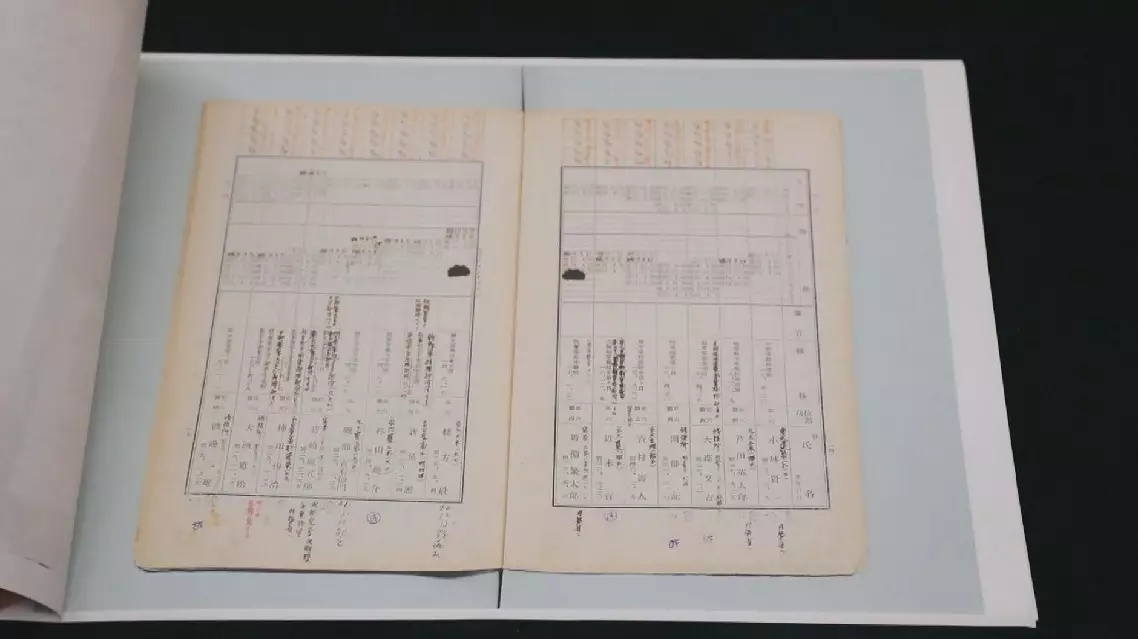
Japanese Army Unit 731, a biological and chemical warfare unit stationed in northeast China during World War II, had a strict evaluation and assessment system for technicians, allowing those who conducted live human experiments to be promoted, according to a newly discovered document of the notorious unit.
The new document was disclosed by Japanese scholar Seiya Matsuno, a specially-appointed professor at Heilongjiang International University, in September ahead of the 93rd anniversary of the September 18 Incident of 1931. The archive is important evidence for deepening the research on Japan's bacterial warfare system and is of great significance to fully exposing Japan's biological warfare crimes.
The September 18 Incident of 1931 taking place in the city of Shenyang in northeast China was a precursor to Japan’s launch of a full-scale invasion of China, and a key event ahead of the outbreak of World War Two in Asia.
The new files include the evaluation forms of Unit 731 technicians. On these forms, red words such as "excellent" and "good" are marked. For example, Yoshimura Hisato,a war criminal and leader of the unit’s frostbite study squad, has four "excellent" and one "good" ratings. During this period, Hisato compiled the relevant content of the experiments conducted in Unit 731 into a paper and published it in Japan.
"This paper is a confidential document written by Yoshimura Hisato, a technician with Unit 731, about frostbite. It was published on October 26, 1941. There is a table called Experiment 5, which contains the frostbite resistance index of people under various living conditions. The subjects are marked with ABCDE, and then the data of frostbite resistance indexes are counted under various living conditions, such as soaking in cold water, soaking in warm water, fasting for two days, fasting for three days, and the subjects staying awake day and night. Such data obtained through live human experiments can be seen everywhere in the paper," said Tan Tian, researcher at the exhibition hall of evidence of crimes of Unit 731 in Harbin, northeast China's Heilongjiang Province.
According to staff from the International Research Center of Unit 731 under the Harbin Academy of Social Sciences, Hisato joined Unit 731 in March 1938 as a sixth-class technician. While conducting frostbite research and experiments, he was also responsible for the management of the special prison where the subjects were detained, making him a researcher as well as a core secrets administrator of the of Unit 731. He was promoted to the rank of fourth-class technician in October 1942.
"From the perspective of Yoshimura Hisato, he joined Unit 731 in 1938 and completed a three-step career jump in less than four years until 1942. Lying behind such fruitful achievements were the bloody live human experiments he made. Yoshimura Hisato published at least 200 medical papers in his career. The Japanese medical community tacitly approved the anti-human atrocities and human experiments of Unit 731, which further reflects the organized nature of these crimes," said Gong Wenjing, director of the International Research Center of Unit 731 under Harbin Academy of Social Sciences.
Unit 731 was a covert biological and chemical warfare research and development unit of the Imperial Japanese Army that engaged in lethal human experimentation and biological weapons manufacturing in China during World War II. The unit is estimated to have killed between 200,000 and 300,000 people. It was based in the Pingfang District of Harbin, the largest city in the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo (now Northeast China, formerly named Manchuria) and had active branch offices throughout China and Southeast Asia.
Unit 731 was responsible for some of the most notorious war crimes committed by the Japanese aggressor troops. It routinely conducted tests on people who were dehumanized and internally referred to as "logs". Experiments included disease injections, controlled dehydration, biological weapons testing, hypobaric pressure chamber testing, vivisection, organ procurement, amputation, and standard weapons testing. Victims included not only kidnapped men, women (including pregnant women) and children but also babies born from the systemic rape perpetrated by the staff inside the compound.
Newly discovered document exposes evaluation system of technicians under wartime Japan's germ warfare unit