As the pregnant woman's contractions rolled in every two minutes, staff at Our Lady of the Lake Regional Medical Center in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, dispatched an ambulance to send her elsewhere.
Just two minutes later, she gave birth to a 6-pound baby girl in the cab of the ambulance down the road from the 900-bed hospital.
The incident, government investigators concluded last year, was a violation of a federal law that requires emergency rooms to stabilize patients in medical distress before discharging or transferring them.
Yet, Our Lady of the Lake has never been penalized for that incident or any of its other violations of the law. Few emergency rooms ever are.
Just a dozen hospitals have been fined for refusing to treat patients — pregnant or not — over the past two years, an Associated Press analysis of civil monetary penalties issued by the U.S. Health and Human Services Office of Inspector General found. It took years for the government to decide those penalties.
Not one of the more than 100 emergency rooms that mistreated or turned away pregnant women since 2022, when the Biden administration pledged to toughen enforcement of the law, has been fined.
“What little we know about the investigations have yielded very rare results,” said Sara Rosenbaum, a George Washington University health law and policy professor.
At Our Lady of the Lake, which did not provide comment for this article, inspectors determined the emergency room’s staff members violated the federal mandate seven times since 2017, when they refused a needed surgery to a Medicaid patient with a broken spine, left a suicidal teenager unattended in the lobby and failed to examine another pregnant woman before sending her to another hospital, federal records show.
Other emergency rooms denied care to pregnant women, sometimes leaving them to miscarry in bathrooms, deliver babies in cars or develop risky infections. Some repeatedly flouted the mandate without consequence, including one Tennessee emergency room with such long wait times that a pregnant woman had to be hospitalized for a week after an 8-hour wait and a man with chest pain collapsed in the lobby, then died.
HHS does not demand fines from hospitals that violate the law except in unusual cases where they refuse to improve their practices, agency officials said.
“Because the consequences are so real, we have seen hospitals work with us almost every single time,” HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra said in a statement to the AP. “We have been and will continue to be forward leaning here, communicating our intent directly and very seriously to hospital executives and provider associations which is, in part, why we have seen such good cooperation.”
After the Supreme Court overturned the nationwide right to an abortion, the Biden administration turned to a longstanding federal law, the Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act, in a frantic effort to ensure abortion access for women in dire medical circumstances. The White House has argued that to comply with the law, hospitals must provide emergency abortions for pregnant women who need them to save their lives or reproductive organs, despite state abortion bans.
Asked about the AP’s findings on Friday, White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre put blame on former President Donald Trump for appointing three Supreme Court justices who ruled to upend U.S. abortion rights.
The Biden administration has sent letters to hospitals repeatedly reminding them of that law and the penalties — up to $129,232 per violation or loss of Medicare funding — for flouting it.
It also has rolled out a new website making it easier for patients to file a complaint if they are rejected, and it promised to expediate those investigations.
Last year, for example, HHS announced that two facilities — Freeman Health System in Joplin, Missouri, and University of Kansas Health System in Kansas City, Kansas — ran afoul of the federal law after refusing an emergency abortion to Mylissa Farmer.
Doctors at both hospitals told the 41-year old Missouri woman that her baby had no chance of surviving after her water broke at 17 weeks but because a fetal heartbeat was still detectable, her condition needed to worsen before they’d be willing to terminate her pregnancy.
Neither hospital has been fined.
“It would be welcomed if the federal government took a stronger enforcement role in those cases.” said Alison Tanner, an attorney for National Women’s Law Center who represents Farmer. “We have a maternal health crisis in this country and in states with bans on abortion care, it is far worse and more dangerous."
Tanner said the HHS Office of Inspector General, which is responsible for issuing fines for violations of the law, is investigating Farmer’s case. The office declined to comment on cases under review.
The government’s most recent fines against hospitals that turned away pregnant patients were cases from years ago.
A Tennessee hospital agreed to pay a $100,000 fine for a 2018 case involving a pregnant patient who was discharged and gave birth in a car at 42 weeks pregnant. A Kentucky hospital was fined $90,000 for refusing to help a patient with an ectopic pregnancy in 2021.
After a complaint against a hospital is filed, a state surveyor investigates the hospital. A physician and the federal government review the findings to determine whether or not a patient received inadequate treatment. If an emergency room violated the federal law, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services may refer the case to the HHS inspector general to consider penalties.
Those investigations are “slow, insufficiently staffed, with a lot of pushback tolerated from hospitals,” Rosenbaum, an expert on the law, said.
Emergency rooms were supposed to stop turning away patients in medical crisis decades ago, when Congress passed bipartisan legislation designed to prohibit patient dumping that then-Republican President Ronald Reagan signed in 1986.
The law requires facilities that accept Medicare funding to provide a medical screening exam to anyone who shows up at or near their door and offer stabilizing treatment, if needed. Emergency rooms without the resources or staff to properly treat that patient are required to arrange a medical transfer to another hospital, after they’ve confirmed the facility can accept the patient.
The law, Sen. David Durenberger promised nearly 40 years ago as he rallied for its passage, would be a warning to private hospitals that had been dumping pregnant patients and gunshot victims on the doorsteps of public hospitals.
“This amendment is to send a clear signal to the hospital community,” he said on the floor of Congress. “That all Americans, regardless of wealth or status, should know that a hospital will provide what services it can when they are truly in distress.”
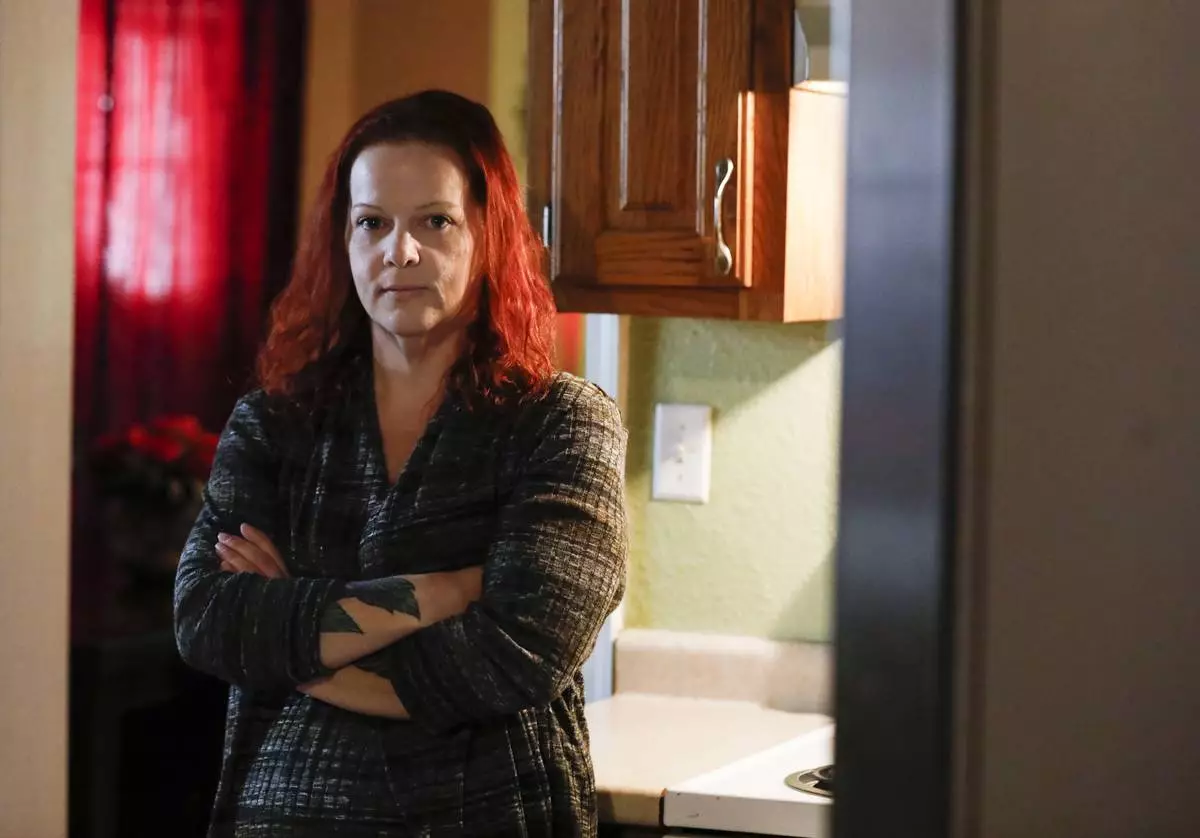

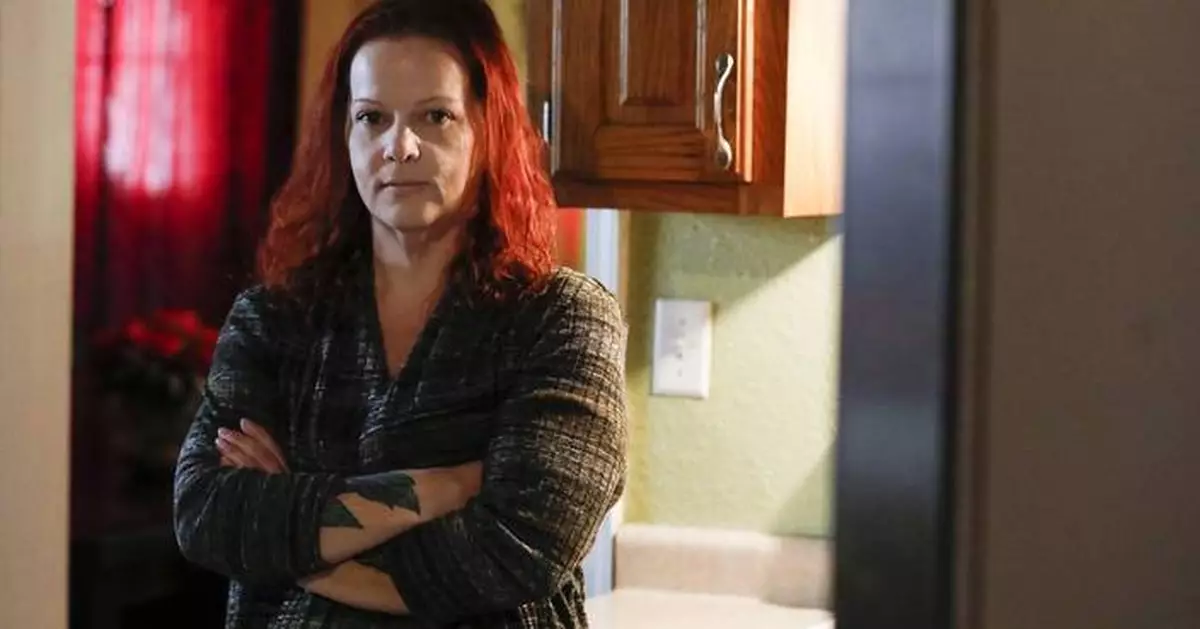
FILE - Mylissa Farmer stands for a portrait at her home in Joplin, Mo., on Sept. 28, 2022. (Nathan Papes/The Springfield News-Leader via AP, File)