Chinese researchers have discovered key differences between lunar samples collected by the Chang'e-6 mission and those by the Chang'e-5, according to the first research paper on the Chang'e-6 samples published on Tuesday.
The study was carried out jointly by members from the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Lunar Exploration and Space Engineering Center, and the Beijing Institute of Spacecraft System Engineering. The research paper was published in the National Science Review journal on Tuesday, also the traditional Mid-Autumn Festival.
"I have processed both separate samples from Chang'e-5 and 6. We have observed notable differences in their physical properties. For example, when viewed under a microscope, the particles from Chang'e-6 show a bimodal distribution, whereas Chang'e-5's particles present a single peak," said Liu Jianjun, researcher at National Astronomical Observatories.
The bimodal distribution of Chang'e-6's lunar particles indicates the presence of two distinct sizes of material, suggesting that the sample may have originated from multiple regions of the Moon.
"Another difference is that during the selection process, we found that there were noticeably fewer rock fragments in the Chang'e-5 sample, while Chang'e-6 contained more. We believe this is likely due to the impact crater near the Chang'e-6 landing site, which measures about 50 meters in diameter. It's possible that ejecta from the crater was collected by Chang'e-6," Liu added.
The team also found that the Chang'e-6 soil samples have a lower density than previous samples, indicating a more porous and loosely structured composition. The plagioclase content of the Chang'e-6 samples is significantly higher than that of the Chang'e-5 samples, while their olivine content is significantly lower.
The study has also revealed that the Chang'e-6 lithic fragment samples are primarily composed of basalt, breccia, agglutinate, glasses and leucocrate.
Geochemical analysis of the Chang'e-6 lunar samples has shown that their concentration of trace elements such as thorium, uranium and potassium is markedly different from the samples retrieved by the Apollo missions and the Chang'e-5 mission.
"The density [of Chang'e-6 sample] is smaller than that of Chang'e-5's, likely indicating that there are more lightweight minerals inside. Its bulk density is relatively low and small, which suggests that it may contain lightweight minerals and is also relatively loose. We need further research to understand what this looseness represents geologically and what space weathering effects it represents," said Li Chunlai, deputy chief designer of Chang'e-6 mission.
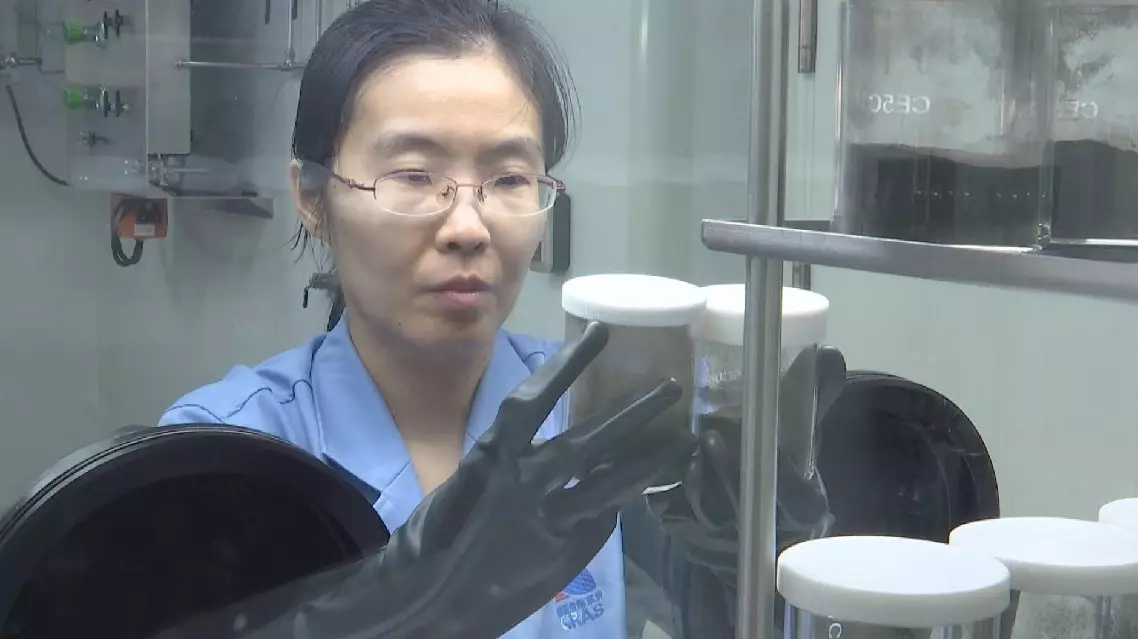

Lunar samples taken by Chang'e 6 show key differences from Chang'e 5
Zhengzhou City, the provincial capital of central China's Henan, is using tiny sensors to leverage a hundred-billion-level industrial chain, as cities across the province are taking actions to promote the high-quality economic development through vigorously developing high-tech manufacturing industry.
Zhengzhou has been witnessing the rapid development of the local sensor industry, with the number of related companies doubling to 3,000 over the past three years.
A reporter from the China Central Television visited an intelligent sensor laboratory in Zhengzhou on Saturday, where a newly developed "electronic skin" has been tested. The flexible tactile sensor, like a thin film glove, can accurately capture slight touch of the hand and precisely record external pressure changes.
This precise perception is achieved by the sensing points on the surface. There are about 100 sensing points per square centimeter responding at about 1 millisecond, making it possible to reflect pressure changes in real time.
More than a decade ago, China's locally produced sensors were large in size and low in precision, and could easily be replaced in the market. But now, with heavy investment in research and breakthroughs in core technology, the companies in Zhengzhou have the capability to produce extremely small sensors that integrate two different sensing functions in the volume of a grain of rice.
The use of sensors has already been expanded beyond the traditional fields of everyday objects. Their applications include manufacturing and machinery, airplanes and aerospace, cars, medicine, robotics and many other aspects of people's daily life.
In Zhengzhou, the combination of sensors and wind turbines has made power generation safer and more efficient.
At the Huicuishan wind farm in Dengfeng, a county-level city under the jurisdiction of Zhengzhou, each wind wheel makes only 14 revolutions per minute, but it can generate 2,000 kilowatts of electricity an hour, which means that it uses less rotation to make more power than an ordinary full-load generator. "This is the laser wind detection radar dubbed 'wind catching master' which is developed by us. It is more timely and efficient than the conventional wind measurement, and can increase the power generation efficiency by 3 percent to 5 percent, so that the income produced by each wind turbine can be raised by over one million yuan (about 142,000 U.S. dollars). Now we are conducting joint development with enterprises, universities, and scientific research institutes, aiming to develop more sensor products that meet market demand in chip design," said Fang Xin, assistant director of the Zhengzhou Zhongke Integrated Circuit and System Application Research Institute.
"Here, we can do packaging tests on sensors of gas, temperature, pressure and others, and provide the best technical solutions for companies," said Zhou Jirui, deputy director of the advanced packaging test center of the institute.
With the focus on the four key links of intelligent sensor industry -- R and D design, processing and manufacturing, packaging test, material and equipment -- and the traditional dominant position in the gas sensor market, Henan has invested more than 2 billion yuan (about 283.6 million U.S. dollars) to establish the micro nano photoelectron platform of Mozi Laboratory, a key research institution for semiconductor optoelectronic chips based in Zhengzhou.
The construction of an innovation base of Zhengzhou's "quantum valley" has also been launched to further enhance its chip design and production capacity and support the sensor industry's transformation to high-end manufacturing.
Back in 2019, the Programme for China (Zhengzhou) Intelligent Sensor Valley was released, aiming to promote the large-scale, distinctive, differentiated and high-end development of the city's sensor industry. At present, the construction of the project is progressing steadily.
"The China (Zhengzhou) Intelligent Sensor Valley has a space layout of 'one valley with various parks.' The 'one valley' refers to the sensor industry town covering three square kilometers in Gaoxin District of Zhengzhou, and the 'various parks' refer to the themed zones featuring different application scenarios in various cities. This is the pilot plant testing base for intelligent sensing, where Henan's first eight-inch MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) pilot test line is under construction. At the start-up area of the valley, entrepreneurs are provided with one-stop industrial services ranging from product development, pilot testing, mass production to product launching," said Shen Pan, operations director of the valley.
Henan has given full play to the leading role of the high-level platforms such as intelligent sensor MEMS R and D service platform, Mozi Laboratory, integrated circuit public R and D platform and integrated circuit pilot test platform. The province is also guiding establishments with advantages in innovation resource to provide pilot scale testing and maturation and secondary development services of R and D results for more colleges, research institutes and related enterprises, so as to transform the scientific research and technology advantages of local intelligent sensor and semiconductor industry chain into product advantages and profit advantages.
Tiny sensors leverage hundred-billion-level industrial chain in China's Henan










