PITTSBURG, Kan. (AP) — A new abortion clinic has brought the debate over reproductive rights to a small college town in the southeast corner of Kansas. It’s one of the few states left in the region still allowing abortions.
A religious, Republican-leaning semi-rural location like Pittsburg, Kansas, would have been unlikely to host an abortion clinic before Roe v. Wade was overturned in 2022, but that is changing across the country.
Click to Gallery
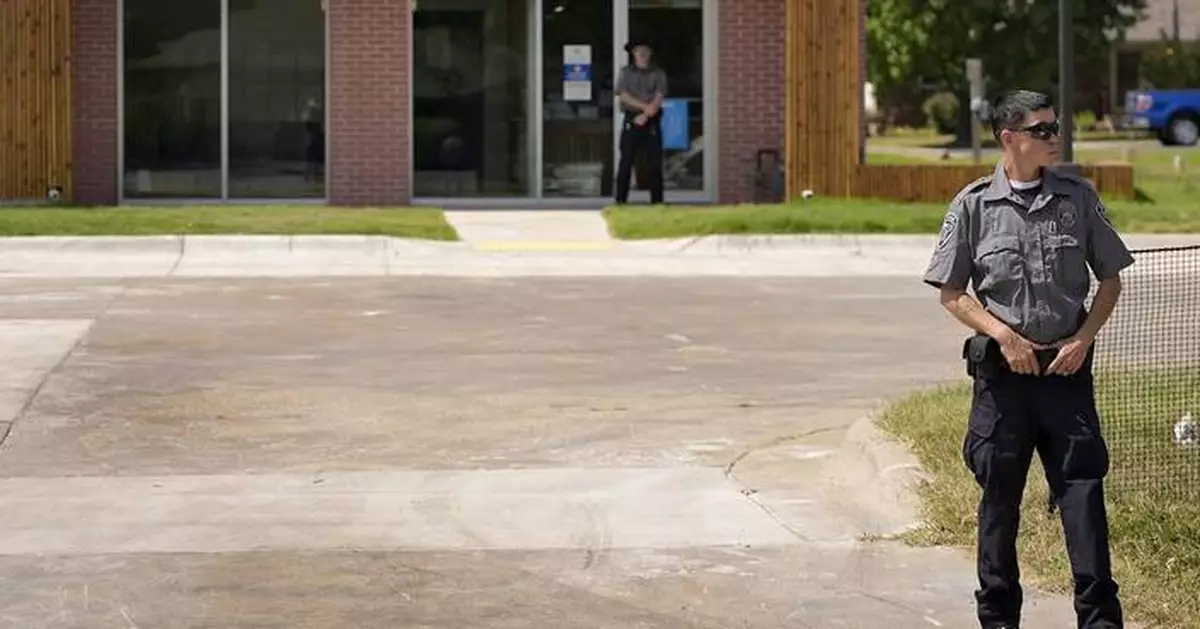
Security personnel stand outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan., that is serving patients from Kansas as well as nearby Missouri, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Texas, and other states. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
+3
Anti-abortion protester Deborah Green-Myers, from Pittsburg, Kan., demonstrates outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
Anti-abortion protester Deborah Green-Myers, from Pittsburg, Kan., demonstrates outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
Security personnel stand outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
Anti-abortion protester Deborah Green-Myers, from Pittsburg, Kan., demonstrates outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
Security personnel stand outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan., that is serving patients from Kansas as well as nearby Missouri, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Texas, and other states. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
People drive through downtown Pittsburg, Kan., Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, that is home to a new Planned Parenthood clinic serving patients from Kansas as well as nearby Missouri, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Texas, and other states where abortions have become illegal or hard to get. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
Security personnel stand outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
The Associated Press reported on the new clinic and the town's reactions. Here are key takeaways.
Over the past two years, Kansas is one of five states that people are most likely to travel to in order to get an abortion if their state doesn't offer the procedure, said Caitlin Myers, an economics professor at Middlebury College who researches abortion policies.
Abortions have spiked by 152% in Kansas after Roe, according to a recent analysis by the Guttmacher Institute, which supports abortion rights.
Using Myers’ count, six of the clinics in Kansas, Illinois, New Mexico, North Carolina and Virginia that have opened or relocated post-Roe are in communities with fewer than 25,000 people. Two others are in communities of fewer than 50,000.
Five weeks after Roe was overturned, voters in Kansas had to decide whether to strip the right to an abortion from the state constitution, which could have led to an outright ban.
Pittsburg is in Crawford County, where 55% of voters were part of the 59% of voters statewide who killed the proposal. But the rural counties surrounding Pittsburg voted for the amendment.
Kansas' statewide percentage is in line with an Associated Press-NORC poll from 2024 that showed 6 in 10 Americans think their state should generally allow a person to obtain a legal abortion if they don’t want to be pregnant for any reason.
Abortion in Kansas is generally legal up until the 22nd week of pregnancy.
The new abortion clinic will be run by Planned Parenthood Great Plains. Its location is a few minutes' drive from the Missouri border and is less than an hour away from Oklahoma.
All of Kansas' other abortion clinics are in larger metro areas, where clinics have expanded hours — but appointments are still in short supply. About 60% to 65% of people who call Planned Parenthood clinics in Kansas for an abortion appointment are turned away because there isn’t enough capacity, said Emily Wales, president and CEO of Planned Parenthood Great Plains.
The bulk of people looking for abortions in Kansas are from out of state — mostly Texas, which is about five hours south, Wales said. She added that some come from as far away as Louisiana and even Florida, which now prohibits the procedure after six weeks.
Experts said smaller-sized clinics can be less overwhelming for women who are coming from rural areas, like those surrounding Pittsburg. But, often, there is little anonymity in these places where religious and family ties often run deep.
Pittsburg is home to a state university with about 7,400 students. The town is also is increasingly religious, with twice as many white evangelical Protestants as the national average, and the area is increasingly Republican.
Pittsburg State students who The Associated Press talked to are supportive of the clinic, as are many of the Democrats in town.
But churches in Pittsburg are training people on how to protest at the abortion clinic, and Vie Medical Clinic, a crisis pregnancy center, has seen an increase in donations.
Hanna reported from Topeka, Kansas.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.

Anti-abortion protester Deborah Green-Myers, from Pittsburg, Kan., demonstrates outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)

Anti-abortion protester Deborah Green-Myers, from Pittsburg, Kan., demonstrates outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
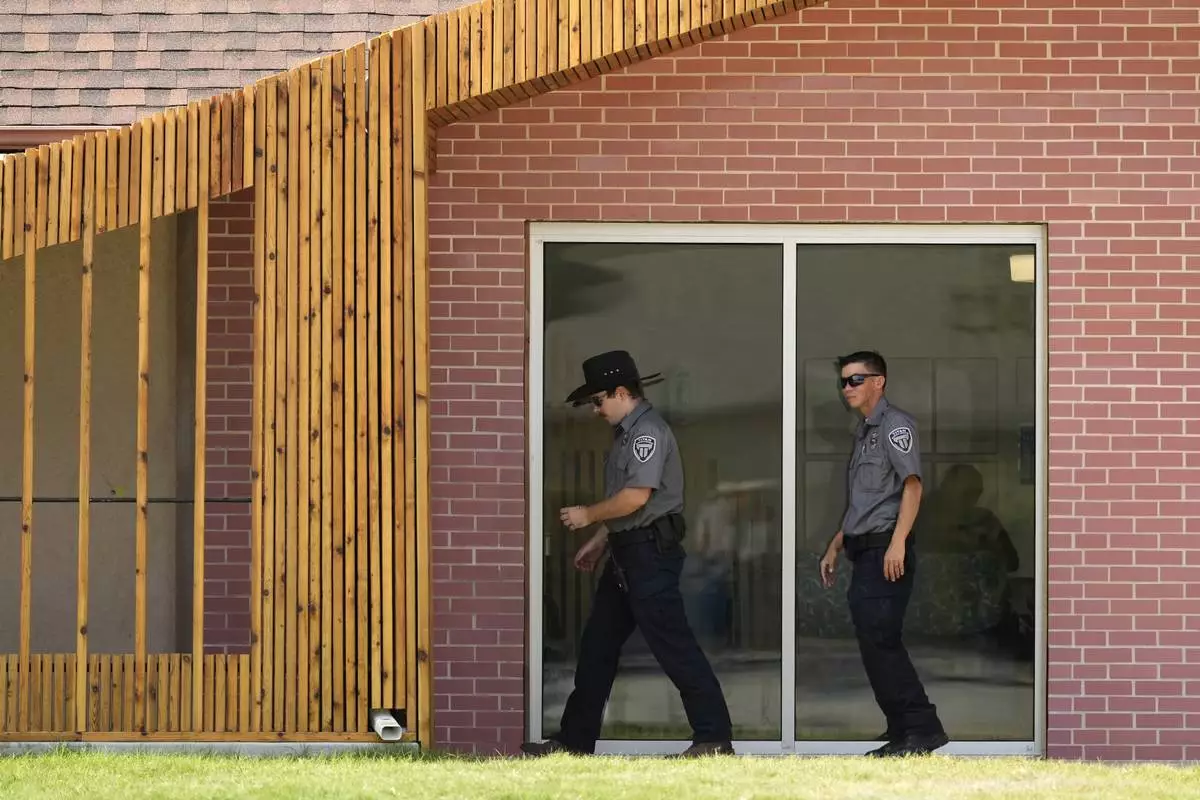

Security personnel stand outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)

Anti-abortion protester Deborah Green-Myers, from Pittsburg, Kan., demonstrates outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
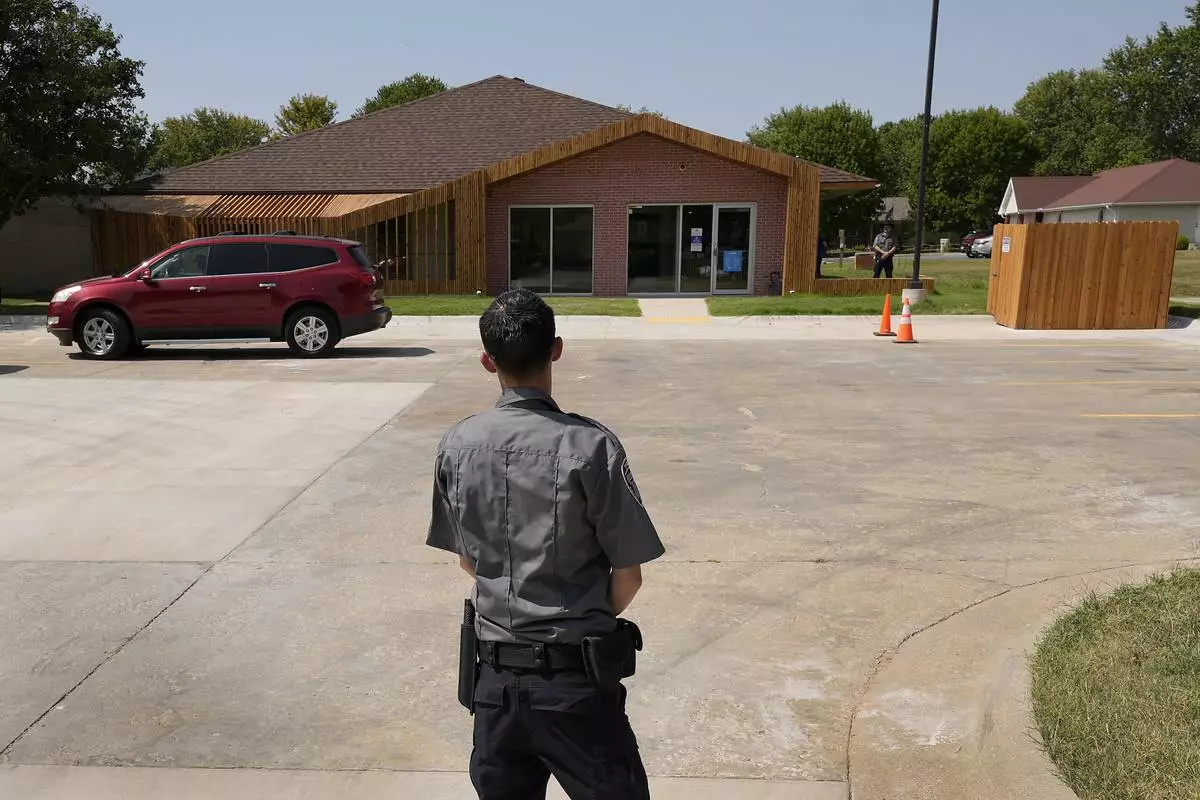

Security personnel stand outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan., that is serving patients from Kansas as well as nearby Missouri, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Texas, and other states. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
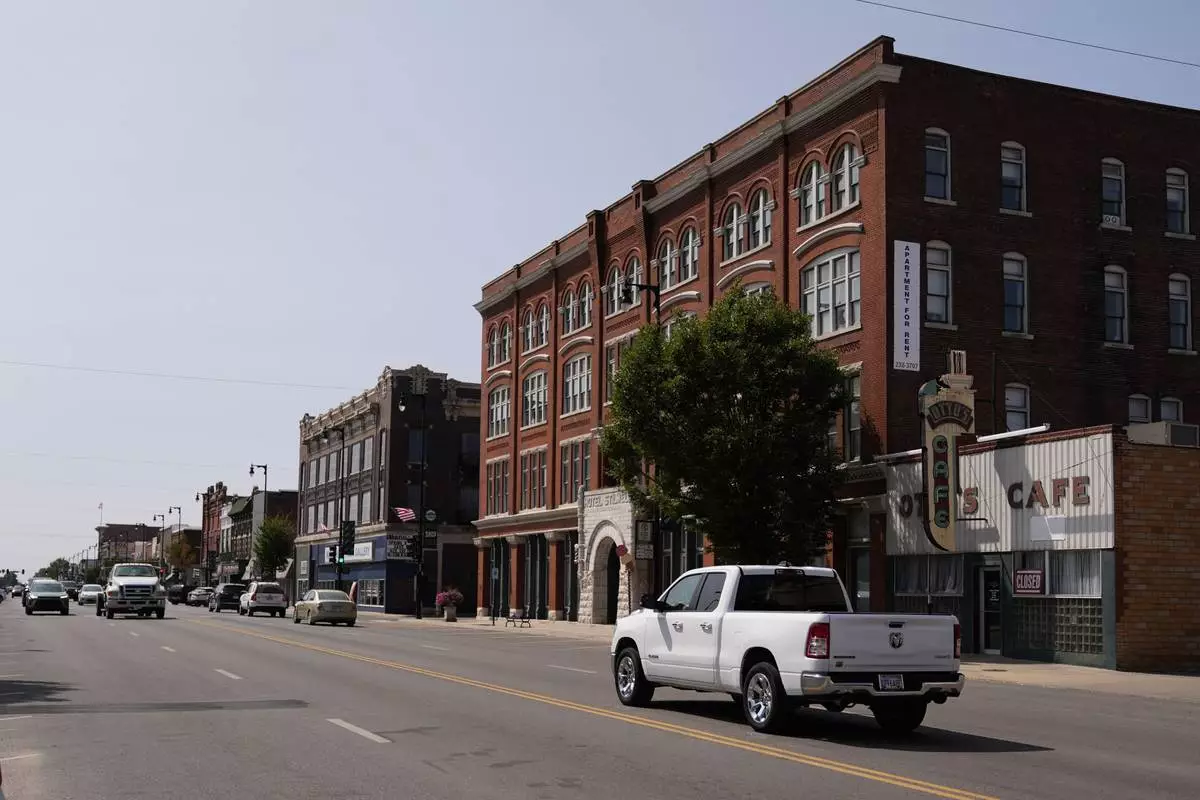

People drive through downtown Pittsburg, Kan., Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, that is home to a new Planned Parenthood clinic serving patients from Kansas as well as nearby Missouri, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Texas, and other states where abortions have become illegal or hard to get. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
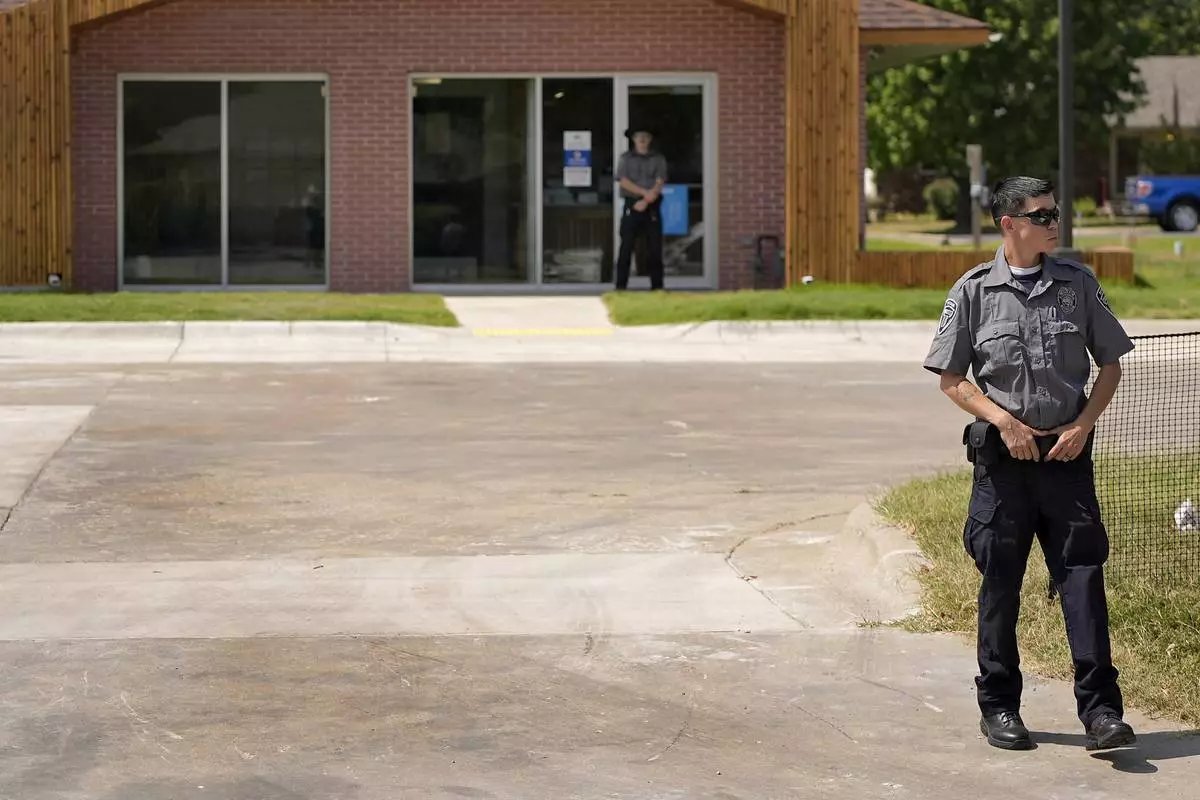

Security personnel stand outside a recently opened Planned Parenthood clinic, Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2024, in Pittsburg, Kan. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel)
MEXICO CITY (AP) — All of a sudden, women contacting one of the biggest sources of information about abortion in Mexico through the encrypted messaging app WhatsApp were met with silence.
The nongovernmental organization’s business account had been blocked. Weeks later, a similar digital blackout struck a collective in Colombia.
Across the Americas, organizations that guide women seeking abortions in various countries are raising alarm, decrying what they see as a new wave of censorship on platforms owned by tech giant Meta — even in countries where abortion is decriminalized. The organizations believe this is due to a combination of changes to Meta policies and attacks by anti-abortion groups that denounce their content.
While this also occurs on Instagram and Facebook, the blocking of organizations’ verified WhatsApp business accounts, which they use to communicate with people seeking help, has been particularly disruptive. These accounts are crucial for communicating with people seeking help, and their blockage has significantly complicated daily interactions between women and support providers.
Meta usually attributes its content blocking to policy violations, though it has acknowledged occasional mistakes. Since January, Meta changed the way it moderates content, now relying on user-generated notes “to allow more speech and reduce enforcement mistakes.” U.S. President Donald Trump has said the changes were “probably” made in response to his threats over what conservatives considered a liberal bias in fact-checking.
Among the organizations whose WhatsApp business accounts were suspended is the MSI Foundation (part of MSI Reproductive Choices, formerly Marie Stopes) a network working in Mexico for 25 years. Its account was suspended in February, and the Colombian group Oriéntame, or Guide Me, which has worked in women's health in Colombia for decades, was labeled by Instagram as “dangerous.”
While conservatives cheered the change in Meta moderation policies, organizations helping women who seek abortions say that, even if they just apply in the U.S., they often result in over-enforcement, likely driven by Artificial Intelligence, which disproportionately flags or removes their posts — obstacles that have increased since the start of the Trump administration.
“It is not always intentional censorship, but the outcome is still more censorship for us and our partners,” said Martha Dimitratou, cofounder of Repro Uncensored, an organization that monitors digital suppression of reproductive health content.
In additional comments on Thursday, Meta rejected any link between the groups’ experiences and its policy changes.
“Our policies and enforcement regarding abortion medication-related content have not changed recently and were not part of the content moderation changes,” Meta said in a statement.
“From one day to the next they blocked communication between our users and women who need first-hand information” to address doubts or look for medical follow-up with MSI, said Araceli López-Nava, the organization’s Latin America director.
In the days after the suspension, appointments dropped 80%
López Nava said that MSI had previously faced issues with regular WhatsApp numbers, because it’s easy to file complaints. So, the organization thought it would be different with a business account, which gives them a platform to manage the thousands of messages they receive every month.
That wasn't the case. After an initial suspension, MSI's WhatsApp business account was permanently suspended two weeks later. The reason cited in Meta’s notification? “Sending spam.”
“The argument is that they’ve received complaints, but from whom?” López-Nava asked. She said the organization can’t be accused of sending spam because they only answer those who contact them and provide information in line with Mexican law. Abortion is decriminalized in Mexico at the federal level and in the majority of its 32 states.
“It looks like an orchestrated strategy to us,” López-Nava said. “And not necessarily by Meta."
Dimitratou, who is also digital strategist for Canada-based Women on Web and the U.S.-based Plan C, said cases of blocked content have increased since Trump’s election, not only in the U.S., but around the world, likely driven by anti-abortion groups.
Conservative or religious groups have a history of attempting to leverage technology companies to obstruct abortion supporters’ efforts, but the anonymity of app reporting prevents organizations from proving who is behind it.
That is why MSI and an ally NGO, Women’s Link Worldwide, have asked Meta to implement transparent mechanisms to be able to appeal the company’s decisions and to respect international human rights standards. They have not received a response.
A Meta spokesperson told The Associated Press that MSI's WhatsApp business account was blocked for valid reasons, saying that organizations receiving numerous negative comments receive warnings before suspension. Meta declined to provide details about the nature of the negative comments or comment on whether they could be coordinated by anti-abortion groups aiming to paralyze MSI.
The Instagram accounts of Women on Web United States and Women on Web Latin America were suspended right after the U.S. presidential election in November, though they were later reinstated. Dimitratou said that Meta has also limited the organization’s ability to place ads on accounts in Latin America, South Korea and West Africa.
Repro Uncensored has documented at least 60 instances of similar digital censorship since January. The most recent occurred this week, when Thailand's TamTang Group said that Facebook had accused them of violating rules on selling medicines simply for sharing information about free abortion pills provided by the Thai government.
A 2025 report by the California-based Center for Intimacy Justice, based on a survey of 159 nonprofits worldwide, found that major tech platforms were removing ads and content related to abortion and other women’s sexual and reproductive health issues like menopause.
When asked about the report, Meta downplayed its findings, noting that it was based on a small number of examples.
Tech companies often cite policies against explicit or inappropriate sexual content or the advertisement of unsafe substances, such as abortion pills, even though the World Health Organization has said they’re safe.
In April, months after Meta announced changes to ensure greater freedom of expression, Oriéntame, the Colombian collective that offers reproductive health services, posted on Instagram a drawing of a heart and the phrase “Abort without pain.” The post was blocked with the explanation: “Dangerous people and organizations, photo removed.”
While Colombia legalized abortion in 2022, Oriéntame experienced censorship of at least 14 of their posts on Instagram in April 2025. That same month, their WhatsApp business account was suspended, said Tatiana Martínez, who manages their social media. Although the WhatsApp account was restored after a week, they worry it could happen again.
A Meta spokesperson said this week that the Instagram posts were mistakenly taken down and not the result of a change in its content standards.
Oriéntame director María Vivas says the organization has been battling Google for years over online content limitations. The tech giant said in a message to the AP that it only restricts content when it violates policies. But Google keeps Colombia on the list of countries with restrictions on abortion ads — even though abortion was decriminalized there in 2022.
As for their problems with Meta, Vivas said they started in late 2024, when the company started to make some data management adjustments.
Taking legal action against tech giants, when each country has its own laws, is complicated. As a result, affected organizations have turned to creative strategies, like operating multiple backup accounts, having a substitute ready when one is blocked and reformulating language in posts to avoid censorship triggers.
“It feels like Meta is our boss,” Vivas joked about the ongoing struggle with the tech giant over the basic right to provide health information. “We live to respond to Meta, to adapt ourselves to Meta,” she said. “That's absurd.”
AP journalist Maria Cheng contributed to this report from New York.
Follow AP’s coverage of Latin America and the Caribbean at https://apnews.com/hub/latin-america
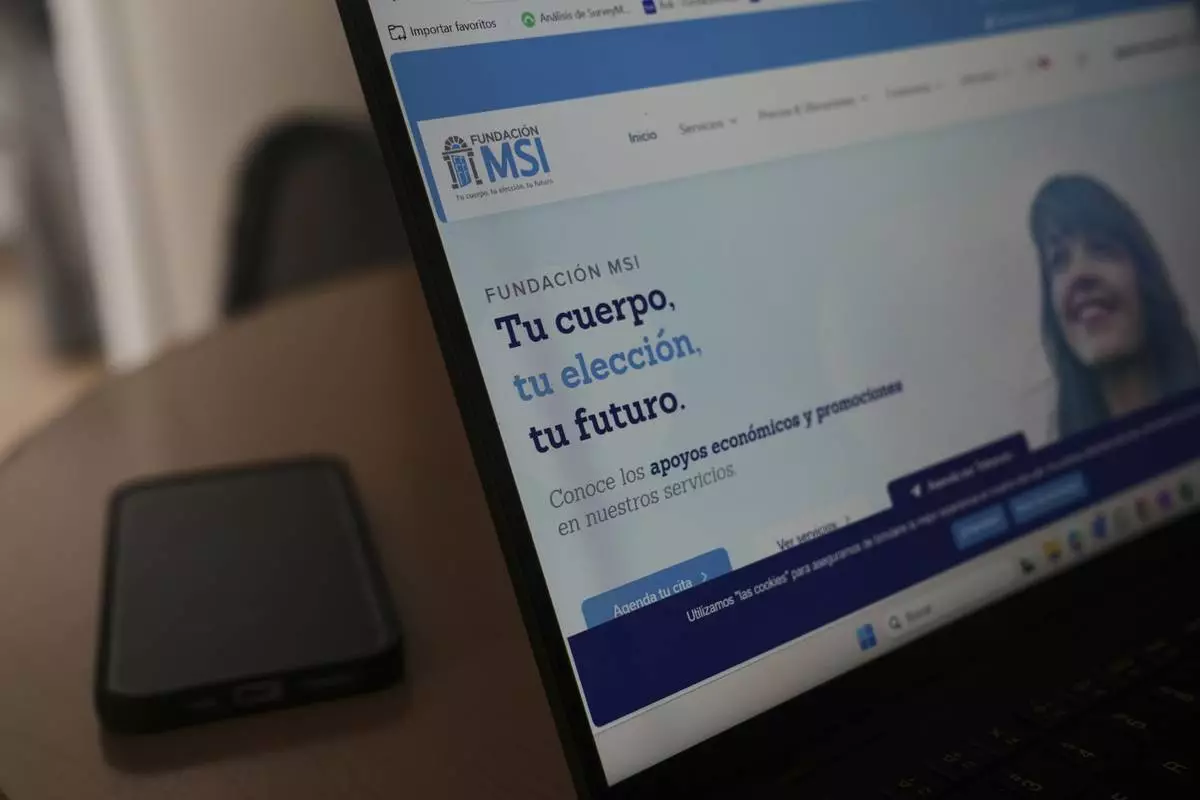
A computer monitor shows the splash page of the MSI Foundation website with a message that reads in Spanish: "Your body, your choice, your future", during a tour of the foundation, a non-governmental agency that offers information and help to women seeking abortions, in Mexico City, Thursday, May 8, 2025. (AP Photo/Marco Ugarte)
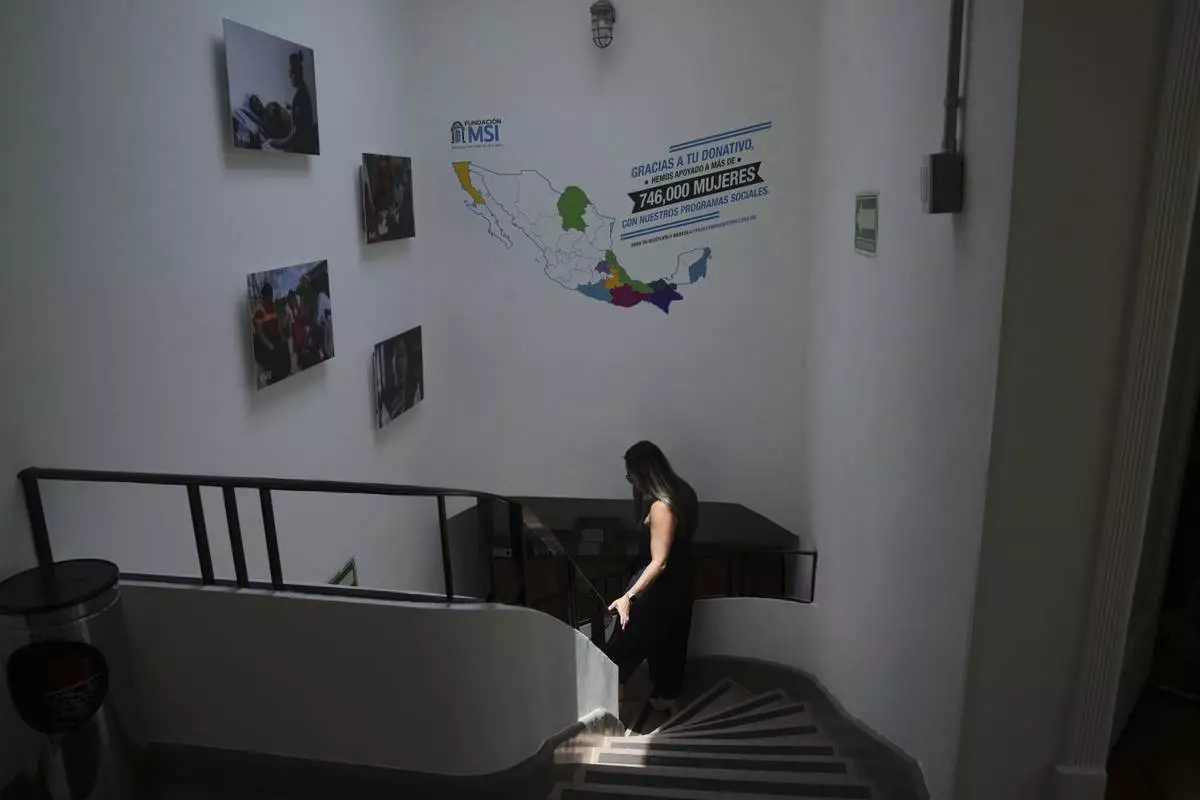

A health worker gives a tour of the MSI Foundation, an organization that offers information and help to women seeking abortions, in Mexico City, Thursday, May 8, 2025. (AP Photo/Marco Ugarte)

A health worker gestures towards a message that reads in Spanish; "My decisions, my road, my steps" during a tour of the MSI Foundation, an organization that offers information and help to women seeking abortions, in Mexico City, Thursday, May 8, 2025. (AP Photo/Marco Ugarte)
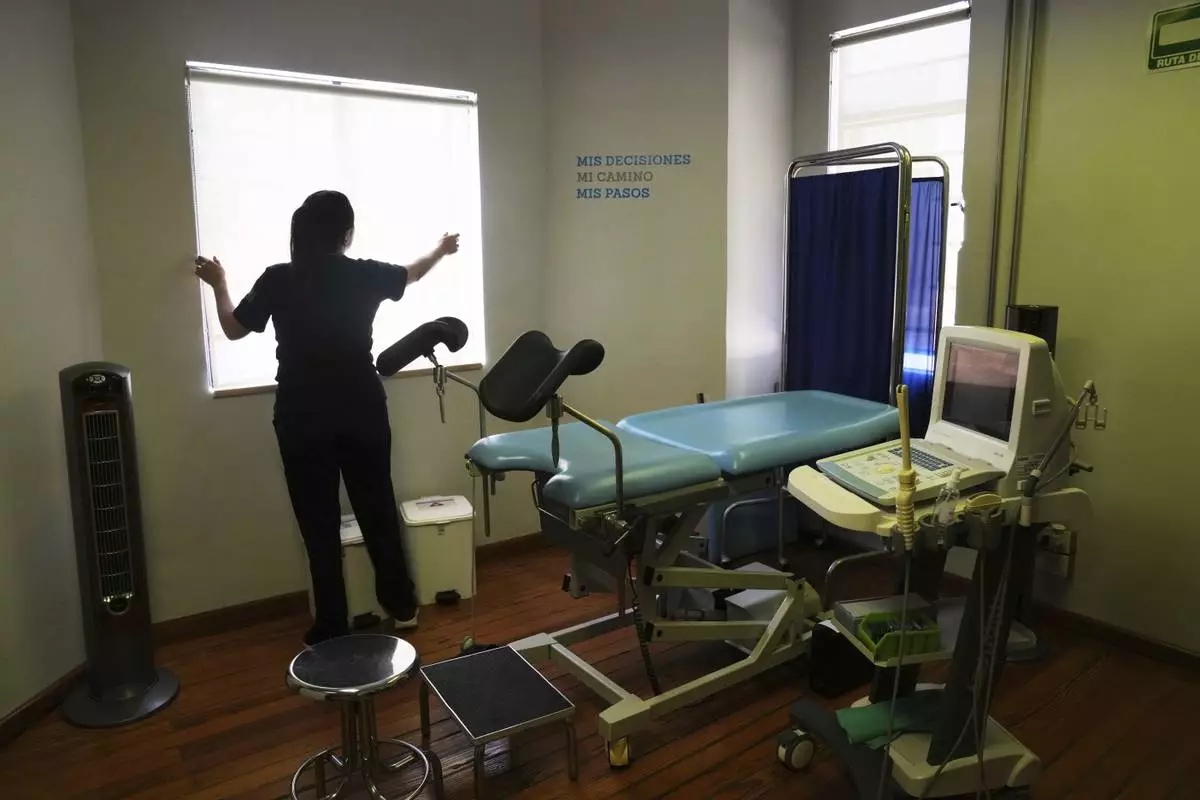
A health worker gives a tour of the MSI Foundation, an organization that offers information and help to women seeking abortions, in Mexico City, Thursday, May 8, 2025. (AP Photo/Marco Ugarte)