The small plastic box that beeped and flashed numbers was a lifeline to Laurie Dove in 1993. Pregnant with her first baby in a house beyond any town in rural Kansas, Dove used the little black device to keep in touch with her husband as he delivered medical supplies. He carried one, too. They had a code.
“If I really needed something I would text ‘9-1-1.’ That meant anything from, ‘I’m going to labor right now’ to ‘I really need to get ahold of you,’” she recalls. “It was our version of texting. I was as nervous as a long-tailed cat in a room full of rockers. It was important.”
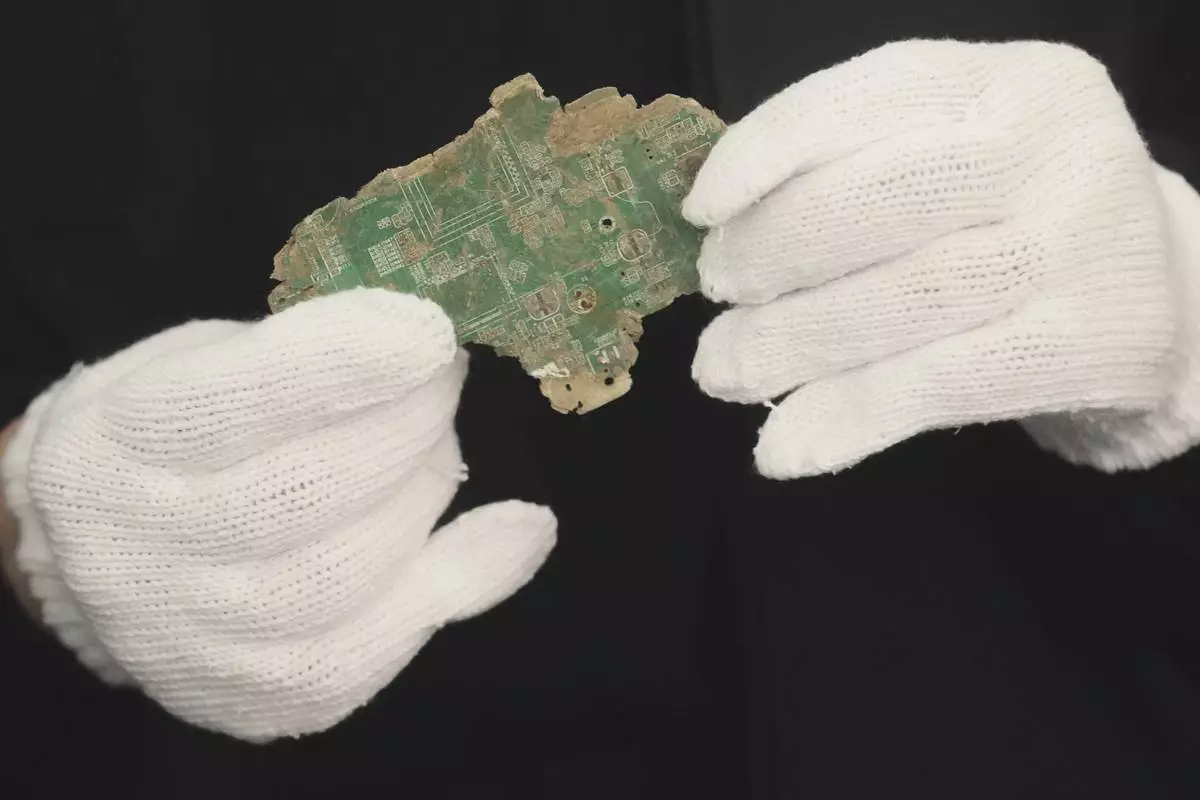
Beepers and all they symbolized — connection to each other or, in the 1980s, to drugs — went the way of answering machines decades ago when smartphones wiped them from popular culture. They resurfaced in tragic form Tuesday when thousands of pagers exploded simultaneously in Lebanon, killing at least a dozen people and injuring thousands in a mysterious, multiday attack as Israel declared a new phase of its war on Hezbollah.
In many photos, blood marks the spot where pagers tend to be clipped — to a belt, in a pocket, near a hand — in graphic reminders of just how intimately people still hold those devices and the links — or vulnerability — they enable.
Then as now — albeit in far smaller numbers — pagers are used precisely because they are old school. They run on batteries and radio waves, making them impervious to dead zones without WiFi, basements without cell service, hackings and catastrophic network collapses such as those during the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks.
Some medical professionals and emergency workers prefer pagers to cell phones or use the devices in combination. They're handy for workers in remote locations, such as oil rigs and mines. Crowded restaurants use them, too, handing patrons blinking, hockey puck-like contraptions that vibrate when your table is ready.
To those who distrust data collection, pagers are appealing because they have no way to track users.
“A mobile phone at the end of the day is like a computer that you’re carrying around, and a pager has got a fraction of that complexity,” said Bharat Mistry, the UK’s technical director for Trend Micro, a cybersecurity software company. “Nowadays it’s used by people who want to maintain their privacy ... You don’t want to be tracked but you do want to be contactable.”
From the start, people have been ambivalent about pagers and the irksome feeling of being summoned when it's convenient for someone else.
Inventor Al Gross, regarded by some as the “founding father” of wireless communication, patented the pager in 1949 intending to make it available to doctors. But they balked, he said, at the prospect of being on-call 24/7.
“The doctors wanted to have nothing to do with it because it would disturb their golf game or it would disturb the patient,” Gross said in a video made when he received the Lemelson-MIT Lifetime Achievement Award in 2000. “So it wasn't a success, as I thought it would be when it was first introduced. But that changed later.”
By the 1980s, millions of Americans used pagers, according to reports at the time. The devices were status symbols — belt-clipped signals that a wearer was important enough to be, in effect, on call at a moment's notice. Doctors, lawyers, movie stars and journalists wore them through the 1990s. In 1989, Sir Mix-a-Lot wrote a song about them, rapping: “Beep diddy beep, will I call you maybe.”
By then, pagers also had become associated with drug dealers and schools were cracking down. More than 50 school districts, from San Diego to Syracuse, New York, banned their use in schools, saying they hampered the fight to control drug abuse among teenagers, The New York Times reported in 1988. Michigan prohibited the devices' use in schools statewide.
"How can we expect students to ‘just say no to drugs’ when we allow them to wear the most dominant symbol of the drug trade on their belts,″ James Fleming, associate superintendent for the Dade County Public Schools in Florida, was quoted as saying.
By the mid-90s, there were more than 60 million beepers in use, according to Spok, a communications company.
Dove, who went on to serve as the mayor of Valley Center, Kansas, and become an author, says she and her family use cell phones now. But that means accepting the risk of identity theft. In some ways, she fondly recalls the simplicity of pagers.
“I do worry about that," she says. “But that risk just feels like a part of life now.”
The number of pagers globally is hard to come by. But more than 80% of Spok’s paging business deals with healthcare, with about 750,000 subscribers across large hospital systems, according to Vincent Kelly, CEO of the company.
“When there’s an emergency, their phones don’t always work,” Kelly said, adding that pager signals are often stronger than cell phone signals in hospitals with thick walls or concrete basements. Cell networks are “not engineered to handle every single subscriber trying to call at the same time or send a message at the same time.”
Members of Iran-backed Hezbollah on Israel’s northern border have used pagers to communicate for years. In February, the group’s leader, Hassan Nasrallah, directed Hezbollah members to ditch their cell phones in an effort to dodge what’s believed to be Israel’s sophisticated surveillance on Lebanon’s mobile phone networks.
Tuesday’s attack appeared to be a complex Israeli operation targeting Hezbollah. But the widespread use of pagers in Lebanon meant the detonations cost an enormous number of civilian casualties. They exploded in a moment across the landscape of everyday life — including homes, cars, grocery stores and cafes.
Kelly says first responders and large manufacturers also use pagers. The manufacturers have employees use the devices on factory floors to prevent them from taking photos.
Most medical personnel use combinations of pagers, chat rooms, messaging and other services to communicate with patients without revealing home numbers — an effort to be truly off-duty when they’re not working.
Dr. Christopher Peabody, an emergency physician at San Francisco General Hospital, uses pagers every day — albeit grudgingly. “We’re on a crusade to get rid of pagers, but we’re failing miserably,” said Peabody, who is also director of the UCSF Acute Care Innovation Center.
Peabody said he and others at the hospital tested a new system and “the pager won": The doctors stopped answering the two-way text messages and would only respond to pagers.
In some ways, Peabody understands the resistance. Pagers provide a certain autonomy. In contrast, two-way communication carries the expectation to immediately answer and could provide an avenue for follow-up questions.
The problem, Peabody said, is that paging is one-way communication and providers can’t communicate back and forth through the paging system. The technology, he said, is inefficient. And paging systems are not necessarily secure, a critical issue in an industry that must keep patient information private.
“This has been a culture of medicine for many, many years,” he said, “and the pager is here to stay, most likely.”
Parvini reported from Los Angeles.
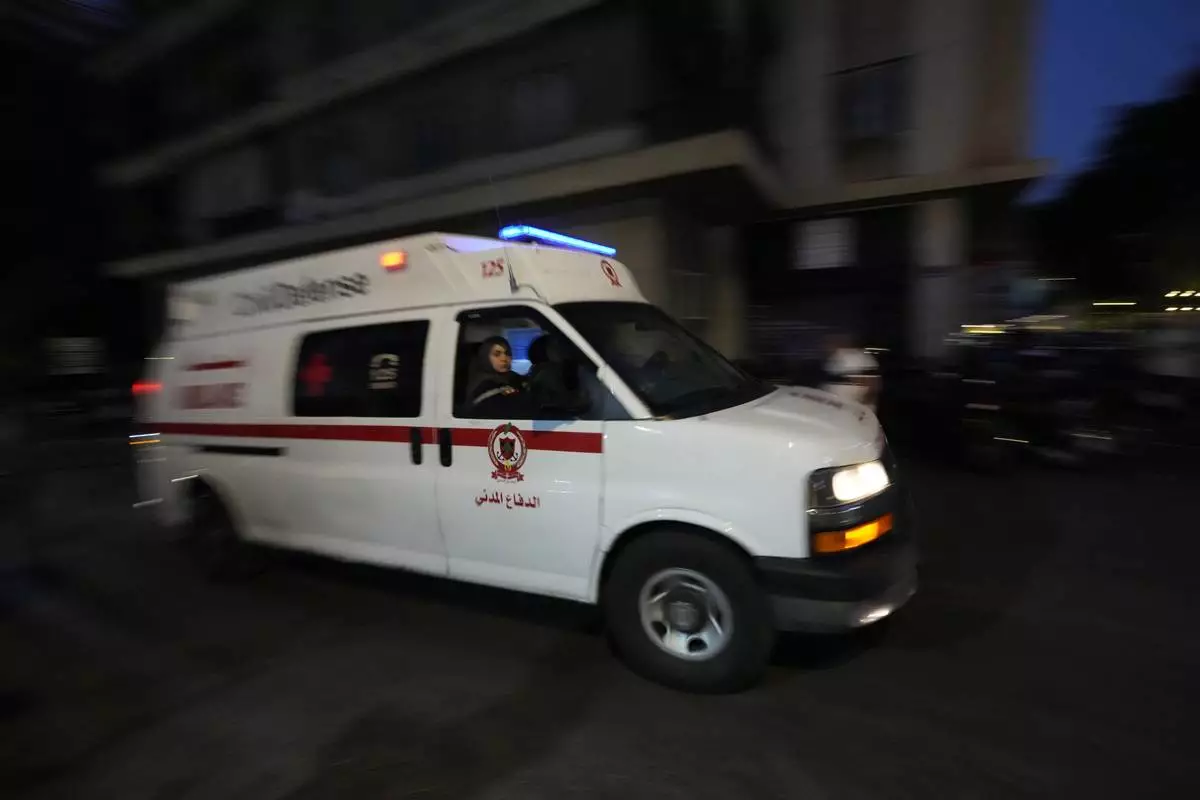

An ambulance carrying wounded people whose handheld pager exploded, arrive at the American University hospital in Beirut, Lebanon, Tuesday, Sept. 17, 2024. (AP Photo/Hassan Ammar)
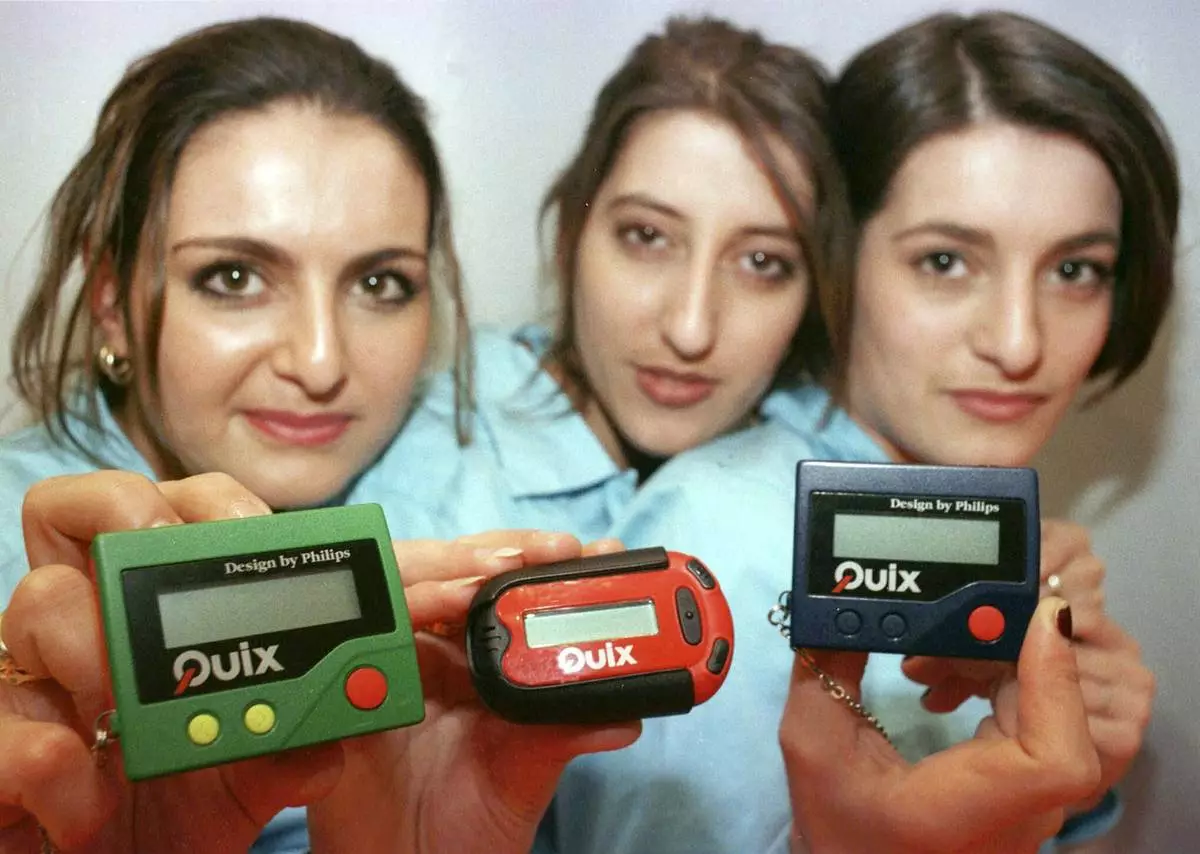

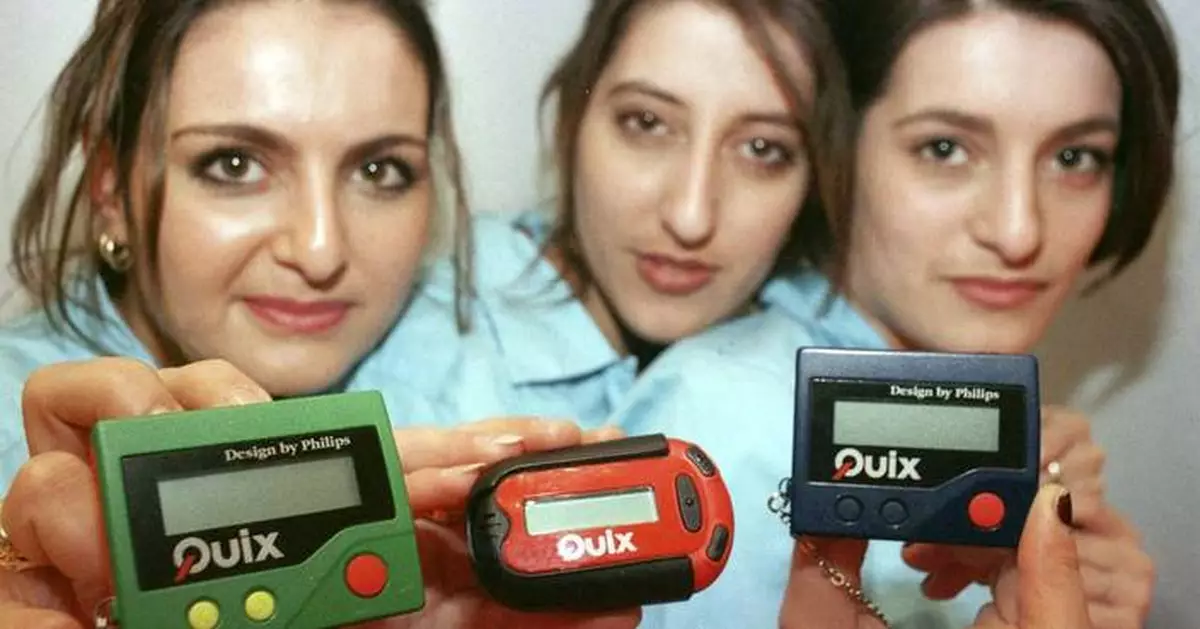
FILE - Three women hold the pager 'Quix' as they present it at CeBIT '97 in Hannover, Germany, Tuesday March 18, 1997. The beep-beep-beep of a small black box on your belt or in your pocket was something of a status symbol decades before the smartphone wiped it from popular culture. (AP Photo/Fabian Bimmer, File)