BANGUI, Central African Republic (AP) — Hours after Russian mercenary leader Yevgeny Prigozhin rebelled against his country’s top military leaders, his private army’s biggest client in Africa panicked, turning for help to his foe in the West.
Officials from Central African Republic, where some 1,500 of Prigozhin’s shadowy Wagner Group mercenaries were stationed, wrote a letter that day, requesting to “rapidly” arrange a meeting with a private U.S. security firm to discuss collaboration.
Dated June 23, 2023, the day Prigozhin launched the armed rebellion, the letter sparked a series of private meetings, culminating in a deal with the central African nation and Bancroft Global Development. That sparked backlash from Russian mercenaries, according to a dozen diplomats, locals, and analysts.
The tensions in Central African Republic are a window into a larger battle playing out across the continent as Moscow and Washington vie for influence.
The Russian mercenaries — using success in staving off rebels in this impoverished nation as a model for expansion — have long been accused by locals and rights groups of stripping natural resources such as minerals and timber and are linked to the torture and death of civilians. In the wake of Prigozhin’s rebellion and suspicious death in a plane crash, the Russians are recalibrating their Africa operations. The United States, which has been largely disengaged from the region for years, is attempting to maintain a presence and stymie Russian gains as it pushes African countries to distance themselves from the mercenaries.
U.S. officials blame Russia for anti-American sentiment in the region and say they’re trying to shift the narrative.
“If the U.S. can’t regain a foothold, it could give Russia greater economic and political leverage,” said Samuel Ramani of the Royal United Services Institute, a defense and security think tank. “If Russia loses Central African Republic, its flagship model on the continent, there could be a domino effect in other countries.”
In recent years, Russia has emerged as the security partner of choice for a growing number of governments in the region, displacing traditional allies such as France and the U.S.
Moscow aggressively expanded its military cooperation by using mercenaries like Wagner, who have operated in at least half a dozen countries since around 2017. They’re tasked with protecting African leaders and in some cases helping fight rebels and extremists.
They’re also plagued by their human rights record. Two years ago in Mali, Wagner and the army were accused of executing about 300 men — some suspected of being Islamist extremists, but most civilians — in what Human Rights Watch called the worst single atrocity reported in the country’s decade-long armed conflict. And in Central African Republic, mercenaries train the army on torture tactics, including how to cut hands, remove nails, throw fuel and burn people alive, according to watchdog The Sentry.
A soldier who spoke on condition of anonymity for fear of reprisal confirmed torture tactics and told The Associated Press he saw mercenaries put a fellow soldier into a sweltering container as punishment. He said people could stay locked in containers for three weeks, with many dying inside.
Central African Republic was one of the first places the mercenaries entered. The country has been in conflict since 2013, when predominantly Muslim rebels seized power and forced the president from office. Six of the 14 armed groups that signed a 2019 peace deal later left the agreement. Locals and the government credited Wagner with fighting back rebels who tried to overtake Bangui, the capital, in 2021. The Russians soon expanded to Burkina Faso and Niger, and have ambitions for further growth.
Russia is refurbishing a military base some 50 miles (80 kilometers) from Bangui. Alexander Bikantov, Russia’s ambassador to Central African Republic, said the base will improve the country’s security.
Fidele Gouandjika, adviser to President Faustin-Archange Touadera, said the base aims to have 10,000 fighters by 2030 to engage with more African nations.
Some countries see Russia’s influence as a threat to their own, but conflict analysts say weakening it will be challenging if they won’t offer a similar force to pursue armed groups.
Wagner is steeped in Central African Republic's security system, and experts say that will likely prevent Touadera from easily diversifying security partners.
Touadera’s office didn't reply to written requests for comment for this story. His adviser to the country’s spy agency declined to be interviewed.
The U.S. had been pushing Central African Republic to find an alternative to Wagner for years. A December 2022 private meeting sought ways to improve security without the mercenaries but yielded little tangible progress, according to a U.S. official who is familiar with the talks and spoke on condition of anonymity due to the privacy of ongoing discussions.
“We never really got past the confidence-building steps,” he said. “Steps on how XYZ would replace Wagner were abstract, and the door remains open.”
The more assertive U.S. approach came as it faced new setbacks and tried to rework agreements in the region. Its troops left Chad and Niger, where they were no longer welcome.
Still, the State Department said in a statement early this year that it wasn’t involved in the decision to establish Bancroft Global Development’s presence in Central African Republic.
But Washington could deny such contracts if it wanted, said Sean McFate, a former contractor in Africa and author of “The New Rules of War.”
The U.S. has used private military companies to reduce American “boots on the ground” in Africa, McFate said, and companies like Bancroft have to play by Washington’s rules if they want future government work.
In response to AP questions, the U.S. official who spoke on condition of anonymity said it uses private contractors in Africa to help countries operate more effectively, with U.S. government oversight to ensure accountability. The official said the State Department has overseen Bancroft's work in Somalia but not Central African Republic or elsewhere.
Washington-based Bancroft is a nonprofit working in nine countries — five of them in Africa. Its longest-standing presence is in Somalia, where it’s operated for more than 15 years, in part training troops to fight the militant group al-Shabab.
Bancroft’s involvement in Central African Republic has been shrouded in secrecy since signs emerged of its presence last fall.
During an AP visit months later, rumors swirled about Bancroft’s activities, fueling speculation the U.S was bringing its own Wagner to oust Russia.
But according to Bancroft founder Michael Stock, the group entered at Bangui’s behest.
“Touadera felt his Russian partners were underperforming and distracted, focused too much on other lines of effort ranging from breweries to cultural centers, rather than confronting the rebels,” Stock told AP in his first interview since Bancroft began operating there.
Touadera thought diversifying partners would prompt Russia to get in line and give the Americans what they wanted, Stock said.
Stock received the letter from the presidency within a day of Prigozhin’s mutiny, and the two signed a deal in September, he said.
Fewer than 30 Bancroft personnel work there, Stock said, helping Central African Republic with intelligence systems, interagency cooperation and law enforcement.
Bancroft has invested some $1.4 million there, Stock said.
Much of Bancroft’s overall funding has come from U.S. and United Nations grants. From 2018 to 2020, it received more than $43 million from the U.S., according to audits required as part of tax forms.
Amal Ali, former U.S. intelligence analyst, is among critics who say that despite its yearslong presence in Somalia, Bancroft hasn’t contributed to any real eradication of terrorism.
Stock dismissed such comments as uninformed and said the Somali and U.S. governments "agree Bancroft has done a great deal to damaging illegal armed groups and developing the capacity of the government to perform its national defense functions professionally.”
Rights groups say a lack of transparency about Bancroft’s operations has fostered an atmosphere of distrust in a country already rampant with armed actors. Wagner, a U.N. peacekeeping mission and Rwandan troops are all on the ground to try to quell violence.
“Operating in a vague and nontransparent way in the Central African Republic only leads to suspicion,” said Lewis Mudge, of Human Rights Watch.
Stock defended Bancroft’s work and policies. “It is perfectly normal for a government not to publicize how it is defending the people and the state,” he told AP.
Last fall, as reports of possible collaboration with Bancroft emerged, Stock said he positioned a staff member at a hotel in Bangui to wait for Russia’s reaction.
“We expected Russia to freak out, so for our lone staff member in Bangui we chose a Russian speaker, who was tasked to do nothing but sit in the hotel garden reading a book all day, waiting for Russians to show whether they wanted to be cooperative, hostile, or ignore us,” Stock said.
Stock said that weeks later, in January, the employee was detained and questioned for hours by Russian forces and released only when Touadera stepped in.
Officials in both Central African Republic and Russia didn't respond to requests for comment on any such incident. Bikantov, Russia’s ambassador to Central African Republic, has said Bancroft’s presence had no effect on cooperation with Russia’s military.
In the following months, aggression toward Americans and U.S. entities continued. Several American citizens were detained and had their passports confiscated, a diplomat who dealt with their cases said on condition of anonymity because he wasn’t allowed to speak to reporters. Rare anti-American protests erupted outside the U.S. embassy in Bangui, and local youths formed the Committee to Investigate U.S. Activities to monitor Bancroft’s movements.
Gouandjika, the presidential adviser, said the government has no problem with Americans and those denied entry lacked proper paperwork.
As the U.S. and Russia jockey for power, African governments say they want to make their own choices.
Central African Republic officials approached Bancroft, which shows that these governments haven’t become Russian puppets, said Jack Margolin, an expert on private military companies.
But, he added, Russia’s reaction to Bancroft could hurt Moscow’s standing with other nations.
After Prigozhin’s death, Russia moved quickly to take control of Wagner’s assets, and the defense ministry told countries where Wagner operated that it would take over. The country and its military intelligence arm have taken a more direct role in Africa operations, deploying more official detachments from its army.
Russia is trying to rebrand the mercenaries, creating Africa Corps, a parallel group that could absorb Wagner, said John Lechner, a Wagner expert.
In Central African Republic, it’s still unclear how much sway the Russian state has with the mercenaries, who are beloved by many and embedded in society, brewing beer and visiting markets. Still, they largely keep to themselves, walking through streets with faces covered and driving in unmarked cars.
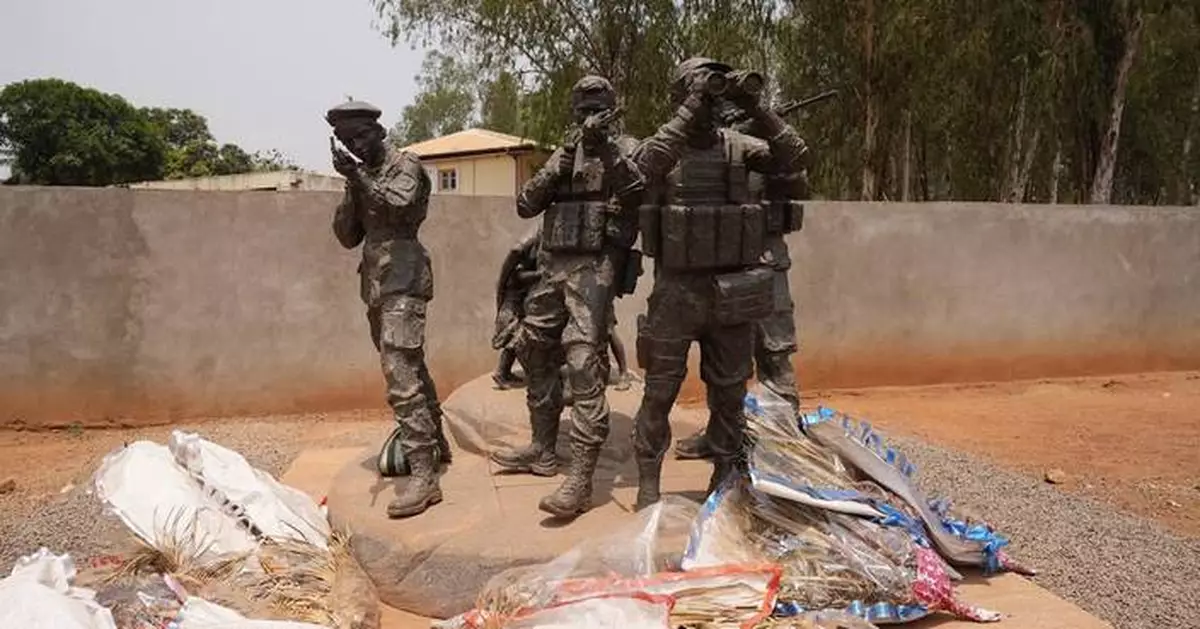
For many, Prigozhin was a national hero. Standing at a downtown monument of Russian soldiers, people lay flowers at its feet paying respects, a year after his death.
For most people here, there’s little interest in squabbles among foreign nations.
“There are problems between the Americans and Russians, but that doesn’t matter to us,” said Jean Louis Yet, who works at Bangui’s market. “We are here working, trying our best to make a living.
“All we want is security.”
AP reporters James Pollard in New York; Michael Biesecker in Washington; Dasha Litvinova in Tallinn, Estonia; and Jean Fernand Koena in Central African Republic contributed to this report.

People walk on the streets in Bangui, Central African Republic, on March 11, 2024. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick)

Jean Louis Yet sips from a cup at the market in Bangui, Central African Republic, on March 11, 2024. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick)

FILE - Supporters of Niger's ruling junta hold a Russian flag at the start of a protest called to fight for the country's freedom and push back against foreign interference in Niamey, Niger, on Aug. 3, 2023. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick, File)

FILE - This undated photograph provided by the French military shows three Russian mercenaries in northern Mali. (French Army via AP, File)

A woman gets her hair braided on the streets of Bangui, Central African Republic, on March 11, 2024. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick)

A woman prepares plantains to sell in the market in Bangui, Central African Republic, on March 11, 2024. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick)

A woman sells vegetables at a market in Bangui, Central African Republic, on March 11, 2024. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick)

Vegetables are displayed at a market in Bangui, Central African Republic, on March 11, 2024. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick)

FILE - Russian President Vladimir Putin, right, and Central African Republic President Faustin-Archange Тouadera walk during their meeting on the sideline of the Russia Africa Summit in St. Petersburg, Russia, Friday, July 28, 2023. (Artyom Geodakyan/TASS Host Photo Agency Pool Photo via AP, File)

A satellite image taken on Sept. 25, 2022, shows what Central African Republic says will be a refurbished base for Russian soldiers. The area is approximately 50 miles (80 km) from the capital, and an adviser to President Faustin-Archange Touadera said it aims to have 10,000 Russian soldiers by 2030. (Planet Labs PBC via AP)

FILE - Central African Army Forces (FACA) cadets display a fake rocket launcher on Jan. 26, 2014, in Jean Bedel Bocassa's Berengo palace near Pissa, some 80kms (45 miles) south west of Bangui, Central African Republic. Ten years on, Russia is said to be helping to refurbish the site as a military base. (AP Photo/Jerome Delay, File)

An arial view of Bangui, Central African Republic, is seen on March. 8, 2024. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick)

FILE - Nigeriens, some holding Russian flags, participate in a march called by supporters of coup leader Gen. Abdourahmane Tchiani in Niamey, Niger, on July 30, 2023. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick, File)

FILE - This undated photograph handed out by French military shows Russian mercenaries boarding a helicopter in northern Mali. (French Army via AP, File)

Flowers are laid at the statue of Russian mercenaries as a tribute to the late Wagner leader Yevgeny Prigozhin in Bangui, Central African Republic, on March. 5, 2024. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick)