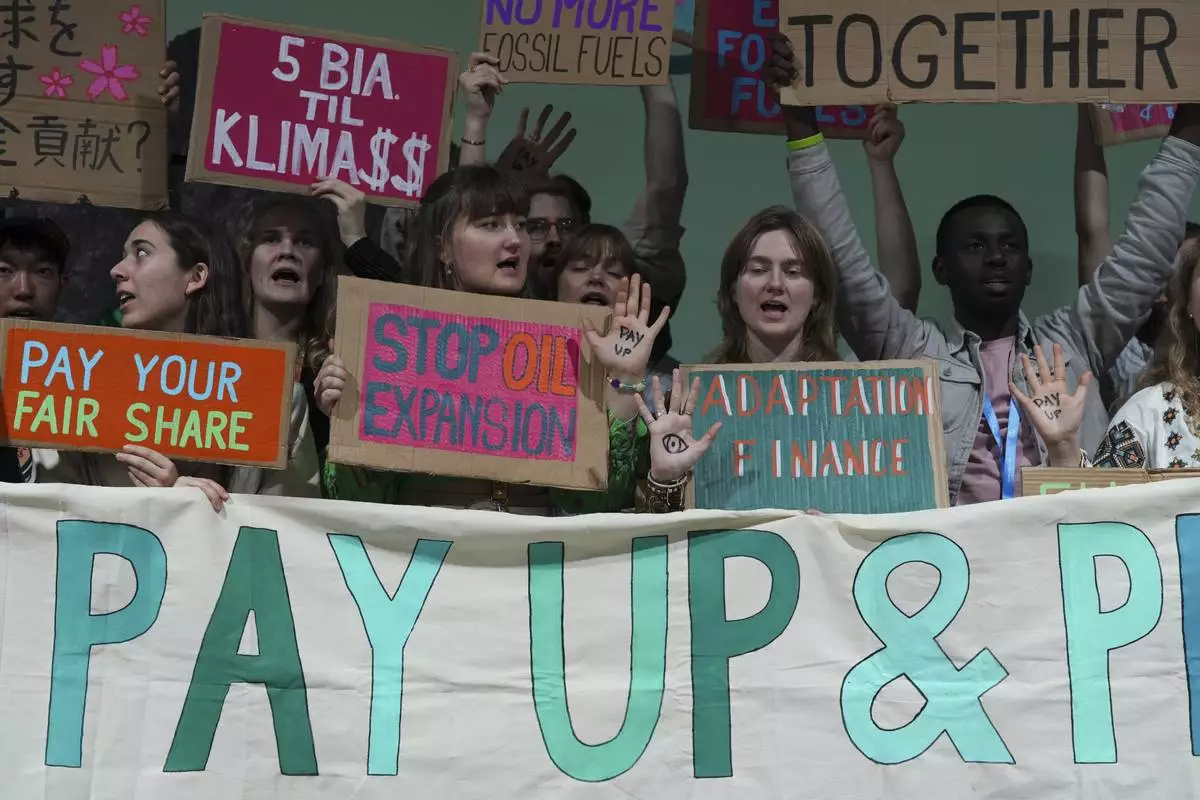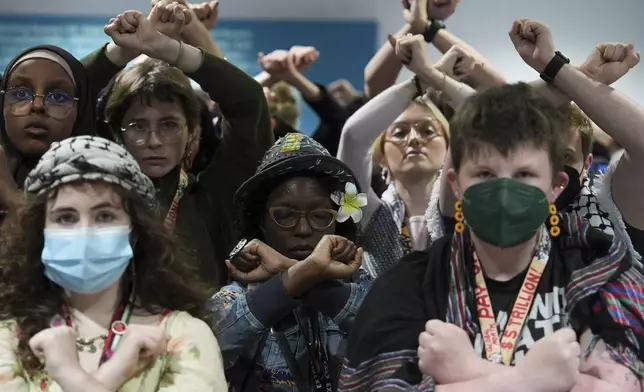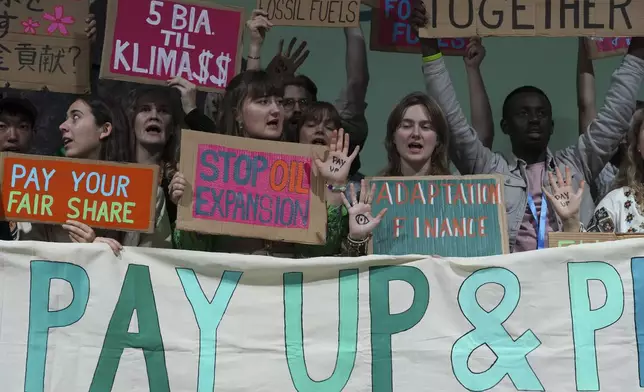BAKU, Azerbaijan (AP) — A new draft of a deal on cash to curb and adapt to climate change released Friday at the United Nations climate summit pledged $250 billion annually by 2035 from wealthy countries to poorer ones. The amount pleases the countries who will be paying, but not those on the receiving end.
It's more than double the previous goal of $100 billion a year set 15 years ago, but less than a quarter of the number requested by developing nations struck hardest by extreme weather. But rich nations say it's realistic and about the limit of what they can do.
Click to Gallery
Furniture is wrapped up during the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
Marina Silva, Brazil environment minister, speaks during a news conference at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
Activists hold an inflatable globe as they demonstrate in silence protesting a draft of a proposed deal for curbing climate change at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
Activists demonstrate in silence protesting a draft of a proposed deal for curbing climate change at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Joshua A. Bickel)
Demi Afasene, of Tuvalu, right, looks through a draft of a proposed deal for curbing climate change at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
An activist works on a display that reads in Portuguese persistir, that translates to persist, during the COP29 U.N. Climate SuRafiq Maqbool Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
A person reads a draft of a proposed deal for curbing climate change during the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
Toeolesulusulu Cedric Schuster, Samoa environment minister, waits outside a room at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
A draft of a proposed deal for curbing climate change sits on a table at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
Activists participate in a demonstration for climate finance at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)
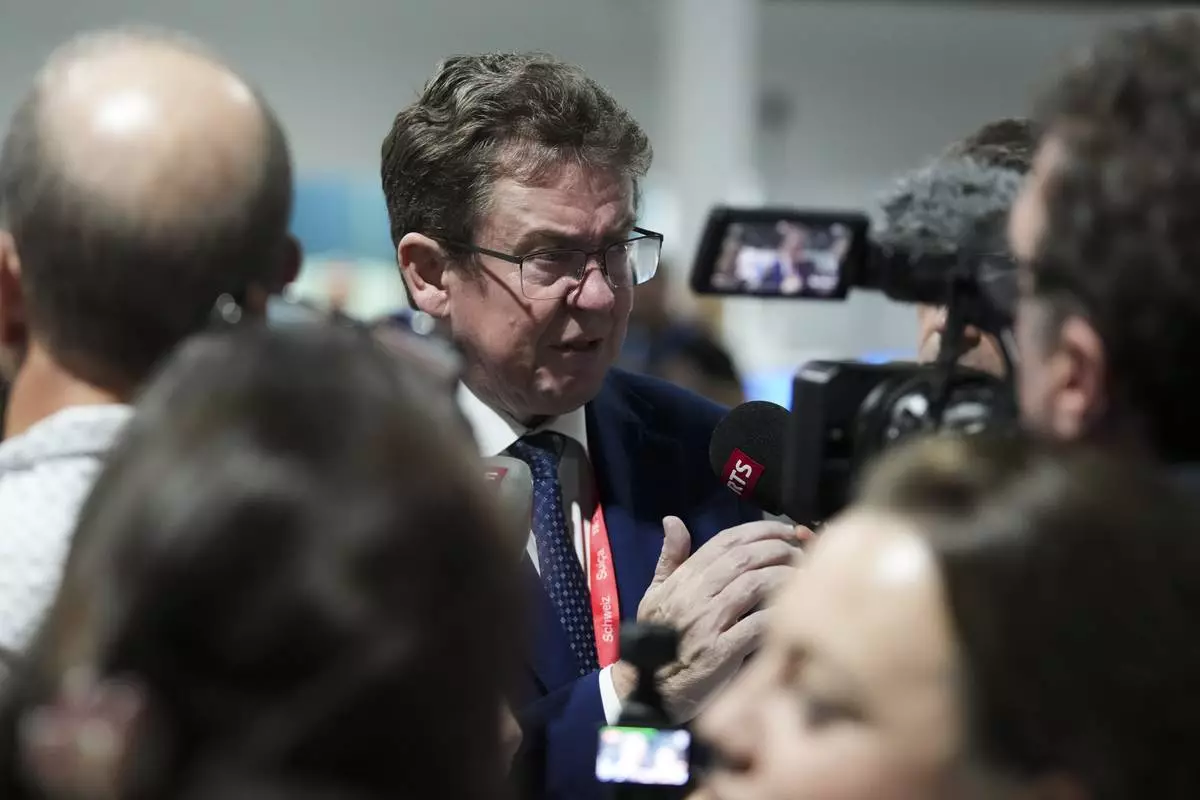
Albert Rosti, of Switzerland, speaks to members of the media at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)
Mukhtar Babayev, COP29 President, rehearses in the plenary at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
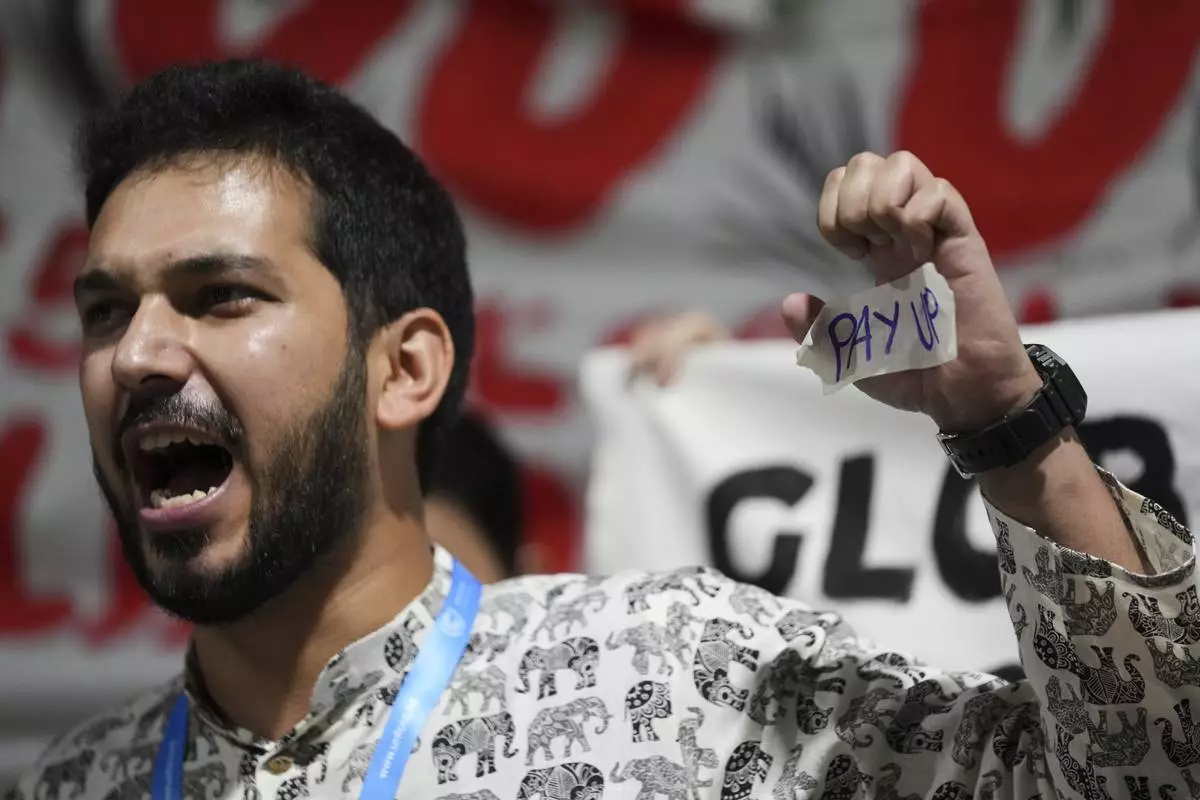
An activist displays "pay up" on his hand during a demonstration for climate finance at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)
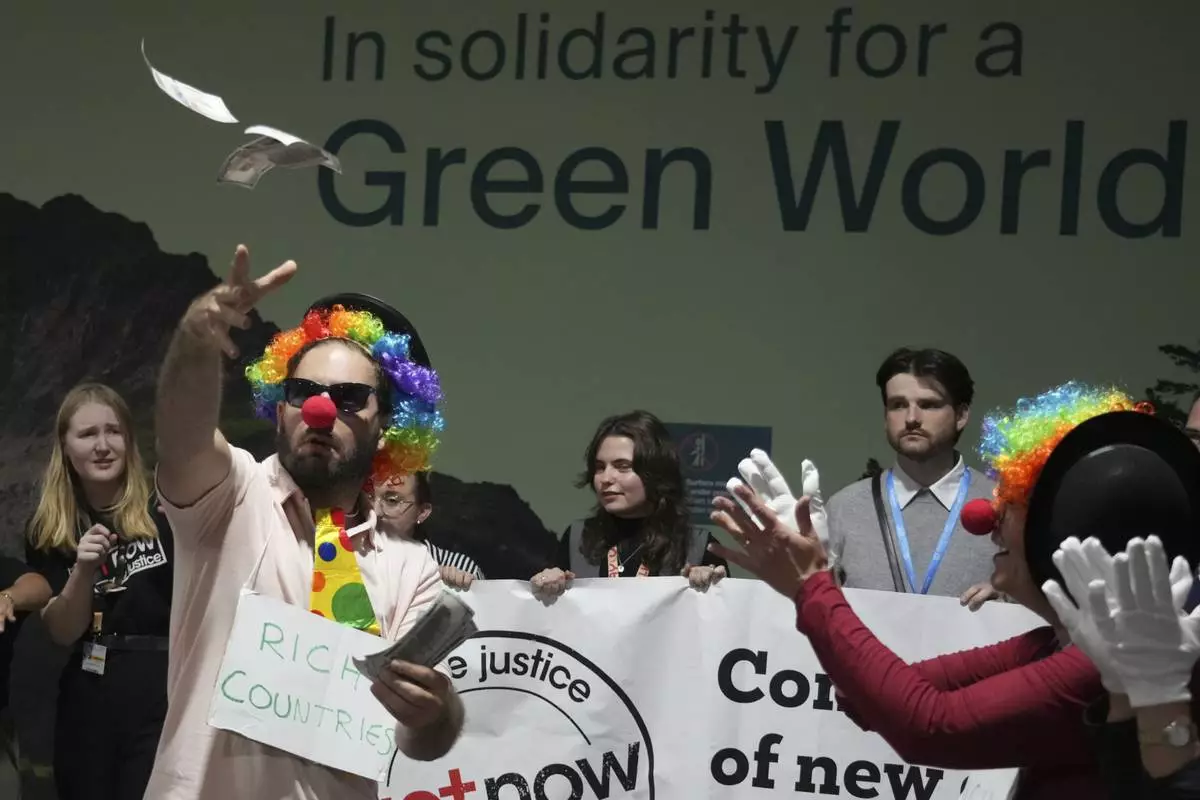
Activists dressed as clowns participate in a demonstration for climate finance at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)
Activists participate in a demonstration for climate finance at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
Activists participate in a demonstration for climate justice at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
The sun rises visible behind a transmission tower during the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
Dion George, South Africa environment minister, left, walks past a person in a dugong costume during the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
It struck a sour note for developing countries, which see conferences like this one as their biggest hope to pressure rich nations because they aren't part of meetings of the world's biggest economies.
"Our expectations were low, but this is a slap in the face,” said Mohamed Adow, from Power Shift Africa. “No developing country will fall for this. They have angered and offended the developing world.”
The proposal came from the top: the presidency of the climate talks — called COP29 — in Baku, Azerbaijan.
Lead negotiator Yalchin Rafiyev, Azerbaijan's deputy foreign minister, said the presidency hopes to push countries to go higher than $250 billion, saying “it doesn't correspond to our fair and ambitious goal. But we will continue to engage with the parties.”
Brazil responded with a higher number taken from a report by an expert financial panel appointed by the United Nations secretary-general. Brazil Environment Minister Marina Silva proposed $300 billion a year until 2035 when the number would jump to $390 billion a year.
Brazil is set to host next year's COP30. When asked whether lack of an ambitious agreement at COP29 would put Brazil in a bad position next year, Silva said the consequences were bigger that that.
“More than just hurting COP30, it will hurt the life of all of us and hurt the conditions that give us life on Earth,” she said.
Climate Analytics CEO Bill Hare, a veteran negotiator, said the presidency's figure is likely just the first of two or three proposals.
“We’re in for a long night and maybe two nights before we actually reach agreement on this,” Hare said.
Just like last year's initial proposal, which was soundly rejected, this plan is “empty” on what climate analysts call “mitigation” or efforts to reduce emissions from or completely quit coal, oil and natural gas, Hare said.
Tina Stege, Marshall Islands' climate envoy, called the drafts “shameful.”
“It is incomprehensible that ... (we) receive only sympathy and no real action from wealthy nations,” she said.
The Least Developed Countries negotiating group said they were “deeply concerned” about the draft deal. “It dilutes the existing commitments of the developed countries and does not reflect the ambition needed for global climate action,” their statement said.
“It is a disgrace that despite full awareness of the devastating climate crises afflicting developing nations and the staggering costs of climate action — amounting to trillions — developed nations have only proposed a meagre $250 billion per year," said Harjeet Singh of the Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty.
Experts put the need at $1.3 trillion for developing countries to cover damages resulting from extreme weather, help those nations adapt to a warming planet and wean themselves from fossil fuels, with more generated by each country internally.
The amount in any deal reached at COP negotiations — often considered a “core” — will then be mobilized or leveraged for greater climate spending. But much of that means loans for countries drowning in debt.
Iskander Erzini Vernoit, director of Moroccan climate think-tank Imal Initiative for Climate and Development, said “the EU and the U.S. and other developed countries cannot claim to be committed to the Paris Agreement while putting forward such amounts."
Countries reached the Paris Agreement in 2015, pledging to keep warming below 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 Fahrenheit) since pre-industrial times. The world is now at 1.3 degrees Celsius (2.3 degrees Fahrenheit), according to the U.N.
Activists were angered, too. Several dozen marched in silence outside the halls where delegates meet, raising and crossing their arms in front of themselves to indicate rejection of the draft text.
Nikki Reisch, director of the climate and energy program at the Center for International Environmental Law, said the offering was unacceptable not just because the money is low, but because “it's really designed to escape and evade the legal obligation that developed countries have” to pay for the climate change they have largely caused.
Switzerland environment minister Albert Rösti said it was important that the climate finance number is realistic.
“I think a deal with a high number that will never be realistic, that will never be paid … will be much worse than no deal,” he said.
A lack of a bigger number from European nations and the U.S. means that the “deal is clearly moving toward the direction of China playing a more prominent role in helping other Global South countries,” said Li Shou of the Asia Society Policy Institute.
“We think this is at least a text we can work with. Now we have a map on the way forward instead of nowhere where we don’t know where we are going," said German climate envoy Jennifer Morgan.
Analysts said the proposed deal is the start of what could likely be more money.
“This can be a good down payment that will allow for further climate action in developing countries,” said Melanie Robinson, global climate program director at the World Resources Institute. “But there is scope for this to go above $250 billion.”
Rob Moore, associate director at E3G, said that whatever figure is agreed “will need to be the start and not the end" of climate cash promises.
"If developed countries can go further they need to say so fast to make sure we get a deal at COP29,” he said.
Associated Press journalists Ahmed Hatem, Olivia Zhang and Aleksandar Furtula contributed to this report.
The Associated Press’ climate and environmental coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.

Furniture is wrapped up during the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
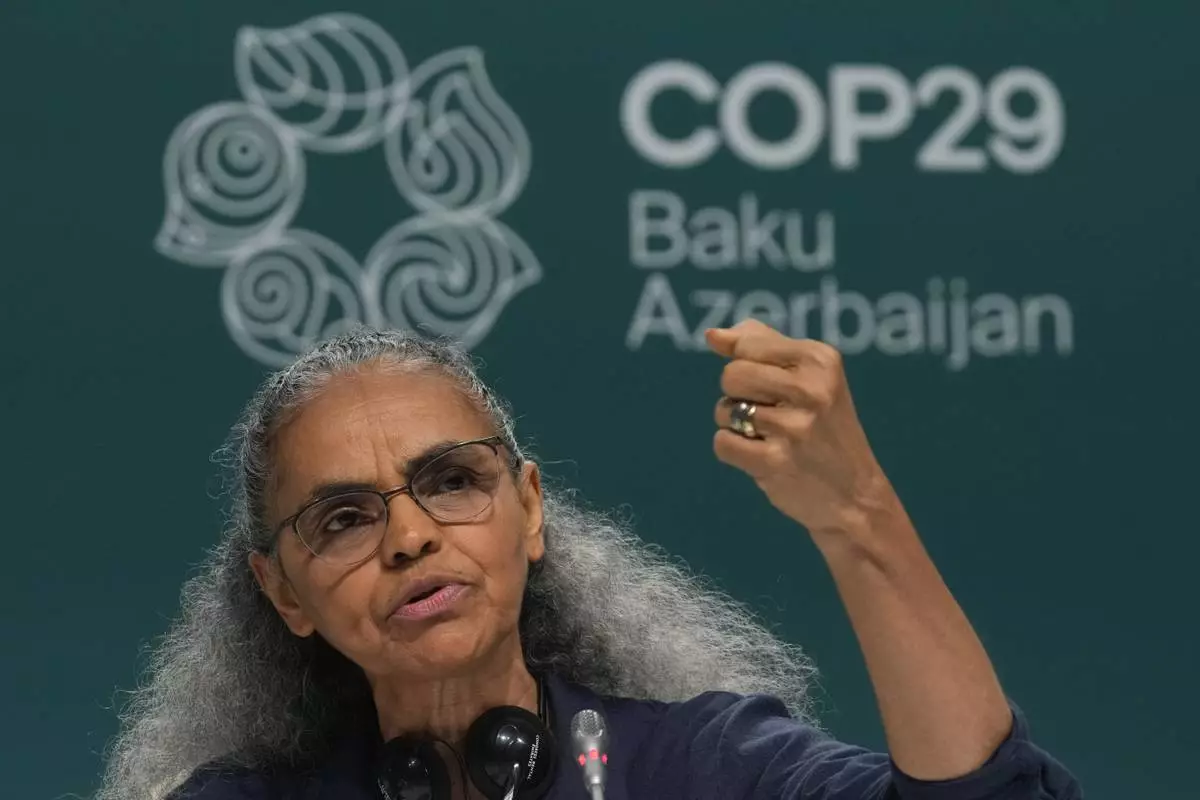

Marina Silva, Brazil environment minister, speaks during a news conference at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
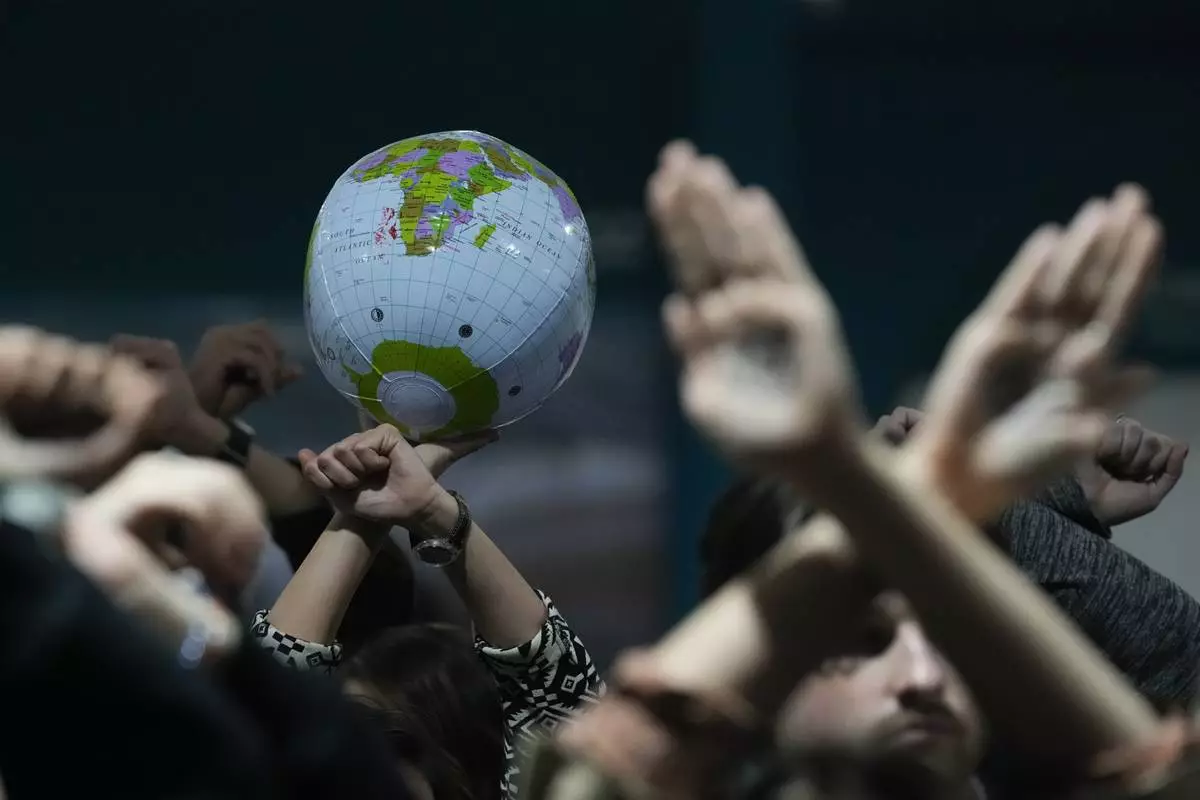

Activists hold an inflatable globe as they demonstrate in silence protesting a draft of a proposed deal for curbing climate change at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
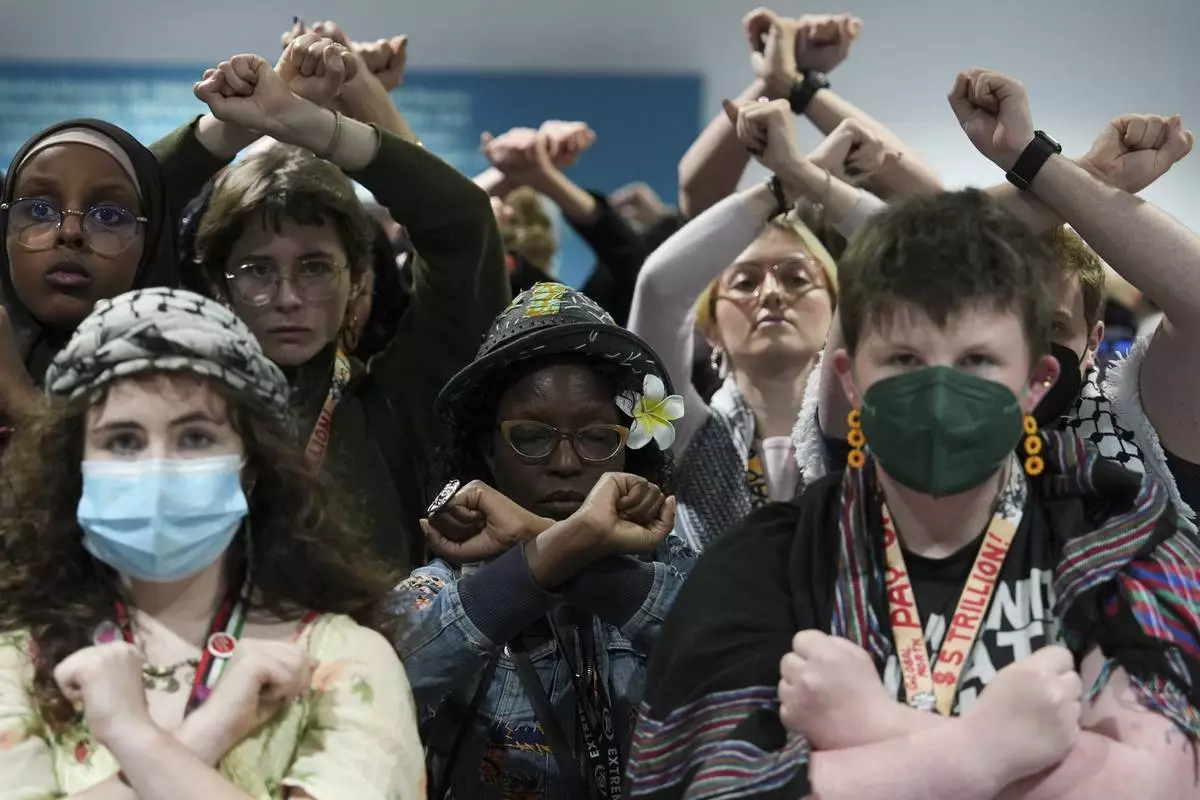

Activists demonstrate in silence protesting a draft of a proposed deal for curbing climate change at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Joshua A. Bickel)
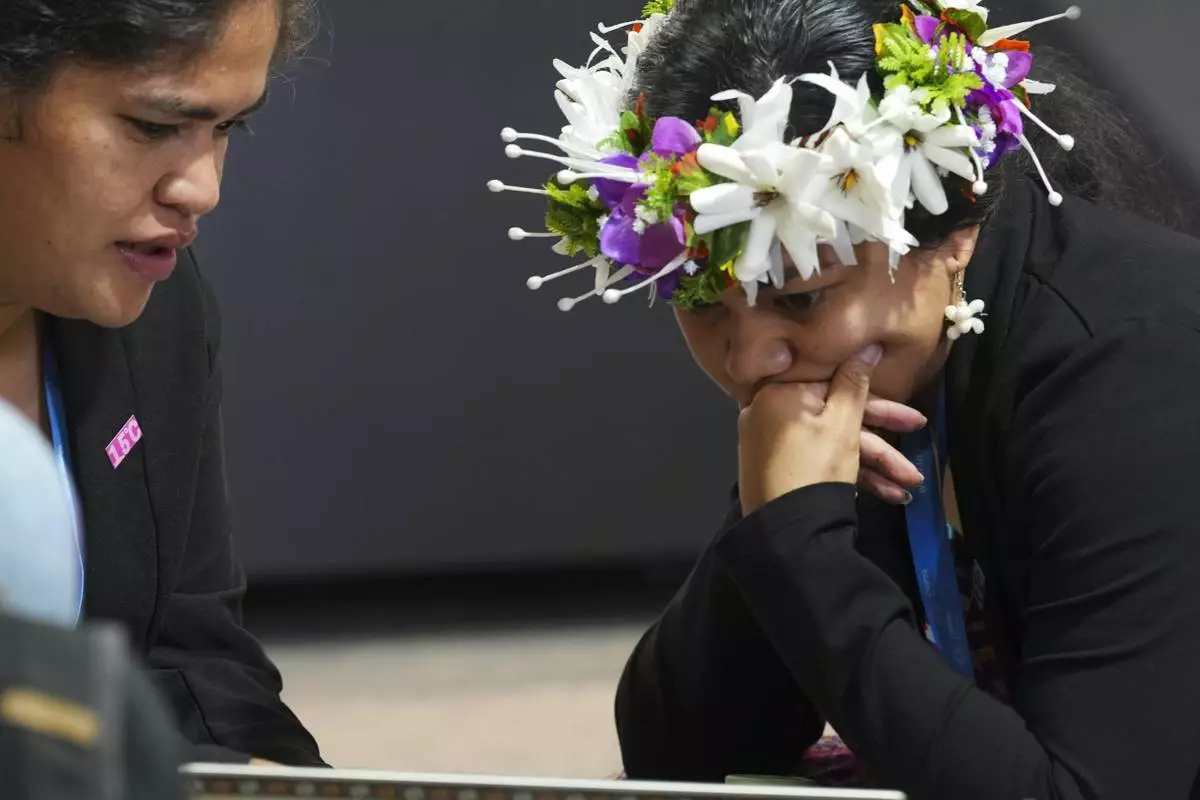

Demi Afasene, of Tuvalu, right, looks through a draft of a proposed deal for curbing climate change at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
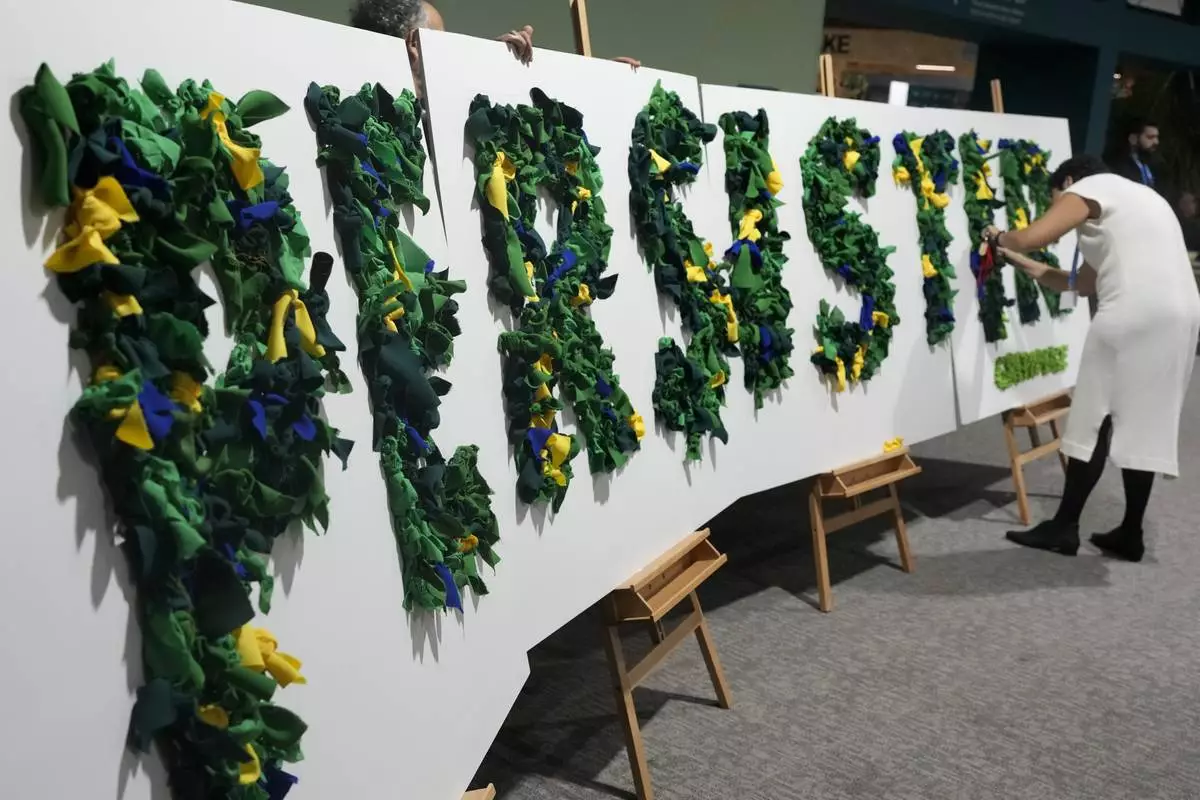

An activist works on a display that reads in Portuguese persistir, that translates to persist, during the COP29 U.N. Climate SuRafiq Maqbool Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)

A person reads a draft of a proposed deal for curbing climate change during the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)

Toeolesulusulu Cedric Schuster, Samoa environment minister, waits outside a room at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)

A draft of a proposed deal for curbing climate change sits on a table at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
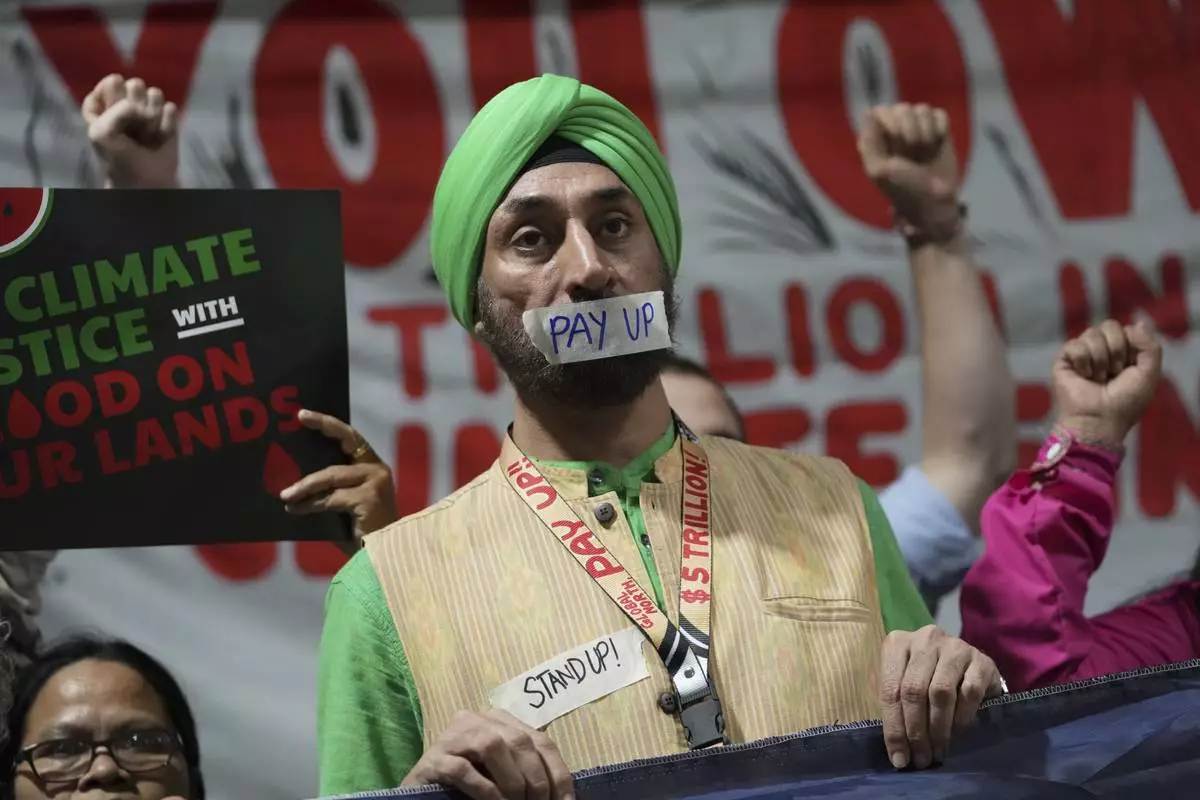

Activists participate in a demonstration for climate finance at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)

Albert Rosti, of Switzerland, speaks to members of the media at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)

Mukhtar Babayev, COP29 President, rehearses in the plenary at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)

An activist displays "pay up" on his hand during a demonstration for climate finance at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)

Activists dressed as clowns participate in a demonstration for climate finance at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)
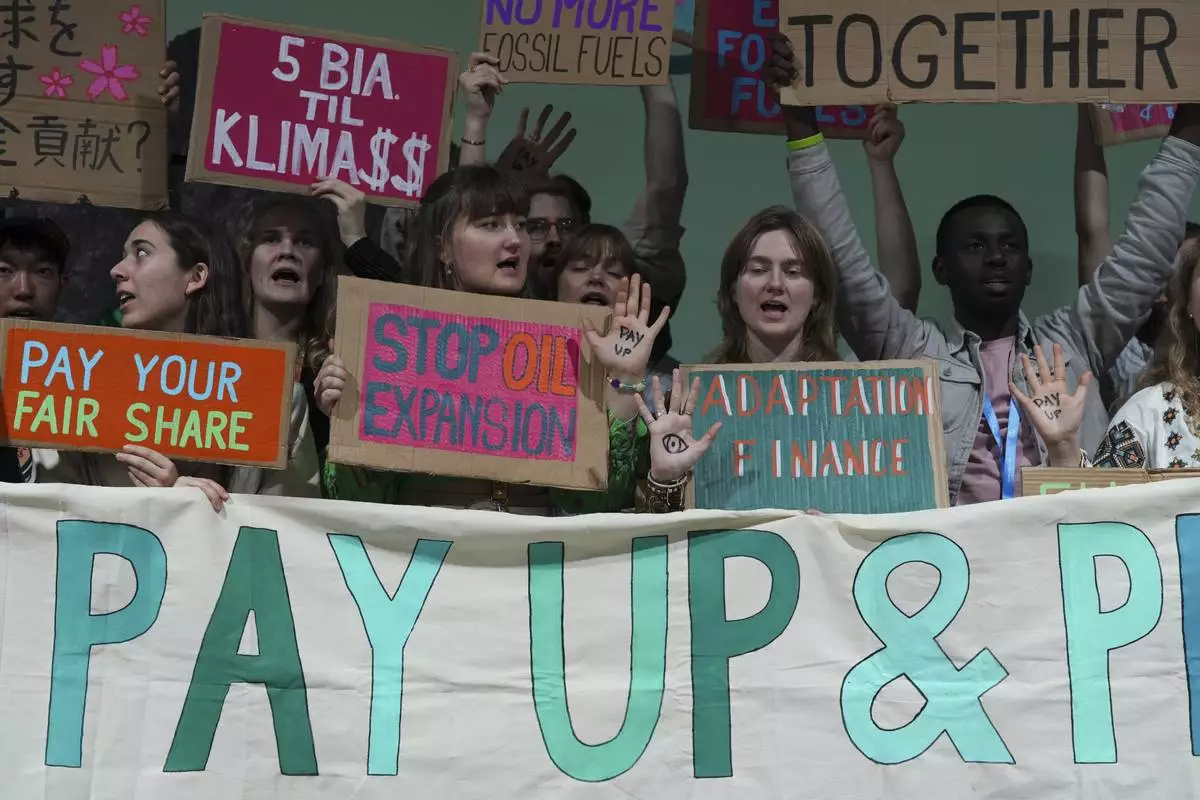
Activists participate in a demonstration for climate finance at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)

Activists participate in a demonstration for climate justice at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)

The sun rises visible behind a transmission tower during the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)

Dion George, South Africa environment minister, left, walks past a person in a dugong costume during the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Friday, Nov. 22, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
SEOUL, South Korea (AP) — South Korea’s fire agency says 96 people have been confirmed dead after a plane caught fire during a landing at an airport in the country’s south.
The fire engulfed the aircraft carrying 181 people when it skidded off the runway just after landing and struck a barrier on Sunday. The country’s emergency office said its landing gear appeared to have malfunctioned.
The National Fire Agency said that a total of 96 people on board have been found dead as a result of the incident.
THIS IS A BREAKING NEWS UPDATE. AP’s earlier story is below:
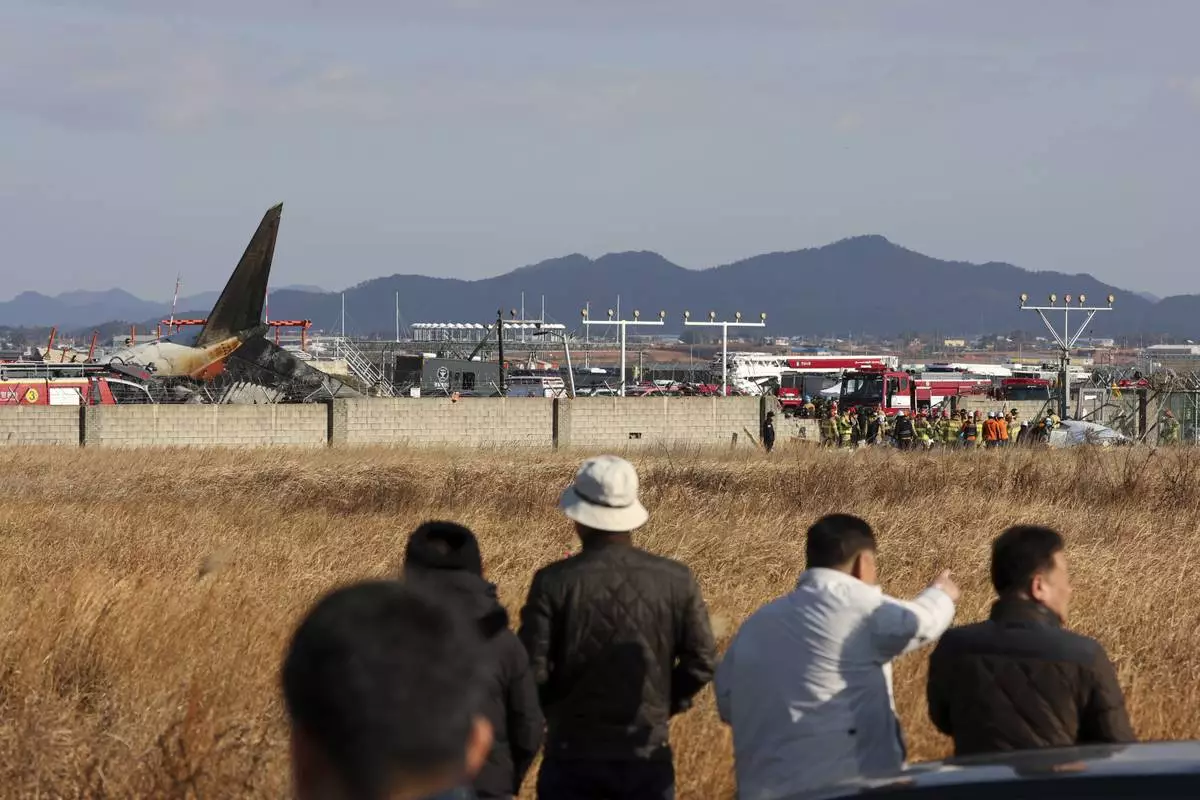
A passenger plane burst into flames Sunday after it skid off a runway at a South Korean airport and slammed into a concrete fence when its front landing gear apparently failed to deploy, killing at least 85 people, officials said, in one of the country's worst aviation disasters.
The National Fire Agency said rescuers raced to pull people from the Jeju Air passenger plane carrying 181 people at the airport in the town of Muan, about 290 kilometers (180 miles) south of Seoul. The Transport Ministry identified the plane as a 15-year-old Boeing 737-800 jet and said the crash happened at 9:03 a.m. local time.
At least 85 people — 46 women and 39 men — died in the fire, the agency said. Emergency workers pulled out two people, both crew members, and local health officials said they remain conscious. It said it deployed 32 fire trucks and several helicopters to contain the fire.
Footage of the crash aired by YTN television showed the Jeju Air plane skidding across the airstrip, apparently with its landing gear still closed, and colliding head-on with a concrete wall on the outskirts of the facility. Other local TV stations aired footage showing thick pillows of black smoke billowing from the plane engulfed with flames.
Lee Jeong-hyeon, chief of the Muan fire station, told a televised briefing that rescue workers are continuing to search for bodies scattered by the crash impact. The plane was completely destroyed, with only the tail assembly remaining recognizable among the wreckage, he said.
Workers were looking into various possibilities about what caused the crash, including whether the aircraft was struck by birds that caused mechanical problems, Lee said. Senior Transport Ministry official Joo Jong-wan separately told reporters that government investigators arrived at the site to investigate the cause of the crash and fire.
Emergency officials in Muan said the plane’s landing gear appeared to have malfunctioned. The Transport Ministry said the plane was returning from Bangkok and its passengers include two Thai nationals.
Thailand’s prime minister, Paetongtarn Shinawatra, expressed deep condolences to the families of those affected by the accident through a post on social platform X. Paetongtarn said she had ordered the Ministry of Foreign Affairs to provide assistance immediately.
Jeju Air in a statement expressed its “deep apology” over the crash and said it will do its “utmost to manage the aftermath of the accident.”
It’s one of the deadliest disasters in South Korea’s aviation history. The last time South Korea suffered a large-scale air disaster was in 1997, when a Korean Airline plane crashed in Guam, killing 228 people on board. In 2013, an Asiana Airlines plane crash-landed in San Francisco, killing three and injuring approximately 200.
Sunday’s accident was also one of the worst landing mishaps since a July 2007 crash that killed all 187 people on board and 12 others on the ground when an Airbus A320 slid off a slick airstrip in Sao Paulo and collided with a nearby building, according to data compiled by the Flight Safety Foundation, a nonprofit group aimed at improving air safety.
The incident came as South Korea is embroiled into a huge political crisis triggered by President Yoon Suk Yeol’s stunning imposition of martial law and ensuing impeachment. Last Friday, South Korean lawmakers impeached acting President Han Duck-soo and suspended his duties, leading Deputy Prime Minister Choi Sang-mok to take over.
Choi ordered officials to employ all available resources to rescue the passengers and crew before he headed to Muan. Yoon’s office said his chief secretary, Chung Jin-suk, will preside over an emergency meeting between senior presidential staff later on Sunday to discuss the crash.

Firefighters and rescue team members work at Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Cho Nam-soo/Yonhap via AP)
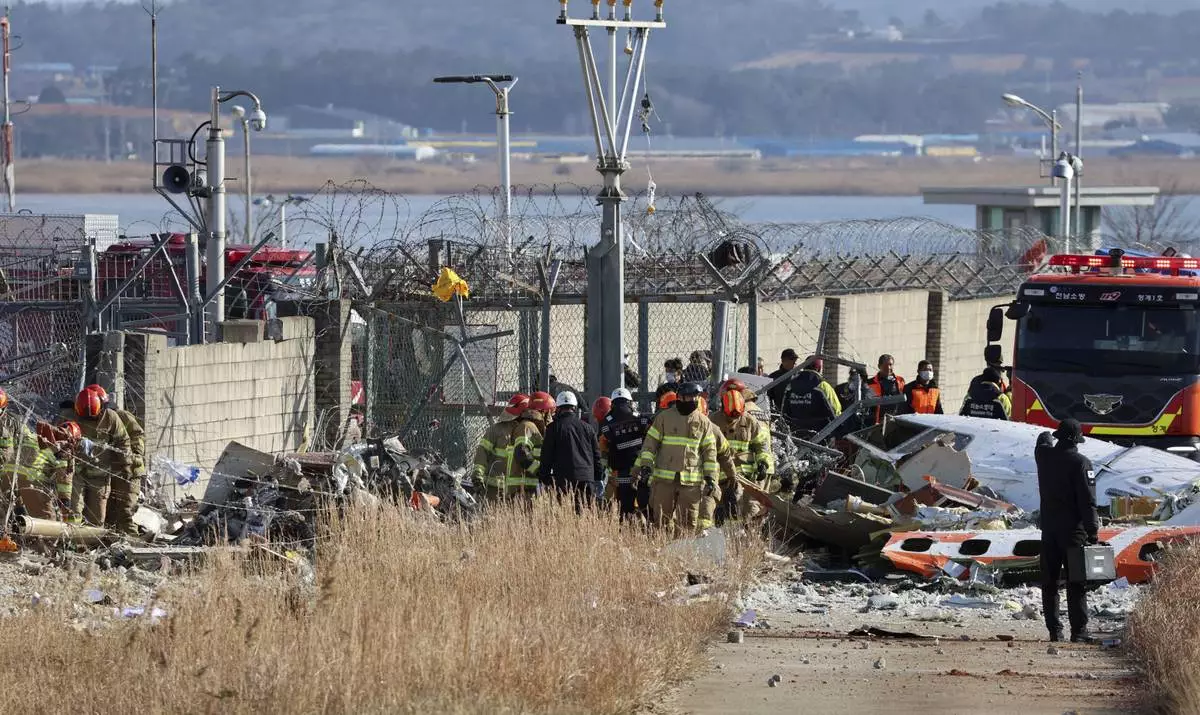

Firefighters and rescue team members work at Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Cho Nam-soo/Yonhap via AP)
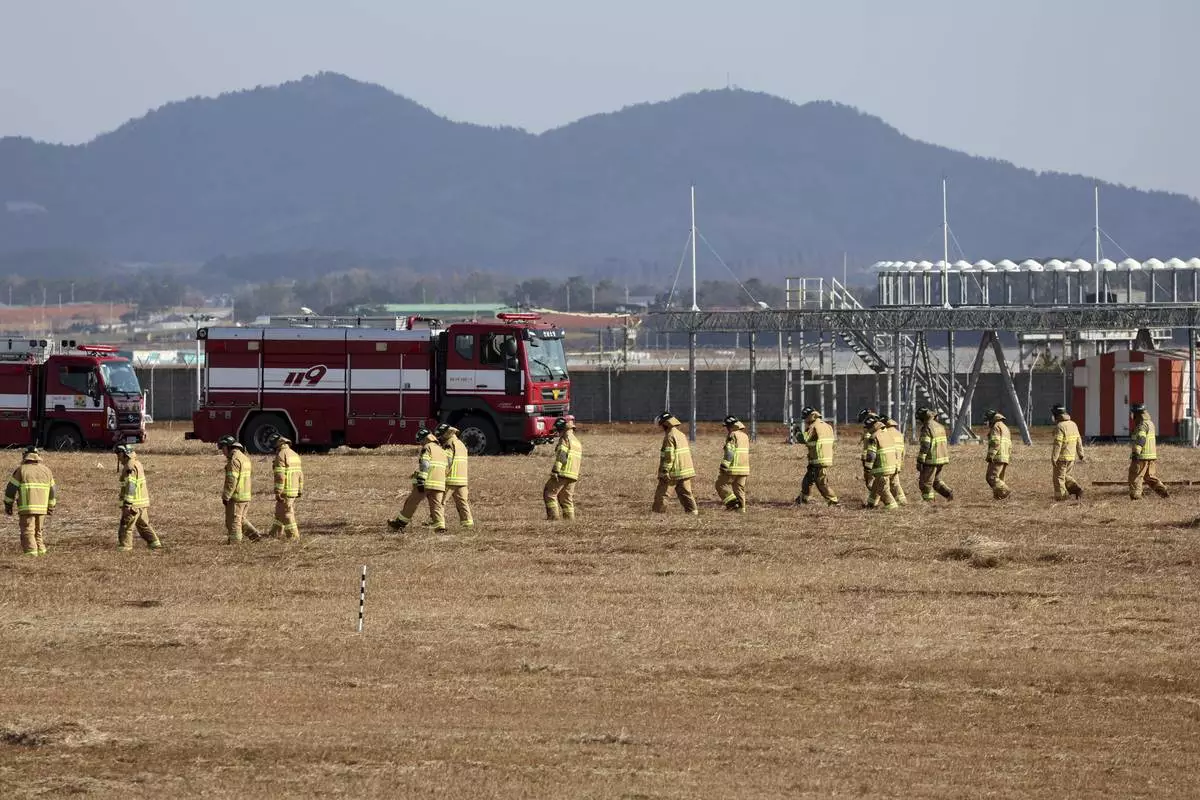

Firefighters and rescue team members work at Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Cho Nam-soo/Yonhap via AP)
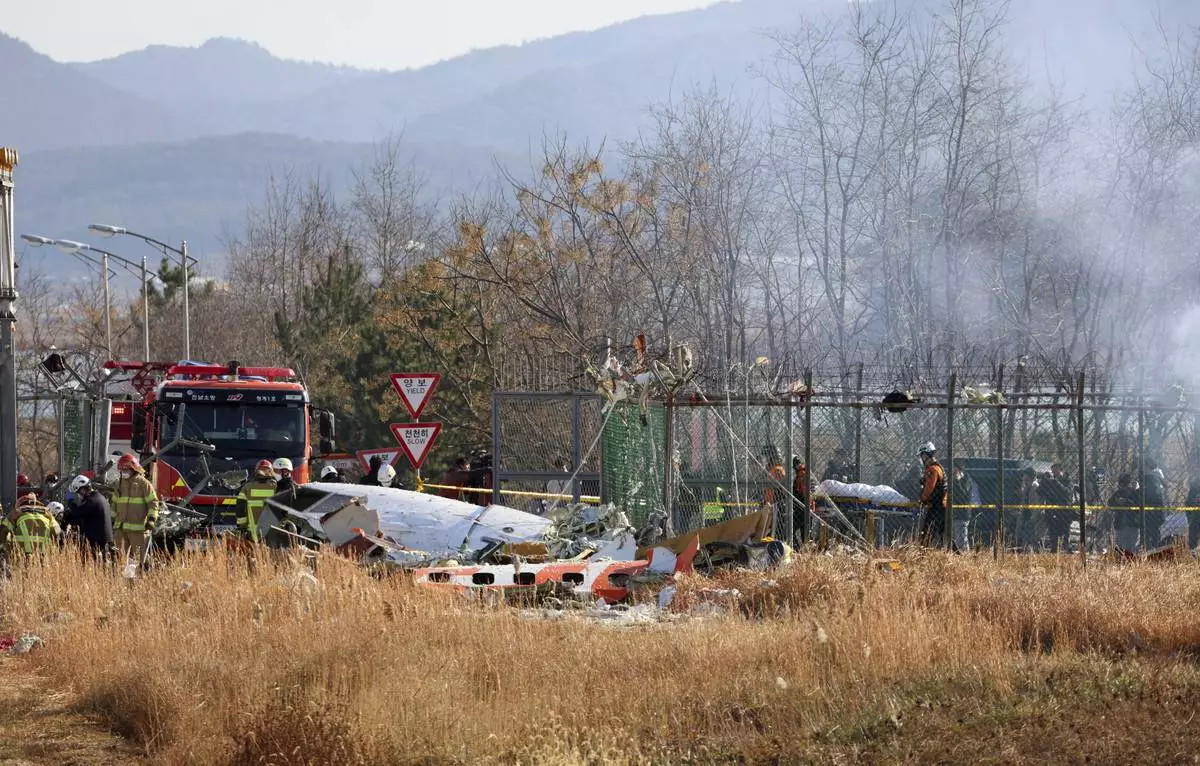

Firefighters and rescue team members work at Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Cho Nam-soo/Yonhap via AP)
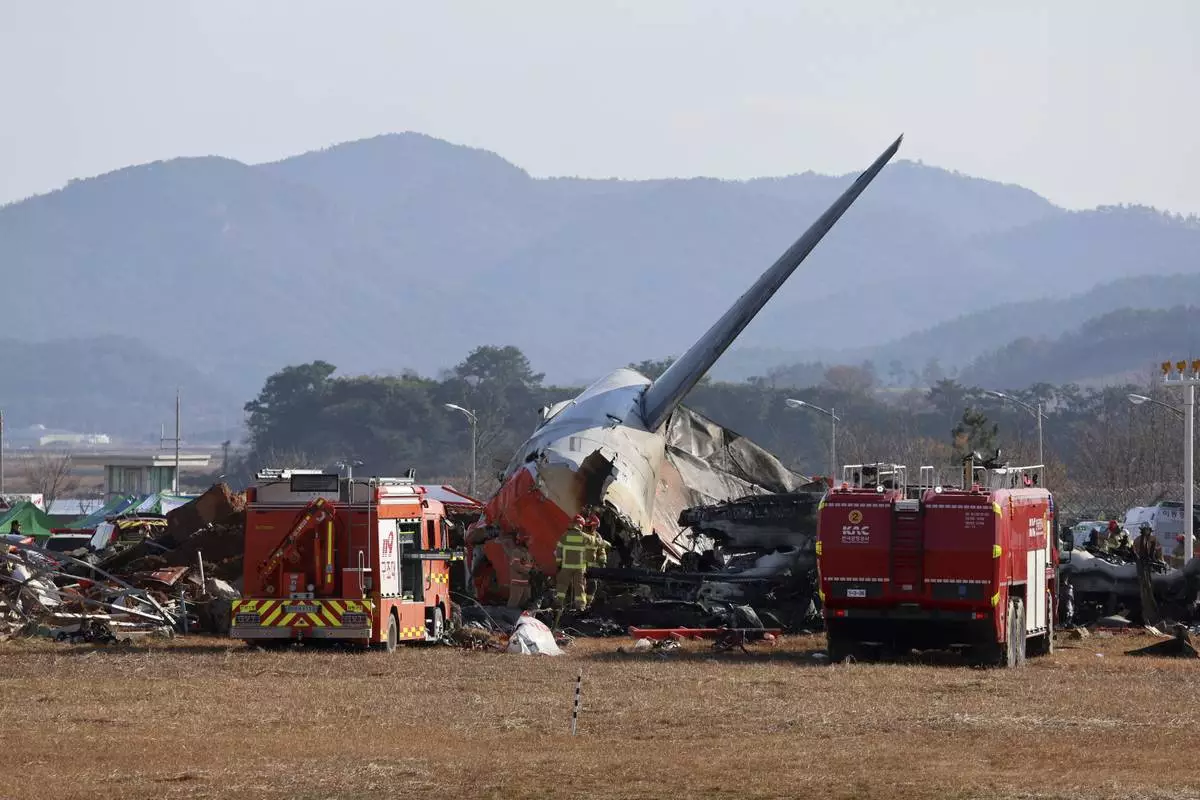

Firefighters and rescue team members work at Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Cho Nam-soo/Yonhap via AP)
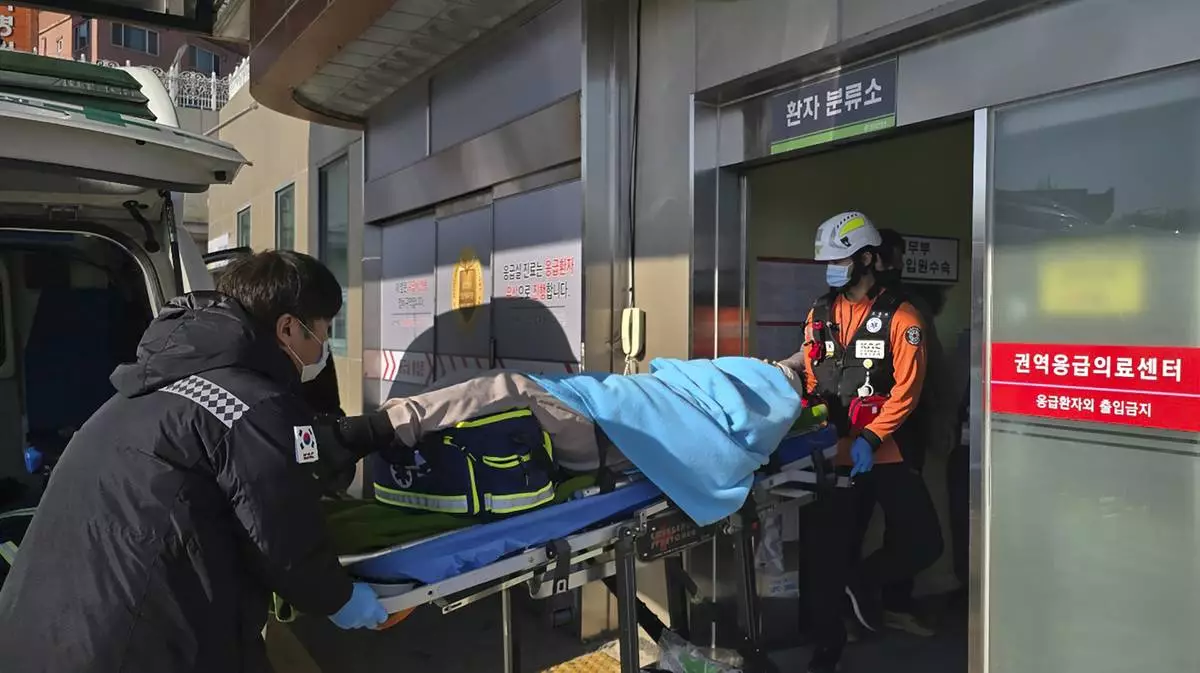

A victim rescued from a plane crash is transported to a hospital in Mokpo, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Cho Geun-young/Yonhap via AP)
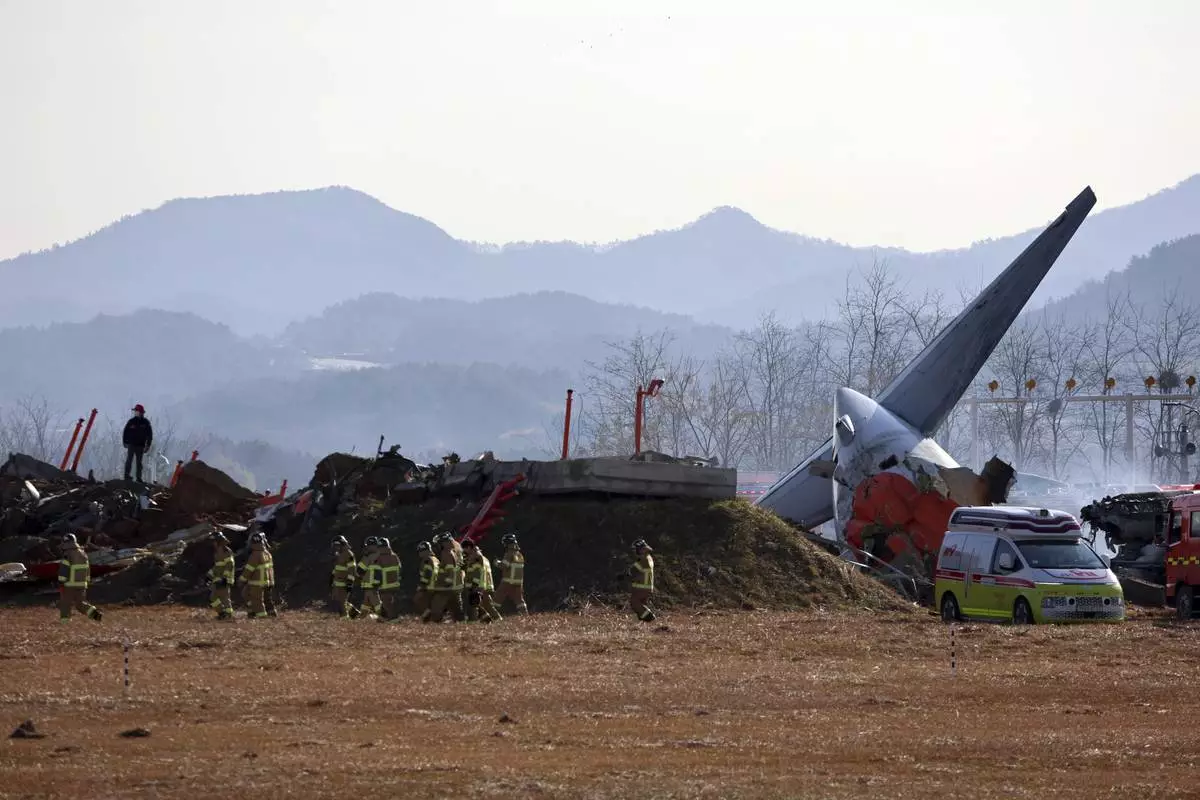

Firefighters and rescue team members work at Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Cho Nam-soo/Yonhap via AP)
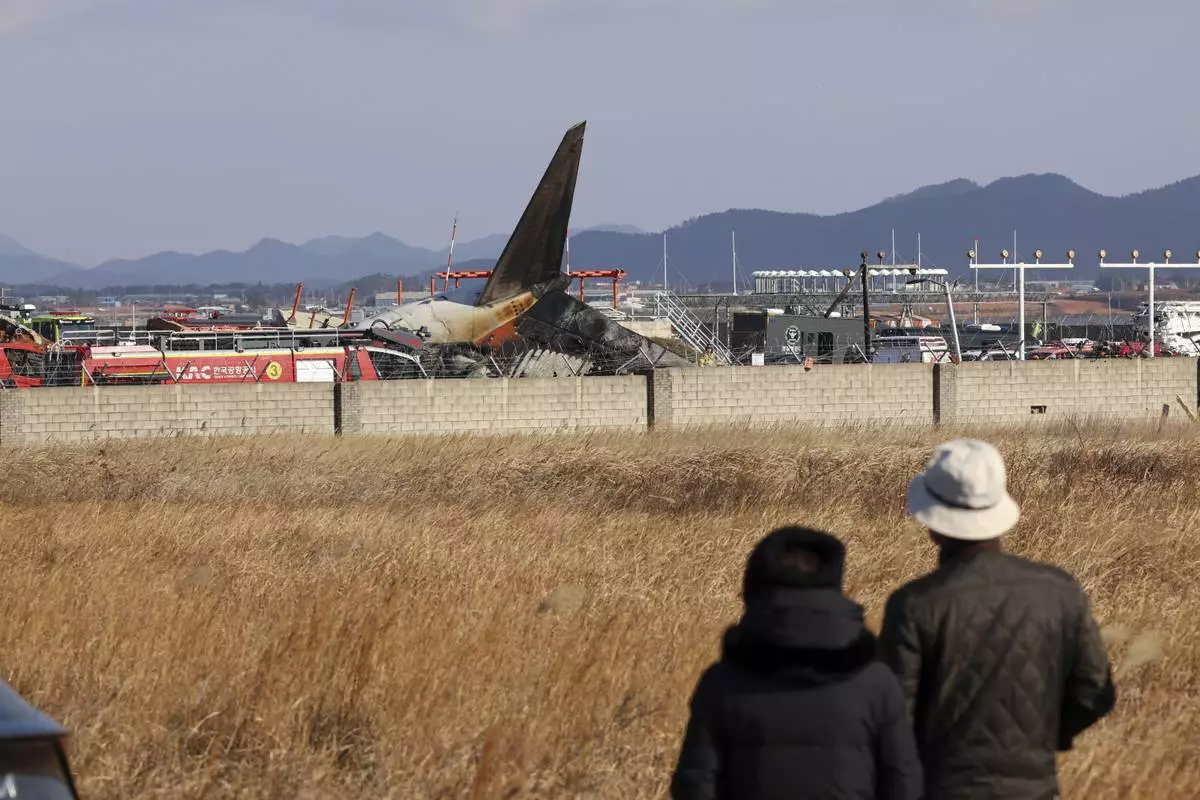

People watch as firefighters and rescue team members work at Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Cho Nam-soo/Yonhap via AP)
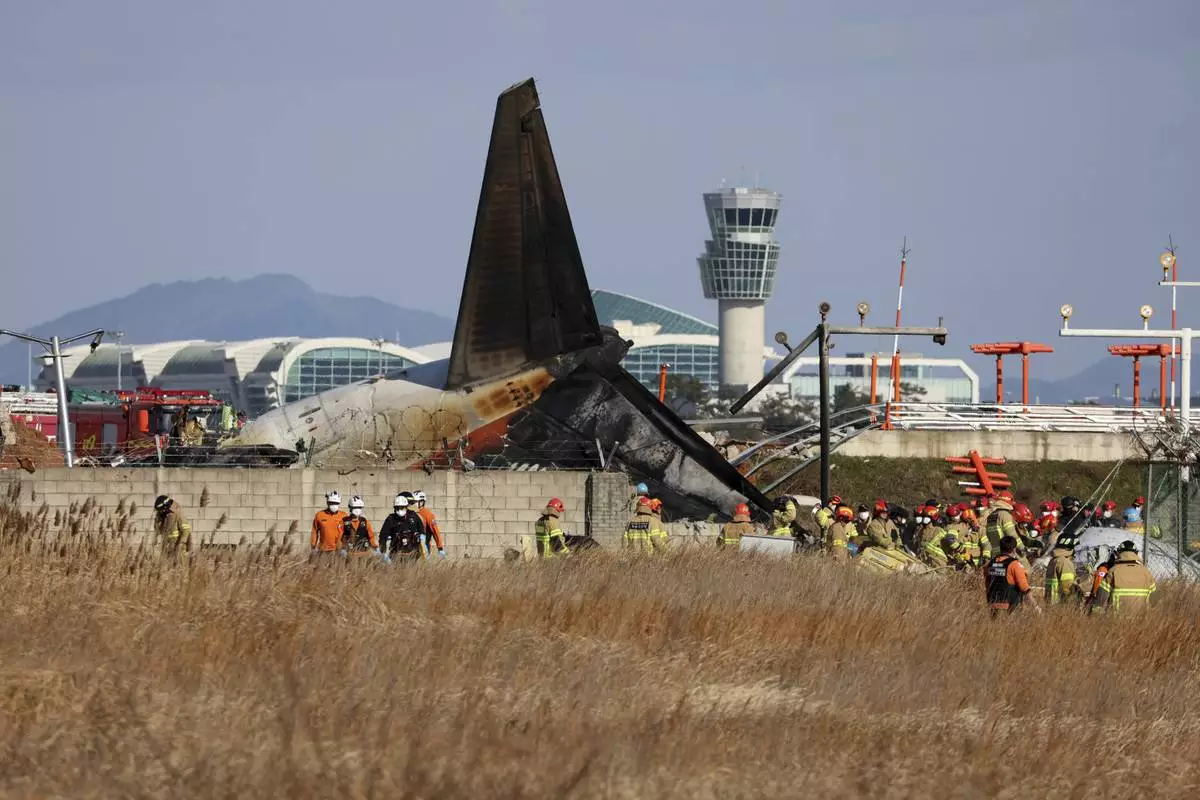

Firefighters and rescue team members work at Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Cho Nam-soo/Yonhap via AP)
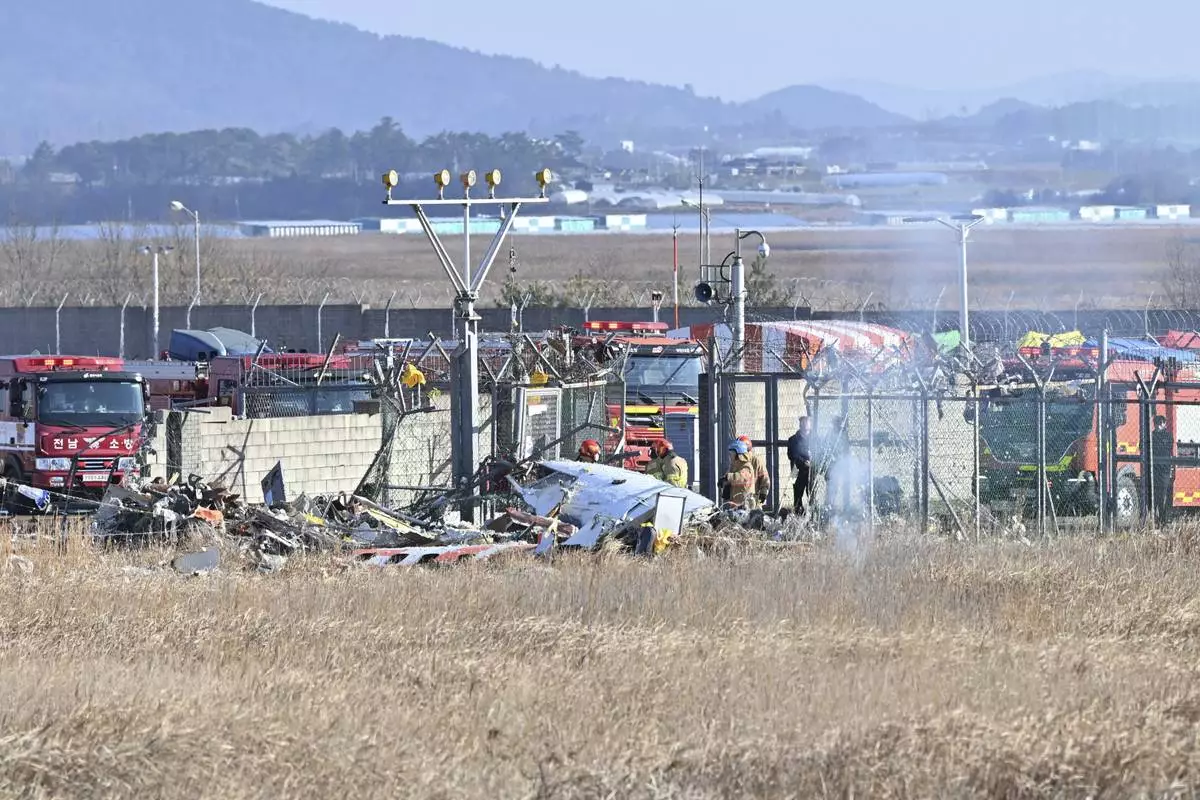

Firefighters and rescue team members work at Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Lee Young-ju/Newsis via AP)
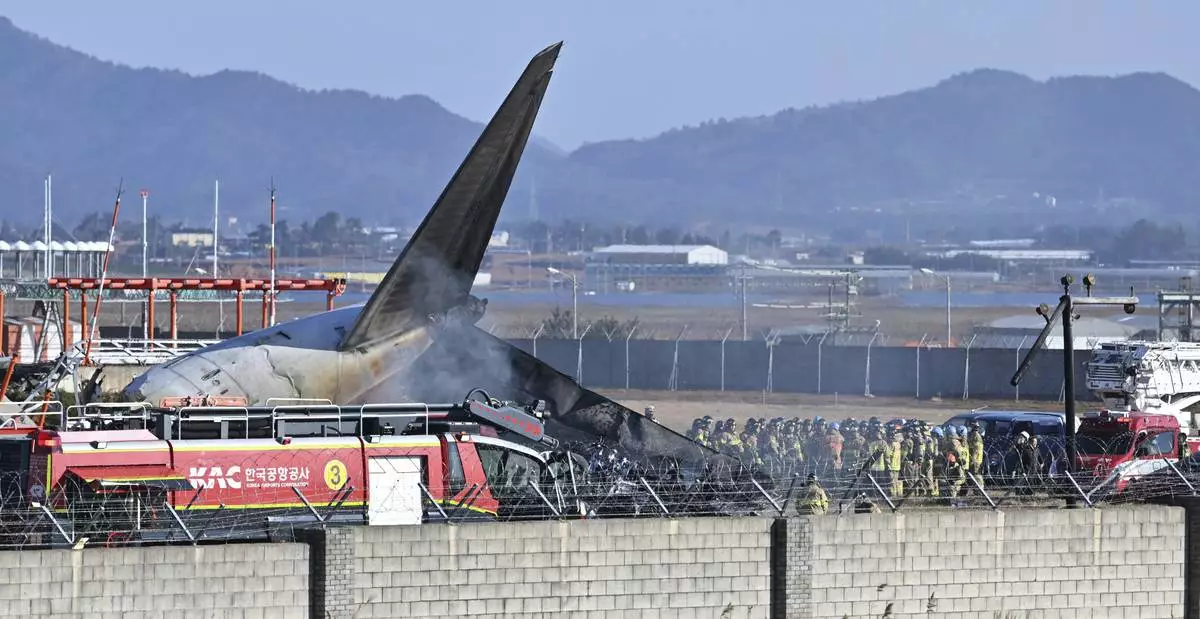

Firefighters and rescue team members work on the runway of Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Lee Young-ju/Newsis via AP)
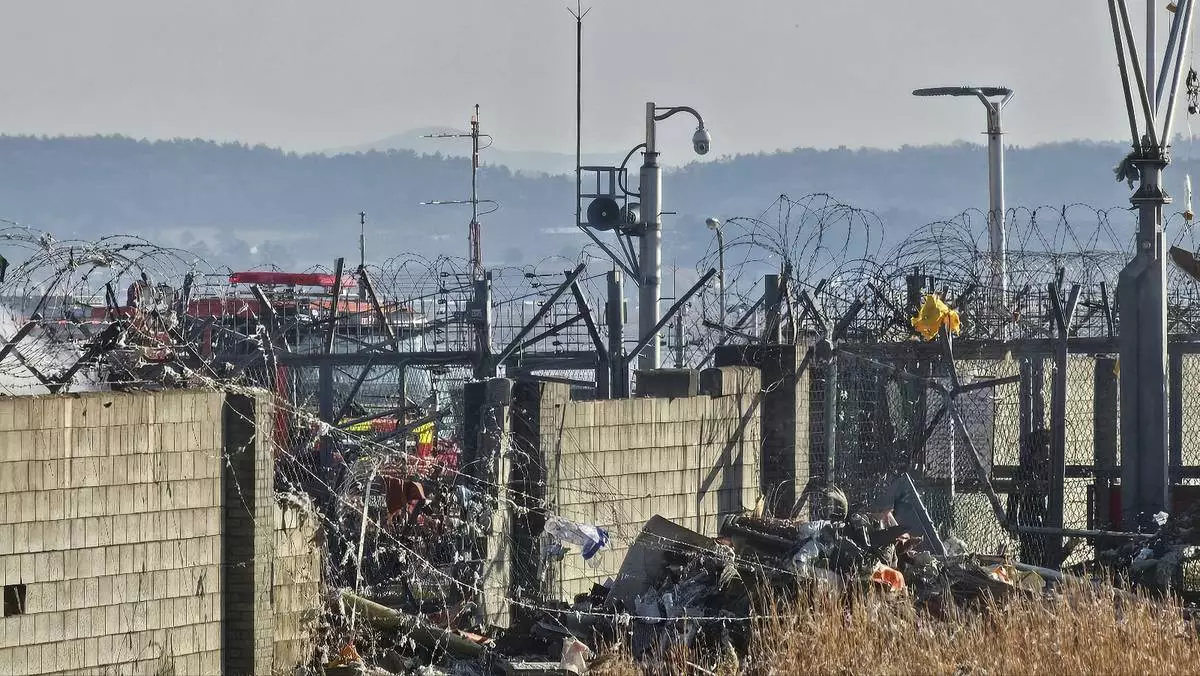

A rescue team works to extinguish a fire at the Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Maeng Dae-hwan/Newsis via AP)
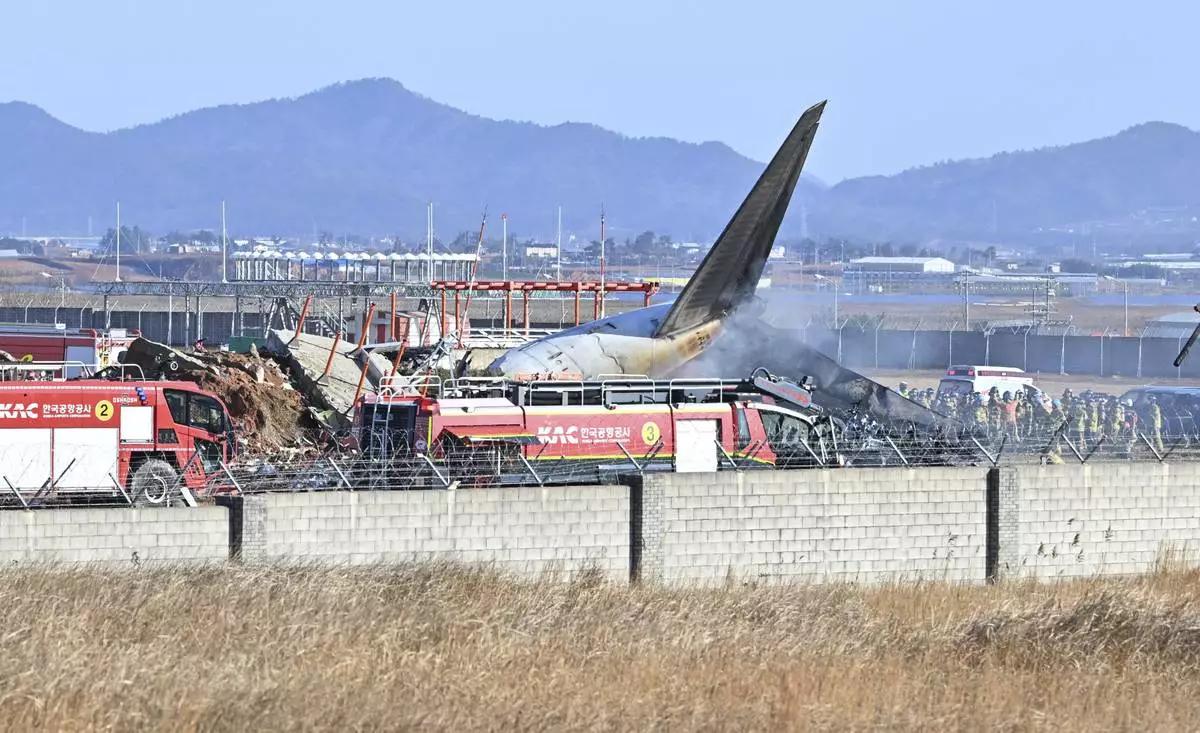

Firefighters and rescue team members work on the runway of Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Lee Young-ju/Newsis via AP)
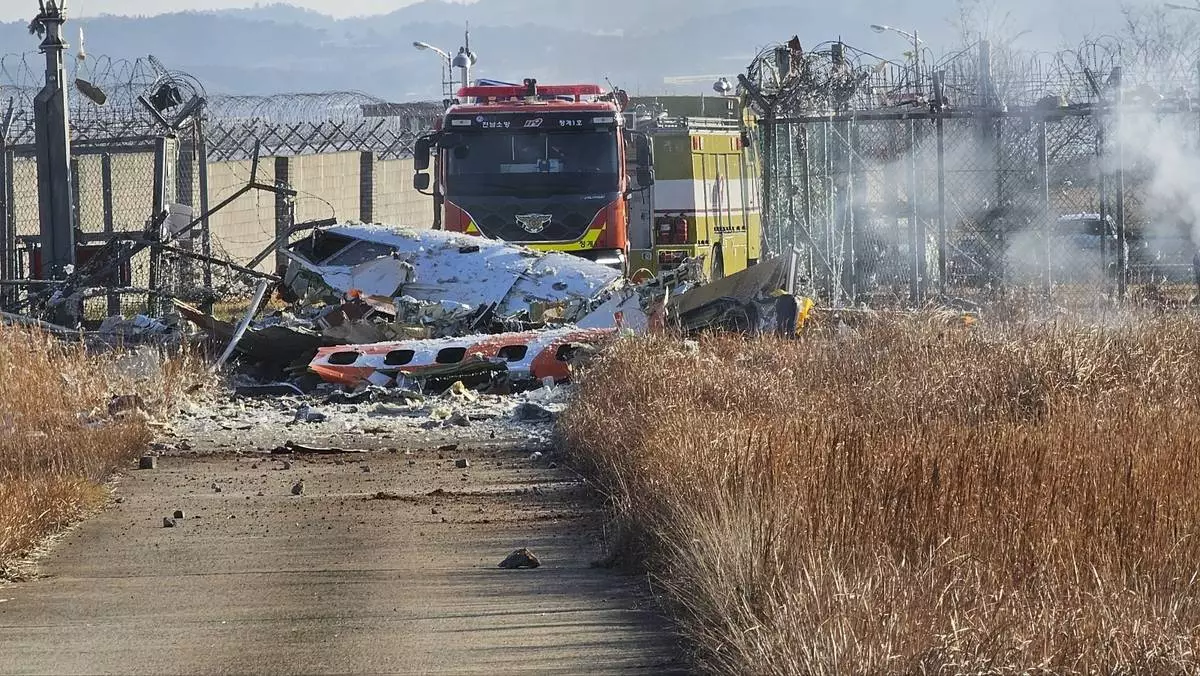

Fire engines work to extinguish a fire at the Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Maeng Dae-hwan/Newsis via AP)

Firefighters and rescue team members work at the Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Maeng Dae-hwan/Newsis via AP)

A rescue team prepares to work at Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Maeng Dae-hwan/Newsis via AP)

Firefighters work to extinguish a fire off the runway of Muan International Airport in Muan, South Korea, Sunday, Dec. 29, 2024. (Maeng Dae-hwan/Newsis via AP)