Soviet Union.
The couple maintained their innocence until the end, and their sons, Robert and Michael Meeropol, have worked for decades to establish that their mother was falsely implicated in spying. The brothers consider the memo a smoking gun and are urging President Joe Biden to issue a formal proclamation saying she was wrongly convicted and executed.
Historians have long regarded Julius Rosenberg as a Soviet spy. But questions about Ethel Rosenberg’s role have simmered for years, dividing those who side with the Meeropols and say she had zero role in espionage from some historians who contend there’s evidence she supported her husband’s activities.
The handwritten memo from Meredith Gardner, a linguist and codebreaker for what later became known as the National Security Agency, cites decrypted Soviet communications in concluding that Ethel Rosenberg knew about Julius' espionage work “but that due to ill health she did not engage in the work herself.”
Ethel Rosenberg went on trial with her husband months after the memo was written despite Gardner's assessment, which the Meeropols believe would have been available to FBI and Justice Department officials investigating and prosecuting the case.
“This puts it on both sides of the Atlantic — in other words, both the KGB and the NSA ended up agreeing that Ethel was not a spy," Robert Meeropol said in an interview. "And so we have a situation in which a mother of two young children was executed as a master atomic spy when she wasn’t a spy at all.”
The Meeropols recently obtained the Aug. 22, 1950, memo from the NSA through a Freedom of Information Act request and provided it to the AP.
“This piece of documentation, juxtaposing my father’s work with her not doing the work, it seems to me nails it,” Michael Meeropol said.
The document was written more than a week after Ethel Rosenberg's arrest — her husband was arrested a month earlier — presumably to summarize what was known about a Soviet spy ring operating in the U.S. at the height of the Cold War and associated with the development of the atomic bomb.
It refers to Julius Rosenberg, who worked as a civil engineer, by his Soviet code names — first “Antenna” and later “Liberal” — and characterizes him as a recruiting agent for Soviet intelligence.
In a separate paragraph titled, “Mrs. Julius Rosenberg,” Gardner describes a decoded message as saying Ethel Rosenberg was a “party member" and "devoted wife” who knew of her husband's work but didn't engage in it.
Harvey Klehr, a now-retired Emory University historian, said this week that the memo notwithstanding, his position is that Ethel Rosenberg conspired to commit espionage even if she did not spy herself or have access to classified information.
“Ethel may not have been a spy — that is, she might not have actually passed on classified information — but she was an active participant in her husband’s spy network, not just someone who happened to agree with her husband about politics,” Klehr wrote in a 2021 piece for Mosaic Magazine.
Another historian, Mark Kramer of Harvard University, said this week that the interpretation of the Russian communication was debatable and that in any event other documents contain “damning evidence” of Ethel Rosenberg's involvement in spying, and her participation in tasks, even “if she was not directly participating in the way Julius Rosenberg was.”
The Meeropols adamantly dispute that, insisting the evidence is clear that the Soviets never considered their mother an asset and that she had no role in recruiting spies or assisting her husband's espionage.
The memo is the latest information that Ethel Rosenberg’s supporters say casts doubt on her criminal conviction and the public view of her. For instance, previously deciphered Soviet cables showed that she, unlike her husband, was not given a code name. The Meeropols also point to a separate memo from Gardner stating Ethel Rosenberg did “not work.”
In a 2001 television interview, Ethel Rosenberg's brother, David Greenglass, acknowledged that he lied on the stand about his sister to assure leniency for himself and keep his wife out of prison so she could care for their two children. A fellow communist sympathizer, he was indicted as a co-conspirator and served 10 years in prison.
In 2015, secret grand jury testimony from Greenglass was unsealed that contradicted damaging statements he made during the Rosenbergs' trial that helped secure their convictions.
Greenglass claimed at trial that he had given the Rosenbergs research data he obtained while working as an Army machinist at the Los Alamos, New Mexico, headquarters of the Manhattan Project, where the first atomic weapons were produced. He also said he recalled seeing his sister using a portable typewriter at the Rosenbergs' apartment to type up handwritten notes to give to the Soviets.
But in his grand jury testimony, which a judge unsealed after Greenglass’ 2014 death in response to a request from historians and archivists, he never implicated his sister.
Greenglass told the grand jury that Julius Rosenberg was adamant he should stick with his Army service so Greenglass could “continue giving him information.” But when Greenglass was asked whether his sister was similarly insistent, he replied, “I said before, and say it again, honestly, this is a fact: I never spoke to my sister about this at all.”
The Meeropols believe the newly released memo would almost certainly have reached high levels of the FBI given that Gardner, its author, worked closely with an FBI agent. They say the information may have influenced then-FBI Director J. Edgar Hoover's recommendation that Ethel Rosenberg not receive the death penalty, though she ultimately did.
Robert Meeropol, 77, said the memo's release is a capstone of decades of work to clear his mother's name. As young boys, the brothers visited the White House in 1953 in a failed bid to get President Dwight Eisenhower to prevent their parents’ executions. They were later adopted.
In 2016, they cited the newly released grand jury testimony to try to persuade President Barack Obama to exonerate their mother.
“I'm incredibly relieved to have this out while I'm still alive, because for a lot of time, I didn't think I was going to survive to see it,” he said.
Michael Meeropol, 81, said he recalled his brother saying in 1973 that in a few years they were going to “blow the lid off the case.”
“Well, 1973 to 2024 is a little bit more than a few years, but it’s just happened as far as I’m concerned. This memo being released, thank God, blows the lid off it in terms of our mother,” Michael Meeropol said.
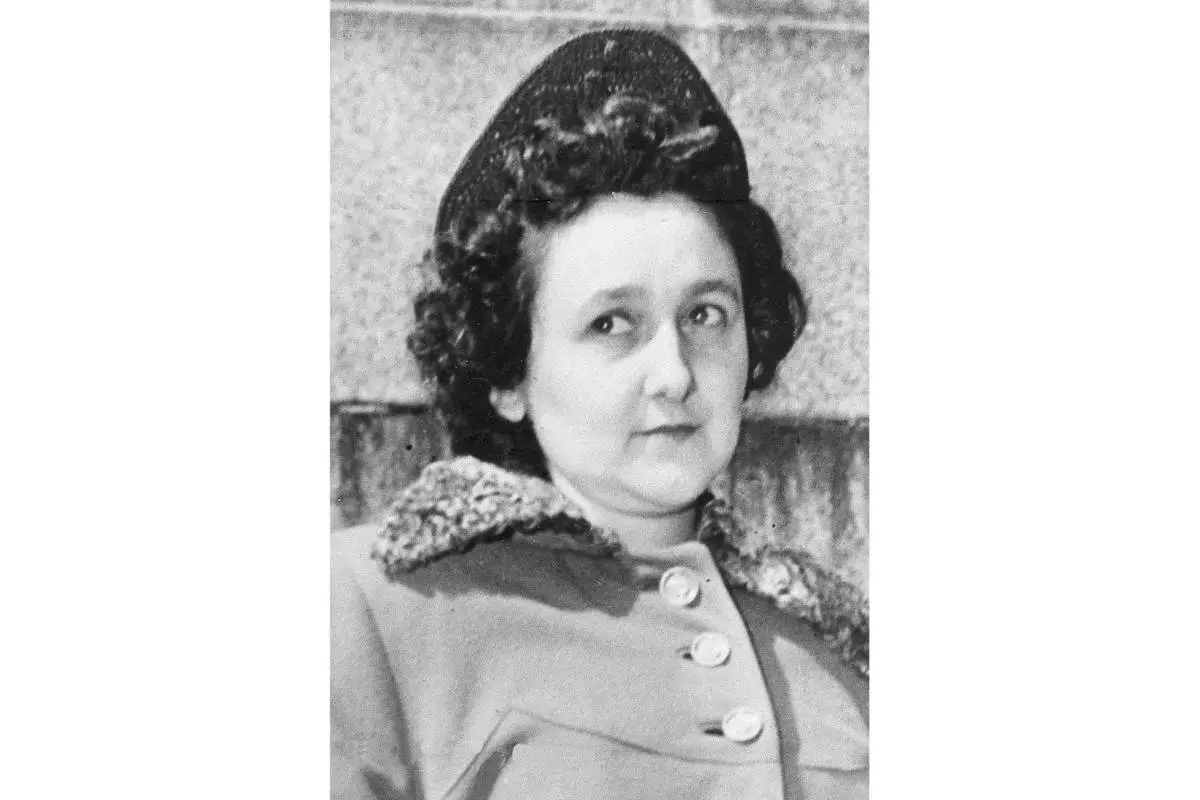

FILE - Ethel Rosenberg, the convicted wife of the Cold War atomic spying case, in this undated file photo. (AP Photo, File)