TOKYO (AP) — A remote-controlled robot has safely returned with a tiny piece of melted fuel it collected from inside one of three damaged reactors at the tsunami-hit Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant for the first time since the 2011 meltdown.
The Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, which manages the plant, said Saturday that the extendable fishing rod-like robot successfully clipped a piece of gravel of about 5 millimeters (0.2 inches), the size of a tiny bit of granola, from the top surface of a mound of molten fuel debris that sits on the bottom of the No. 2 reactor’s primary containment vessel.
The “telesco” robot, with its frontal tongs still holding the melted fuel bit, returned to the enclosed container for safe storage after workers in full hazmat gear pulled it out of the containment vessel earlier Saturday.
The sample return marks the first time the melted fuel is retrieved out of the containment vessel. But the mission is not over until it's certain that the sample's radioactivity is below a set standard and safely placed into a container.
If the radioactivity exceeds the limit, the robot must go back inside the reactor to find another piece. TEPCO officials said they expect the piece is small enough to meet the requirement.
The mission initially started in August for what was supposed to be a two-week round trip but had been suspended twice due to mishaps.
First one was the procedural mistake at the beginning that held up the work for nearly three weeks, then the robot’s two cameras designed to transmit views of the target areas for its operators in the remote control room failed. The camera problem required the robot to be pulled out all the way for replacement before the mission resumed Monday.
Fukushima Daiichi lost its key cooling systems during the 2011 earthquake and tsunami, causing meltdowns in its three reactors. An estimated 880 tons of fatally radioactive molten fuel remains in them, and TEPCO has carried out a number of robotic probes to figure out how to decommission the plant.
Telesco on Wednesday successfully clipped a piece presumably measuring less than 3 grams (0.1 ounce) from the planned area right underneath the Unit 2 reactor core, from which large amounts of melted fuel fell during the meltdown 13 years ago, TEPCO said.
Plant chief Akira Ono said only the tiny spec can provide key data to plan decommissioning strategy, develop necessary technology and robots and retroactively learn how the accident had developed.
The government and TEPCO have set a 30-to-40-year target for the cleanup, which experts say is overly optimistic and should be updated.
No specific plans for the full removal of the fuel debris or its final disposal have been decided.
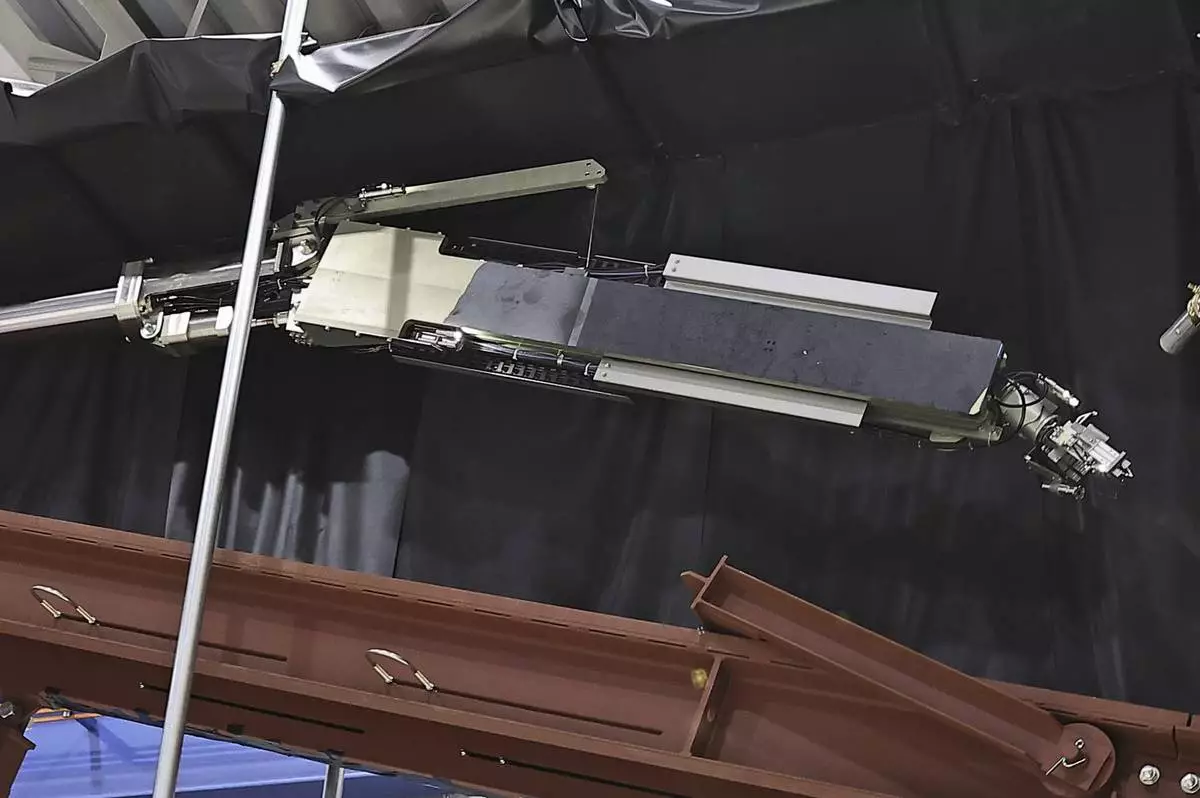

FILE - Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, also known as TEPCO, the operator of Japan's wrecked Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, reveals a robot to be used to retrieve debris at the power plant in Kobe, western Japan, May 28, 2024. (Kyodo News via AP, File)
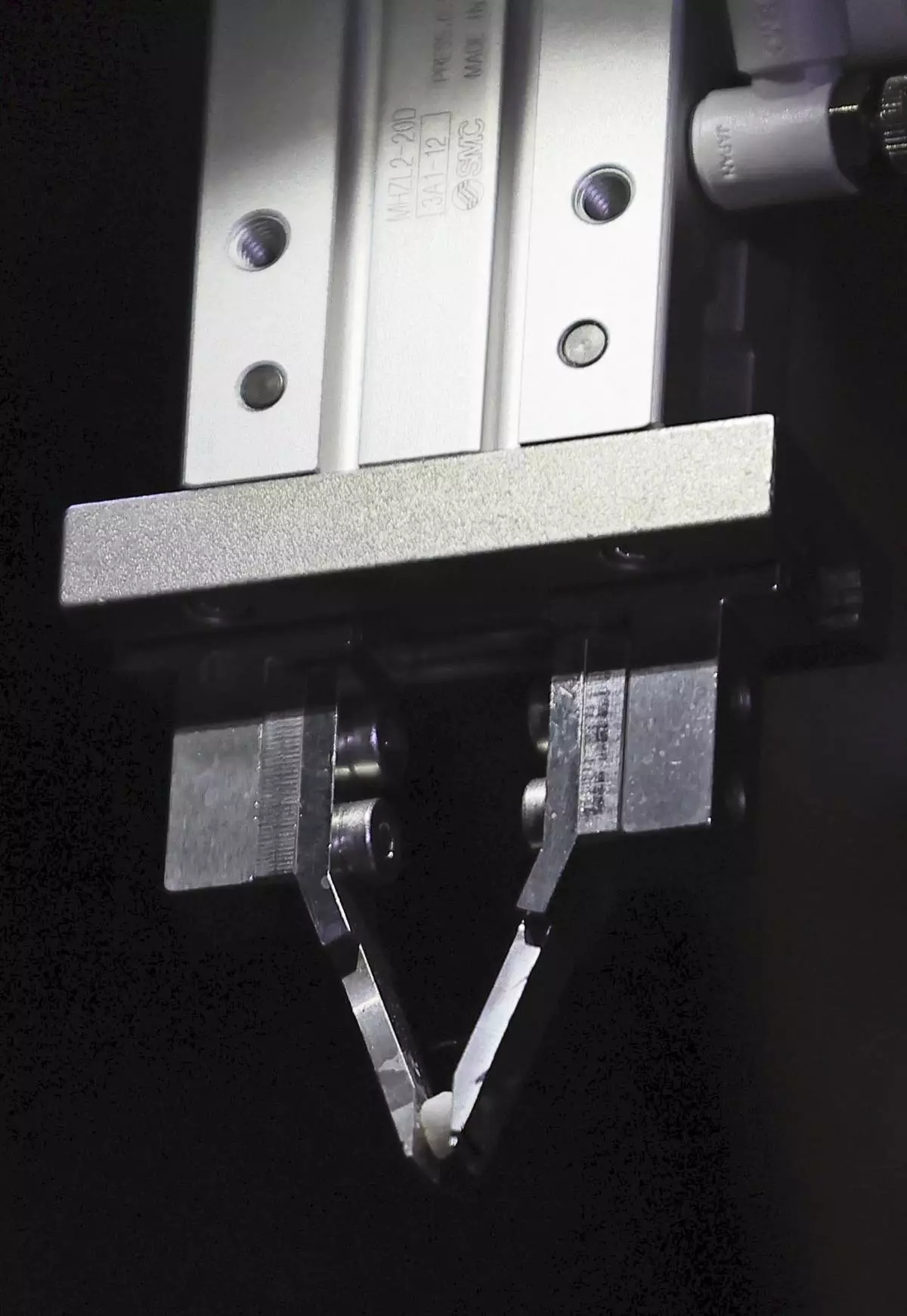
A device to remove debris from a reactor at the damaged Fukushima Nuclear power plant demonstrates to pinch a stone, as revealed in Kobe, western Japan, May 28, 2024. (Kyodo News via AP, File)
WASHINGTON (AP) — When the Justice Department lifted a school desegregation order in Louisiana this week, officials called its continued existence a “historical wrong” and suggested that others dating to the Civil Rights Movement should be reconsidered.
The end of the 1966 legal agreement with Plaquemines Parish schools announced Tuesday shows the Trump administration is “getting America refocused on our bright future,” Assistant Attorney General Harmeet Dhillon said.
Inside the Justice Department, officials appointed by President Donald Trump have expressed desire to withdraw from other desegregation orders they see as an unnecessary burden on schools, according to a person familiar with the issue who was granted anonymity because they were not authorized to speak publicly.
Dozens of school districts across the South remain under court-enforced agreements dictating steps to work toward integration, decades after the Supreme Court struck down racial segregation in education. Some see the court orders' endurance as a sign the government never eradicated segregation, while officials in Louisiana and at some schools see the orders as bygone relics that should be wiped away.
The Justice Department opened a wave of cases in the 1960s, after Congress unleashed the department to go after schools that resisted desegregation. Known as consent decrees, the orders can be lifted when districts prove they have eliminated segregation and its legacy.
The Trump administration called the Plaquemines case an example of administrative neglect. The district in the Mississippi River Delta Basin in southeast Louisiana was found to have integrated in 1975, but the case was to stay under the court’s watch for another year. The judge died the same year, and the court record “appears to be lost to time,” according to a court filing.
“Given that this case has been stayed for a half-century with zero action by the court, the parties or any third-party, the parties are satisfied that the United States’ claims have been fully resolved,” according to a joint filing from the Justice Department and the office of Louisiana Attorney General Liz Murrill.
Plaquemines Superintendent Shelley Ritz said Justice Department officials still visited every year as recently as 2023 and requested data on topics including hiring and discipline. She said the paperwork was a burden for her district of fewer than 4,000 students.
“It was hours of compiling the data,” she said.
Louisiana “got its act together decades ago,” said Leo Terrell, senior counsel to the Civil Rights Division at the Justice Department, in a statement. He said the dismissal corrects a historical wrong, adding it’s “past time to acknowledge how far we have come.”
Murrill asked the Justice Department to close other school orders in her state. In a statement, she vowed to work with Louisiana schools to help them “put the past in the past.”
Civil rights activists say that's the wrong move. Many orders have been only loosely enforced in recent decades, but that doesn't mean problems are solved, said Johnathan Smith, who worked in the Justice Department's Civil Rights Division during President Joe Biden's administration.
“It probably means the opposite — that the school district remains segregated. And in fact, most of these districts are now more segregated today than they were in 1954," said Smith, who is now chief of staff and general counsel for the National Center for Youth Law.
More than 130 school systems are under Justice Department desegregation orders, according to records in a court filing this year. The vast majority are in Alabama, Georgia and Mississippi, with smaller numbers in states like Florida, Louisiana and South Carolina. Some other districts remain under separate desegregation agreements with the Education Department.
The orders can include a range of remedies, from busing requirements to district policies allowing students in predominately Black schools to transfer to predominately white ones. The agreements are between the school district and the U.S. government, but other parties can ask the court to intervene when signs of segregation resurface.
In 2020, the NAACP Legal Defense and Education Fund invoked a consent decree in Alabama’s Leeds school district when it stopped offering school meals during the COVID-19 pandemic. The civil rights group said it disproportionately hurt Black students, in violation of the desegregation order. The district agreed to resume meals.
Last year, a Louisiana school board closed a predominately Black elementary school near a petrochemical facility after the NAACP Legal Defense and Education Fund said it disproportionately exposed Black students to health risks. The board made the decision after the group filed a motion invoking a decades-old desegregation order at St. John the Baptist Parish.
The dismissal has raised alarms among some who fear it could undo decades of progress. Research on districts released from orders has found that many saw greater increases in racial segregation compared with those under court orders.
“In very many cases, schools quite rapidly resegregate, and there are new civil rights concerns for students,” said Halley Potter, a senior fellow at The Century Foundation who studies educational inequity.
Ending the orders would send a signal that desegregation is no longer a priority, said Robert Westley, a professor of antidiscrimination law at Tulane University Law School in New Orleans.
“It’s really just signaling that the backsliding that has started some time ago is complete," Westley said. “The United States government doesn’t really care anymore of dealing with problems of racial discrimination in the schools. It’s over.”
Any attempt to drop further cases would face heavy opposition in court, said Raymond Pierce, president and CEO of the Southern Education Foundation.
“It represents a disregard for education opportunities for a large section of America. It represents a disregard for America’s need to have an educated workforce," he said. “And it represents a disregard for the rule of law.”
Associated Press writer Sharon Lurye contributed from New Orleans.
This story has been corrected to reflect the group that invoked desegregation orders in other Louisiana districts is the NAACP Legal Defense and Education Fund, not the NAACP.
The Associated Press’ education coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.
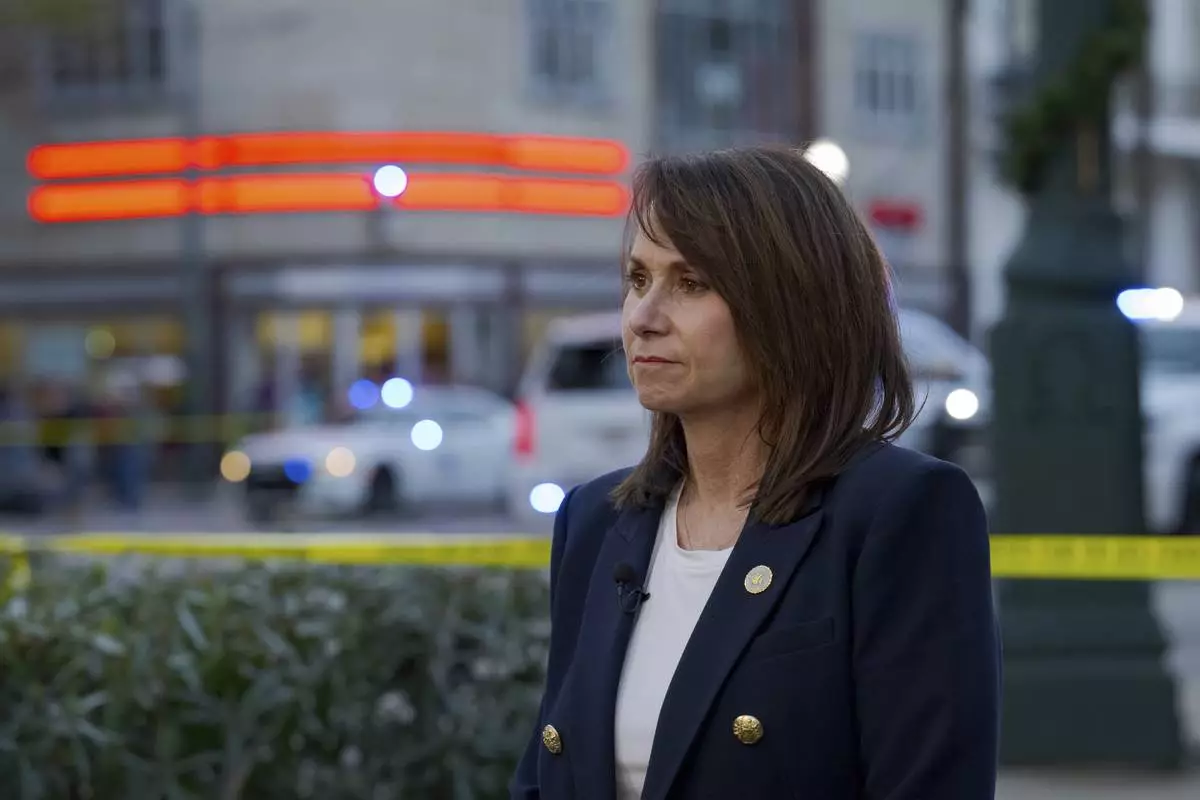

FILE - Louisiana Attorney General Liz Murrill speaks to reporters, Jan. 1, 2025, in New Orleans. (AP Photo/Matthew Hinton, file)

FILE - Children smile from window of a school bus in Springfield, Mass., as court-ordered busing brought Black children and white children together in elementary grades without incident, Sept. 16, 1974. (AP Photo/Peter Bregg, File)
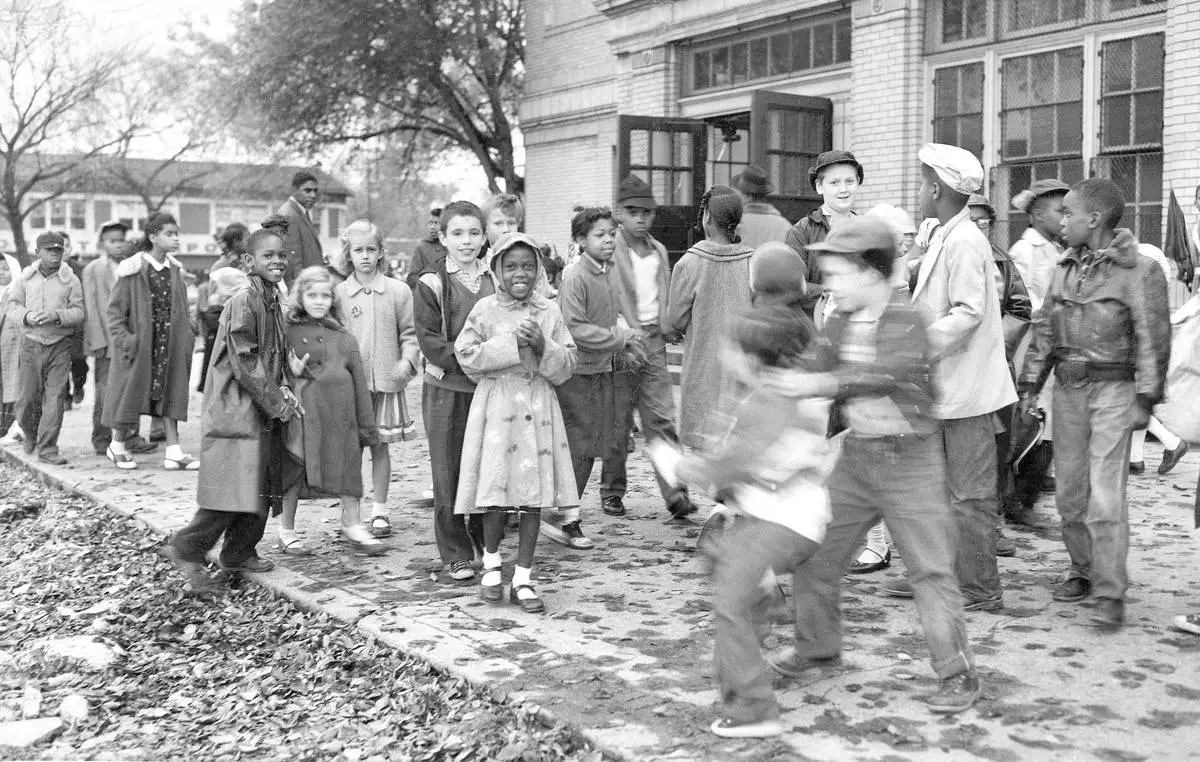

FILE - White and Black children mix freely on the playground outside a school in a racially mixed neighborhood, Oct. 18, 1957, in Detroit. (AP Photo/Alvan Quinn, File)

FILE - Students from Charlotte High School in Charlotte, N.C., ride a bus together, May 15, 1972. (AP Photo/Harold L. Valentine, File)
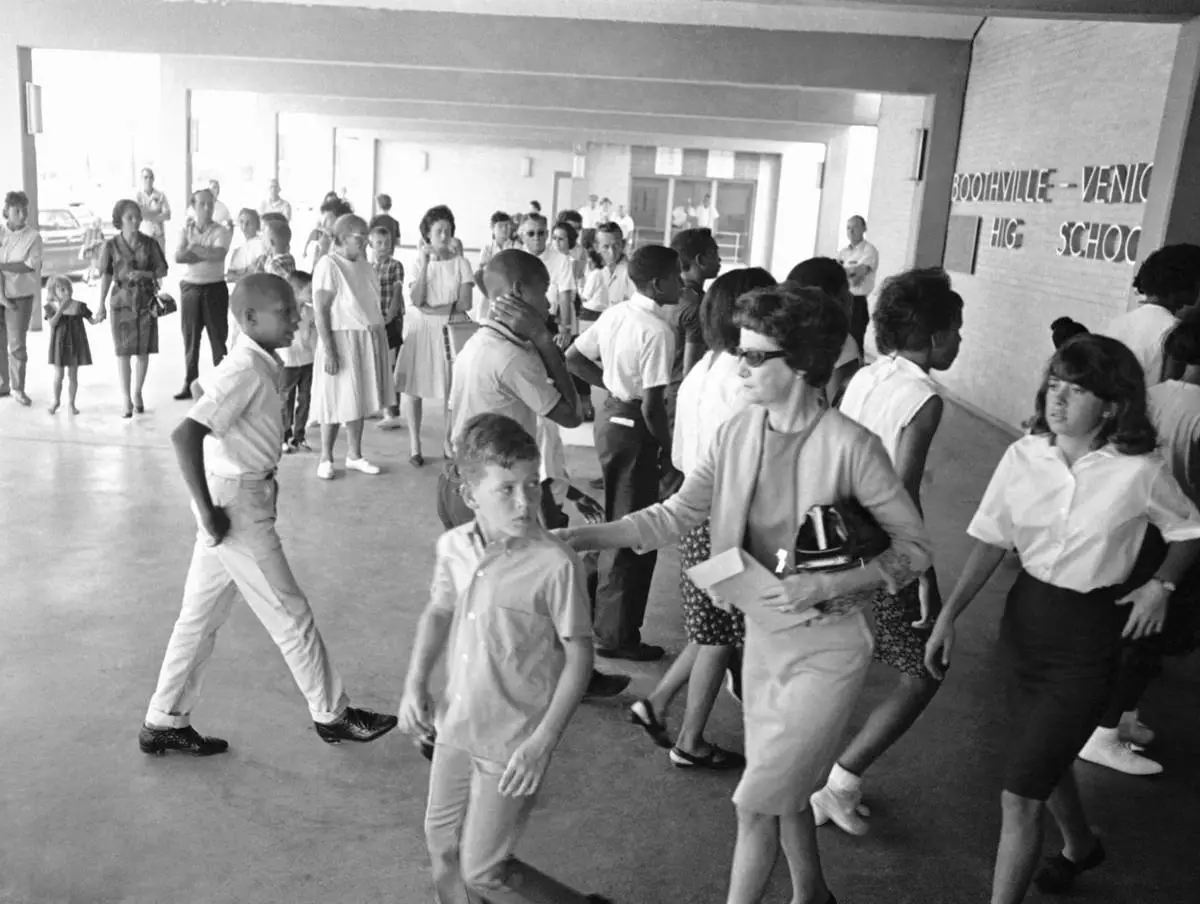

FILE - A white mother walks with her son past a group of African American students arriving for classes at formerly all-white Boothville Venice High School on Monday, Sept. 12, 1966 as racial barriers fell in Plaquemines Parish. (AP Photo/Jack Thornell, file)

FILE - A man plants a sign reading outside Woodlawn High School in Pointe a la Hache, Louisiana on Sept. 1, 1966 where five African Americans applied for registration for the first time in parish history. (AP Photo/Jack Thornell, file)
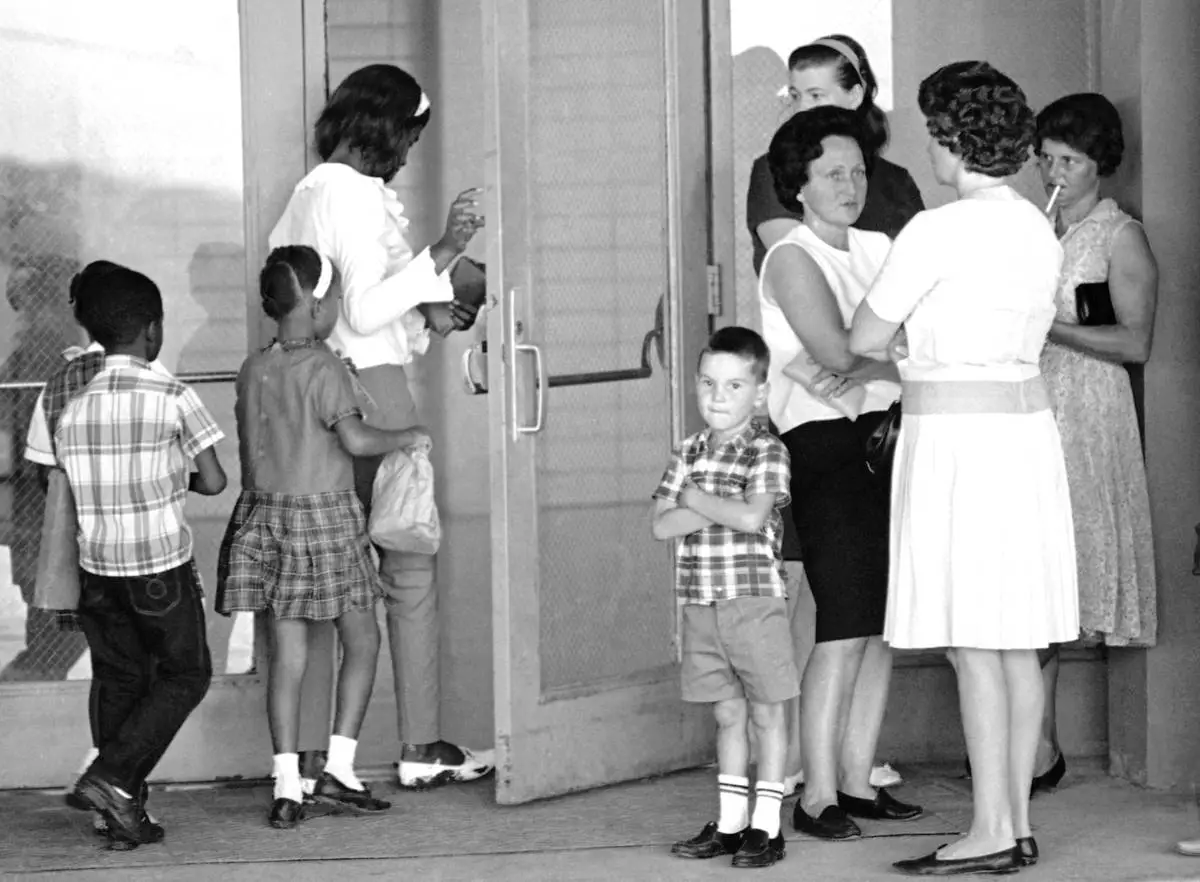

FILE - A group of African American students, left, enter the Boothville-Venice School in Plaquemines Parish, Louisiana on Sept. 12, 1966 as a group of white mothers wait at the entrance of the school. (AP Photo/Jack Thornell, file)