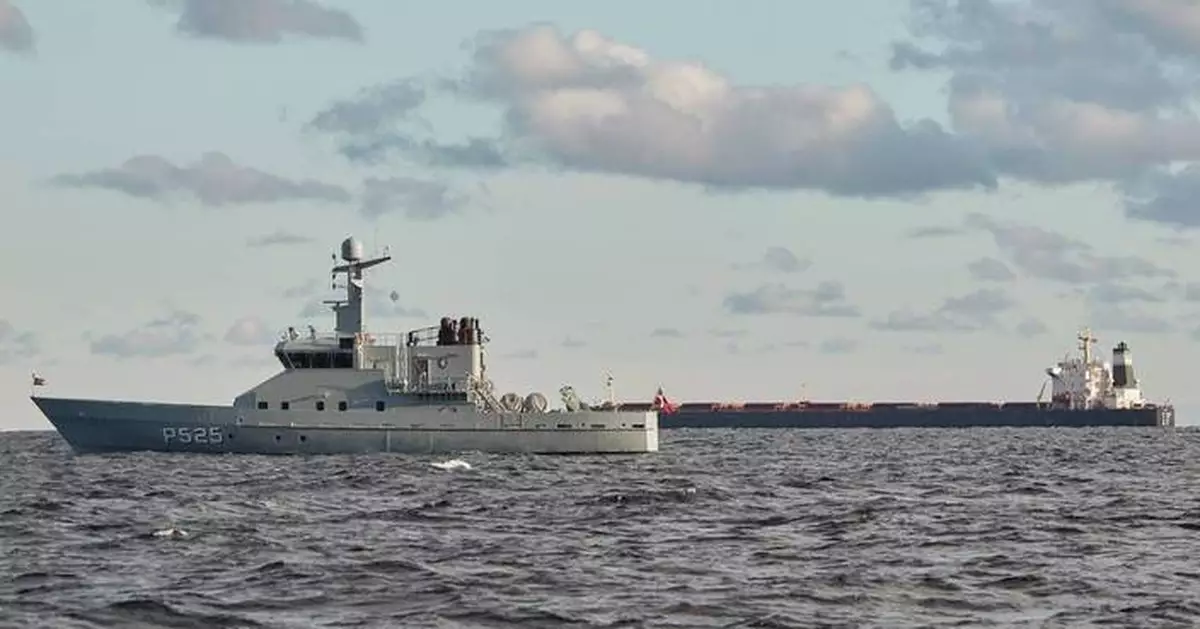
COPENHAGEN, Denmark (AP) — The Danish military confirmed Thursday it was monitoring a Chinese bulk carrier that was reportedly in the area where two undersea data cables ruptured in recent days in the Baltic Sea.
Finnish, Swedish and German authorities have launched investigations into the rupture earlier this week of two undersea cables — one between Finland and Germany, the other between Lithuania and Sweden. All are member countries of the NATO alliance.
News reports said a Chinese-flagged vessel, the Yi Peng 3, had been in the area at the time of the ruptures.
VesselFinder.com, which tracks marine ship movements, located the Danish patrol boat P525 at about one nautical mile away from the Chinese-flagged ship between Denmark and Sweden on Thursday morning Europe time.
“The Danish Defence can confirm that we are present in the area near the Chinese ship Yi Peng 3,” said Henrik Hall Mortensen, a Danish military spokesman, in an email.
In Beijing, Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesman Lin Jian told a regular news briefing that Chinese authorities had no information about the ship but said China was ready to “maintain communication” with relevant parties.
He called for the Chinese ship’s rights to normal navigation to be protected.
The ruptures come more than a year after Sweden announced a “purposeful” rupture of an undersea cable to Estonia through the Black Sea, which was also not explained.
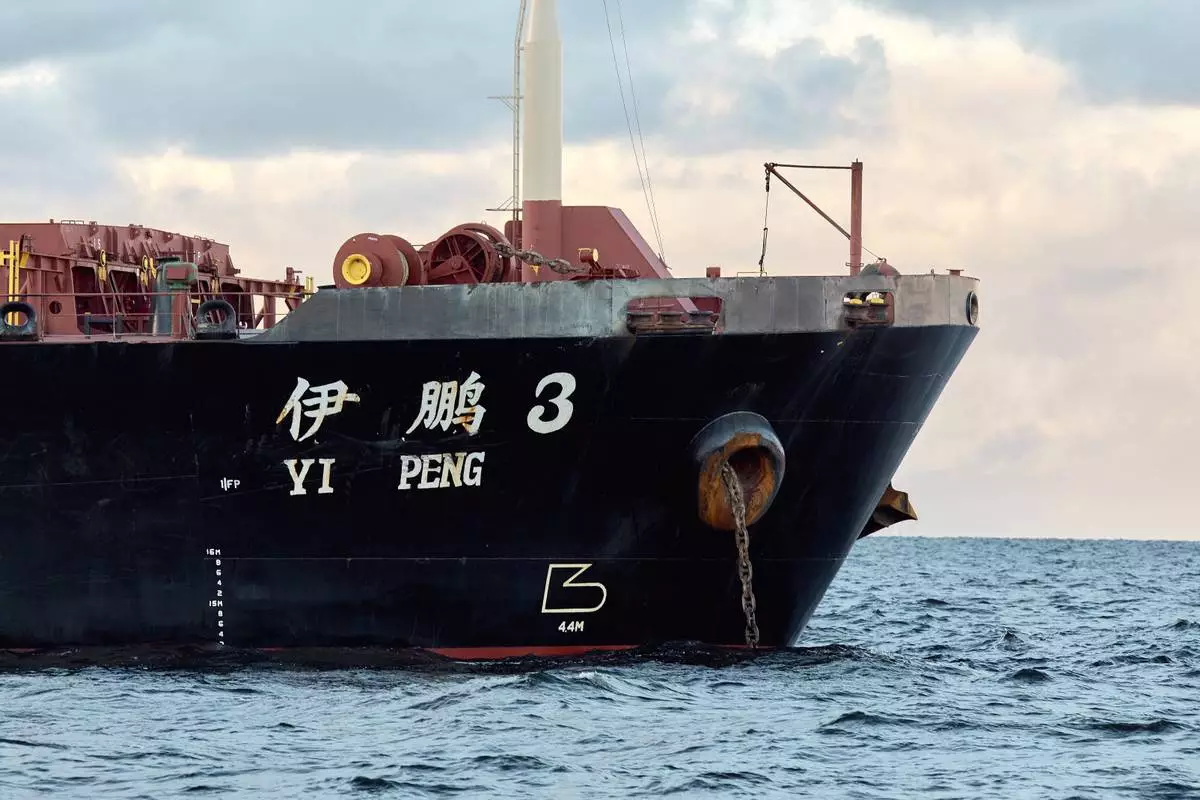

The Chinese ship, the bulk carrier Yi Peng 3 is anchored in the sea of Kattegat, near the city of Granaa in Jutland, Denmark, Wednesday, Nov. 20, 2024. (Mikkel Berg Pedersen/Ritzau Scanpix via AP)
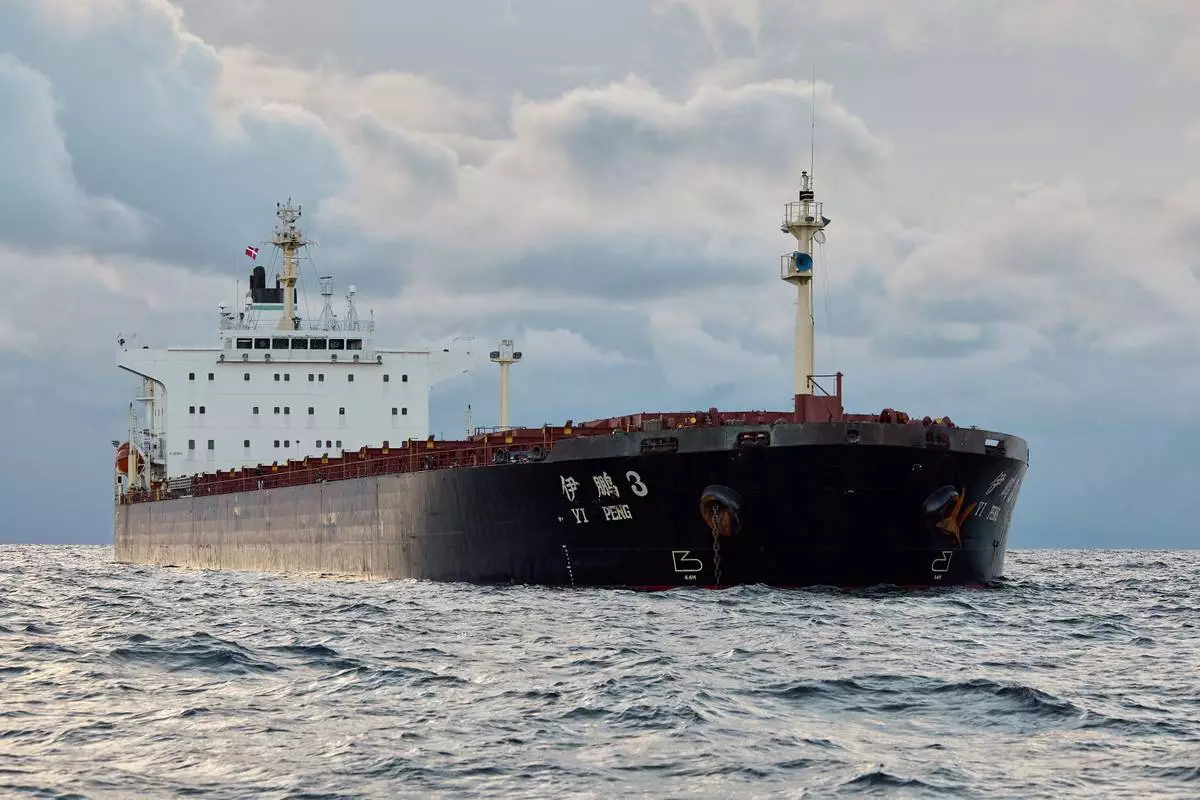

The Chinese ship, the bulk carrier Yi Peng 3 is anchored in the sea of Kattegat, near the city of Granaa in Jutland, Denmark, Wednesday, Nov. 20, 2024. (Mikkel Berg Pedersen/Ritzau Scanpix via AP)
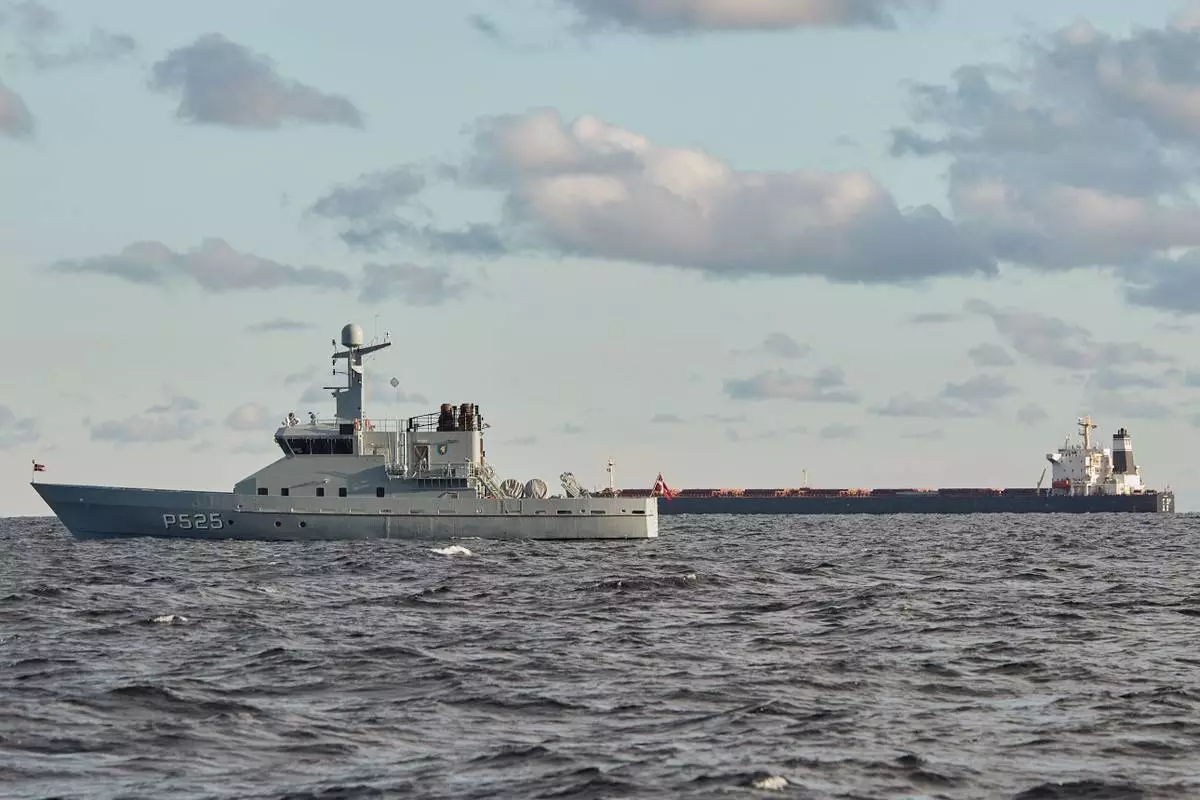

The Chinese ship, the bulk carrier Yi Peng 3, in background, is anchored and being monitored by a Danish naval patrol vessels in the sea of Kattegat, near the city of Granaa in Jutland, Denmark, Wednesday, Nov. 20, 2024. (Mikkel Berg Pedersen/Ritzau Scanpix via AP)
It was late in the afternoon and lightly snowing when four rock climbers, working their way up a steep gully between two peaks in Washington’s North Cascades Range, decided to turn around for a descent down the mountain that would claim three of their lives.
As they climbed down, the four attached their ropes to an piton — a metal spike pounded into rock cracks or ice and used to secure ropes — that had been placed by a past climber. As one of the men began rappelling off the piton, it ripped out of the mountain, sending all four falling past ice and snow and rock.
They fell some 200 feet (60 meters), landing in a more sloping ravine where they tumbled for another roughly 200 feet before coming to a stop in a tangle of rope.
Three were killed by the fall. One was knocked unconscious.
Anton Tselykh awoke in the dark. It had been hours since the fall.
Over the course of several hours, he extricated himself from the tangle of ropes, gear and debris and trekked over rough terrain of rock and snow — with help from a pick-like ice tool — to his car.
He drove for some 40 miles (64 kilometers) before finding a pay phone and calling for help in Newhalem, an unincorporated community about an hour's drive away. It was Sunday morning, eight hours since he regained consciousness.
From a Seattle hospital Wednesday morning, Tselykh, recovering from head trauma and internal bleeding, told authorities what had happened. He was in satisfactory condition at Harborview Medical Center, meaning he was not in the intensive care unit, Susan Gregg, media relations director for UW Medicine, said in an email.
Tselykh, 38, confirmed authorities' theories of what led to the deaths of his three companions, identified as Vishnu Irigireddy, 48; Tim Nguyen, 63; and Oleksander Martynenko, 36.
A three-person search and rescue team had responded to the site of the fall following Tselykh's call, said Cristina Woodworth, who led the team and spoke with the lone survivor by phone Wednesday. The team had followed coordinates from a GPS device the climbers had been carrying, which were shared by a friend of the men.
The rough terrain required a helicopter, which removed the bodies one at a time, Woodworth said.
Responders pored over the recovered equipment, trying to decipher what caused the fall. They found the piton still clipped into the climbers’ ropes, Okanogan County Coroner Dave Rodriguez said. Pitons are difficult to remove from rock, he said, and the anchor's presence on the rope was a clue to what happened.
Generally, setting up a backup anchor is a common practice among climbers, said Joshua Cole, a guide and co-owner of North Cascades Mountain Guides, who has been climbing in the area for about 20 years. It's still unclear whether the four had a backup.
The four climbers were friends, some of whom had climbed together before and appeared fairly experienced, Woodworth said, adding that Tselykh was “obviously very much affected by this.”
Irigireddy was a vice president of engineering at the Fluke Corporation, a test equipment manufacturing company, which released a statement Wednesday.
“Vishnu was an extraordinary leader, and his loss is felt profoundly across our organization,” the statement read.
Martynenko’s wife, Olga, said Tuesday in a Facebook post that her husband, whom she referred to as Alex, also left behind their son. She shared a link to a fundraiser to help “during the most devastating time of our lives.”
“I still cannot believe that you are gone, my love."
Bedayn is a corps member for The Associated Press/Report for America Statehouse News Initiative. Report for America is a nonprofit national service program that places journalists in local newsrooms to report on undercovered issues.
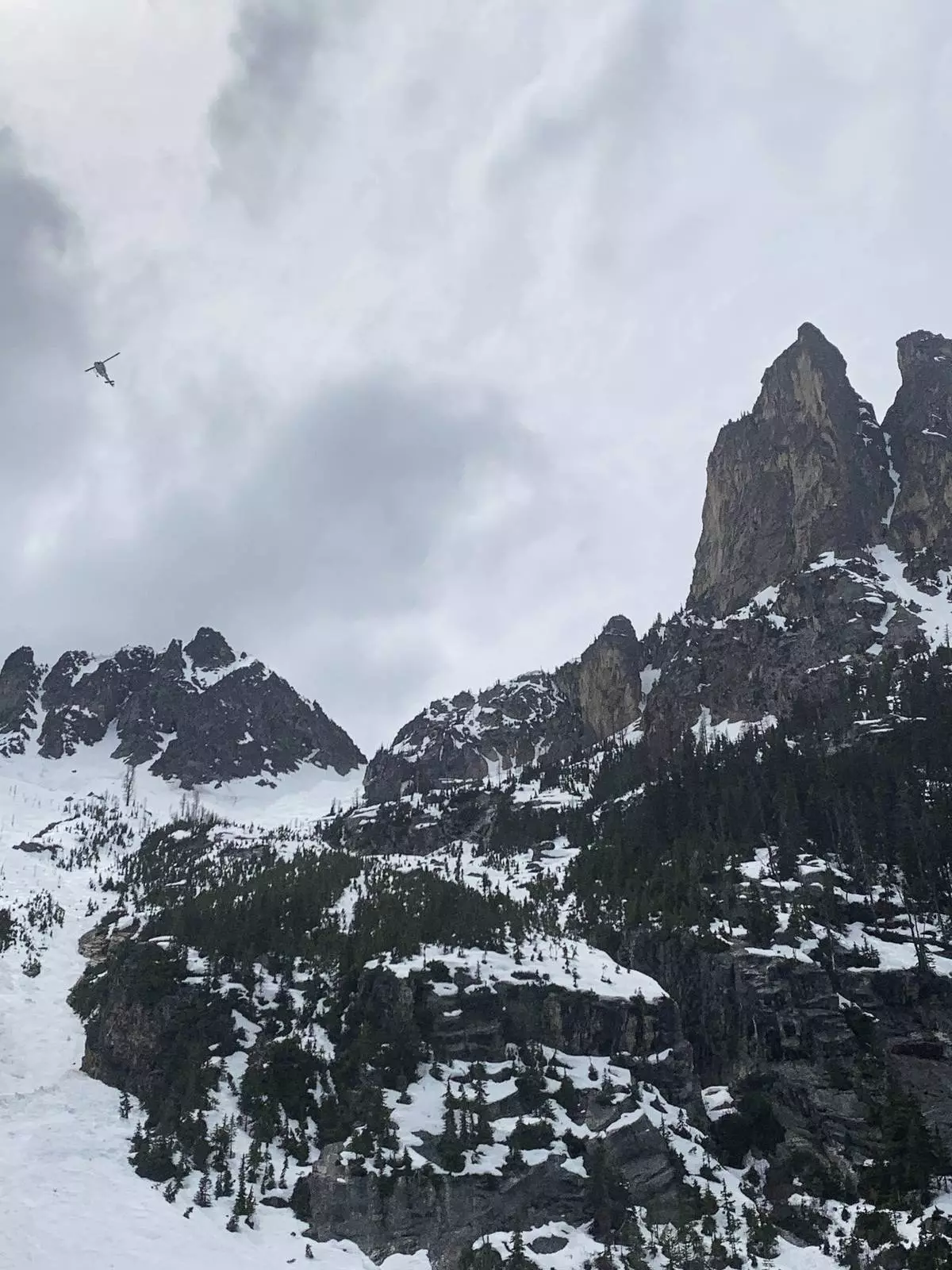

The Okanogan County Search and Rescue team responds to a climbing accident in the North Cascades mountains in Washington on Sunday, May 11, 2025. (Okanogan County Sheriff's Office via AP)
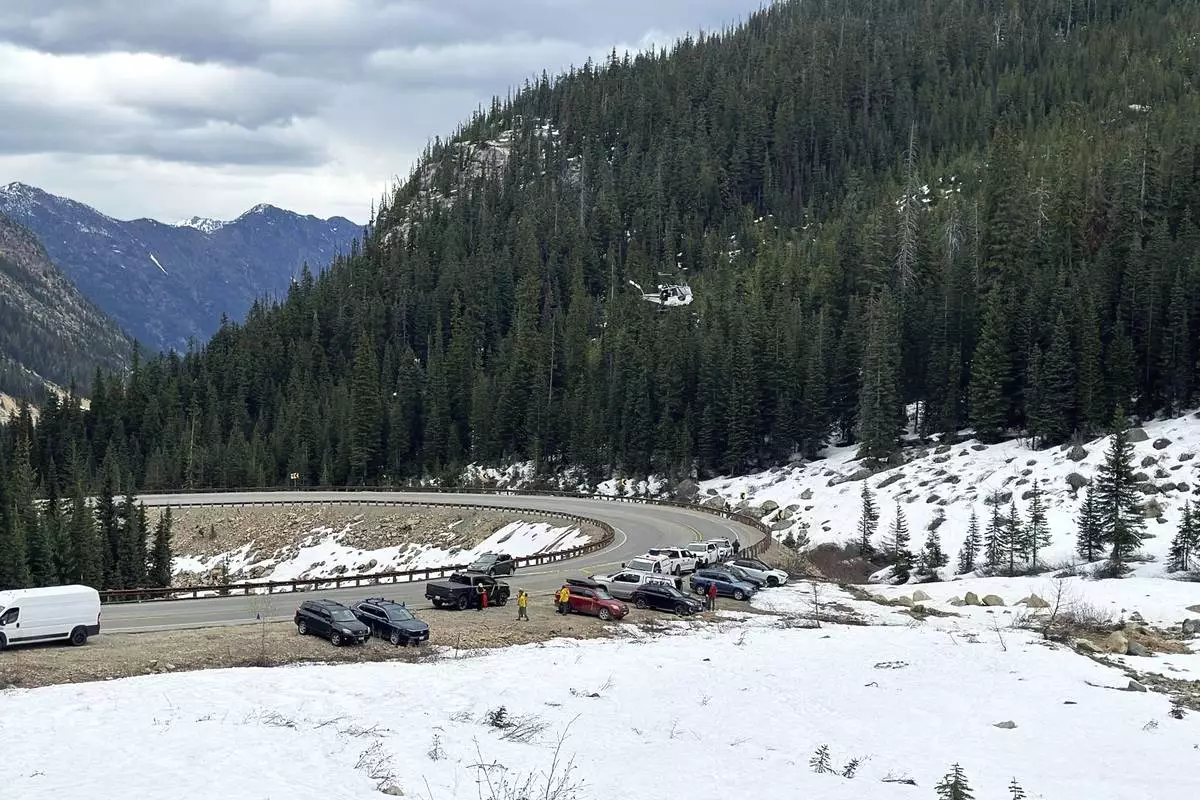

The Okanogan County Search and Rescue team responds to a climbing accident in the North Cascades mountains in Washington on Sunday, May 11, 2025. (Okanogan County Sheriff's Office via AP)
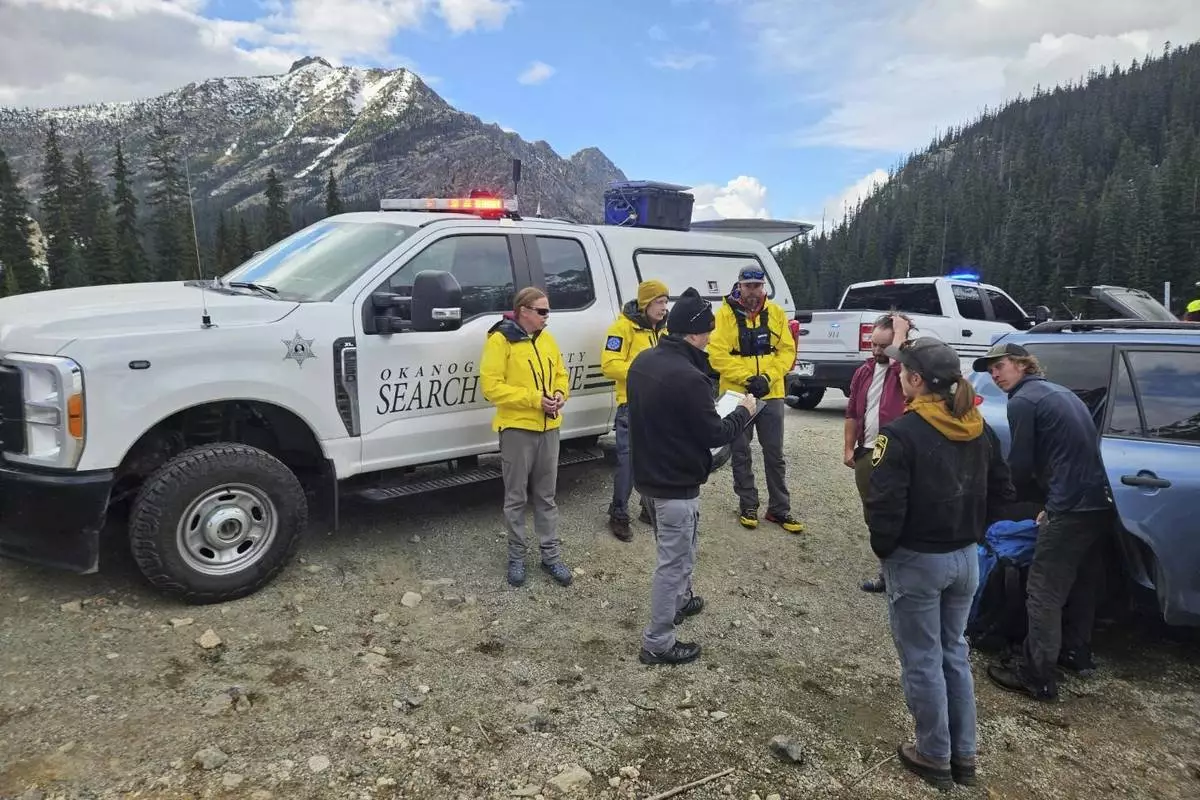

The Okanogan County Search and Rescue team responds to a climbing accident in the North Cascades mountains in Washington on Sunday, May 11, 2025. (Okanogan County Sheriff's Office via AP)