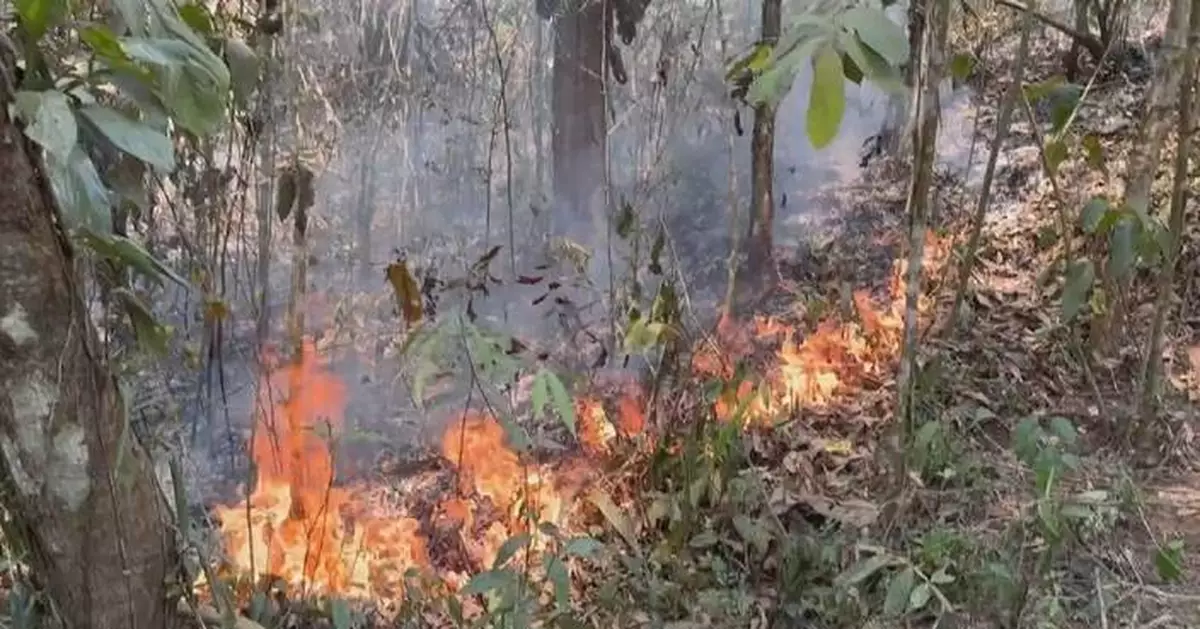
The ongoing seasonal drought and adverse weather conditions such as high wind are hindering firefighters' efforts to put out a wildfire that has been raging in Brazil's Mato Grosso for over half a month.
The state of Mato Grosso, one of the regions worst-affected by wildfires burning across the Amazon, has declared a state of emergency as over half of the state's cities and towns have reported fire emergencies.
In Chapada dos Guimaraes, one of the regions subject to emergency mandate, swathes of forests and farmlands have been burned.
"We have been putting out fires here for 17 consecutive days. About 14 kilometers of the fire line have been suppressed. The vegetation is tall and dense, so it is not easy for us to carry out firefighting. The wind also makes it more difficult for us to extinguish fire," said Robson Luiz, director of Chapada dos Guimaraes' Administrative Department and Municipal Civil Defense.
As the existing resources are inadequate to support the firefighters to work long enough at a fire spot to guarantee a full extinguishment, they had move on to the next spot after clearing leaves and tree branches to contain the fire within a restricted area.
In addition, the seasonal drought that has led to a significant drop of water level has also hindered the firefighters' efforts.
"The water level of the Paraguay River has been dropping, along with the dry season across the state and adverse weather conditions, such as high temperature, low relative air humidity and strong winds. These factors have accelerated the spread of forest fires. Once there is a fire, it will expand quickly, which will be difficult to control," said Felipe Saboia, commander of the environmental emergencies battalion in Mato Grosso.
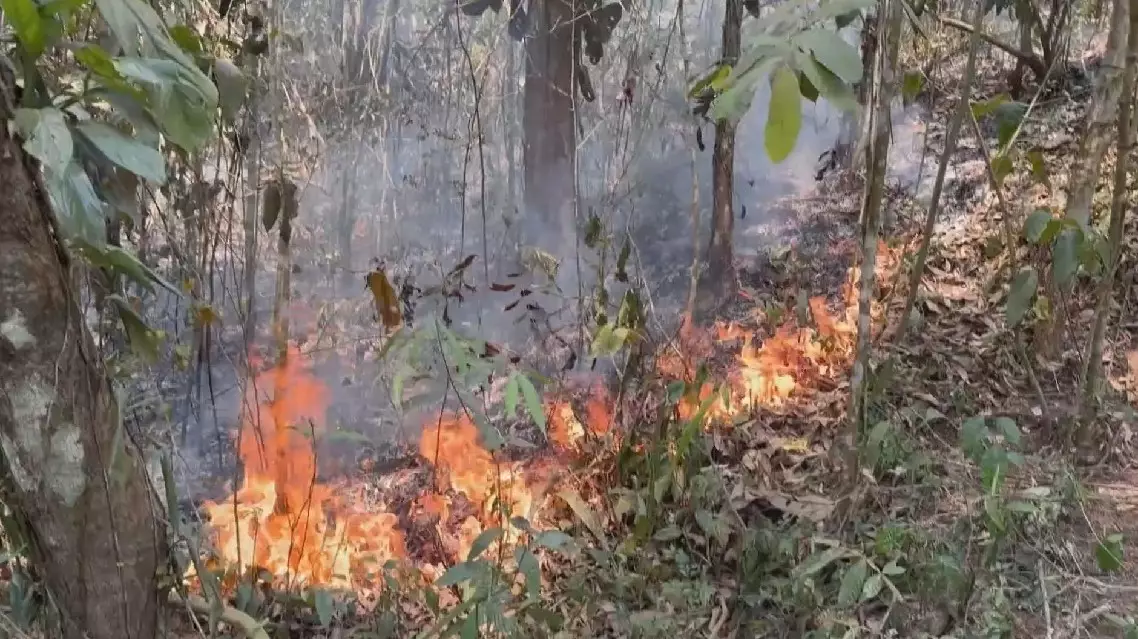

Drought, windy weather worsen wildfire in Brazil's Mato Grosso
The new China-Mongolia cross-border railway is expected to serve as a new bridge for boosting connectivity between the two countries, Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesman Lin Jian said in Beijing on Thursday.
China and Mongolia held a groundbreaking ceremony on Wednesday to mark the official launch of construction on the Gantsmod–Gashuunsukhait rail project, which will be the second cross-border rail link between the two countries.
Lin said at a regular press briefing that the railway would inject new momentum into the development of China-Mongolia bilateral relations.
"On May 14, China and Mongolia held a ceremony to mark the official groundbreaking of the Gantsmod-Gashuunsukhait cross-border railway, which is the second cross-border railway between the two countries. Expanding cooperation in key areas such as economy and trade, energy, mining and connectivity is an important common understanding between President Xi Jinping and Mongolian President Ukhnaa Khurelsukh. In February this year, Premier Li Qiang and Mongolian Prime Minister Luvsannamsrai Oyun-Erdene jointly witnessed the exhibiting of the cooperation agreement on the Gantsmod-Gashuunsukhait railway and coal trade," said Lin.
"The construction of this cross-border railway is not only a concrete step of implementing the important common understanding between the presidents of the two countries, but also an important action to synergize the Belt and Road Initiative and Mongolia's Steppe Road Program. We hope this railway will serve as a new bridge for China-Mongolia connectivity, fostering deeper development integration, promoting industrial synergy, and expanding visits and exchanges, thereby injecting new impetus in to the building of a China-Mongolia community with a shared future," he said.

New cross-border railway to enhance connectivity between China, Mongolia: FM spokesman