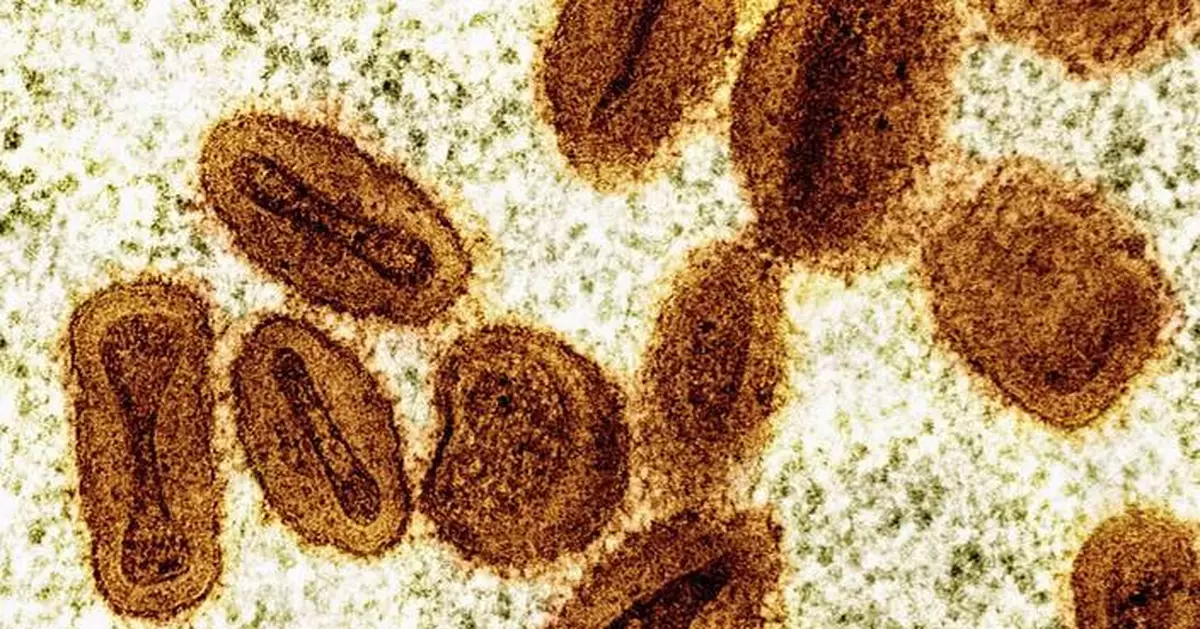
NEW YORK (AP) — Health officials said Saturday they have confirmed the first U.S. case of a new form of mpox that was first seen in eastern Congo.
The person had traveled to eastern Africa and was treated in Northern California upon return, according to the California Department of Public Health. Symptoms are improving and the risk to the public is low.
The individual was isolating at home and health workers are reaching out to close contacts as a precaution, the state health department said.
Mpox is a rare disease caused by infection with a virus that’s in the same family as the one that causes smallpox. It is endemic in parts of Africa, where people have been infected through bites from rodents or small animals. Milder symptoms can include fever, chills and body aches. In more serious cases, people can develop lesions on the face, hands, chest and genitals.
Earlier this year, scientists reported the emergence of a new form of mpox in Africa that was spread through close contact including through sex. It was widely transmitted in eastern and central Africa. But in cases that were identified in travelers outside of the continent, spread has been very limited, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
More than 3,100 confirmed cases have been reported just since late September, according to the World Health Organization. The vast majority of them have been in three African countries — Burundi, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Since then, cases of travelers with the new mpox form have been reported in Germany, India, Kenya, Sweden, Thailand, Zimbabwe, and the United Kingdom.
Health officials earlier this month said the situation in Congo appears to be stabilizing. The Africa CDC has estimated Congo needs at least 3 million mpox vaccines to stop the spread, and another 7 million vaccines for the rest of Africa. The spread is mostly through sexual transmission as well as through close contact among children, pregnant women and other vulnerable groups.
The current outbreak is different from the 2022 global outbreak of mpox where gay and bisexual men made up the vast majority of cases.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
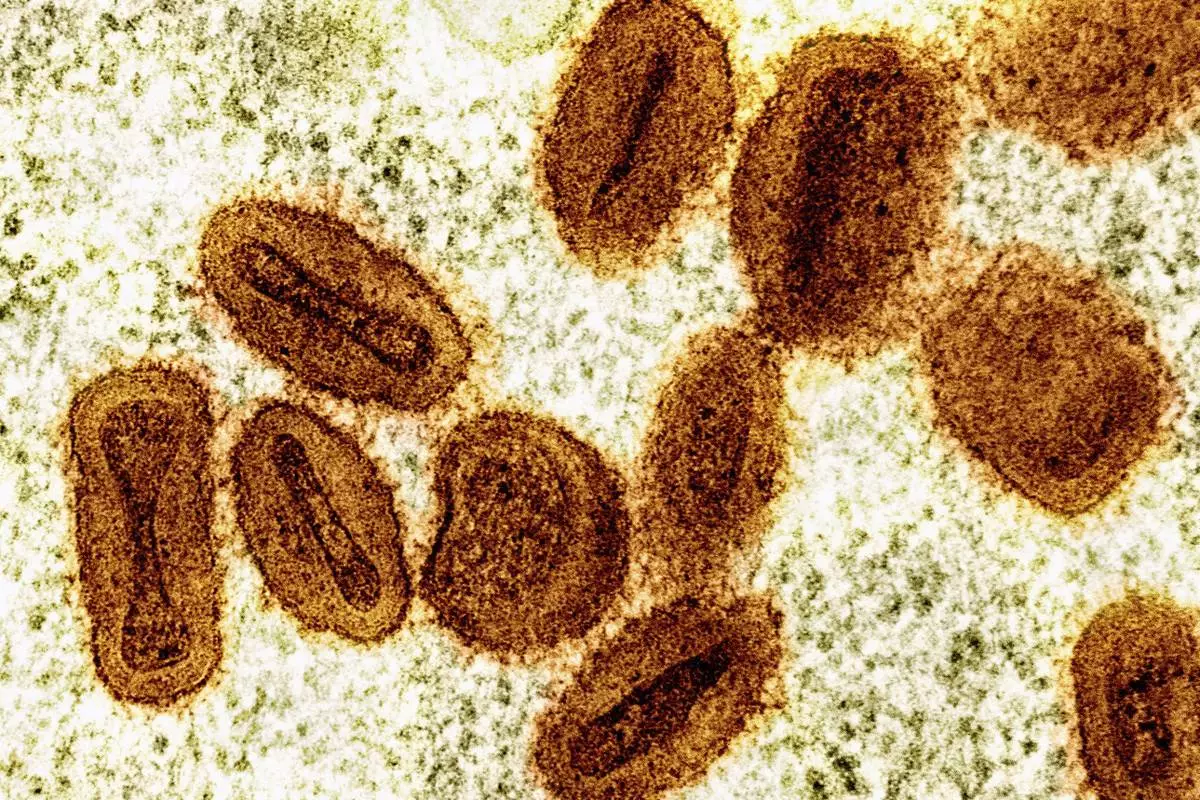
FILE - This colorized electron microscope image provided by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases in 2024 shows Mpox virus particles, orange, found within infected cells, green. (NIAID via AP, File)
WASHINGTON (AP) — The House has passed legislation that would provide full Social Security benefits to millions of people, pushing it one step closer to becoming law.
The Social Security bill on Tuesday won bipartisan support in the House, 327-75, in what is now the lame-duck period for Congress. The bill now heads to the Senate, where passage is not assured despite considerable support.
Here’s what to know about the legislation and what could happen next.
Decades in the making, the bill would repeal two federal policies — the Windfall Elimination Provision and the Government Pension Offset — that currently limit Social Security payouts for roughly 2.8 million people, according to reports from the Congressional Research Service.
The policies broadly reduce payments to two groups of Social Security recipients: people who also receive a pension from a job that is not covered by Social Security and surviving spouses of Social Security recipients who receive a government pension of their own.
People who worked in state, local and federal government jobs have been heavily affected by the policies, as have teachers, firefighters and police officers, according to lawmakers and advocates.
Both provisions would be repealed by the bill, thereby increasing Social Security payments for many.
The budgetary effect of the legislation is considerable, adding an estimated $195 billion to federal deficits over 10 years, according to the Congressional Budget Office.
That means more fiscal strain on the Social Security Trust funds, which were already estimated to be unable to pay out full benefits beginning in 2035. Some conservatives in the House attempted to block the legislation due to its cost.
Supporters of the bill in the House acknowledged the fiscal impact but said it was a matter of fairness.
“For more than 40 years, the Social Security trust funds have been artificially propped up by stolen benefits that millions of Americans paid for and that their families deserve,” said Reps. Garret Graves, R-La. and Abigail Spanberger, D-Va., the lead sponsors of the bill in the House.
“The time to put an end to this theft is now,” they said.
The Social Security bill has 63 sponsors in the Senate — a significant tally because 60 votes are needed to pass most legislation in the chamber.
Sens. Sherrod Brown, D-Ohio, and Susan Collins, R-Maine, the lead sponsors, have urged colleagues to take up the bill as soon as possible.
But the Senate has a jam-packed schedule in the remaining weeks of the year, with government funding, disaster relief and an annual must-pass defense bill likely to eat up considerable floor time.
If passed by the Senate, the bill would go to President Joe Biden. If the bill is signed into law, the changes would be effective for benefits payable after December 2023.
But if the bill doesn’t pass the Senate by Jan. 3, when a new session of Congress begins, it would expire and supporters would have to start over.

The Capitol is pictured, Friday, Nov. 15, 2024, in Washington. (AP Photo/Mariam Zuhaib)