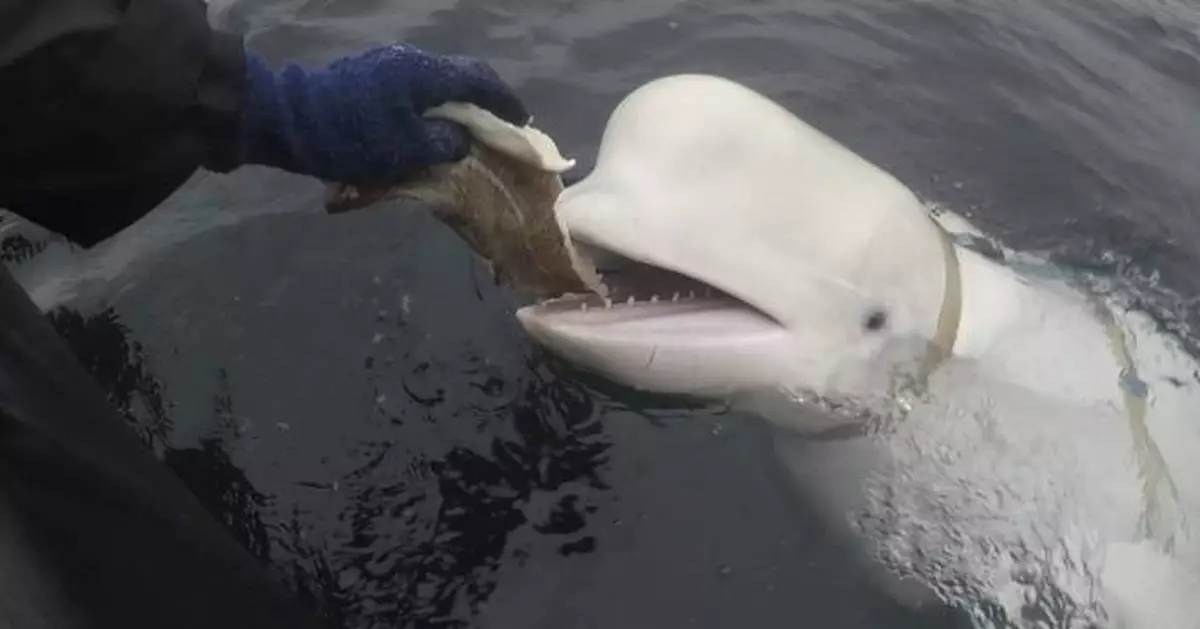
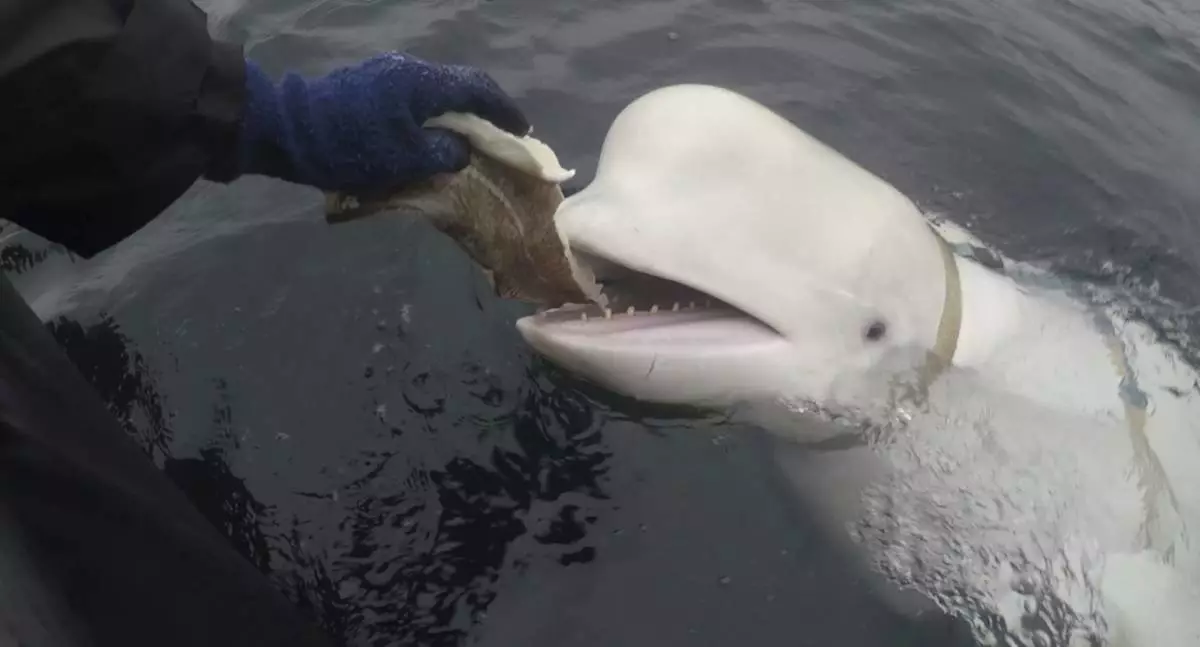
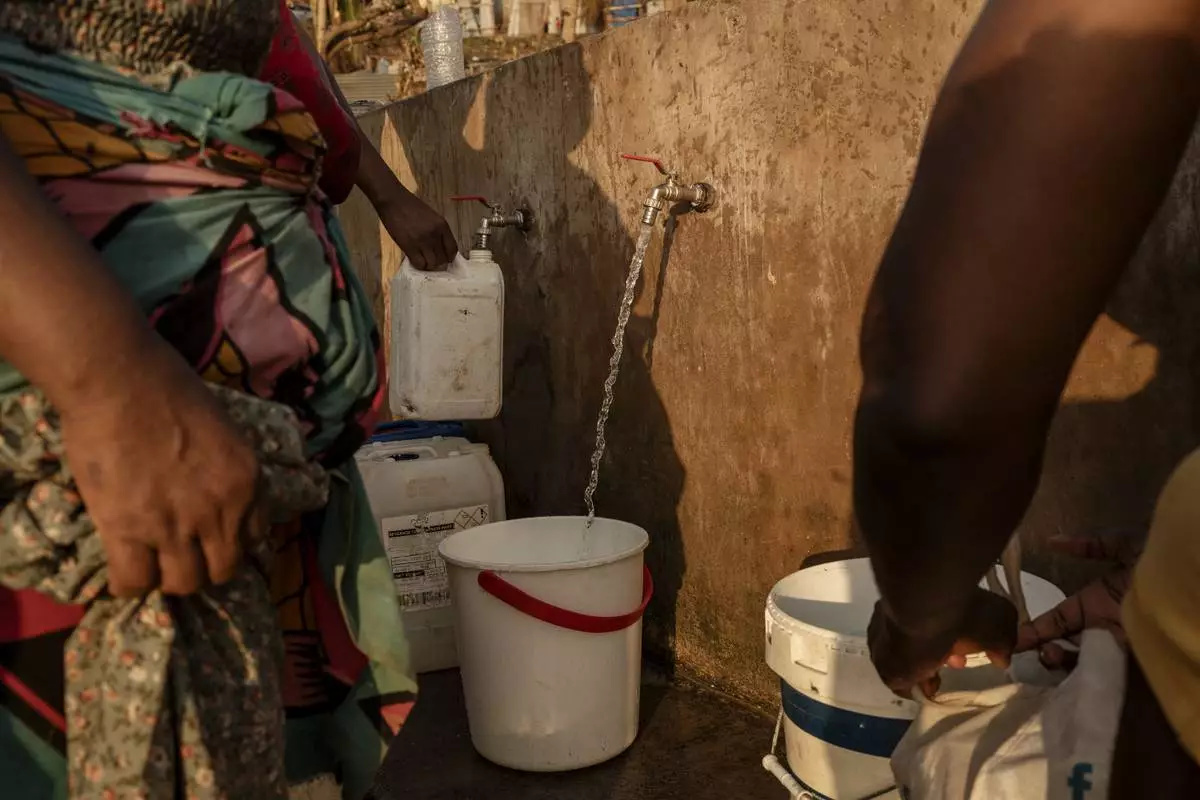OSLO, Norway (AP) — A beluga whale that lived off Norway’s coast and whose harness ignited speculation that it was a Russian spy, was not shot to death as claimed by animal rights groups but died of a bacterial infection, Norwegian police said Friday.
A final autopsy by Norway's Veterinary Institute “concludes that the probable cause of death was bacterial infection -- possibly as a result of a wound in the mouth from a stuck stick,” Amund Preede Revheim, head of the North Sea and Environment section of the police in south-western Norway said.
“There have been no findings from the autopsy that indicate that the whale has been shot,” he stressed, adding that the autopsy had been “made difficult by the fact that many of the whale’s organs were very rotten.” As there was no indication of foul play, there was no reason to start a criminal investigation into its death, Preede Revheim said.
The tame beluga, which was first spotted in 2019 not far from Russian waters with a harness reading “Equipment St. Petersburg,” had been nicknamed "Hvaldimir,” combining the Norwegian word for whale — hval — and the first name of Russian President Vladimir Putin.
It was found floating in a southern Norway bay on Aug. 31.
In September, animal advocate groups OneWhale and NOAH filed a police report saying that the animal’s wounds suggested it was intentionally killed.
They pointed at several wounds found on the animal’s skin, including what was interpreted as a bullet hole.
“Assessments made by the Veterinary Institute and the police’s forensic technicians are that these are not gunshot wounds. X-rays of the chest and head were carried out without any projectiles or other metal fragments being detected,” police said in a statement.
Earlier, police had described a stick about 35 centimeters (14 inches) long and 3 centimeters (1 inch) wide which was found wedged in the animal’s mouth, its stomach was empty and its organs had broken down, police said. No further details were given.
The 4.2-meter (14-foot) long and 1,225-kilogram (2,700-pound) whale was first spotted by fishermen not far from the Arctic town of Hammerfest.
Its harness, along with what appeared to be a mount for a small camera, led to media speculation that it was a “spy whale.” Experts say the Russian navy is known to have trained whales for military purposes. Media reports also have speculated that the whale might have been trained as a therapy animal.
There was no immediate reaction from OneWhale or NOAH.

FILE - In this photo taken in April 2019 a beluga whale found in Arctic Norway is fed. (Jorgen Ree Wiig, Norwegian Directorate of Fisheries via AP)
MAMOUDZOU, Mayotte (AP) — A week after its worst cyclone in nearly a century, France’s impoverished Indian Ocean territory of Mayotte is still grappling to count the dead, restore essential services and aid a beleaguered population. Already stretched thin, hospitals are overwhelmed with patients suffering not only from cyclone-related injuries but dehydration, malnutrition and disease.
At Mayotte’s main hospital in the capital, Mamoudzou, doctors face a cascade of crises.
“We lost 40% of patient rooms, about 50 to 60 beds,” said Dr. Roger Serhal, chief of the obstetrics and gynecology department. “There are so many patients coming to the hospital, and we don’t have space to admit them.” As Cyclone Chido battered the archipelago last weekend and 220 kph (136 mph) winds howled around the hospital, Serhal and his team delivered three babies, including by cesarean section.
The hospital’s structural damage has forced staff to triage patients, prioritizing the most severe cases.
Thirty-five people have been confirmed dead as of Friday in Mayotte but French Health Minister Geneviève Darrieussecq has warned that any estimates were likely major undercounts “compared to the scale of the disaster.”
The storm has devastated entire neighborhoods and many people had ignored warnings, thinking the storm wouldn’t be so extreme. Even worse, many migrants avoided shelters out of fear of deportation, authorities said, adding there could be hundreds or possibly thousands of fatalities.
Doctors fear that the lack of clean water and electricity — compounded by overcrowded living conditions — is setting the stage for a health crisis.
“Patients are coming because their illnesses are untreated, there’s no water, and no electricity. We’re concerned about epidemics, like the cholera outbreak we stopped just months ago,” said Dr. Vincent Gilles, the hospital’s emergency medical director.
The hospital staff continues to work tirelessly, but resources are running dangerously low. “If we have rain,” Serhal added, “it will be catastrophic.”
Among the patients struggling to recover was Saindou Mohamadi, 54, who fractured his arm and sprained his ankle during the storm that left his home completely destroyed. Speaking from his hospital bed, Mohamadi expressed despair for his family.
“My mother is sick, I’m sick, and my child is sick,” he said. “They need to eat, but I’m the one who takes care of the food, and now we have nothing.” With six children to support, Mohamadi is among countless residents left homeless and destitute.
“I’m not alone,” he said. “There are many of us who have lost everything — our houses, our food. I want the government to care about us, to give us food and a place to sleep.”
Mayotte is a densely populated archipelago between Madagascar and the African continent of more than 320,000 people, but authorities have estimated another 100,000 migrants live there from as far away as Somalia.
France’s poorest overseas territory long struggled with systemic neglect and underinvestment. Around 75% of its population lives in poverty, and the archipelago’s infrastructure was ill-equipped to withstand a disaster of this magnitude. Chido’s destruction has compounded these challenges, leaving many residents with little faith in the government’s ability to provide timely and adequate relief.
Efforts to deliver emergency aid, including airlifts of water and food, are underway but the scale of the need is staggering. Mayotte’s airport remains closed to civilian flights due to damage, further complicating logistics.
French President Emmanuel Macron, during his visit on Friday, acknowledged the gravity of the situation and pledged to rebuild but faced criticism from residents frustrated by the slow pace of aid.
France's Interior Ministry estimated that 70% of the population has been gravely affected, with many left homeless and vulnerable.
Adamson reported from Paris.
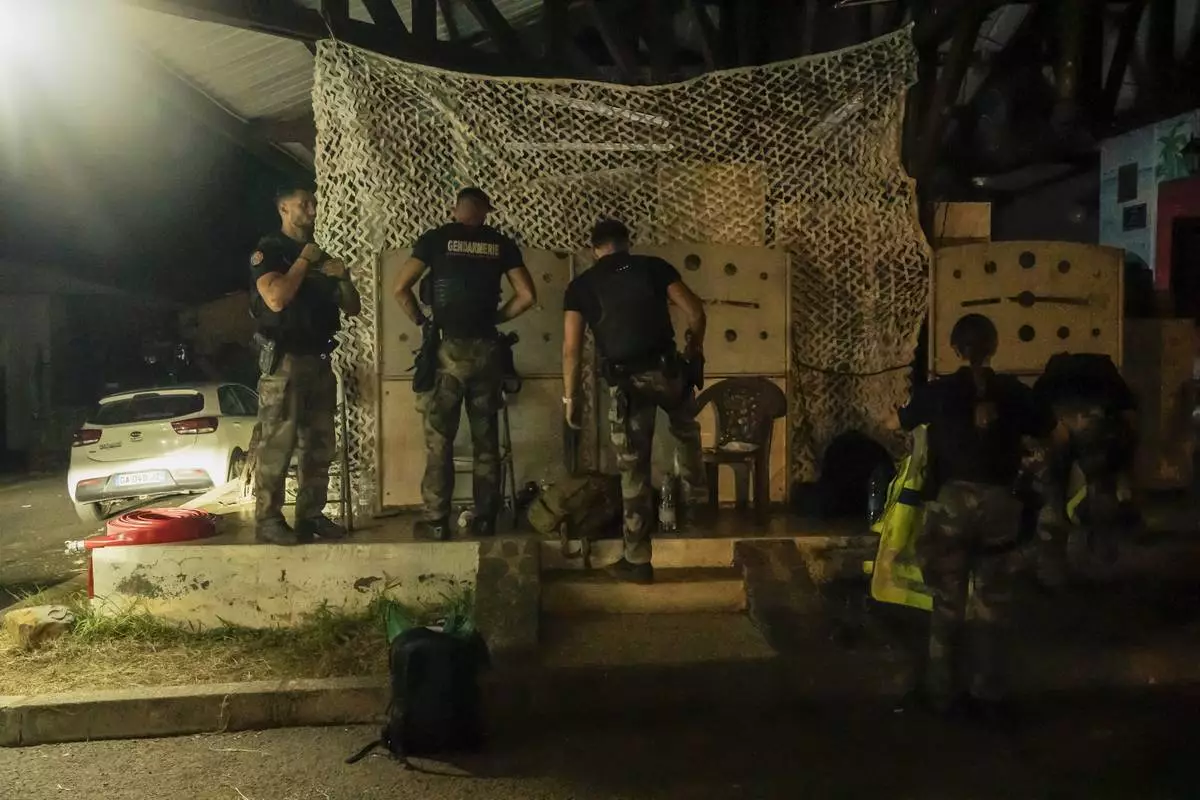

French gendarmes patrol during curfew outside Mamoudzou, Mayotte, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
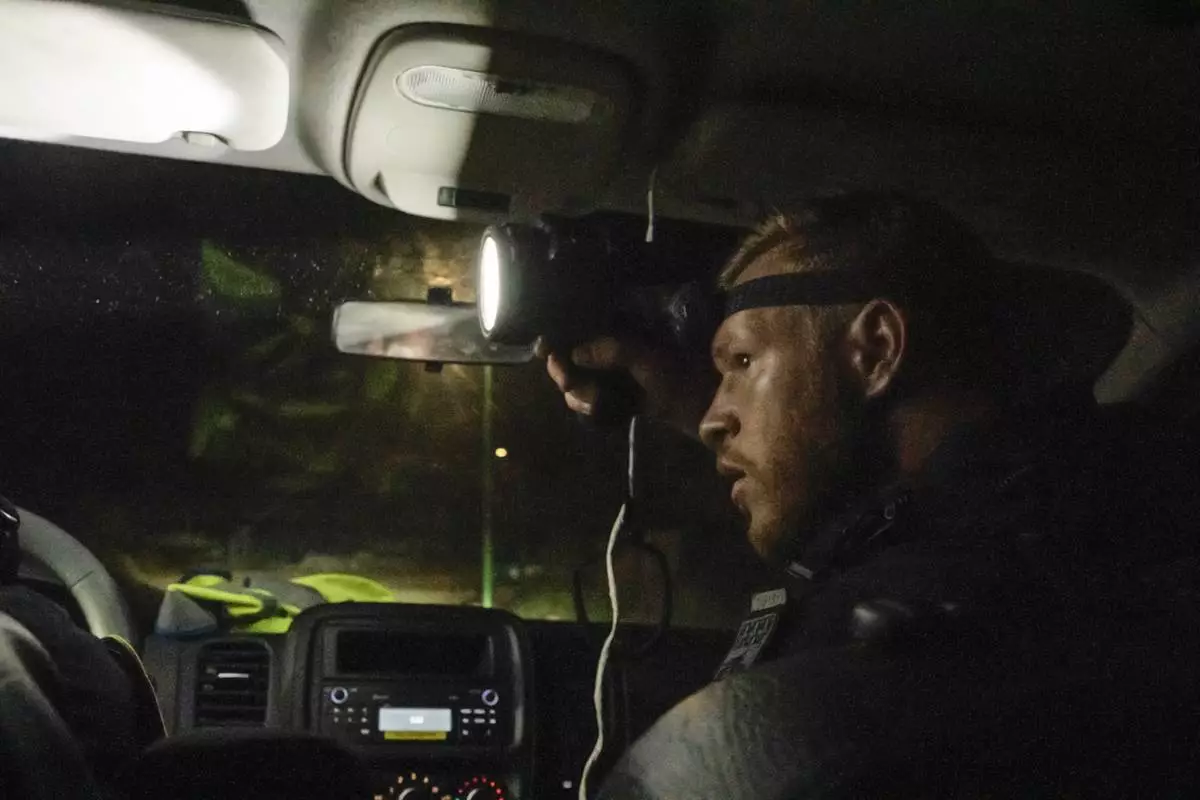

French gendarmes patrol during curfew outside Mamoudzou, Mayotte, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
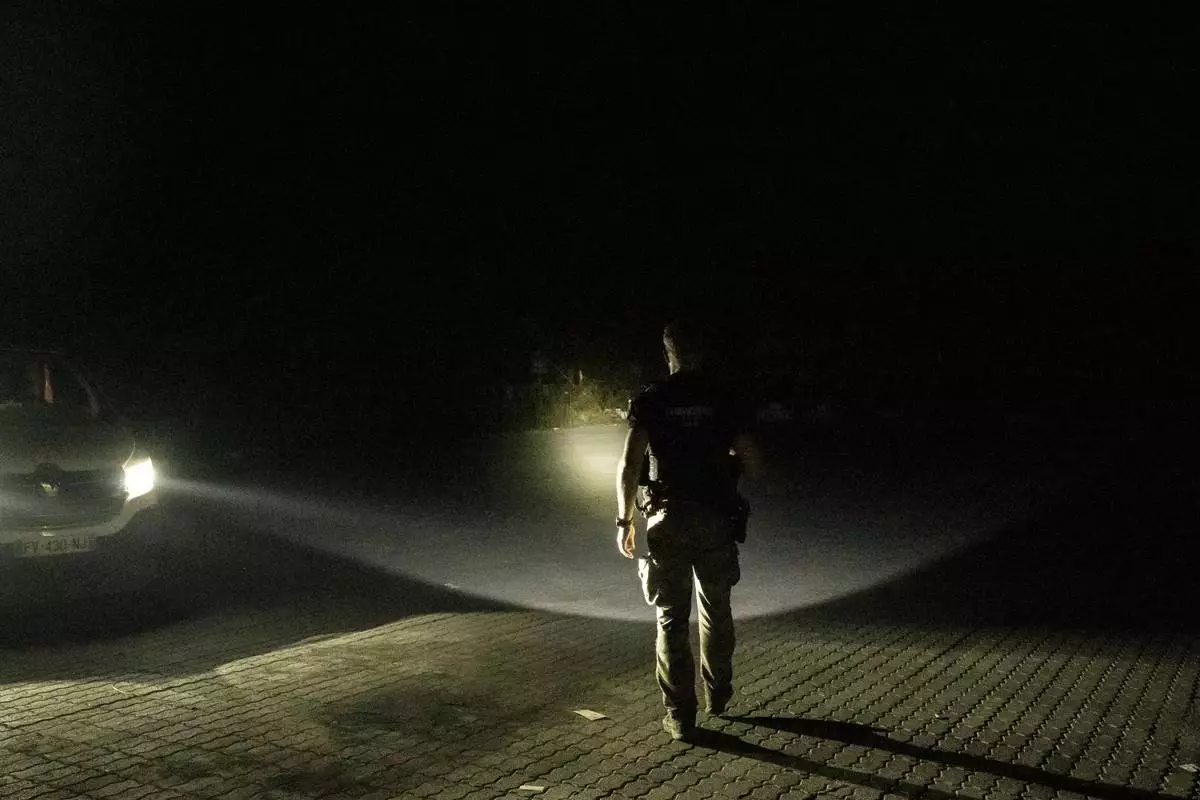

French gendarmes patrol during curfew outside Mamoudzou, Mayotte, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)

People walk by destroyed homes in the Barakani, Mayotte, informal settlement, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
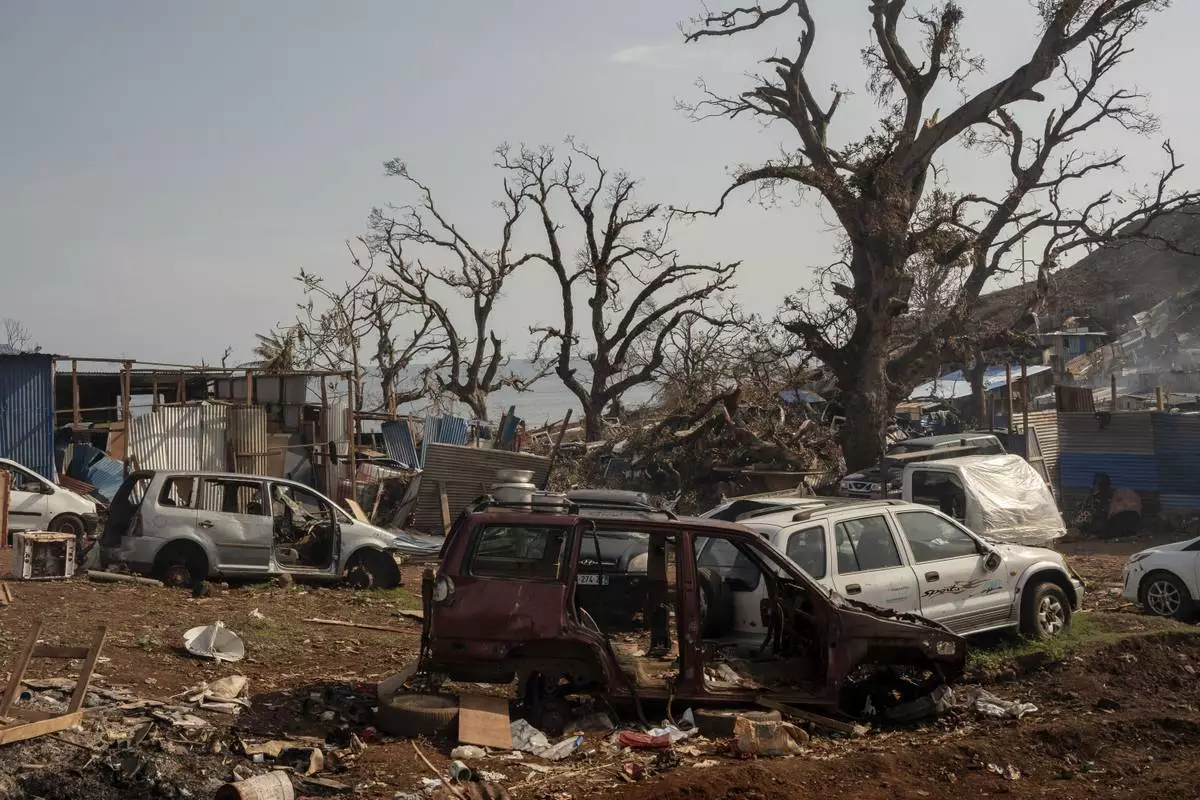

Broken cars are seen in Barakani, Mayotte, France on Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
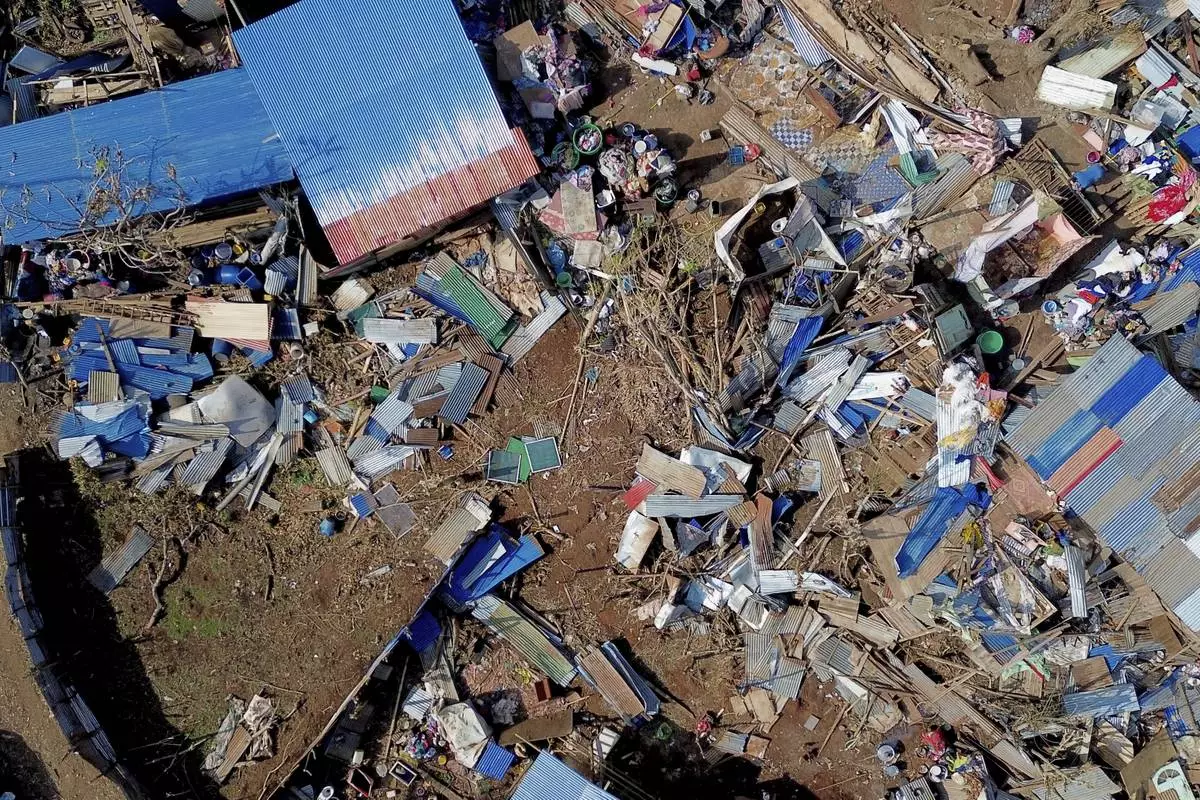

This aerial view shows destroyed homes in the Barakani, Mayotte, informal settlement, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
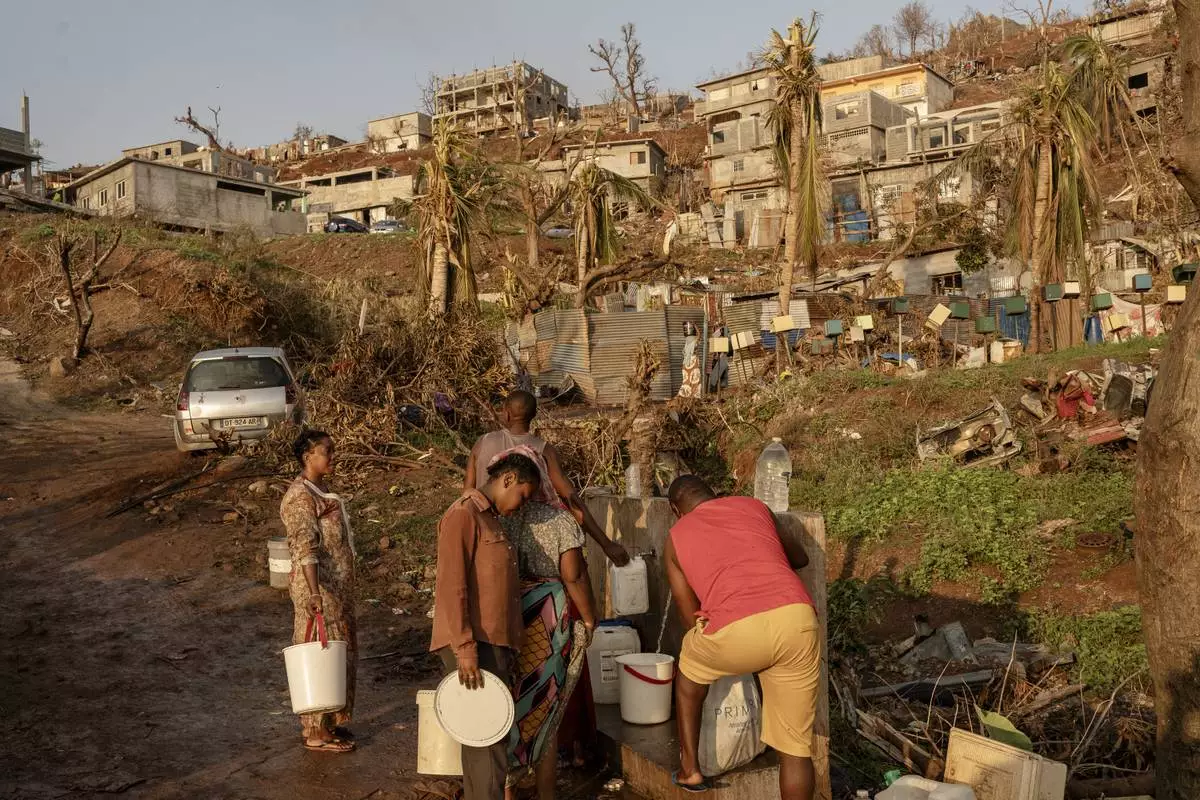

People line up to collect water in Barakani, Mayotte, home Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
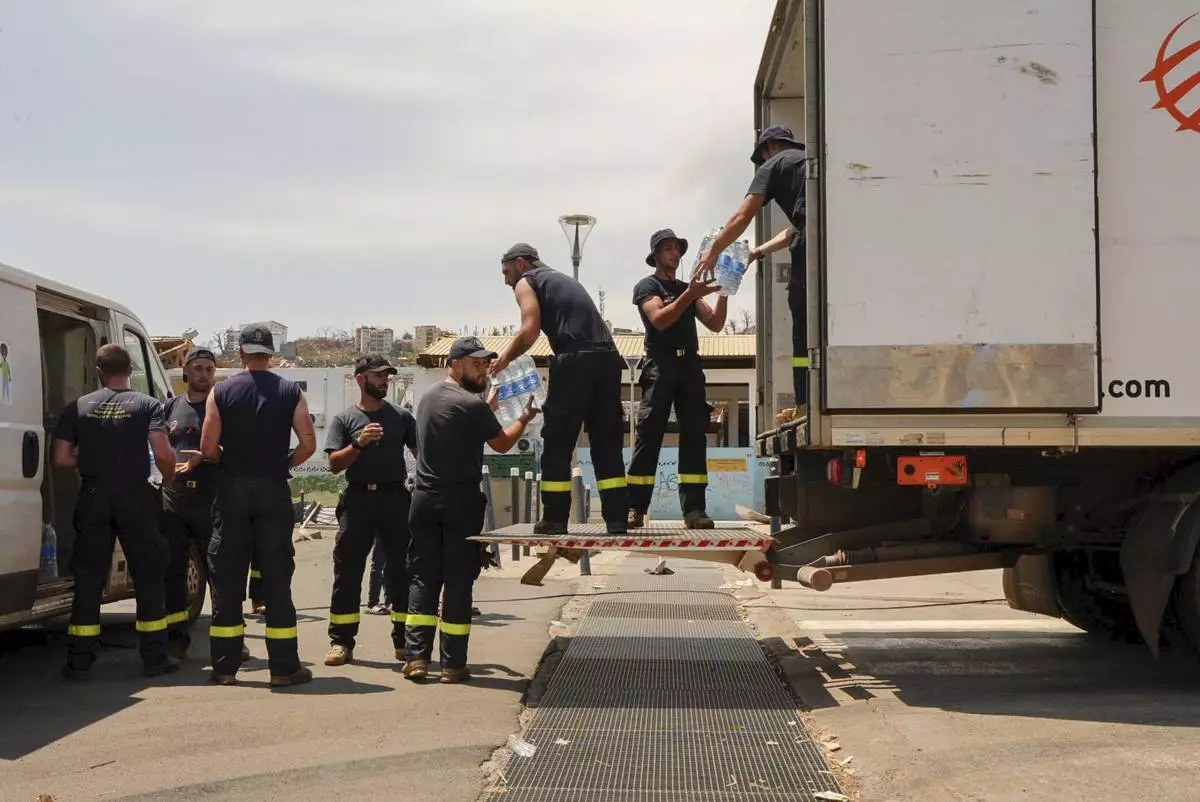

French Civil Security personnel unload water for distribution in Mamoudzou, Mayotte, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
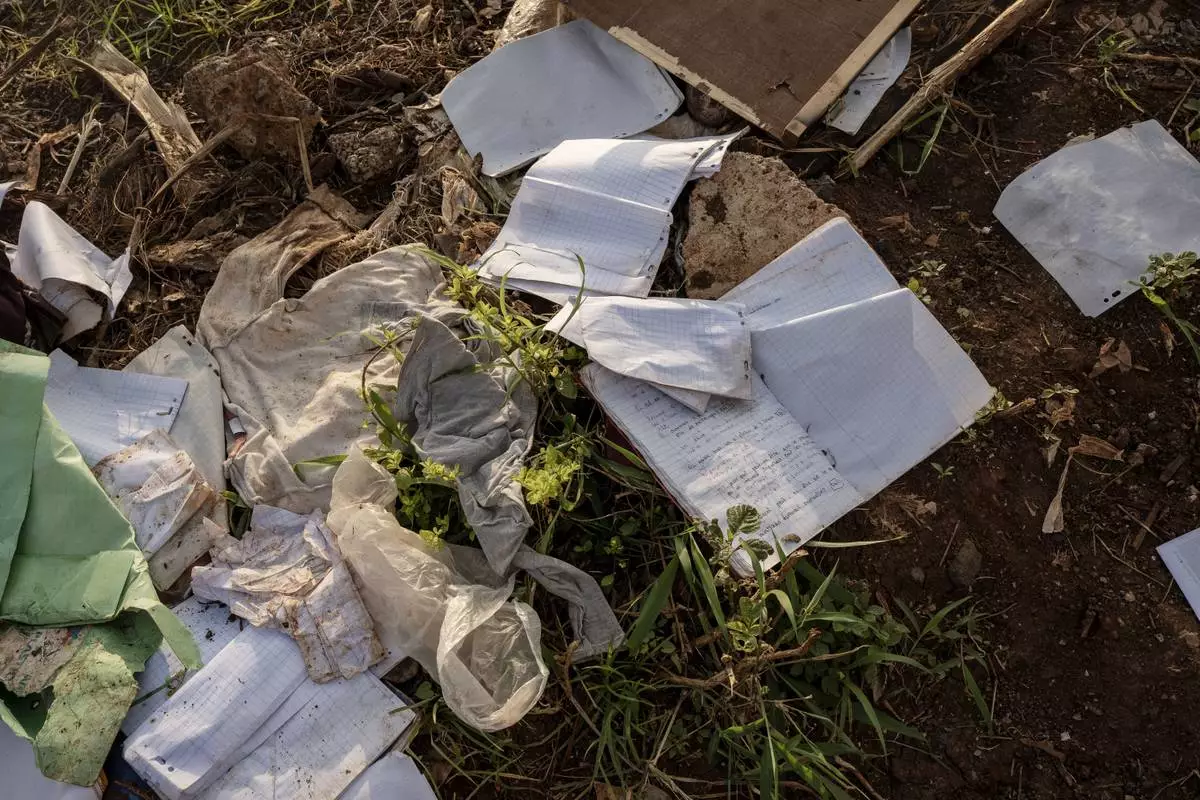

A child's school notebook lays amidst debris in Barakani, Mayotte, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
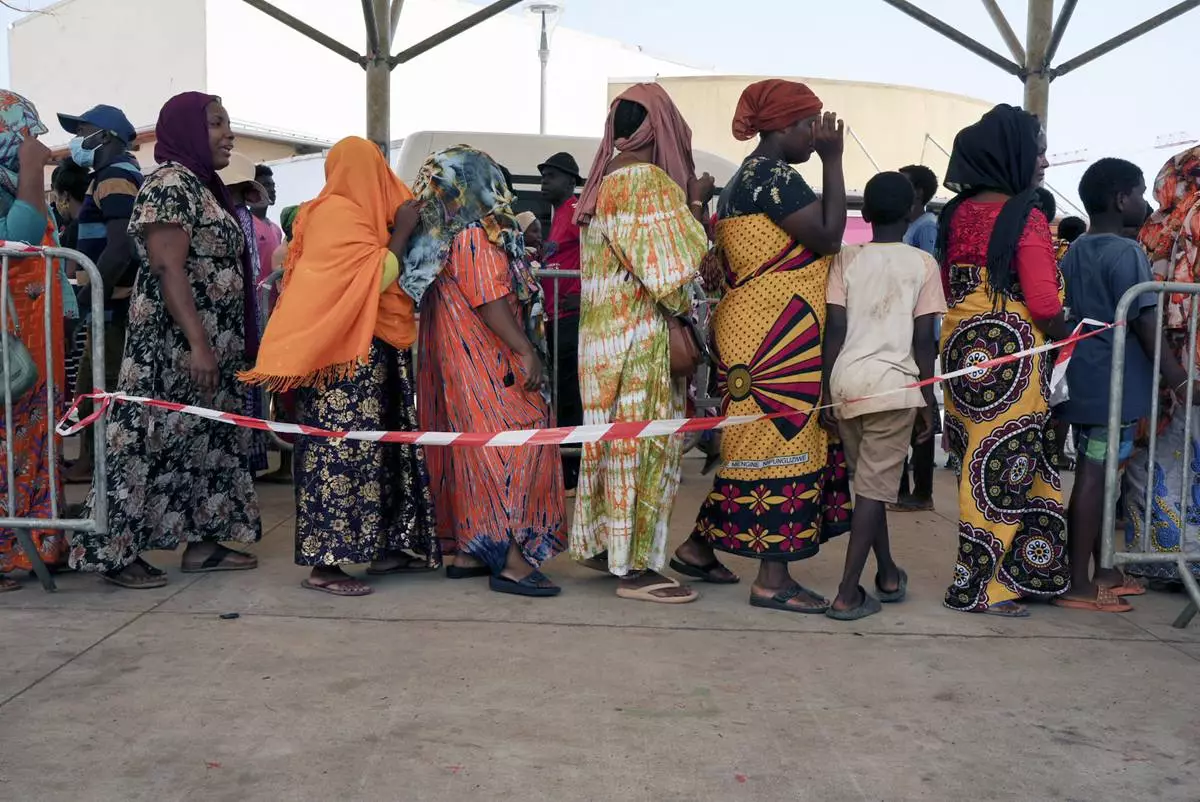

Women wait in line at a water distribution point in Mamoudzou, Mayotte, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
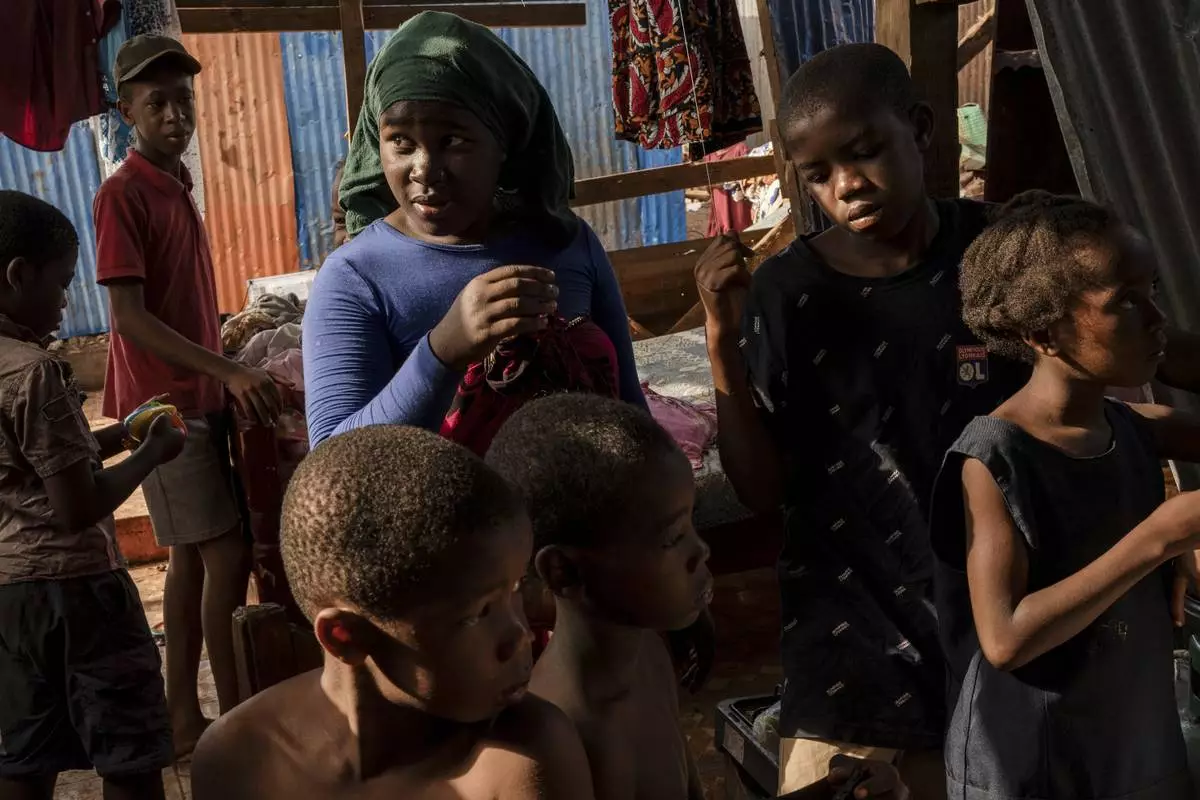

Children stand in the half destroyed house of Zaharia Youssouf in Barakani, Mayotte, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
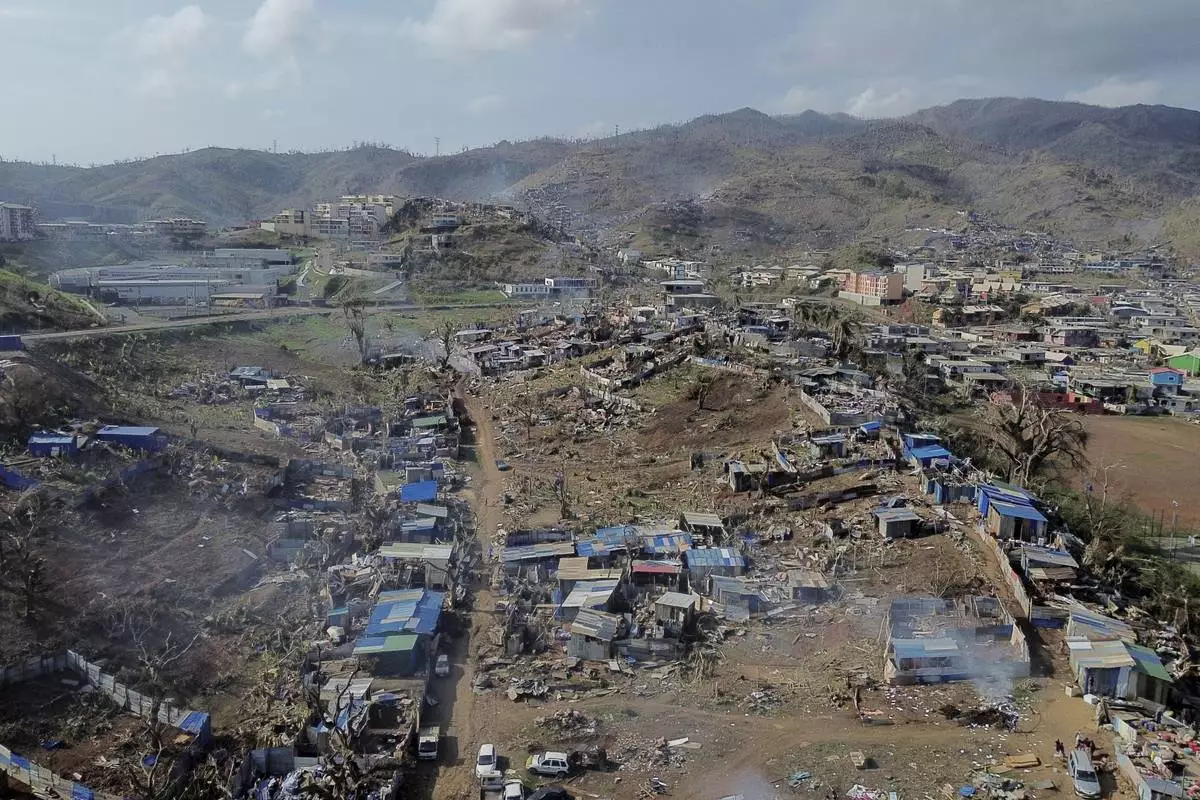

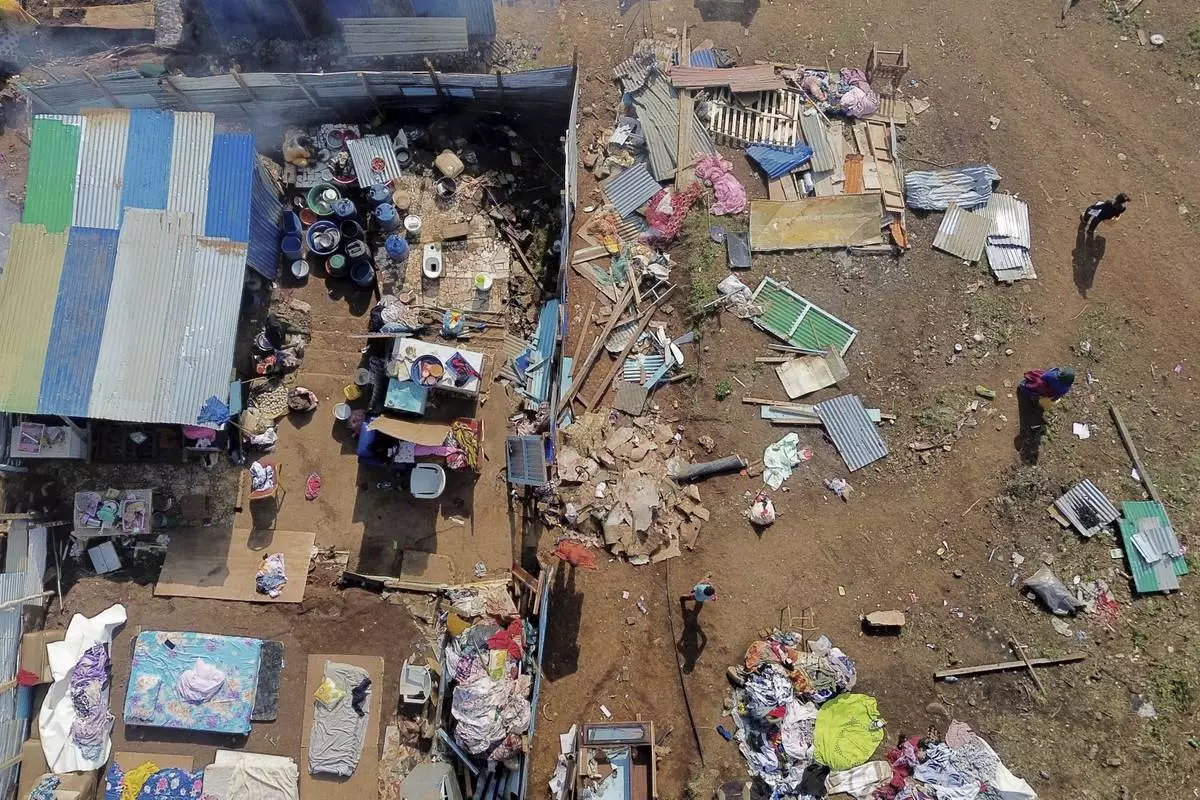
A drone view of the Barakani, Mayotte, informal settlement, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
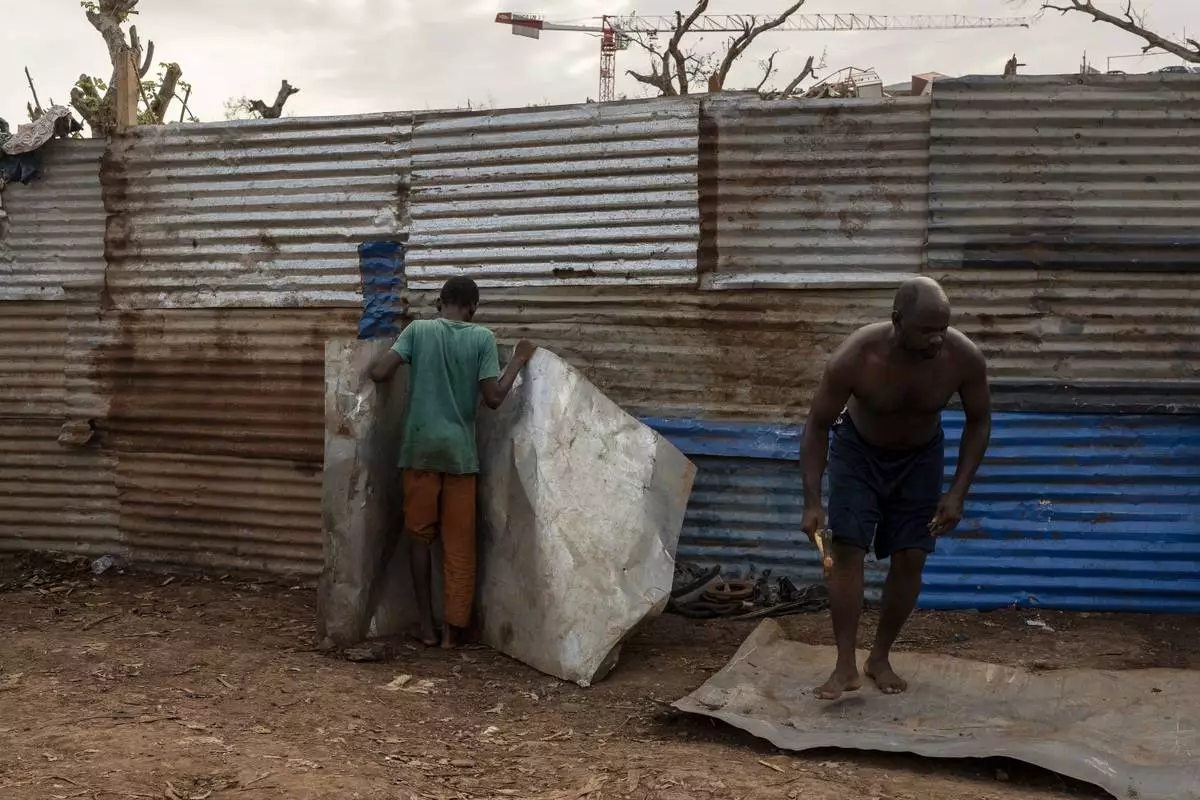

Resident repair their broken homes in Barakani, Mayotte, home Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
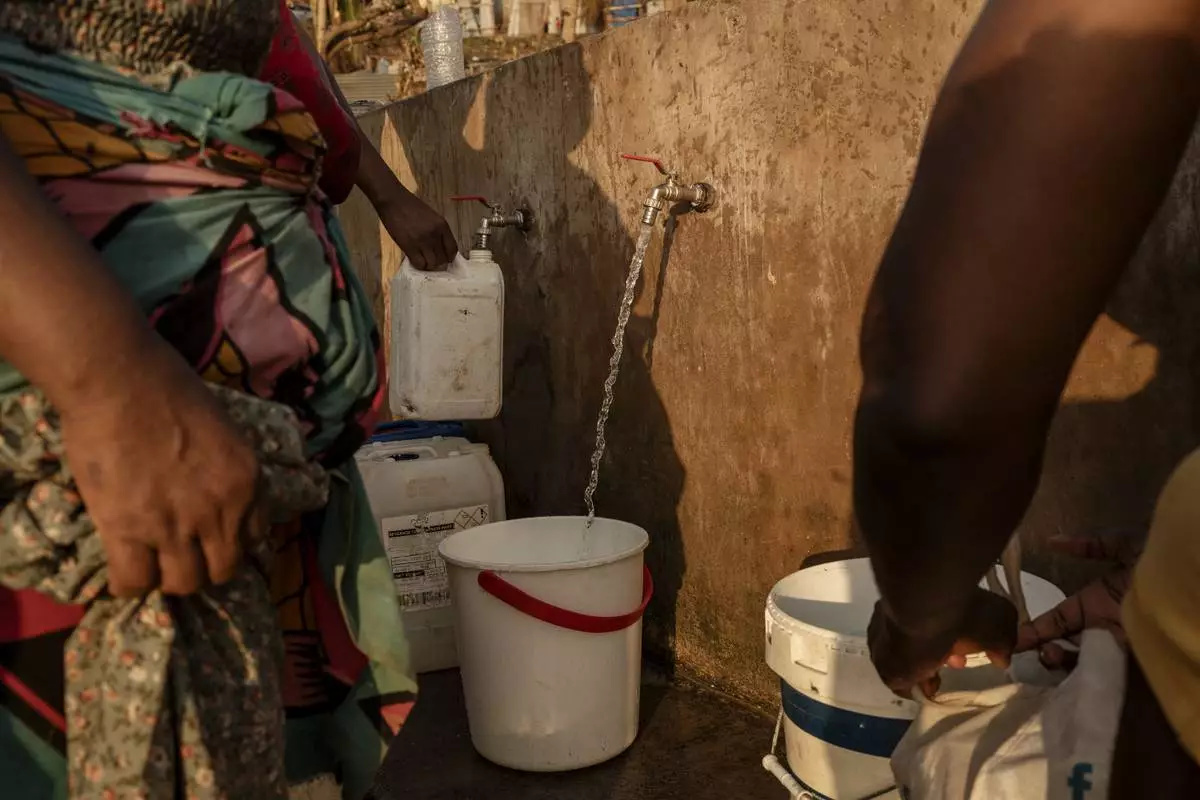
People line up to collect water in Barakani, Mayotte, home Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
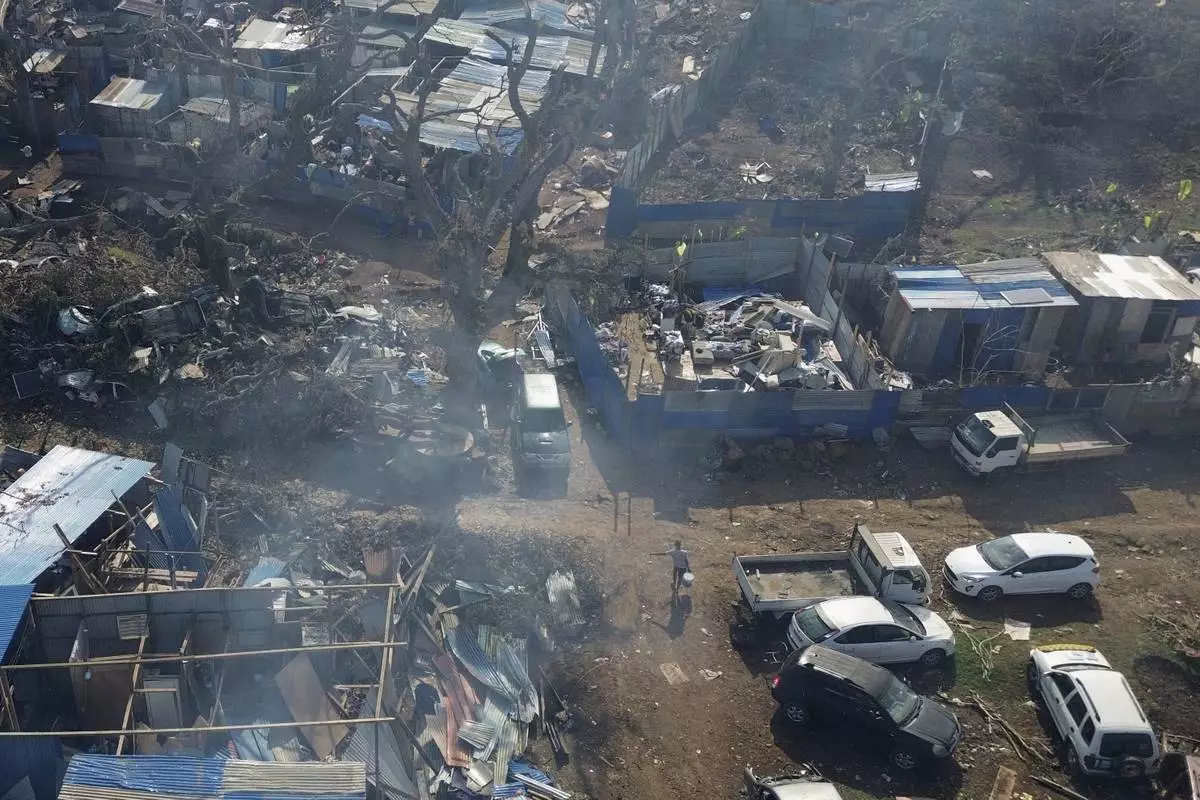

A man walks in the Barakani, Mayotte, informal settlement, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)
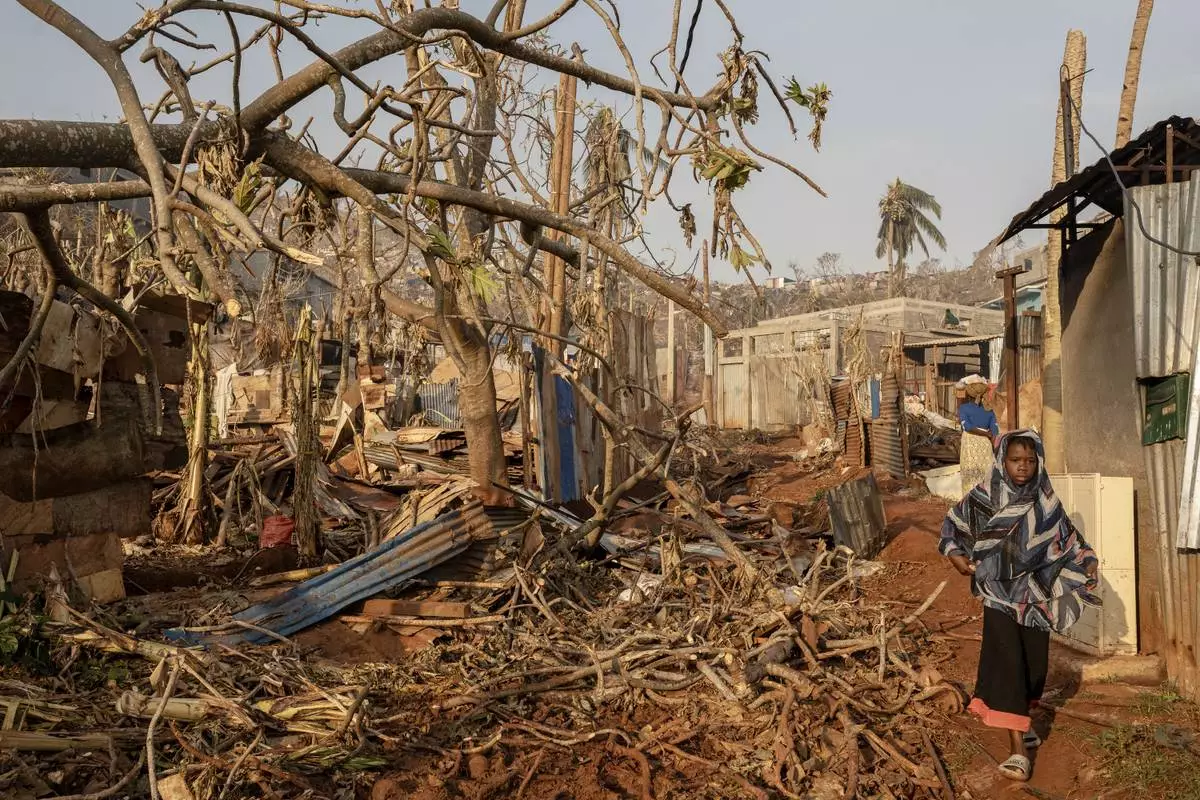

A girl walks amidst destruction in Mbouyougou, Mayotte, Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Adrienne Surprenant)