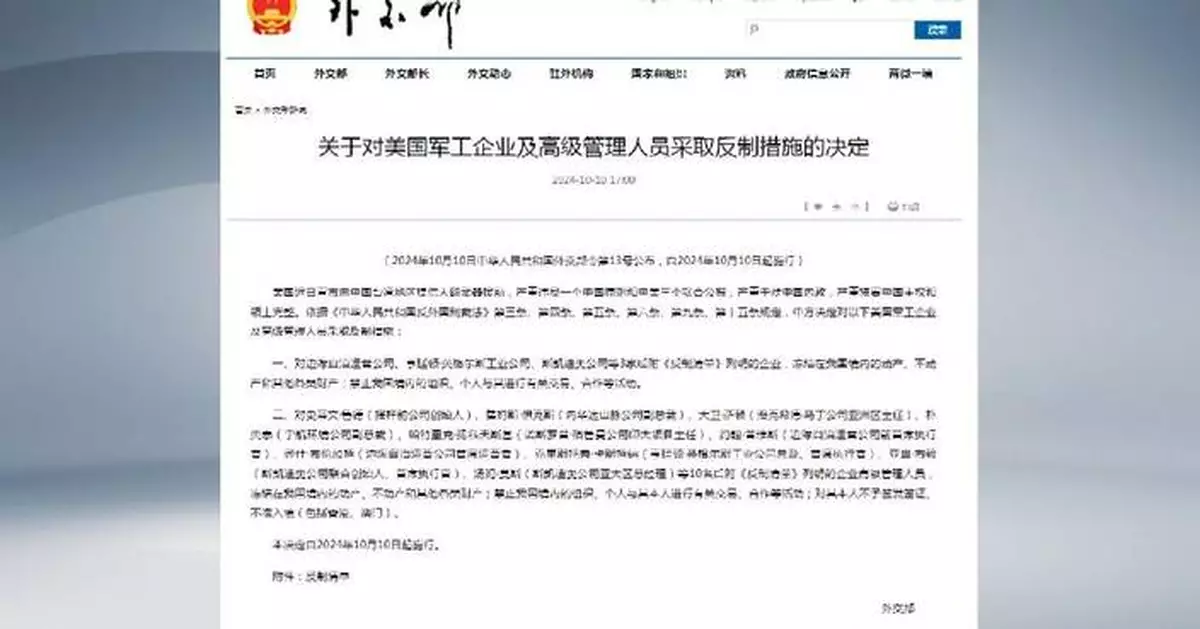
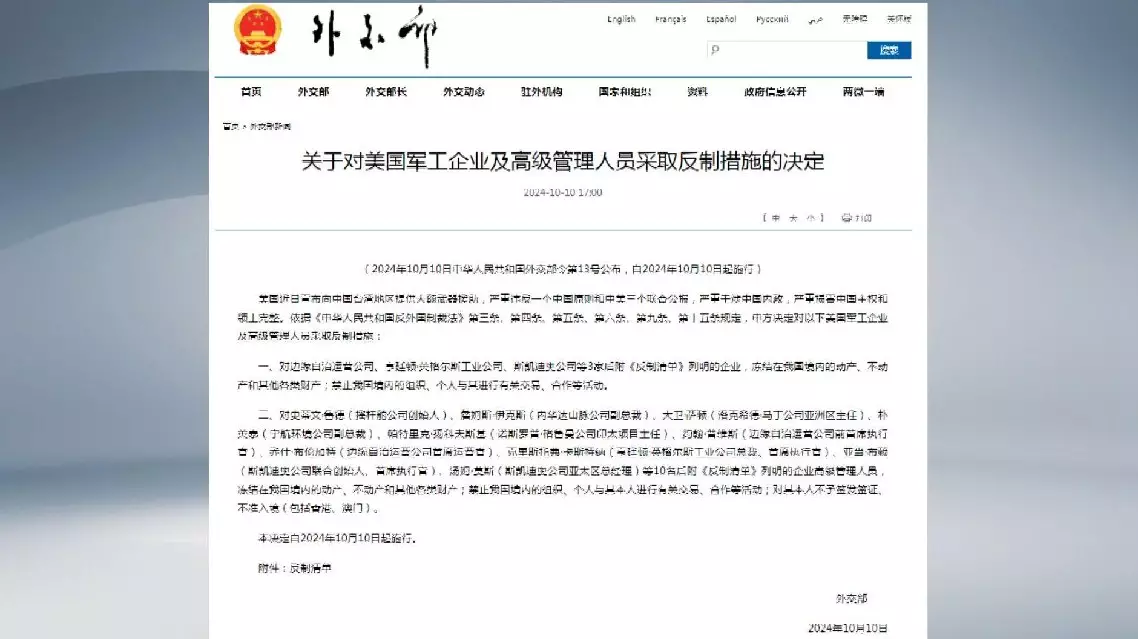
China has decided to adopt countermeasures against three U.S. military companies and 10 senior executives for arms sales to China's Taiwan region, according to a decision published on the Chinese Foreign Ministry's official website on Thursday.
The decision said that the United States recently has once again announced arms sales plans to the Taiwan region, which has seriously violated the one-China principle and the three China-U.S. joint communiques, interfered in China's internal affairs and undermined China's sovereignty and territorial integrity.
Pursuant to Articles 3, 4, 5, 6, 9 and 15 of China's Anti-Foreign Sanctions Law, China has decided to take countermeasures against the following enterprises and executives:
For the three enterprises concerned, namely the Edge Autonomy Operations LLC, Huntington Ingalls Industries Inc. and Skydio Inc., their movable, immovable and all other types of property in China will be frozen.
Organizations and individuals in China will be prohibited from engaging in transactions, cooperation or other activities with any of the three enterprises.
For the 10 senior executives, i.e., Steven Roger Rudder, Founder, Stick Rudder Enterprises LLC; James William Ickes II, Vice President, Sierra Nevada Corporation; David Keith Sutton, Asia Director, Lockheed Martin; Yeong-Tae Pak, Vice President, AeroVironment; Patrick Edward Jankowski, Indo-Pacific Project Director, Northrop Grumman; John Purvis, Former CEO, Edge Autonomy Operations LLC; Josh Brungardt, Chief Operating Officer, Edge Autonomy Operations LLC; Christopher Douglas Kastner, President and CEO, Huntington Ingalls Industries; Adam Bry, Co-Founder and CEO, Skydio Inc.; and Tom Moss, General Manager, Skydio Inc.:
Their movable and immovable properties, and other kinds of assets within China will be frozen.
All organizations and individuals within China will be prohibited from engaging in transaction, cooperation and other activities with any of them.
They will also be denied visas or entry into China (including Hong Kong and Macao).
This decision will come into force from Oct 10, 2024.
The three China-U.S. Joint Communiqués, namely the 1972 communiqué (the Shanghai communiqué), the 1979 communiqué on the establishment of diplomatic relations, and the 1982 communiqué, provide a crucial basis for the development of China-U.S. relations.
In particular, the August 17, 1982 communiqué focuses on a step-by-step approach with the ultimate aim of resolving the issue of U.S. arms sales to Taiwan. The United States declared that its arms sales to Taiwan would not exceed, either in qualitative or in quantitative terms, the level of those supplied in the years since the establishment of diplomatic relations between the United States and China, and that it intended to reduce gradually its sales of arms to Taiwan, leading over a period of time to a final resolution.
In all three communiqués the United States emphasize its acceptance of the one-China principle, which provides political basis for healthy development of China-U.S. relations.
China to adopt countermeasures against US military companies, senior executives for arms sales to Taiwan