WASHINGTON (AP) — The FBI has arrested an Afghan man who officials say was inspired by the Islamic State militant organization and was plotting an Election Day attack targeting large crowds in the U.S., the Justice Department said Tuesday.
Nasir Ahmad Tawhedi, 27, of Oklahoma City told investigators after his arrest Monday that he had planned his attack to coincide with Election Day next month and that he and a co-conspirator expected to die as martyrs, according to charging documents.
Tawhedi, who arrived in the U.S. in September 2021, had taken steps in recent weeks to advance his attack plans, including by ordering AK-47 rifles, liquidating his family's assets and buying one-way tickets for his wife and child to travel home to Afghanistan, officials said.
The arrest comes as the FBI confronts heightened concerns over the possibility of extremist violence on U.S. soil, with Director Christopher Wray telling The Associated Press in August that he was "hard pressed to think of a time in my career where so many different kinds of threats are all elevated at once.”
“Terrorism is still the FBI’s number one priority, and we will use every resource to protect the American people,” Wray said in a statement Tuesday.
An FBI affidavit does not reveal precisely how Tawhedi came onto investigators' radar, but cites what it says is evidence from recent months showing his determination in planning an attack. A photograph from July included in the affidavit depicts a man investigators identified as Tawhedi reading to two young children, including his daughter, “a text that describes the rewards a martyr receives in the afterlife.”
Officials say Tawhedi also consumed Islamic State propaganda, contributed to a charity that functions as a front for the militant group and communicated with a person who the FBI determined from a prior investigation was involved in recruitment and indoctrination of people interested in extremism. He also viewed webcams for the White House and the Washington Monument in July.
Tawhedi's alleged co-conspirator was not identified by the Justice Department, which described him only as a juvenile, a fellow Afghan national and the brother of Tawhedi's wife.
After the two advertised the sale of personal property on Facebook, the FBI enlisted an informant last month to respond to the offer and strike up a relationship. The informant later invited them to a gun range, where they ordered weapons from an undercover FBI official who was posing as a business partner of the informant, according to court papers.
Tawhedi was arrested Monday after taking possession of two AK-47 rifles and ammunition he had ordered, officials said. The unidentified co-conspirator was also arrested but the Justice Department did not provide details because he is a juvenile.
After he was arrested, the Justice Department said, Tawhedi told investigators he had planned an attack for Election Day that would target large gatherings of people.
Tawhedi was charged with conspiring and attempting to provide material support to the Islamic State, which is designated by the U.S. as a foreign terrorist organization. The charge is punishable by up to 20 years in prison.
He appeared in court Tuesday and was ordered detained. An email to an attorney listed as representing him did not immediately return an email seeking comment.
It was not immediately clear if he had a lawyer who could speak on his behalf.
A for-sale sign stood in the yard outside a modest, two-story brick home listed as being connected to Tawhedi’s family in the Oklahoma City suburb of Moore.
A woman who identified herself as Tawhedi’s wife declined to discuss the case.
“We don’t want to talk in the media,” said the woman, who did not give her name.
Tawhedi entered the U.S. on a special immigrant visa in 2021 and has been on parole status pending the conclusion of his immigration proceedings, the Justice Department said. The program permits eligible Afghans who helped Americans, despite great personal risk to themselves and their loved ones, to apply for entry into America with their families.
Eligible Afghans include interpreters for the U.S. military as well as individuals integral to the U.S. Embassy in Kabul. While the program has existed since 2009, the number of applicants skyrocketed after the chaotic U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan in August 2021.
Shawn VanDiver, the president of #AfghanEvac, a coalition of organizations dedicated to helping Afghans trying to leave Afghanistan, said that though the charges are serious, “it’s critical that we do not assign blame to an entire community for the actions of one individual. Thousands of Afghans who resettled in the United States are working to build new lives and contribute to our shared future.”
“These are the same individuals who stood shoulder to shoulder with us in Afghanistan for over two decades, defending the values we hold dear,” he said in a statement. “Now, they are our neighbors, and we must support them as they seek safety and stability in their new home.”
Associated Press writers Rebecca Santana in Washington and Sean Murphy in Oklahoma City contributed to this report.
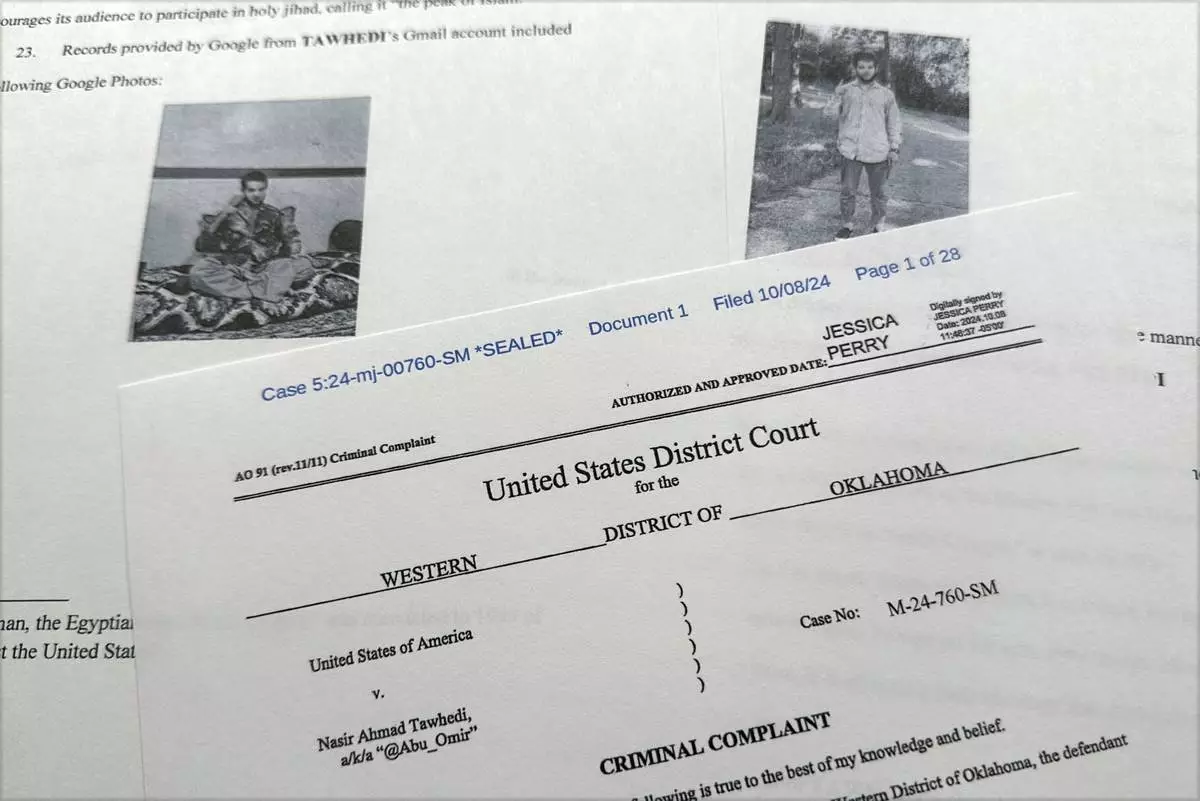
The criminal complaint, filed by the Justice Department, against Nasir Ahmad Tawhedi, 27,of Oklahoma City is photographed Tuesday, Oct. 8, after the FBI arrested the man who officials say was inspired by the Islamic State militant organization and was plotting an Election Day attack targeting large crowds in the U.S. (AP Photo/Jon Elswick)
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Joe Biden on Saturday signed legislation that averts a government shutdown heading into Christmas, bringing a final close to days of upheaval in Washington after Congress passed a bipartisan budget plan just past the deadline and rejected Donald Trump's core demand in the negotiations.
The deal funds the government at current levels through March 14 and provides $100 billion in disaster aid and $10 billion in agricultural assistance to farmers.
House Speaker Mike Johnson, R-La., had insisted lawmakers would “meet our obligations” and not allow federal operations to close. But the outcome at the end of a tumultuous week was uncertain after Trump had insisted the deal include an increase in the government's borrowing limit. If not, he had said, then let the closures “start now.”
Johnson's revised plan was approved 366-34, and it was passed by the Senate by a 85-11 vote after midnight. By then, the White House said it had ceased shutdown preparations.
“There will be no government shutdown,” said Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer, D-N.Y.
Johnson, who had spoken to Trump after the House vote, said the compromise was "a good outcome for the country” and that the president-elect “was certainly happy about this outcome, as well.”
The final product was the third attempt from Johnson, the beleaguered speaker, to achieve one of the basic requirements of the federal government — keeping it open. The difficulties raised questions about whether Johnson will be able to keep his job, in the face of angry Republican colleagues, and work alongside Trump and his billionaire ally Elon Musk, who was calling the legislative plays from afar.
The House is scheduled to elect the next speaker on Jan. 3, 2025, when the new Congress convenes. Republicans will have an exceedingly narrow majority, 220-215, leaving Johnson little margin for error as he tries to win the speaker's gavel.
One House Republican, Rep. Andy Harris of Maryland, criticized Republicans for the deficit spending in the bill and said he was now “undecided” about the GOP leadership. Others are signaling unhappiness with Johnson as well.
Yet Trump's last-minute debt limit demand was almost an impossible ask, and Johnson had almost no choice but to work around that pressure. The speaker knew there wouldn’t be enough support within the slim Republican majority alone to pass any funding package because many Republican deficit hawks prefer to cut the federal government and would not allow more debt.
Instead, the Republicans, who will have full control of the White House, House and Senate in the new year, with big plans for tax cuts and other priorities, are showing they must routinely rely on Democrats for the votes needed to keep up with the routine operations of governing.
The federal debt stands at roughly $36 trillion, and the spike in inflation after the coronavirus pandemic has pushed up the government’s borrowing costs such that debt service next year will exceed spending on national security. The last time lawmakers raised the debt limit was June 2023. Rather than raise the limit by a dollar amount, lawmakers suspended the debt limit through Jan. 1, 2025.
There is no need to raise that limit right now because the Treasury Department can begin using what it calls “extraordinary measures” to ensure that America does not default on its debts. Some estimate these accounting maneuvers could push the default deadline to the summer of 2025. But that’s what Trump wanted to avoid because an increase would be needed while he was president.
GOP leaders said the debt ceiling would be debated as part of tax and border packages in the new year. Republicans made a so-called handshake agreement to raise the debt limit at that time while also cutting $2.5 trillion in spending over 10 years.
It was essentially the same deal that flopped Thursday night — minus Trump’s debt demand. But it's far smaller than the original deal Johnson struck with Democratic and Republican leaders — a 1,500-page bill that Trump and Musk rejected, forcing him to start over. It was stuffed with a long list of other bills — including much-derided pay raises for lawmakers — but also other measures with broad bipartisan support that now have a tougher path to becoming law.
Trump, who has not yet been sworn into office, is showing the power but also the limits of his sway with Congress, as he intervenes and orchestrates affairs from Mar-a-Lago alongside Musk, who is heading up the new Department of Government Efficiency.
Associated Press writers Kevin Freking, Stephen Groves, Mary Clare Jalonick, Darlene Superville and Bill Barrow contributed to this report.
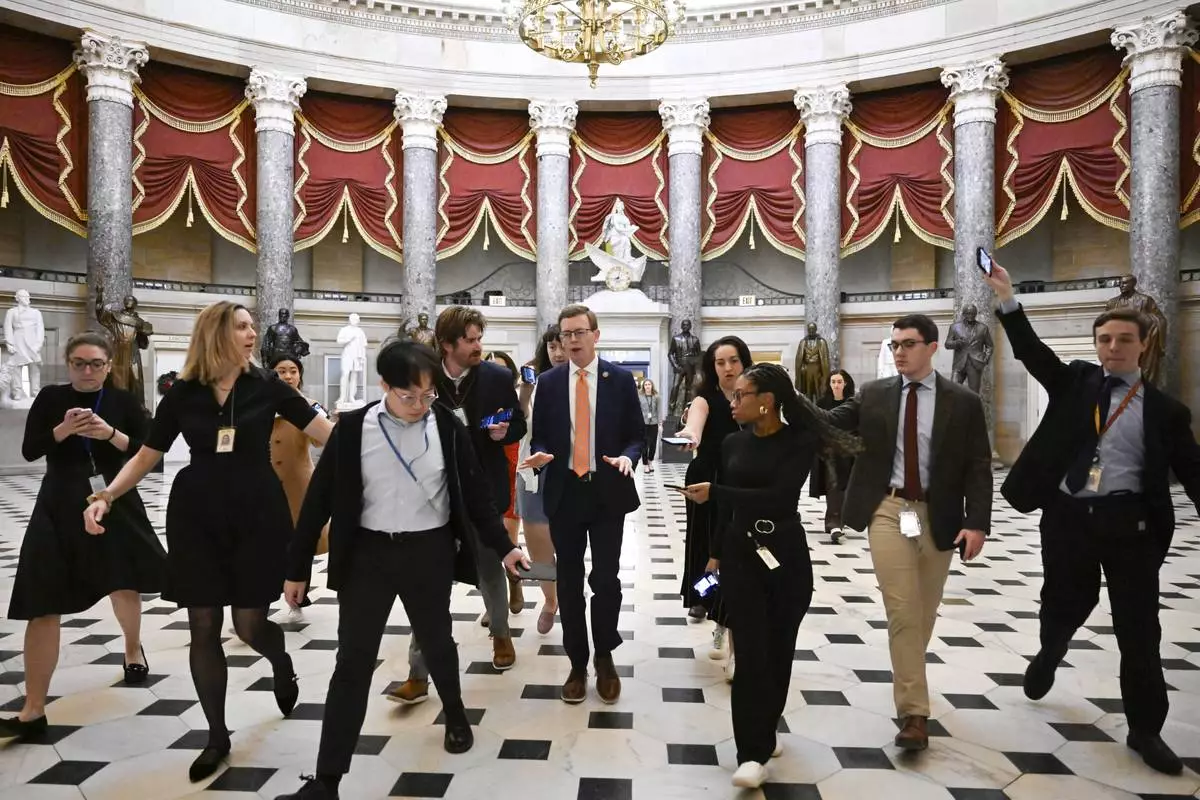

Rep. Dusty Johnson, R-S.D., talks with reporters after attending a meeting with Speaker of the House Mike Johnson, R-La., as the House works on a spending bill to avert a shutdown of the Federal Government, Friday, Dec. 20, 2024, at the Capitol in Washington. (AP Photo/John McDonnell)

The Capitol is pictured in Washington, Friday, Dec. 20, 2024. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
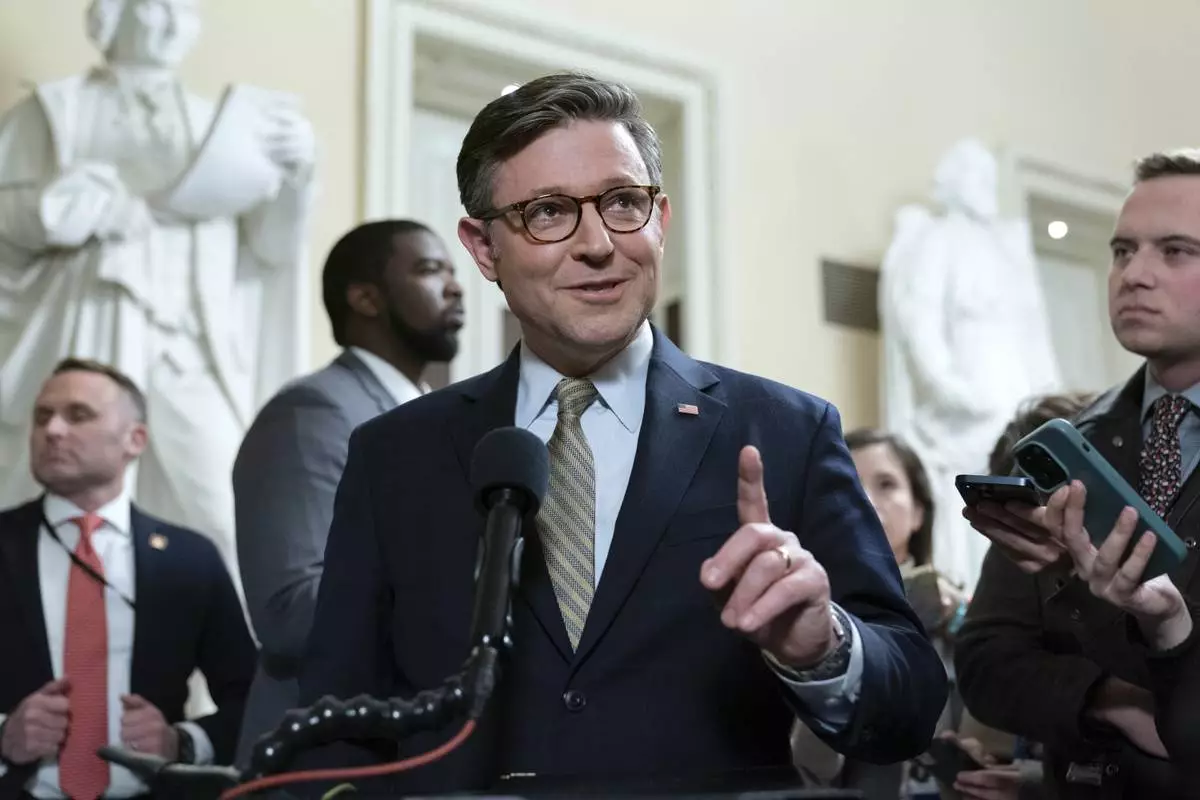

Speaker of the House Mike Johnson, R-La., talks to reporters after passing the funding bill to avert the government shutdown at the Capitol in Washington, Friday, Dec. 20, 2024. (AP Photo/Jose Luis Magana)
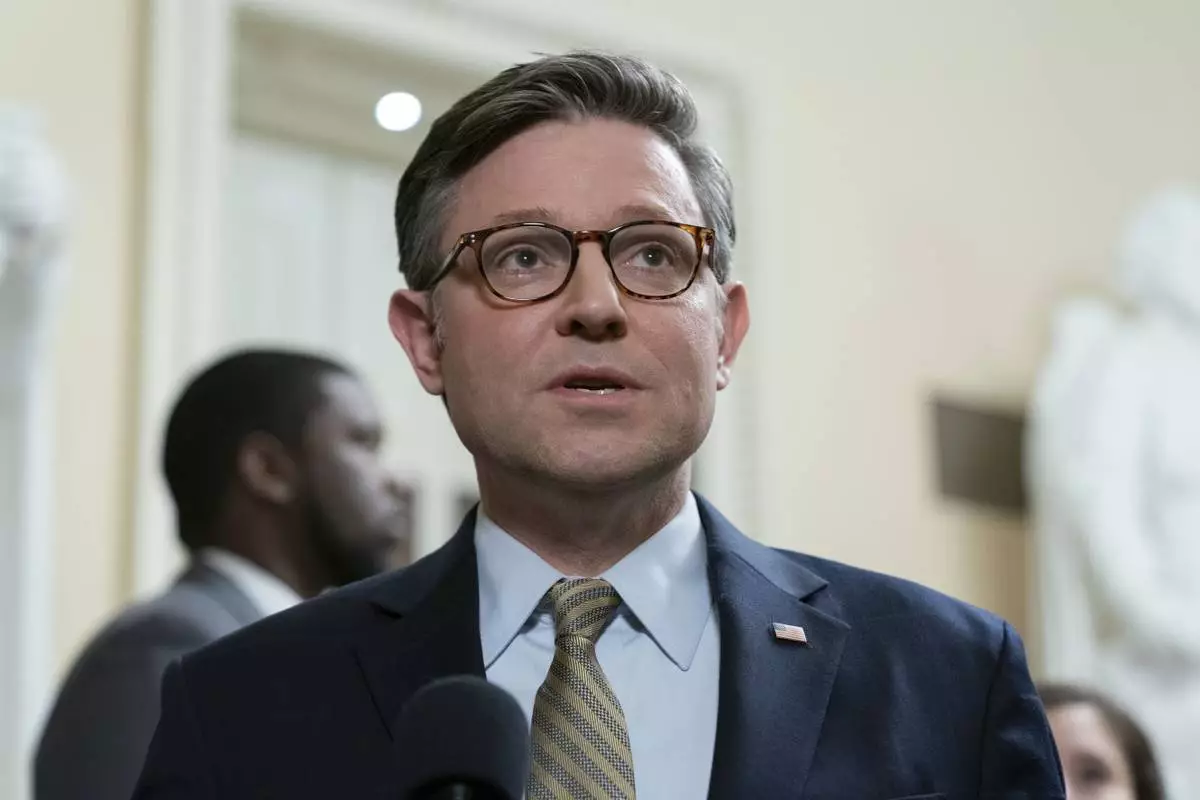

Speaker of the House Mike Johnson, R-La., talks to reporters after passing the funding bill to avert the government shutdown at the Capitol in Washington, Friday, Dec. 20, 2024. (AP Photo/Jose Luis Magana)
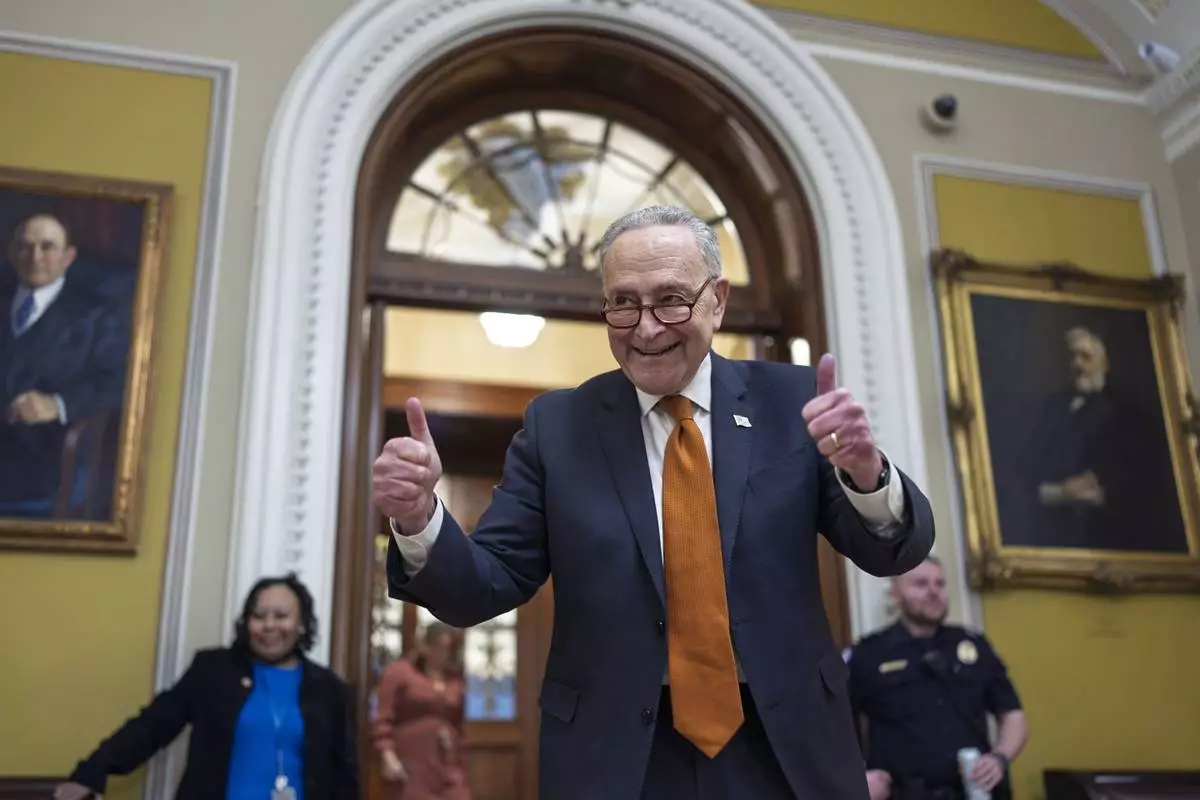

Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer, D-N.Y., celebrates as the Senate begins voting on the government funding bill just in time to meet the midnight deadline, at the Capitol in Washington, Friday, Dec. 20, 2024. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)















