Relying on an advanced heavy ion research facility, Chinese researchers have carried out a string of cutting-edge and applied research in heavy ion physics, with fruitful results yielded to shore up scientific progress and social development.
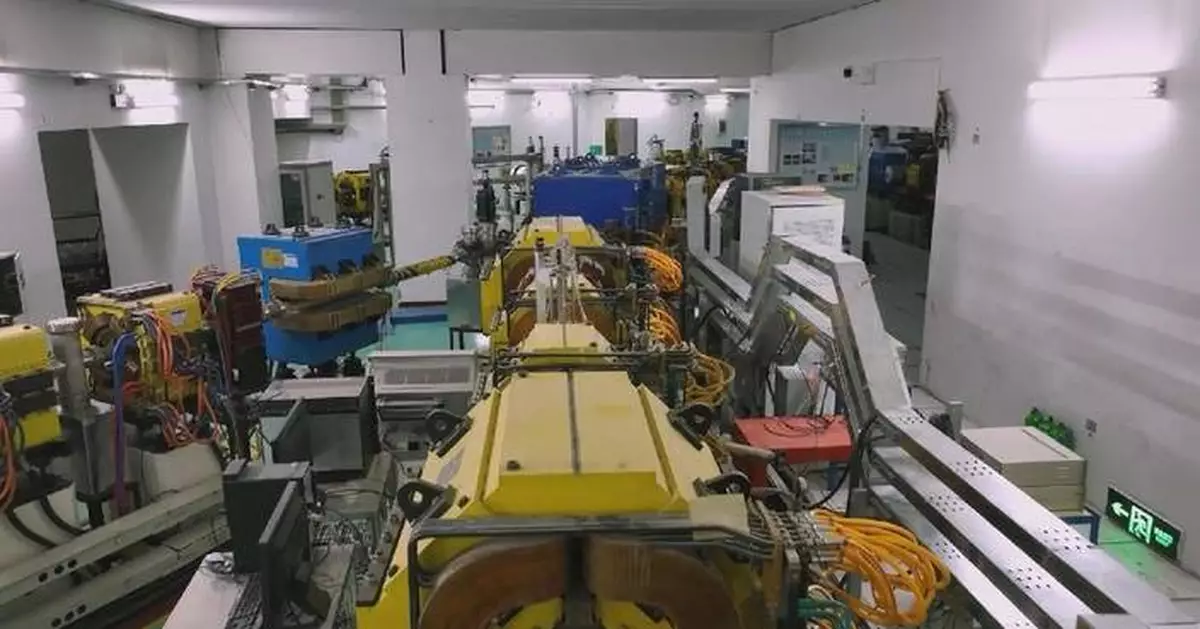
The Heavy Ion Research Facility in Lanzhou (HIRFL), operated by the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), is the largest heavy ion research facility in China and one of a few large-scale full-ion accelerating systems in the world, which can accelerate ions from hydrogen to uranium to high energies.
The HIRFL, also known as the Lanzhou heavy ion accelerator, can be used to filter water, as it can make densely packed, evenly-distributed holes with a diameter of 0.45 microns on the filter membrane, which are capable of blocking all microorganisms with diameters larger than the aperture.
Moreover, the heavy ion accelerator can also play a big role in the development of agriculture.
Multiple new species and strains of several crops have been fostered by utilizing heavy ion irradiation induced mutation.
"Its mutagenic dosage and mutagenic energy are artificially adjustable. By using heavy ion beam-induced mutational breeding technology, we've obtained a new rice variety 'Dongdao 122' with high quality, high yield and salt-alkali tolerance, as well as a new low-cadmium rice variety," said Zhou Libin, deputy director of the Biomedical Research Center of the IMP.
The heavy ion accelerator can simulate high-energy ion beams in space. Hence, the electronic components used on various aspects such as BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, Tiangong space station, Shenzhou spacecraft, and Chang'e lunar missions need to be tested here to ensure that they can work normally in space.
In addition, the heavy ion accelerator also has an important task of exploring the boundaries of science, as it can be used to synthesize new elements.
By resorting to the above-mentioned equipment, the nucleus of one element can be accelerated to nearly the speed of light to bombard the nucleus of another element, and then a new nucleus can be fused through a fusion reaction.
In this way, a new element comes into being.
"It is very difficult to make the experiment successful. Not every collision can produce the atomic nucleus we need. There is a certain probability. Even with the most advanced accelerator technology, it will take several years or even a dozen years for us to get a new atomic nucleus," said Zhang Zhiyuan, deputy director of the Superheavy Nuclide and Nuclear Structure Group of the IMP.
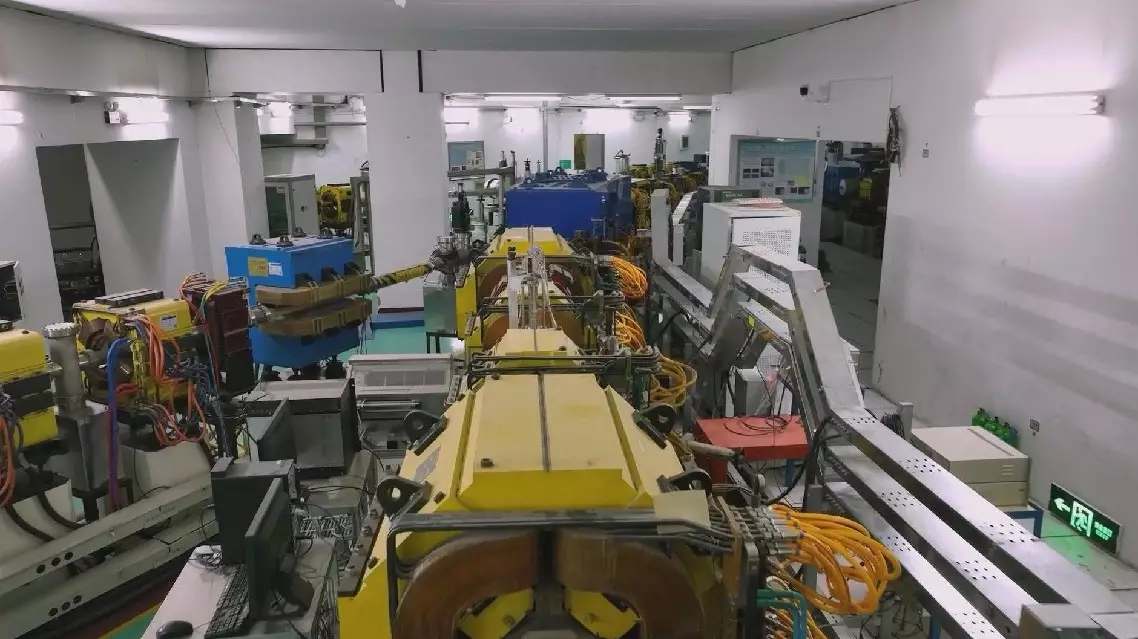
China's heavy ion research facility serves as edge tool to seek scientific progress