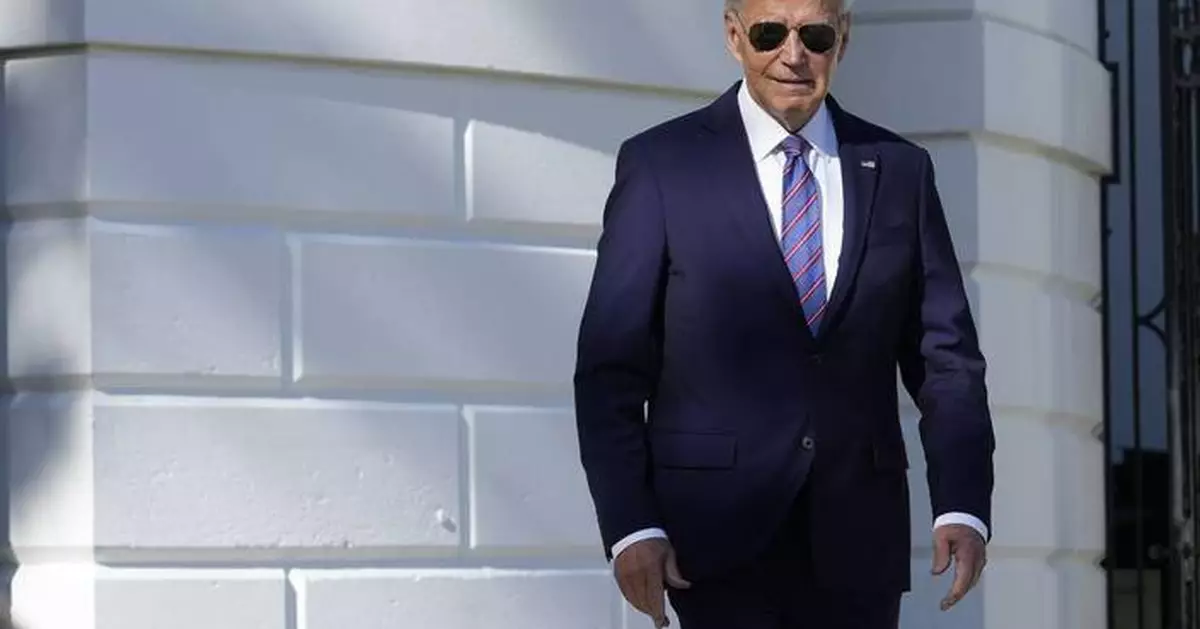
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Joe Biden said Thursday joined scores of advocates and survivors of domestic abuse to mark the 30th anniversary of the landmark Violence Against Women Act, a law he wrote and championed as a U.S. senator because he wanted to “change the culture of America” around this touchy issue.
Biden said that back then “society often looked away” and that violence against women was not treated as a crime in many places. He said a national hotline was not available to those suffering abuse and few police departments with what are known now as special victim units.
“My goal was to do more than change the law,” he said at a White House event marking Friday's 30th anniversary of the law. He said his goal was “to change the culture of America" by providing more protection and support for survivors and accountability for perpetrators.
“I believed the only way we could change the culture was by shining a light on that culture, and speaking its name,” he said.
Biden wrote and championed the legislation as a U.S. senator. It was the first comprehensive federal law that addressed violence against women and sought to provide support for survivors and justice. It sought to shift the national narrative around domestic violence at the time; that it was a private matter best left alone.
The White House said that between 1993 and 2022, annual rates of domestic violence dropped by 67% and the rate of rapes and sexual assaults declined by 56%, according to FBI statistics. A national domestic violence hotline has fielded more than 7 million calls since 1996, Biden said.
“It matters. It saves lives," he said Thursday.
During a hearing on domestic violence in 1990, Biden told the committee that "for too long, we have ignored the right of women to be free from the fear of attack based on their gender. For too long, we have kept silent about the obvious.”
He spent years advocating for the law, moved by horrible stories of domestic violence. Congress passed it in 1994 with bipartisan support. Then-President Bill Clinton signed it into law on Sept. 13, 1994.
“The Violence Against Women Act is my proudest legislative achievement,” Biden said at the event on the White House lawn. It was attended by hundreds of people, including survivors of domestic violence, advocates, administration officials and members of Congress.
The president also spoke about continued efforts to strengthen the law, including announcing that the Justice Department was awarding more than $690 million in grants, along with efforts to serve orders of protection electronically and strategies to address online gender-based violence, a growing problem that law enforcement struggles to combat.
Federal agencies also sent reminders on housing rights for survivors of domestic violence who live in federally funded homes, including that they can request emergency housing transfers.
"Today, officers, prosecutors, judges, families, and society at large understand what should have always been clear: these crimes cannot be cast aside as somehow distinct or private,” said Attorney General Merrick Garland. “Instead, we recognize that they are among the most serious crimes that our society faces and that we must continue to improve access to justice, safety, and services for survivors.”
Jen Klein, the White House gender policy adviser, said the measures are meant to keep pushing efforts to help survivors of domestic violence.
“While we have made tremendous progress since VAWA was signed into law in 1994, we also know that much work remains in the fight to prevent and end gender-based violence,” she said.
The law was reaffirmed in 2022, but it almost didn't happen. The sticking point was a provision in the last proposal, passed by the House in April 2019, that would have prohibited persons previously convicted of misdemeanor stalking from possessing firearms.
Under current federal law, those convicted of domestic abuse can lose their guns if they are currently or formerly married to their victim, live with the victim, have a child together or are a victim’s parent or guardian. But the law doesn’t apply to stalkers and current or former dating partners. Advocates have long referred to it as the “boyfriend loophole.”
Expanding the restrictions drew fierce opposition from the National Rifle Association and Republicans in Congress, creating an impasse. Democrats backed down and did not include the provision.
That provision was later addressed in Biden's bipartisan gun safety legislation signed by Congress in 2022, and now prohibits people convicted of misdemeanor crimes in dating relationships from purchasing or possessing firearms for at least five years.
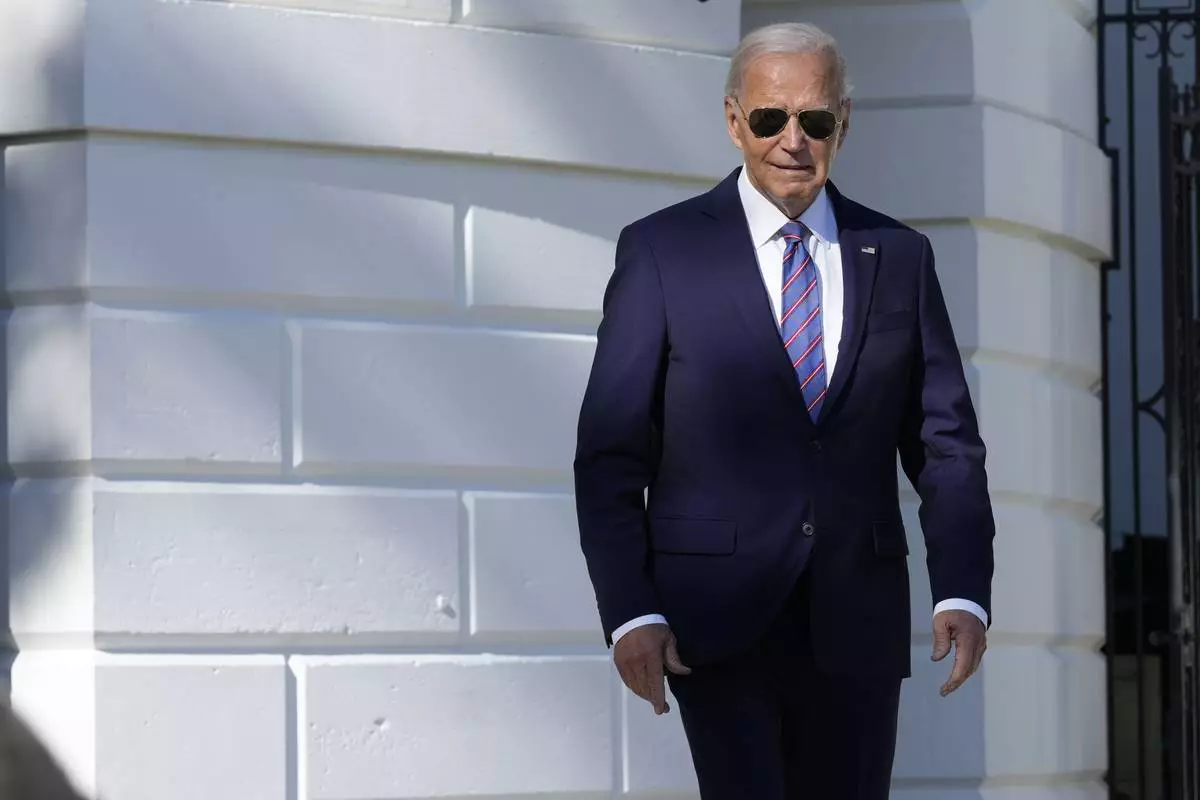

President Joe Biden walk over to talk with reporters before leaving the White House in Washington, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, to travel to New York. (AP Photo/Susan Walsh)