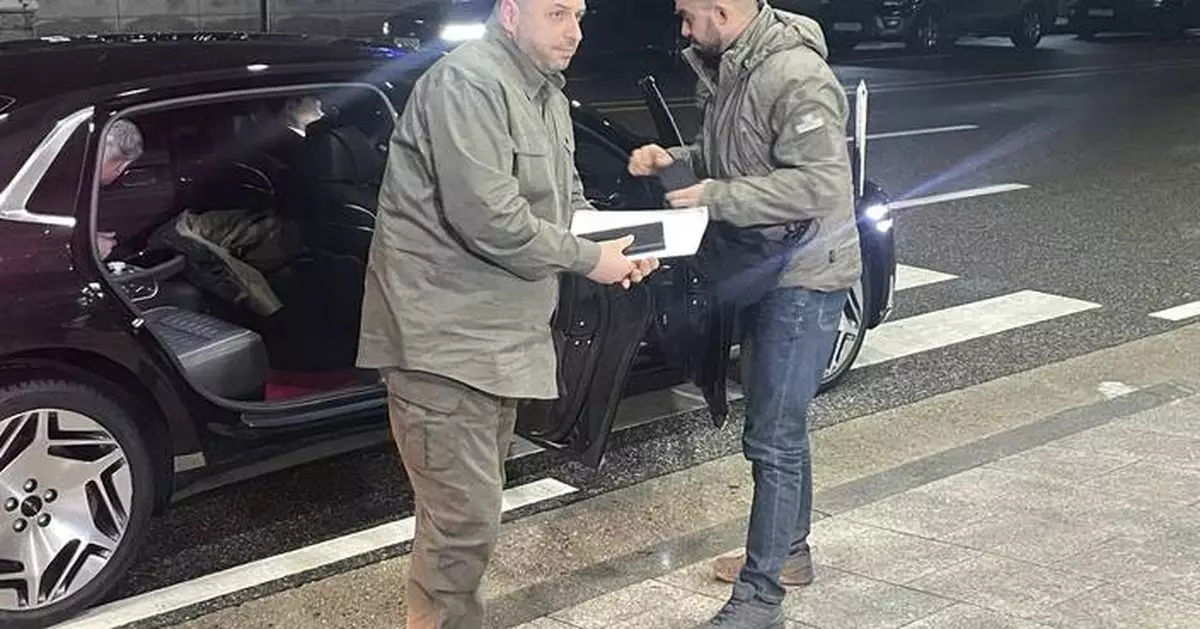
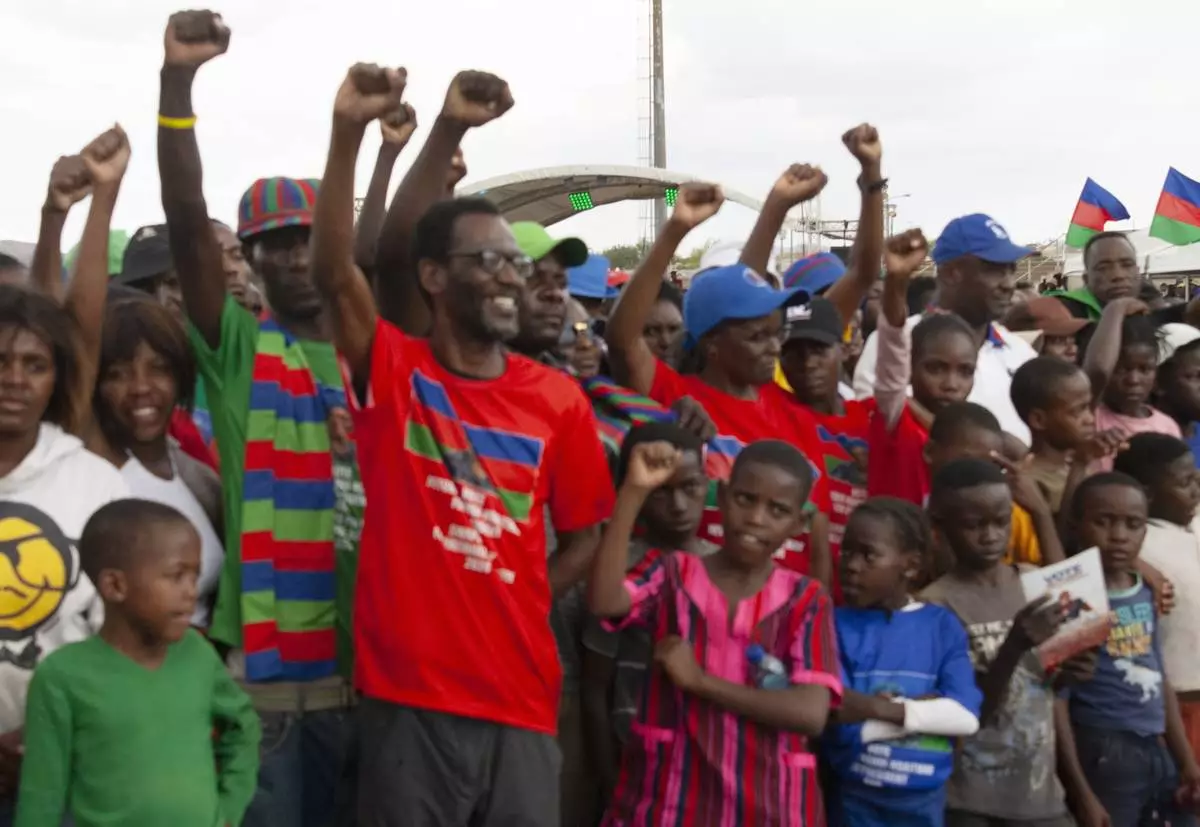SEOUL, South Korea (AP) — South Korea’s president on Wednesday met a visiting Ukraine delegation and called for the two countries to formulate countermeasures in response to the threat posed by North Korea’s recent dispatch of more than 10,000 soldiers to support Russia’s war against Ukraine.
The North Korean troop deployment is threatening to expand the almost three-year war, with Ukraine and the U.S. saying that some of the soldiers have already begun engaging in battle on the front lines. Seoul and Washington also worry that Russia might in return help North Korea build more advanced nuclear weapons targeting them. In late October, South Korea warned it could respond by supplying weapons to Ukraine.
During a meeting with the Ukrainian delegation led by Defense Minister Rustem Umerov, President Yoon Suk Yeol said he hopes that Seoul and Kiev will work out effective ways to cope with the security threat posed by the North Korean-Russian military cooperation including the North’s troop dispatch, Yoon’s office said in a statement.
The Ukrainian delegation later met separately with Yoon’s national security adviser, Shin Wonsik, and Defense Minister Kim Yong Hyun. During the meetings, Umerov briefed the South Korean officials on the status of the Russia-Ukraine war and expressed hope that Kyiv and Seoul will strengthen cooperation, the statement said.
It said the two sides agreed to continue to share information on the North Korean troops in Russia and North Korean-Russian weapons and technology transfers while closely coordinating with the United States.
The South Korean statement didn’t say whether the two sides discussed Seoul’s possible weapons supply to Ukraine.
Many observers say Donald Trump’s victory in the U.S. presidential election could make South Korea more cautious about potentially shipping weapons to Ukraine because Trump has promised to end the war swiftly.
Since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022, South Korea has joined U.S.-led sanctions against Moscow and shipped humanitarian and financial support to Kyiv. But it has avoided directly supplying arms in line with its policy of not supplying lethal weapons to countries actively engaged in conflicts.
South Korean officials have said they will take phased countermeasures, linking the level of their response to the degree of Russia-North Korean cooperation. Shin, the national security adviser, said last week that Russia has supplied air defense missile systems to North Korea in exchange for its sending troops to Russia. Experts say it’s unlikely that Russia will transfer high-tech nuclear and missile technology to North Korea in the initial stage of the troop dispatch.
North Korea and Russia have sharply increased their military and other cooperation as each face confrontations with the U.S. and its allies. The U.S., South Korea and others accuse North Korea of having shipped artillery, missiles and other conventional weapons to Russia.
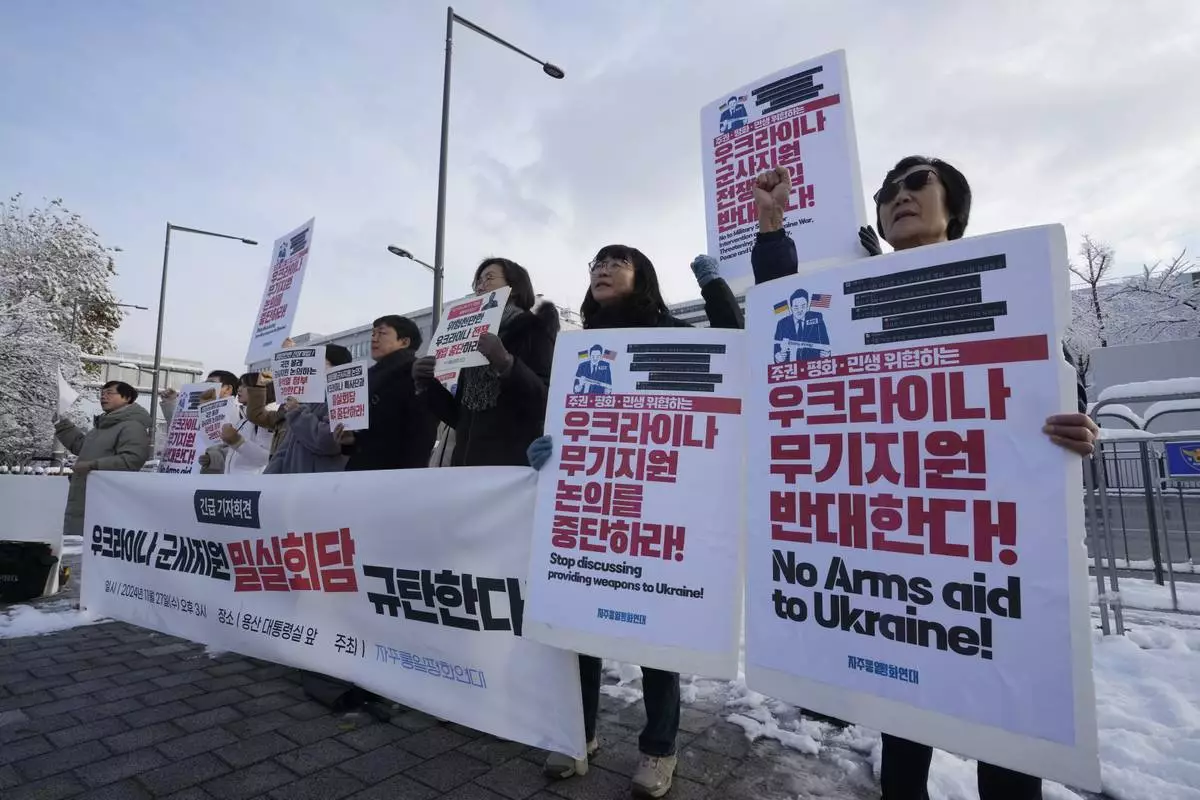

South Korean protesters stage a rally against their government's plans to supply weapons to Ukraine, in front of the Presidential Office in Seoul, South Korea, Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Ahn Young-joon)
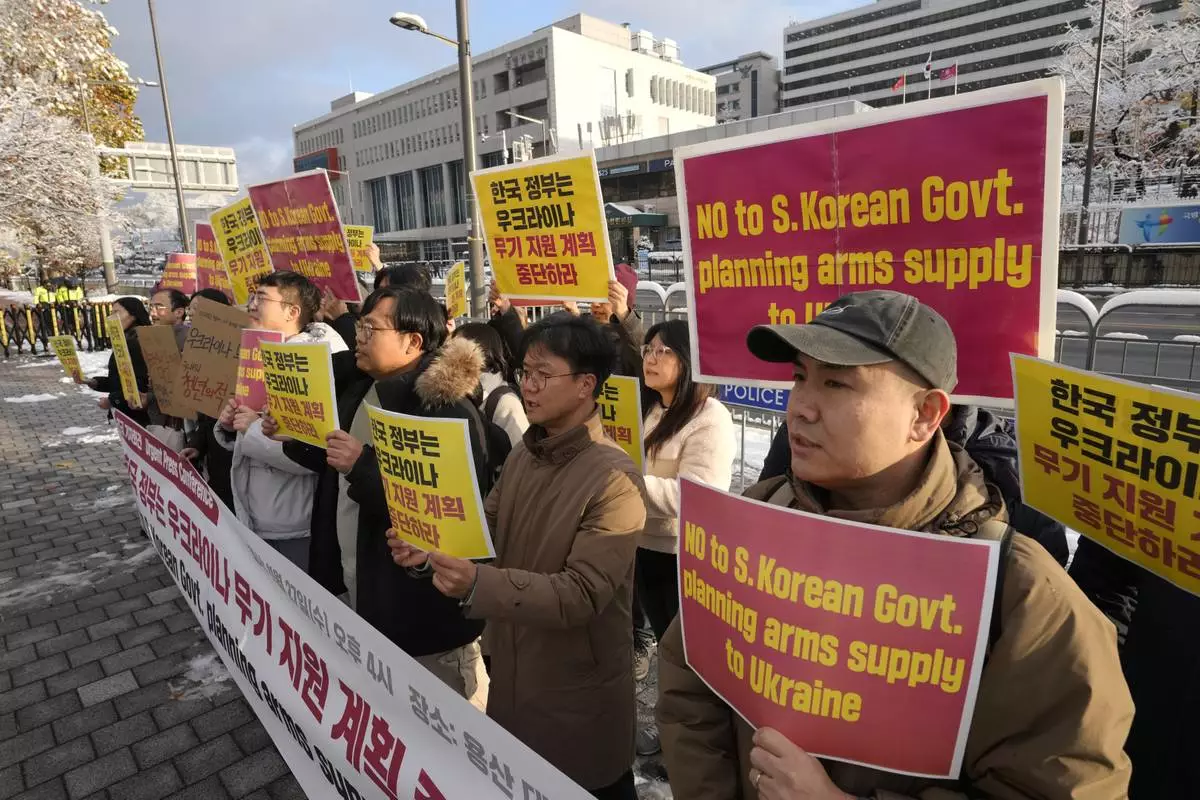

South Korean protesters stage a rally against their government's plans to supply weapons to Ukraine, in front of the Presidential Office in Seoul, South Korea, Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Ahn Young-joon)

South Korean protesters stage a rally against their government's plans to supply weapons to Ukraine, in front of the Presidential Office in Seoul, South Korea, Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Ahn Young-joon)
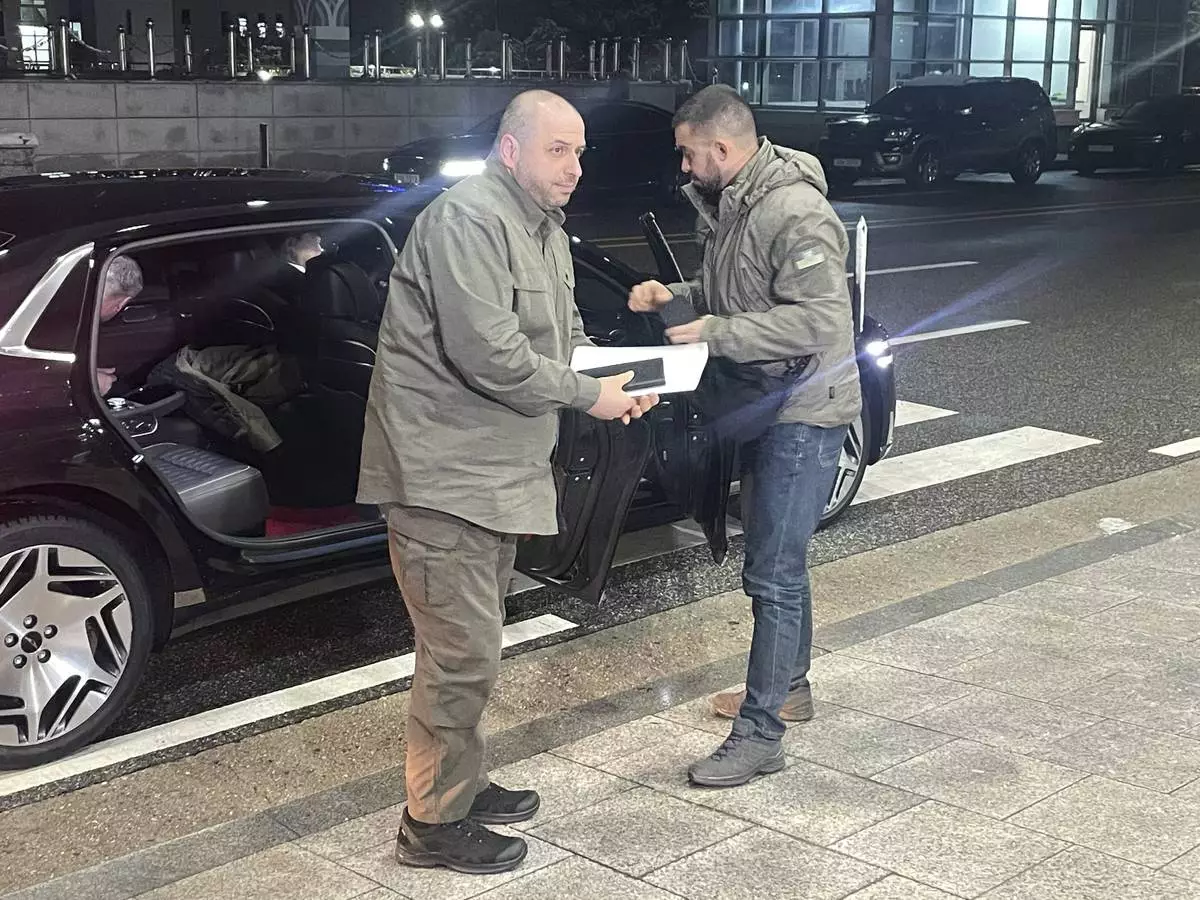

Ukraine's Defense Minister Rustem Umerov, left, arrives at the Defense Ministry in Seoul, South Korea, Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (Kim Ho-jun/Yonhap via AP)
WINDHOEK, Namibia (AP) — A 72-year-old woman who joined Namibia's underground independence movement in the 1970s is a strong contender to become its first female leader as the country voted Wednesday in a presidential election.
Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah, is the current vice president and the ruling SWAPO party's candidate for president. She's already in the lead after special voting among citizens overseas and the armed forces.
But SWAPO, which has governed the southern African country and held the presidency for 34 years since independence from apartheid South Africa in 1990, faces growing frustration caused by high unemployment and economic hardship, especially among young people.
That is a common theme that has led to momentous election upsets in other countries in the region this year. Voters elsewhere in southern Africa have rejected parties that liberated their nations from colonial or white minority rule in favor of era-ending change to address new problems.
In neighboring South Africa, the African National Congress that ruled for three decades since the end of the racist system of apartheid lost its majority in a landmark election result in June. Botswana's ruling party lost in a landslide last month after 58 years in power since independence from Britain, and Mauritius delivered a surprising heavy defeat for its incumbent party this month.
Mozambique's long-ruling Frelimo party was declared the winner of an election in October, prompting claims of vote rigging and sparking ongoing violent protests against the party.
About 1.4 million people — approximately half the Namibian population — are registered to vote to decide the president and the makeup of Parliament for a five-year term. The country on the southwestern coast of Africa is a former German colony that came under South African control after World War I and its Black majority was later subjected to some of South Africa's apartheid policies. SWAPO was at the forefront of the battle for independence.
While Namibia's population is 85% Black, its colonial history is illustrated by large white and biracial communities, and English, German and South Africa's Afrikaans language are all spoken.
Nandi-Ndaitwah voted at an elementary school in the capital, Windhoek. She told reporters that one of her party’s key focuses to fight poverty was attracting more foreign investment to a country with diamond and uranium resources, and untapped oil and gas off its coast that is being explored by international energy companies.
“There should be a balance to make sure that the Namibian people, who are the owners of these resources, benefit from them,” she said.
Fourteen other candidates are also running for president, including Panduleni Itula, a former dentist who was SWAPO’s closest challenger four years ago when he ran as an independent. He is representing the Independent Patriots for Change party this year. A runoff will be held if a candidate fails to win more than 50% of the votes, which has never happened before in Namibia.
Polls close at 9 p.m. (1900 GMT) and results are expected by the weekend.
President Hage Geingob died in office in February and his vice president, Nangolo Mbumba, became head of state.
While Nandi-Ndaitwah represents the rare chance for a female leader in Africa, SWAPO's popularity has slipped and it won the presidency with its lowest share of the vote ever in the last national election in 2019.
Nandi-Ndaitwah, who received part of her education in the then-Soviet Union while in exile during the fight for independence, has promised to create more jobs and tackle the 20% unemployment rate for young people and graduates. She has pledged to spend approximately 85 billion Namibian dollars ($4.7 billion) over the next five years to create more than 500,000 jobs, a goal that her critics call unrealistic.
Opposition candidate McHenry Venaani, the leader of the second biggest party in Parliament, said Namibians should recognize it's time for change.
“Botswana has done it, South Africa has done it, Mauritius has done it. Namibia can also bring about change," he said. “People have no water, people have no houses, people have no electricity. For 34 years."
Issues affecting women, including reproductive rights, equal pay and health care, are also likely to rank high for voters in a country that has the Kalahari Desert running through its center and the Namib Desert along its coast and has one of the sparsest populations in the world. Just over 3 million people live in Namibia, which is more than twice the size of Germany.
Those deserts make it one of the driest countries in southern Africa that's vulnerable to climate shocks, like an El Nino-induced drought that parched the region this year. As a result, Namibian authorities announced they would kill hundreds of wild animals to provide food for hungry people.
AP Africa news: https://apnews.com/hub/africa
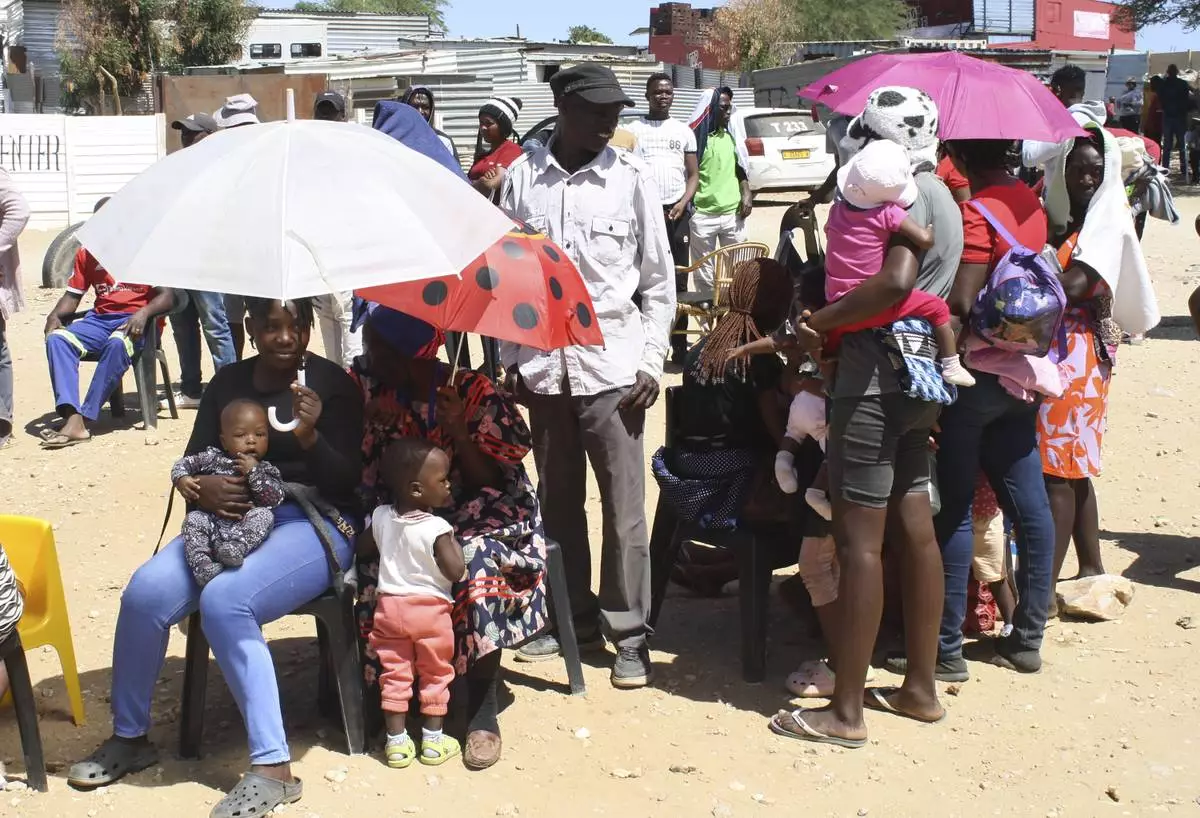

Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election, in Windhoek, Namibia, Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Esther Mbathera)
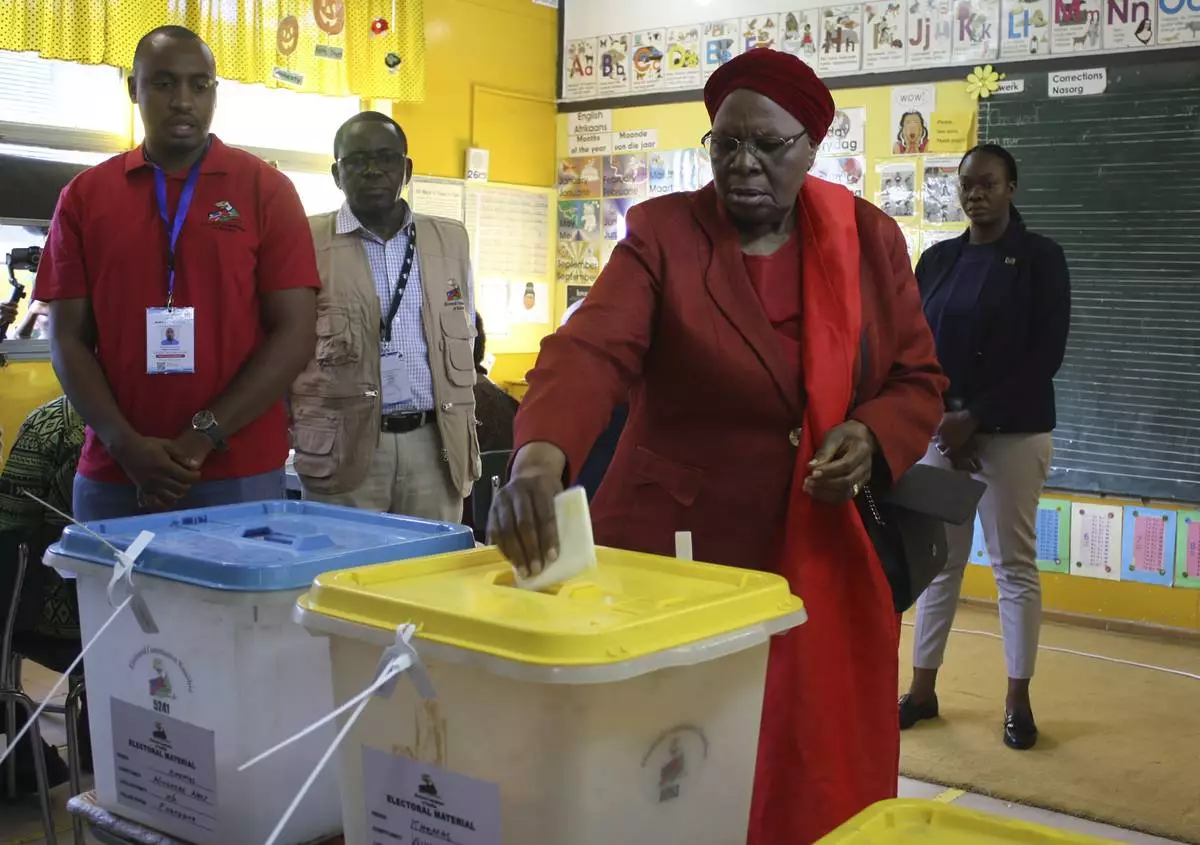

Namibia's vice president, Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah, of the ruling South West Africa People's Organization, (SWAPO) casts her vote in a presidential election, in Windhoek, Namibia, Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Esther Mbathera)
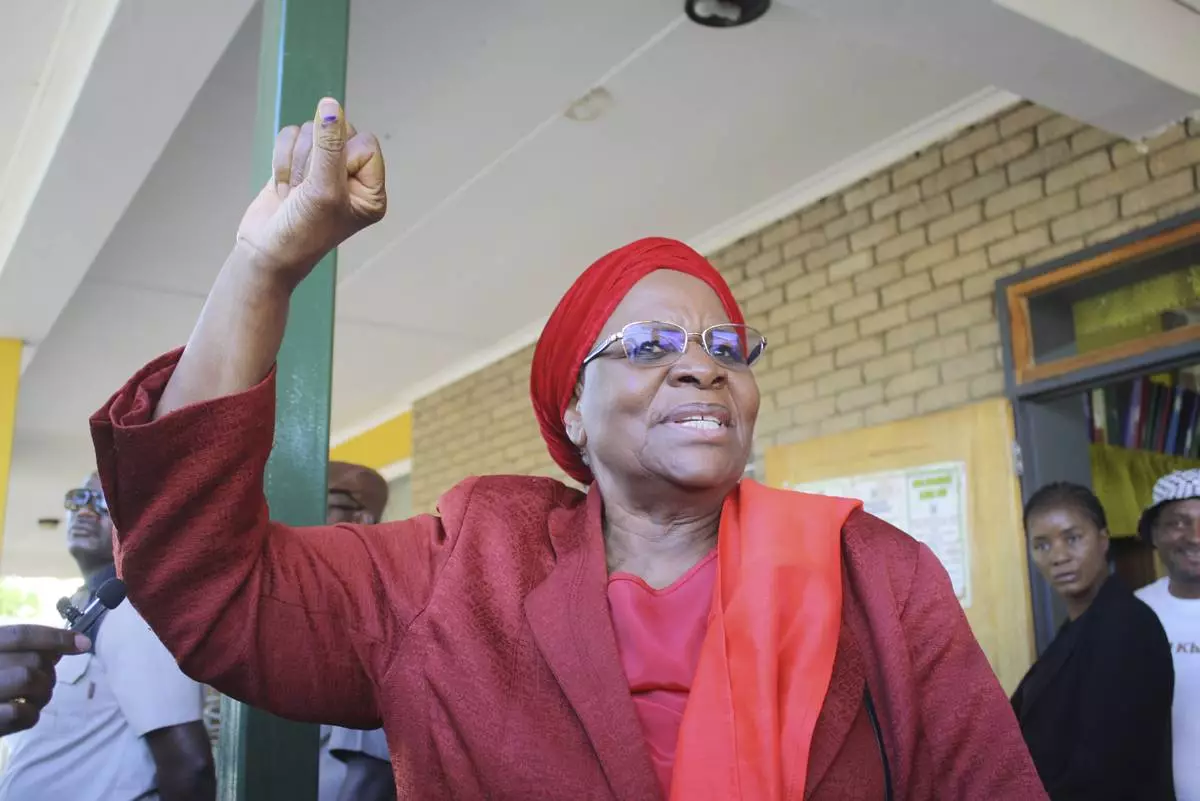

Namibia's vice president, Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah, of the ruling South West Africa People's Organization, (SWAPO) waves as she casts her vote in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia, Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Esther Mbathera)
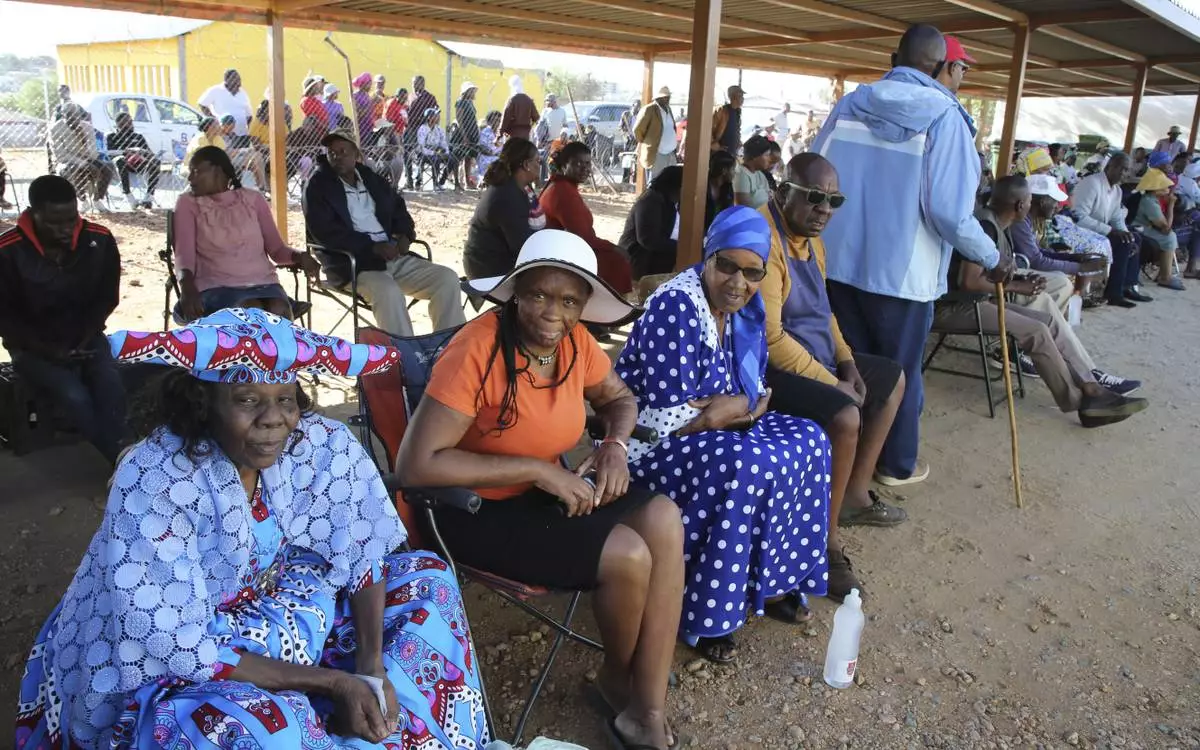

Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
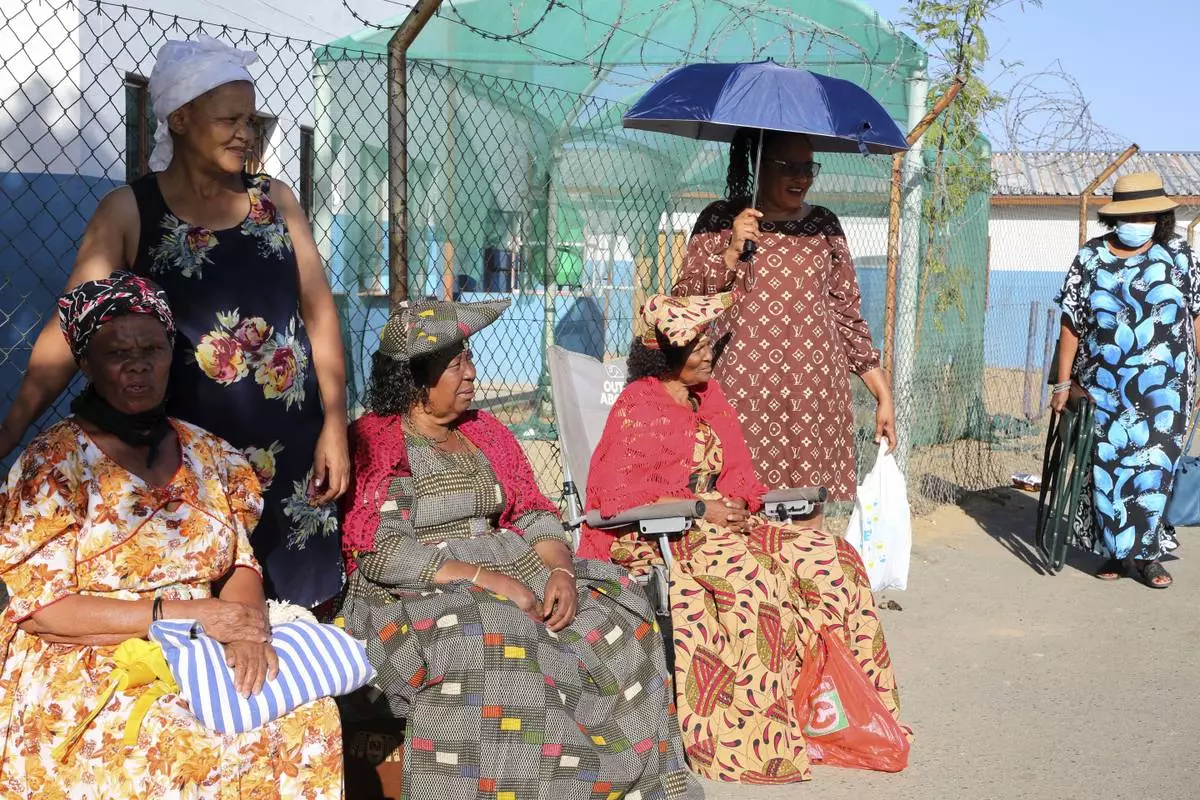

Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
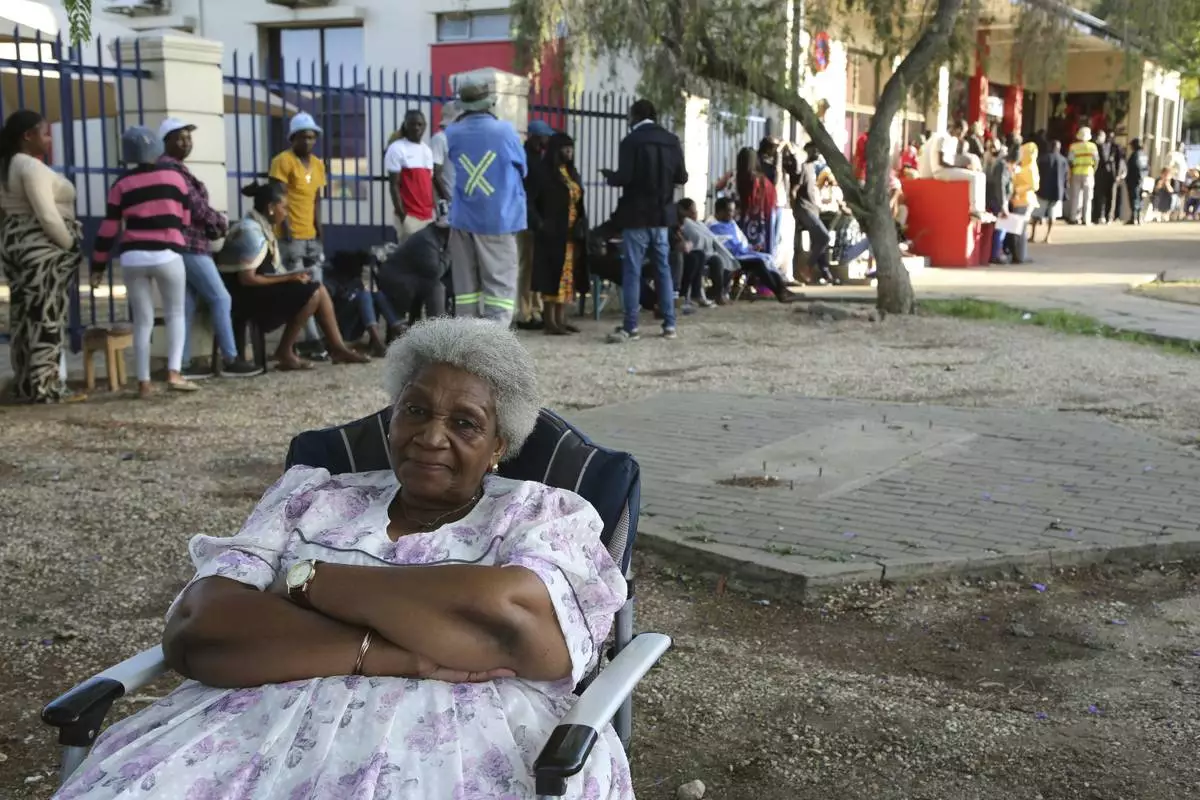

A woman sits as Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
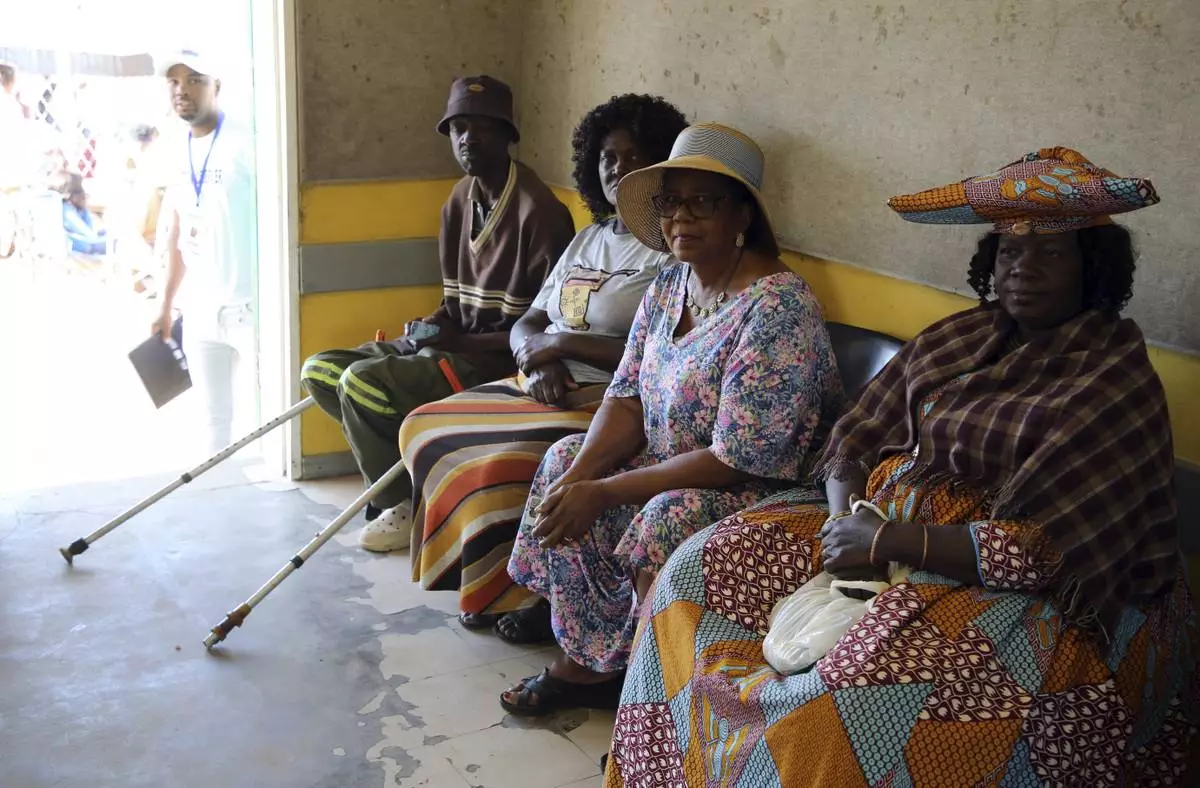

Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
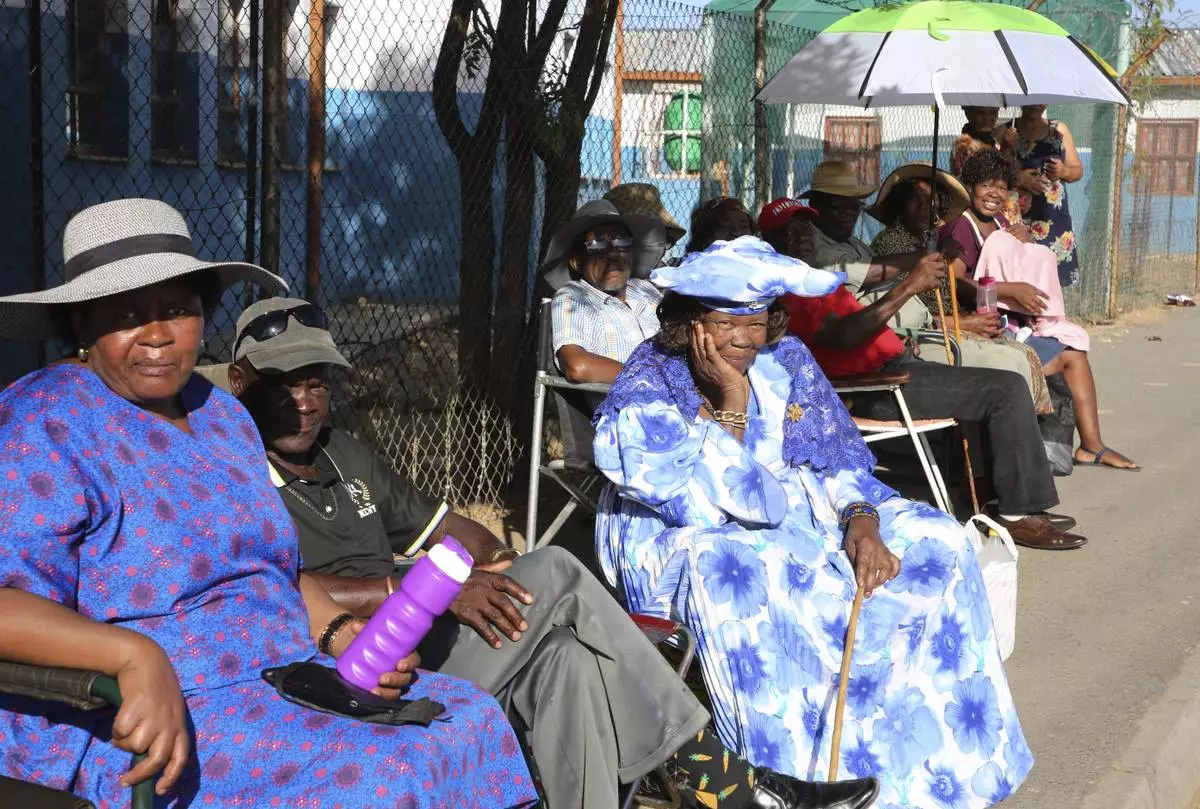

Namibians queue to cast their votes in presidential elections in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
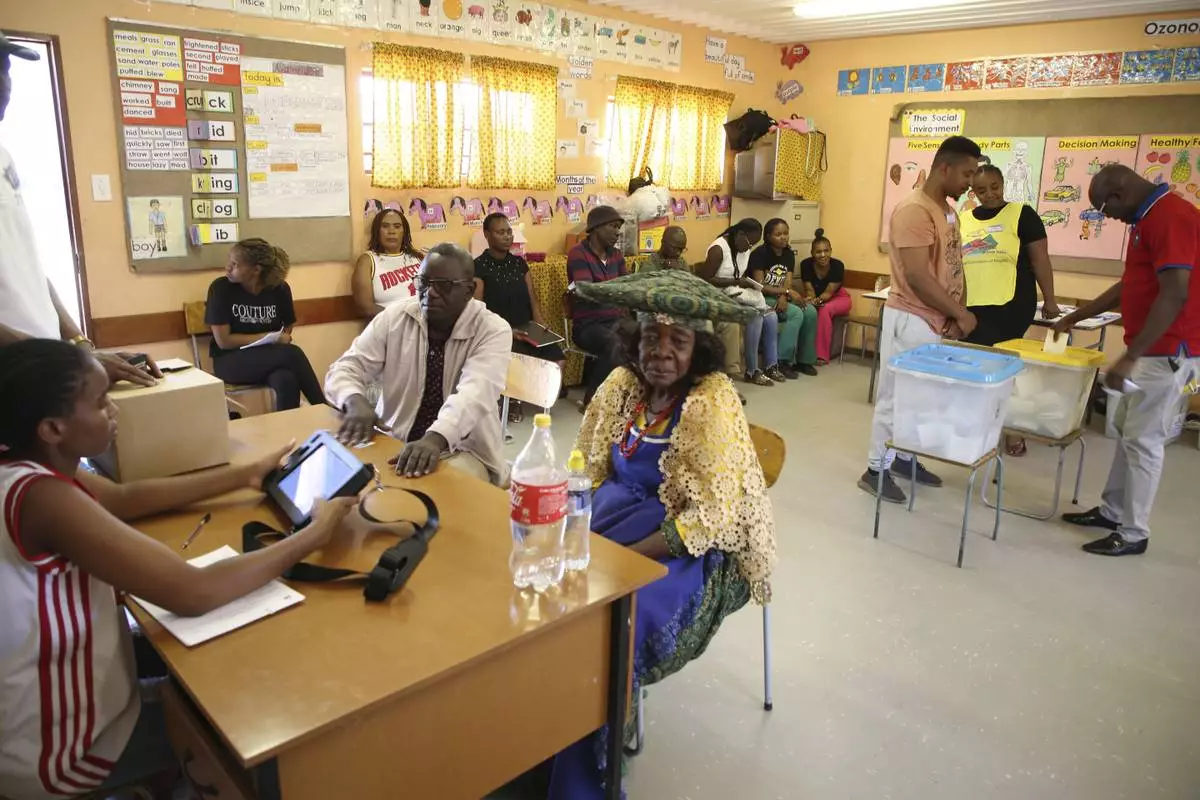

Namibians inside a polling station votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
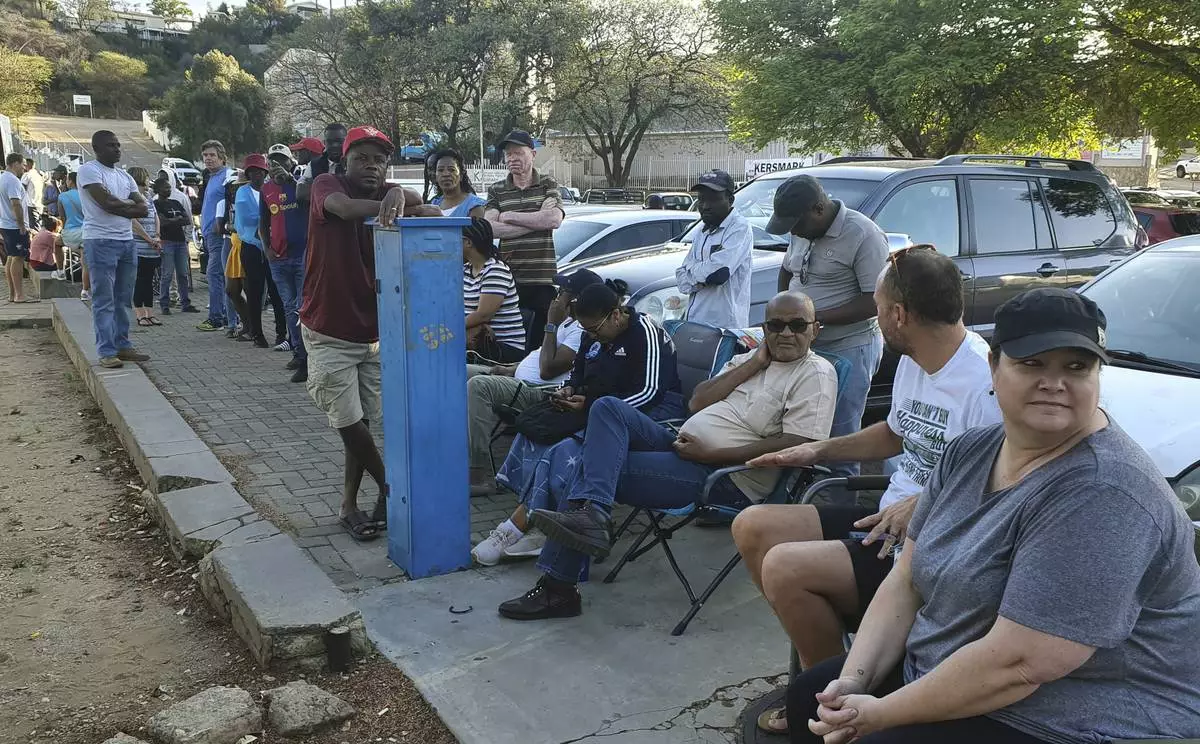

Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
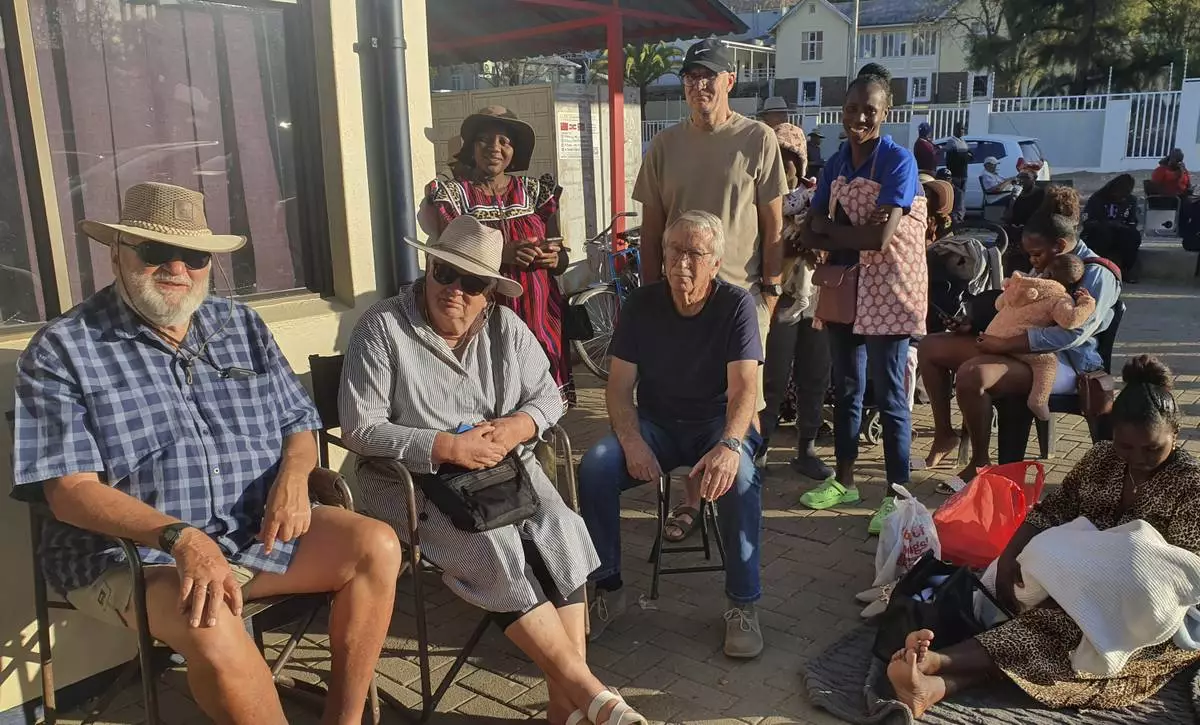

Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
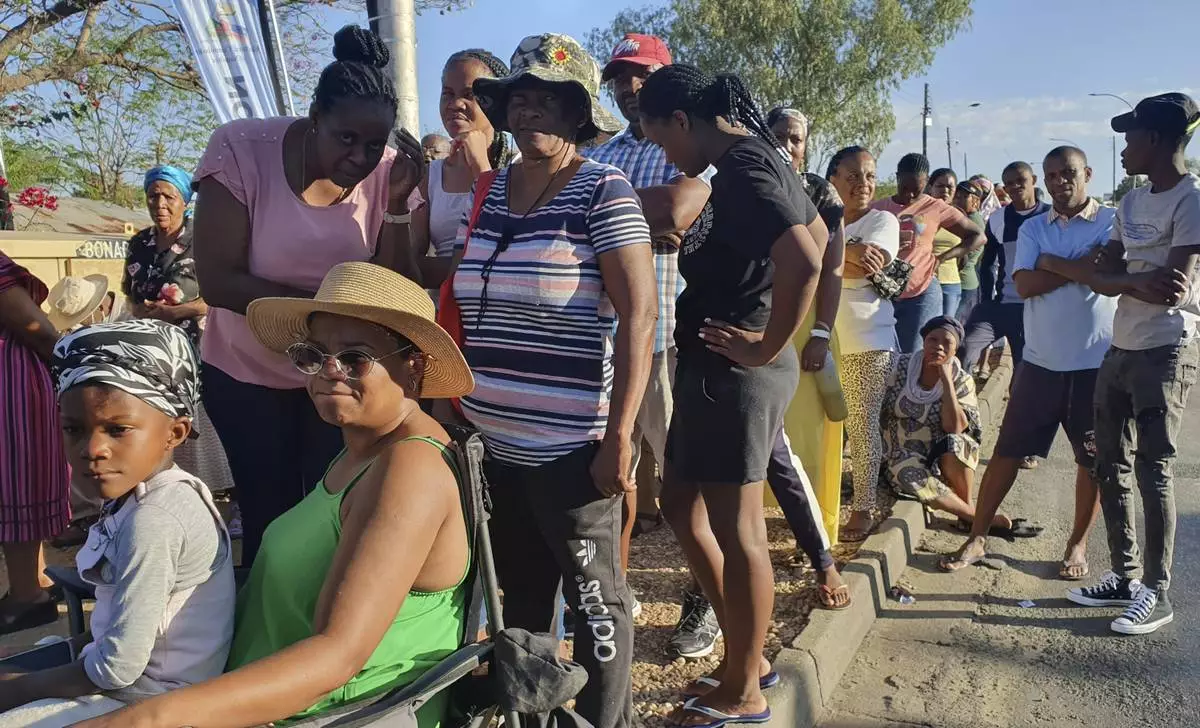

Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
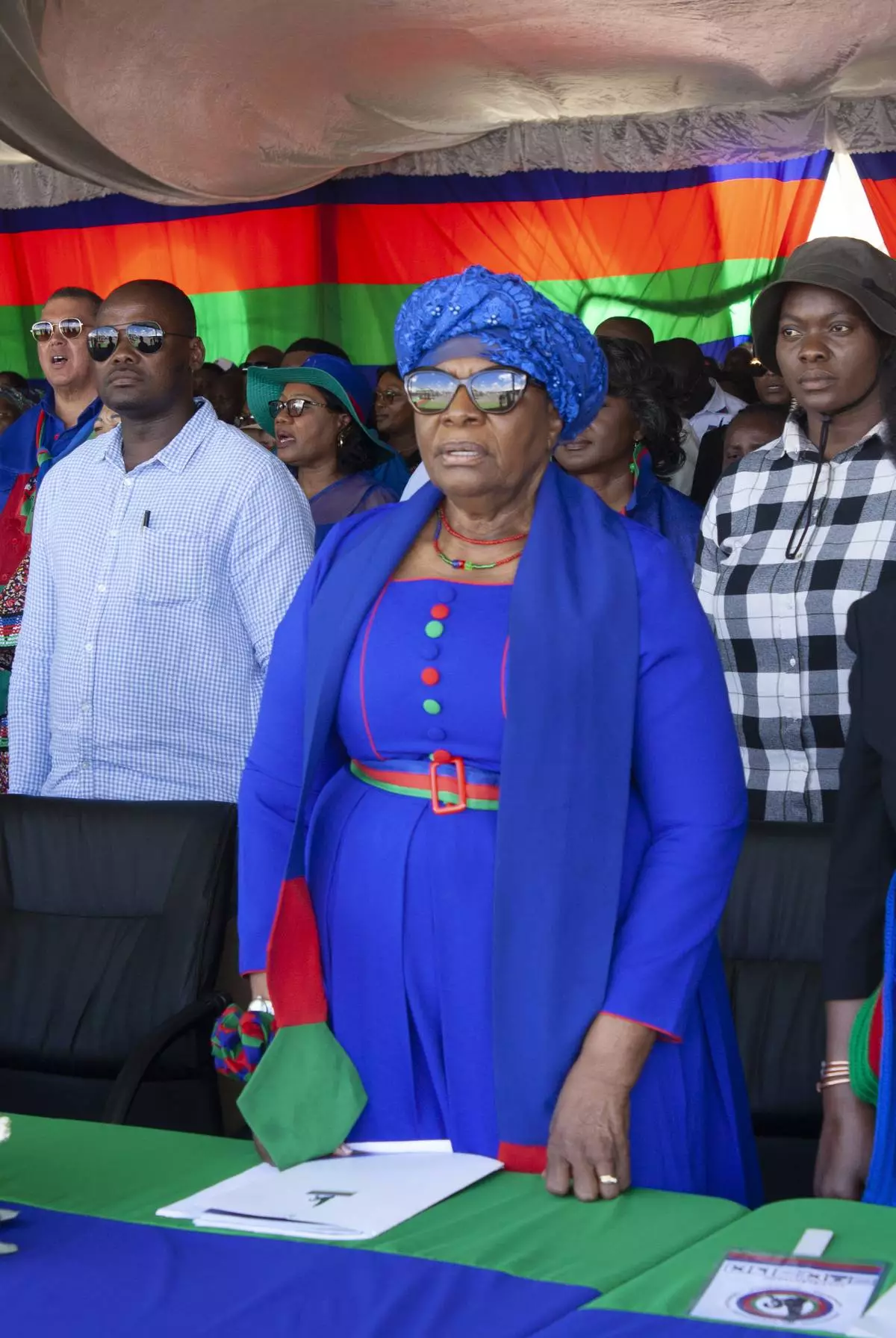

Namibia's vice president Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah, centre, of the ruling South West Africa People's Organization, (SWAPO) attends an election rally in Windhoek, Namibia, Sunday, Nov. 24, 2024 ahead of elections Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Esther Mbathera)
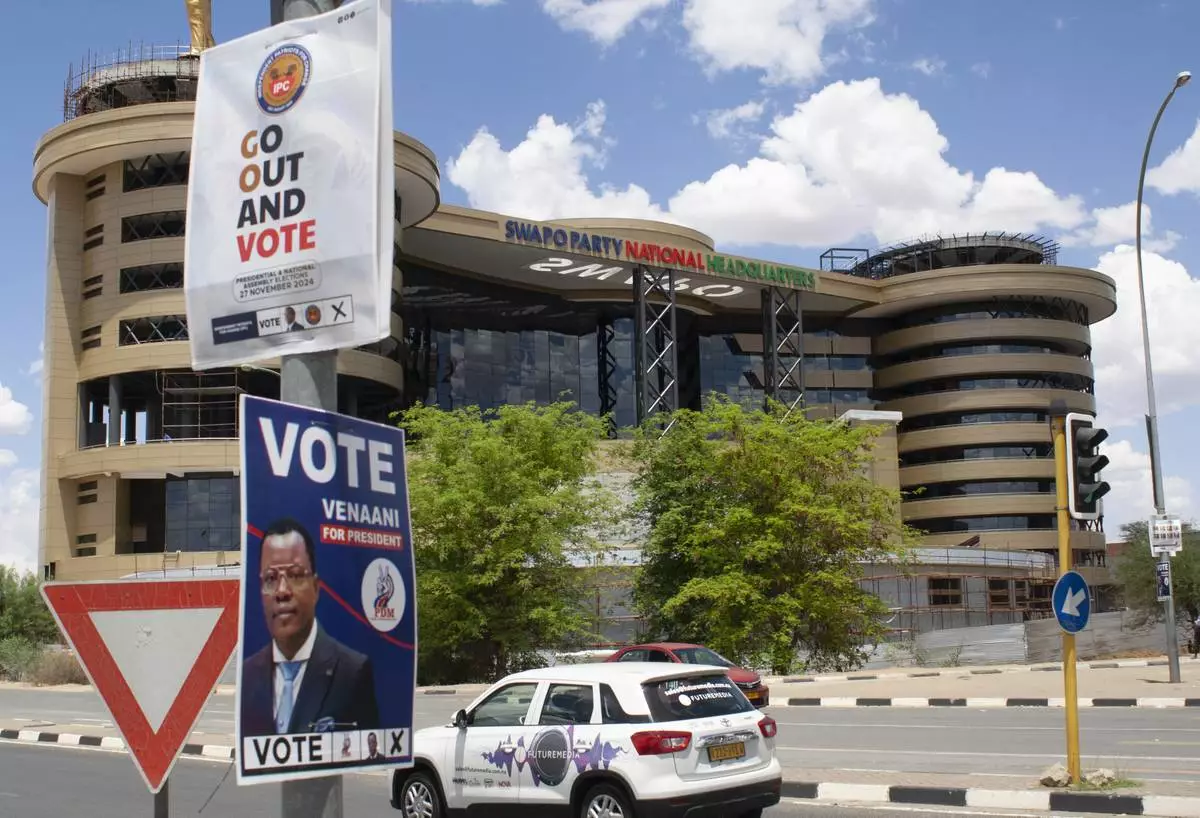

Elections poster of poles in Windhoek, Namibia, Sunday, Nov. 24, 2024 ahead of elections Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Esther Mbathera)
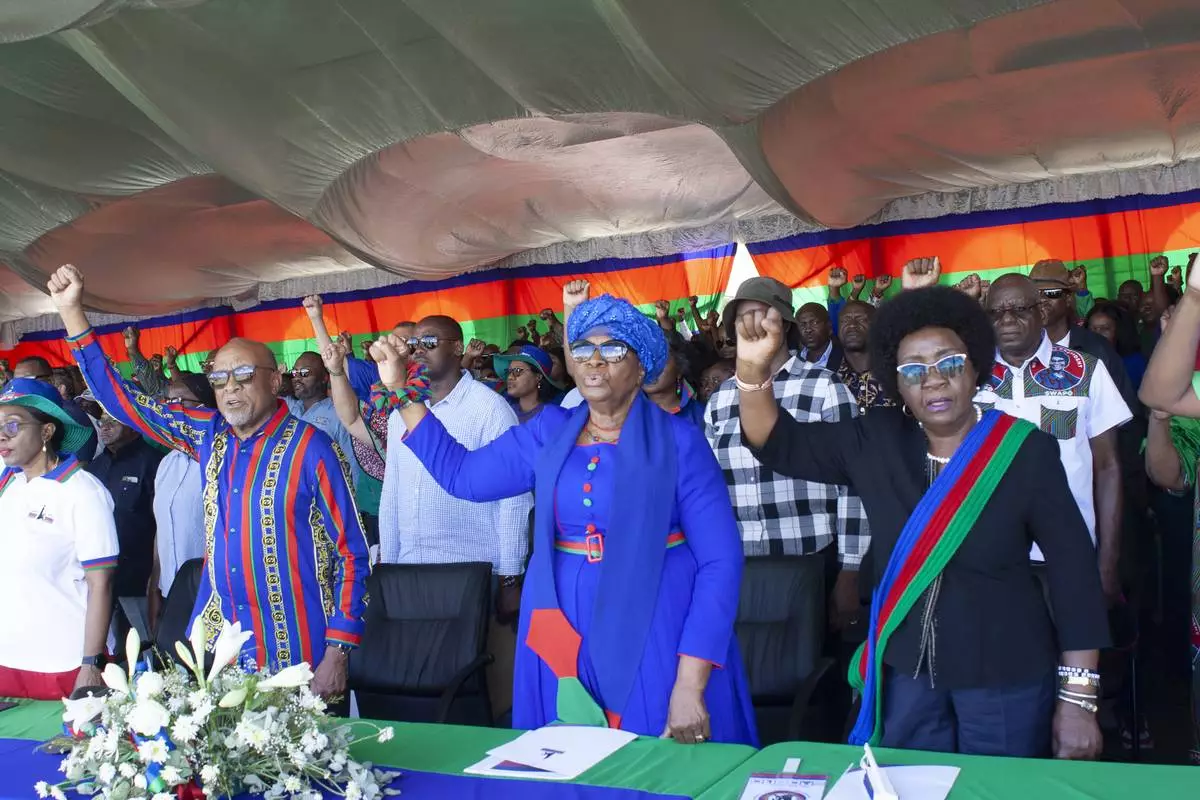

Namibia's vice president Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah, center, of the ruling South West Africa People's Organization, (SWAPO) attends an election rally in Windhoek, Namibia, Sunday, Nov. 24, 2024, ahead of elections Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Esther Mbathera)
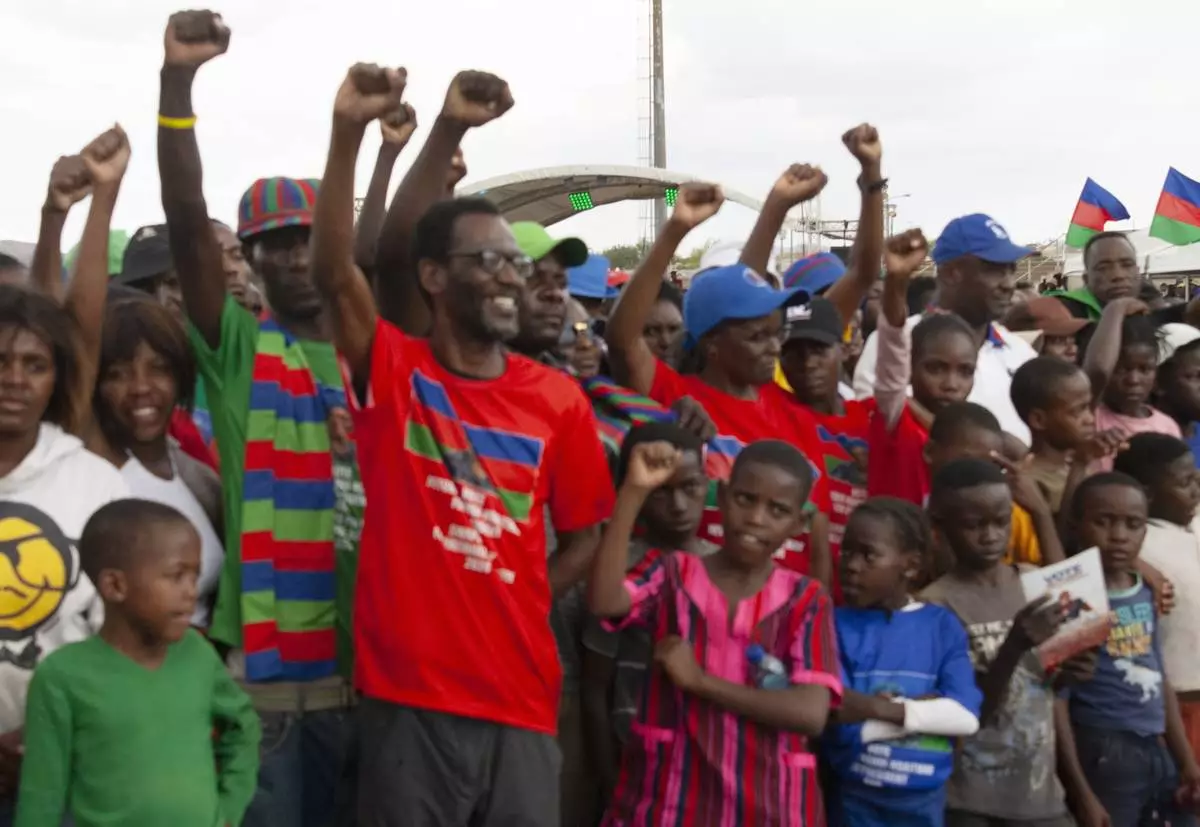
Members of the ruling South West Africa People's Organization, (SWAPO) attends an election rally in Windhoek, Namibia, Sunday, Nov. 24, 2024 ahead of elections Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Esther Mbathera)
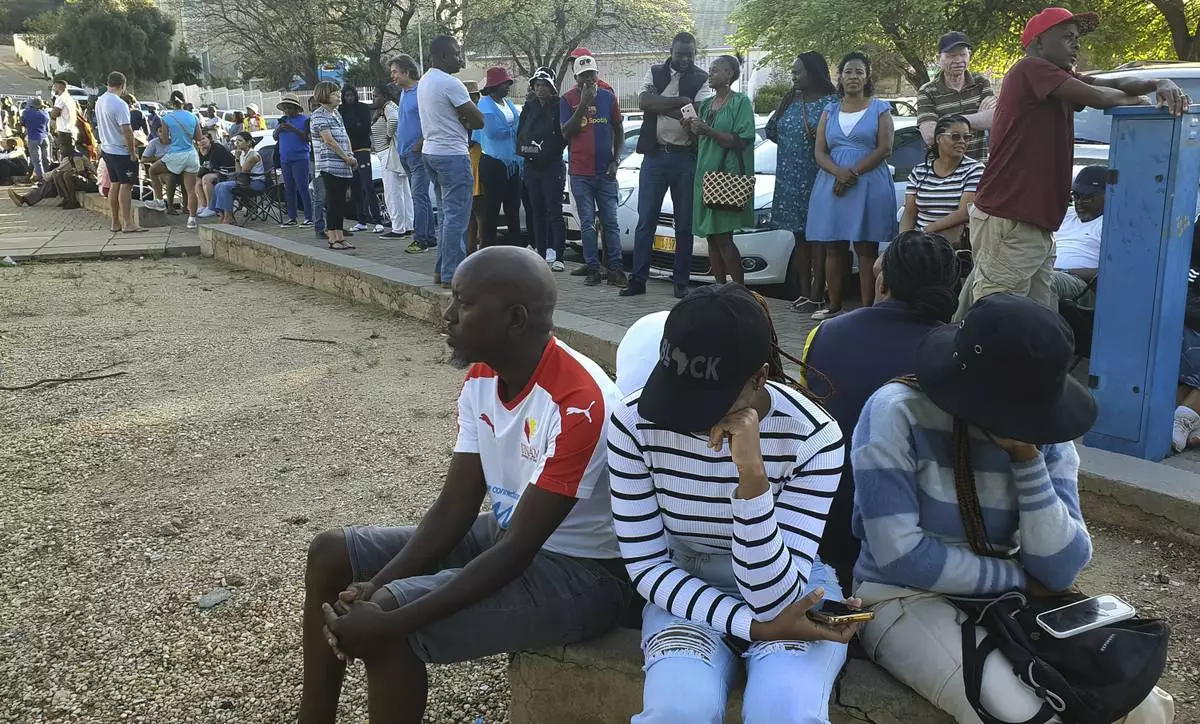

Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
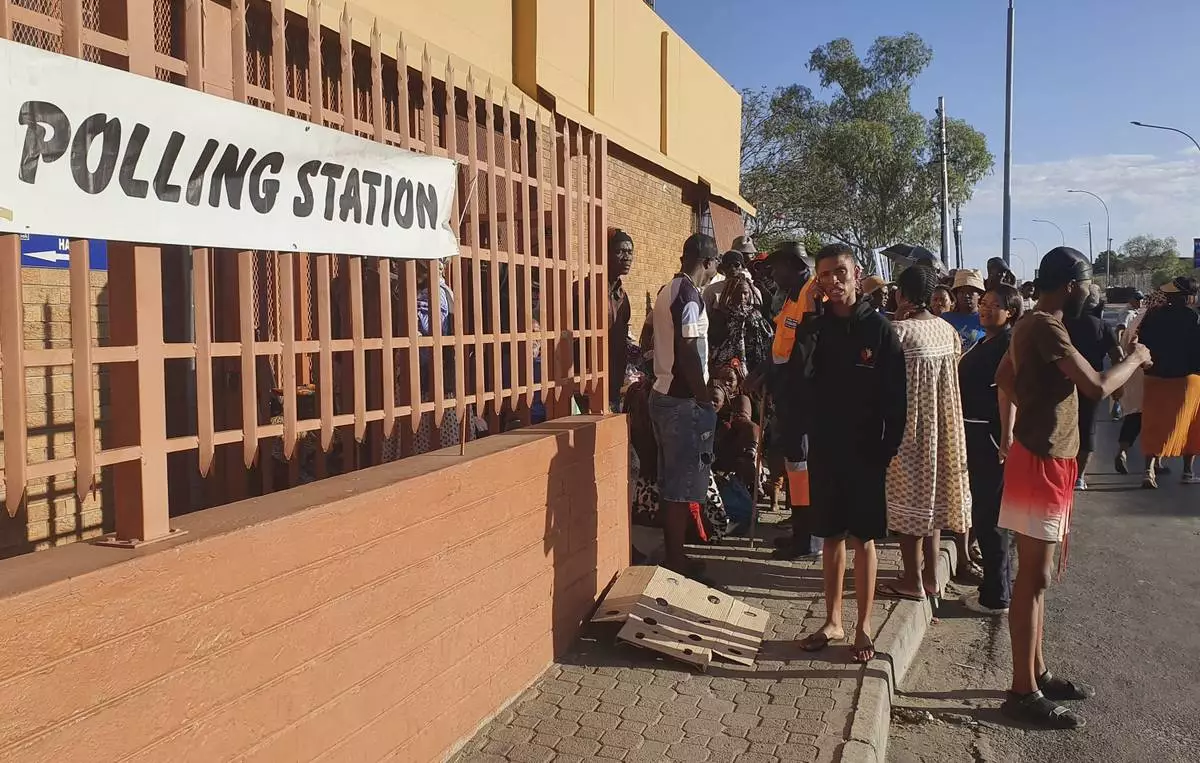

Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)
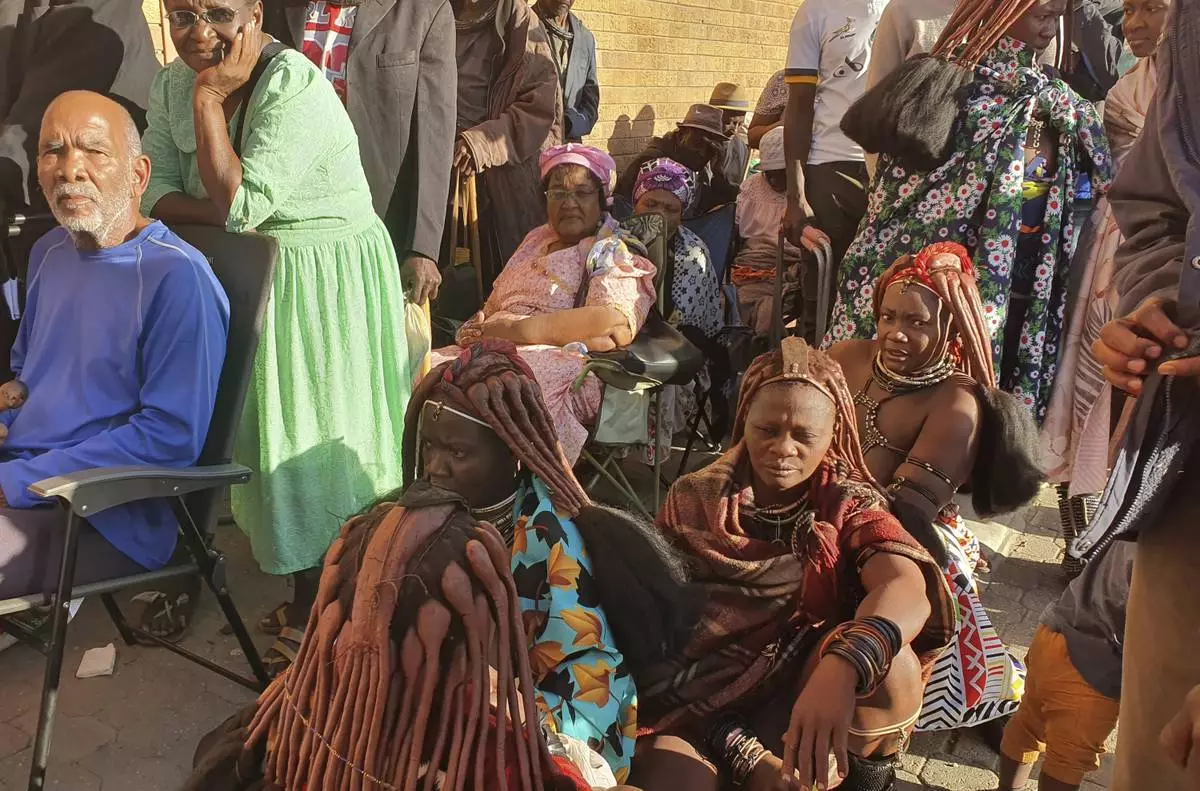

Namibians queue to cast their votes in a presidential election in Windhoek, Namibia Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Dirk Heinrich)