WASHINGTON (AP) — The American economy expanded at a healthy 2.8% annual pace from July through September on strong consumer spending and a surge in exports, the government said Wednesday, leaving unchanged its initial estimate of third-quarter growth.
U.S. gross domestic product — the economy's output of goods and services — slowed from the April-July rate of 3%, the Commerce Department reported Wednesday.
But the GDP report still showed that the American economy — the world's largest — is proving surprisingly durable. Growth has topped 2% for eight of the last nine quarters.
Within the GDP data, a category that measures the economy’s underlying strength rose at a solid 3.2% annual rate from July through September, up from 2.7% in the April-June quarter. This category includes consumer spending and private investment but excludes volatile items like exports, inventories and government spending.
Still, American voters — exasperated by high prices — were unimpressed by the steady growth and chose this month to return Donald Trump to the White House to overhaul the nation's economic policies. He will be supported by Republican majorities in the House and Senate.
Consumer spending, which accounts for about 70% of U.S. economic activity, accelerated to a 3.5% annual pace last quarter, up from 2.8% in the April-June period and fastest growth since the fourth quarter of 2023. Exports also contributed to the third quarter’s growth, increasing at a 7.5% rate, most in two years. Still, the third-quarter growth in both consumer spending and exports was lower than the Commerce Department initially estimated.
But growth in business investment slowed sharply on a drop in investment in housing and in nonresidential buildings such as offices and warehouses. By contrast, spending on equipment surged.
When he takes office next month, President-elect Trump will inherit an economy that looks broadly healthy.
Growth is steady. Unemployment is low at 4.1%. Inflation, which hit a four-decade high 9.1% in June 2022, has fallen to 2.6%. That is still above the Federal Reserve's 2% target, but the central bank felt satisfied enough with the progress against inflation to cut its benchmark interest rate in September and again this month. Most Wall Street traders expect the Fed to cut rates again in December.
Wednesday’s report also contained some encouraging news on inflation. The Federal Reserve’s favored inflation gauge — called the personal consumption expenditures index, or PCE — rose at just a 1.5% annual pace last quarter, down from 2.5% in the second quarter. Excluding volatile food and energy prices, so-called core PCE inflation was 2.1%, down from 2.8% in the April-June quarter.
The public still feels inflation's sting: Prices are about 20% higher than they were in February 2021, just before inflation started picking up
Trump has promised an economic shakeup. On Monday, for example, he vowed to slap new import taxes on goods from China, Mexico and Canada. Mainstream economists view such taxes — or tariffs — as inflationary. That is because they are paid by U.S. importers, who then seek to pass along the higher costs to their customers.
Wednesday's report was the second of three looks at third-quarter GDP. The Commerce Department will issue the final report on Dec. 19.
This story has been corrected to show that consumer spending rose at the fastest pace since the fourth quarter, not the first quarter, of 2023.
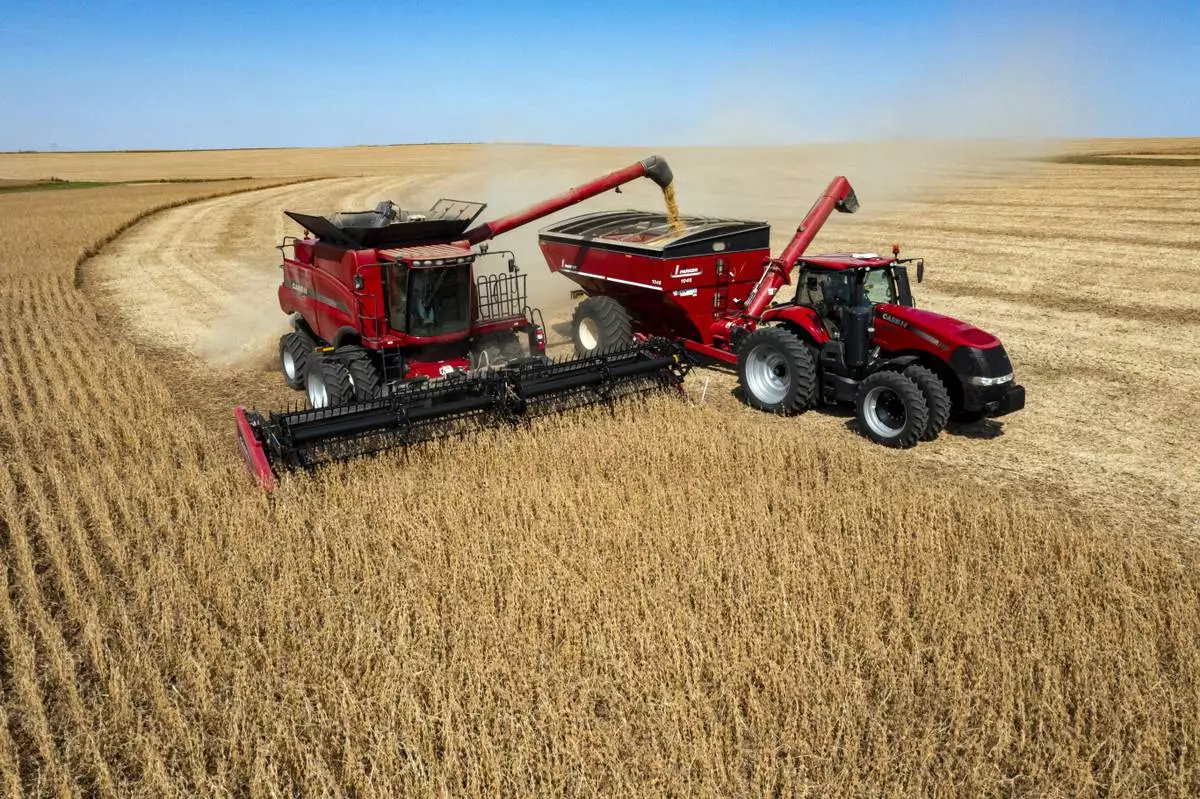

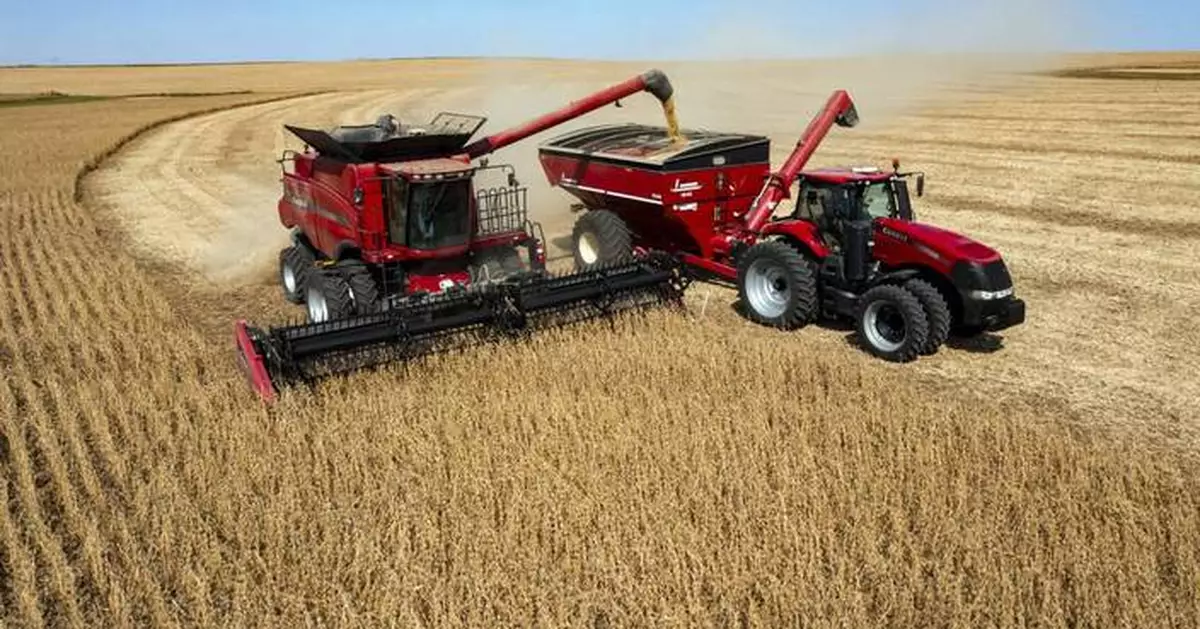
FILE - In this image taken with a drone, Jason Kwapi operates a combine, at left, during soybean harvesting on the Voss farm near Palo, Iowa, Oct. 2, 2024. (Nick Rohlman/The Gazette via AP, File)
THE HAGUE (AP) — The International Criminal Court’s chief prosecutor asked judges on Wednesday to issue an arrest warrant for the head of Myanmar’s military regime for crimes committed against the country’s Rohingya Muslim minority.
Senior Gen. Min Aung Hlaing, who seized power from elected leader Aung San Suu Kyi in 2021, is accused of crimes against humanity for the deportation and persecution of the Rohingya.
Nearly a million people were forced into neighboring Bangladesh to escape what has been called an ethnic cleansing campaign involving mass rapes, killings and the torching of homes.
From a refugee camp in Bangladesh, the court’s top prosecutor, Karim Khan, said in a statement that he intended to request more warrants for Myanmar's leaders soon.
“In doing so, we will be demonstrating, together with all of our partners, that the Rohingya have not been forgotten. That they, like all people around the world, are entitled to the protection of the law,” the British barrister said.
The allegations stem from a counterinsurgency campaign that Myanmar’s military began in August 2017 in response to an insurgent attack. Hlaing, who heads the Myanmar Defense Services, is said to have directed the armed forces of Myanmar, known as the Tatmadaw, as well as the national police to attack Rohingya civilians.
Khan was in Bangladesh where he met with members of the displaced Rohingya population. About 1 million of the predominately Muslim Rohingya live in Bangladesh as refugees from Myanmar, including about 740,000 who fled in 2017.
Rohingyas face widespread discrimination in Buddhist-majority Myanmar, with most denied citizenship. Myanmar's government refuses to recognize the Rohingya as one of the country’s 135 lawful ethnic minorities, instead calling them Bengalis, with the implication that their native land is in Bangladesh and they are illegally settled in Myanmar.
Human rights groups applauded the decision to seek a warrant. The dire situation of the Rohingya has received less attention as the conflicts in Ukraine and Gaza have grabbed headlines. “The ICC prosecutor’s decision to seek a warrant against Sr. Gen. Min Aung Hlaing comes amid renewed atrocities against Rohingya civilians that echo those suffered seven years ago. The ICC’s action is an important step toward breaking the cycle of abuses and impunity,” said Maria Elena Vignoli, senior international justice counsel at Human Rights Watch.
Zin Mar Aung, foreign minister for Myanmar’s opposition National Unity Government, established by elected lawmakers barred from taking their seats in 2021, said on X that ICC judges should “swiftly issue the warrant” and that governments should “act and enforce this warrant to uphold justice and international law.” She posted that the ICC action "represents a critical moment in Myanmar history.”
Myanmar’s military regime issued a short statement, rejecting the proceedings, noting it was not party to the ICC and insisting the country's leadership practiced a policy of “peaceful coexistence.”
Khan’s request now goes to a panel of three judges who will weigh the evidence provided and determine if a warrant should be issued. There is no deadline for a decision. A request for an arrest warrant for Russian President Vladimir Putin took less than three weeks in 2023. However, warrants for Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, his former defense minister and Hamas’ military chief took more than six months to be issued.
Myanmar does not belong to the global court, but Bangladesh does. In 2018, judges at the court ruled the prosecutor could look into crimes that were “completed” on the territory of a member state, such as forcible deportation.
In 2019, Khan’s predecessor, Fatou Bensouda, formally requested to open an investigation into the situation and judges gave the green light for investigations into “any crime, including any future crime” committed at least partly in Bangladesh or another court member state and linked to the Rohingya.
The move paved the way for Khan to pursue crimes beyond forcing men, women and children over the border and into refugee camps.
The request comes days after a powerful rebel group seized a key trading town in northeastern Myanmar on the Chinese border, taking control of a lucrative rare earth mining hub in another setback for the military-led government.
The military seized power from Aung San Suu Kyi's government in February 2021, triggering intensified fighting with long-established armed militias organized by Myanmar’s ethnic minority groups in its border regions which have struggled for decades for more autonomy.
In 2022, the International Court of Justice, the United Nations’ highest court, advanced a separate case against Myanmar brought by Gambia alleging the Southeast Asian nation is responsible for genocide against the Rohingya. Five European countries and Canada have asked the court to back Gambia in the proceedings.
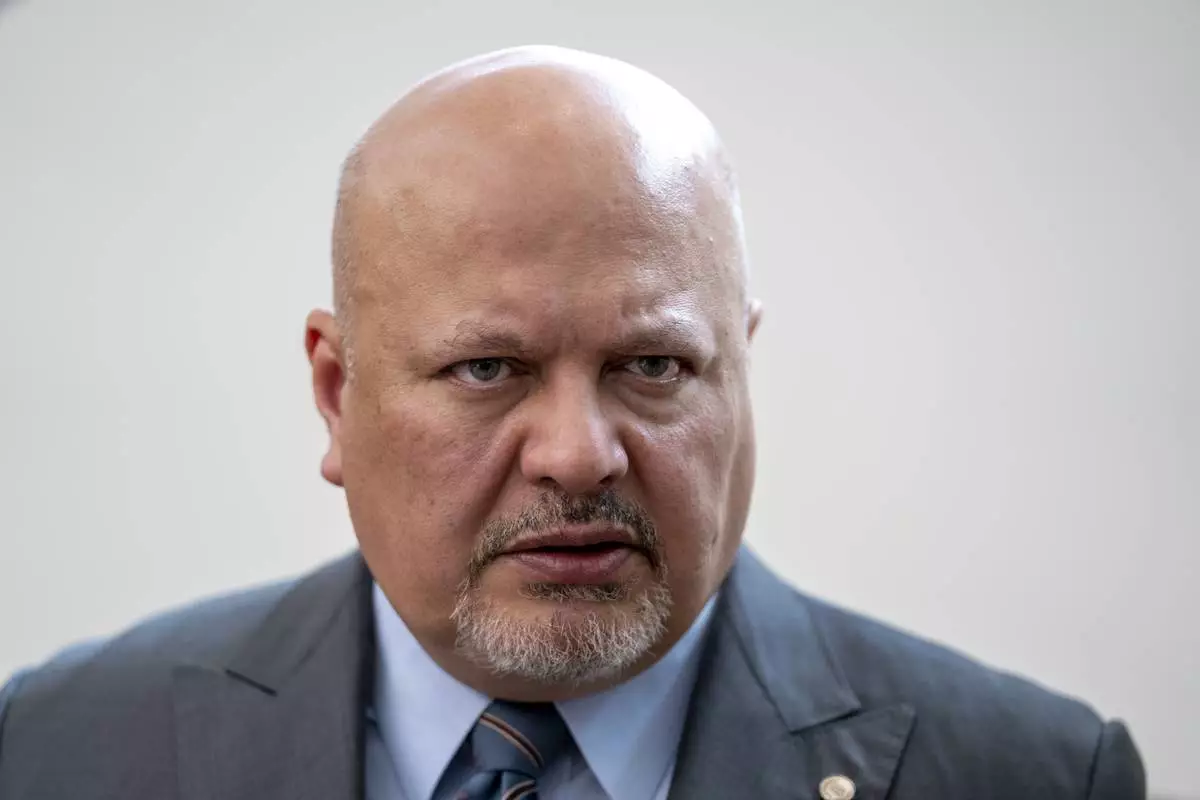

FILE - Karim Khan, Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court looks up prior to a press conference in The Hague, Netherlands, Monday, July 3, 2023. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong, File)
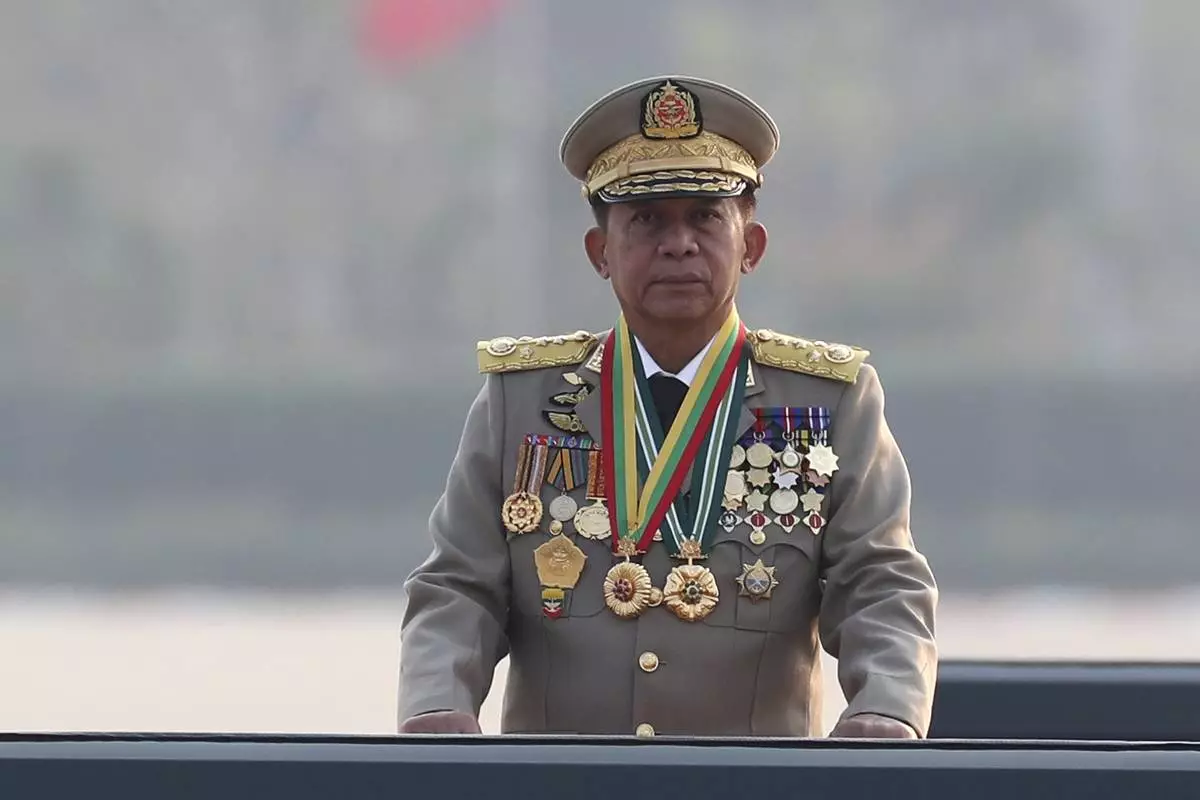

FILE - Senior Gen. Min Aung Hlaing, head of the military council, inspects officers during a parade to commemorate Myanmar's 78th Armed Forces Day in Naypyitaw, Myanmar, on March 27, 2023. (AP Photo/Aung Shine Oo, File)
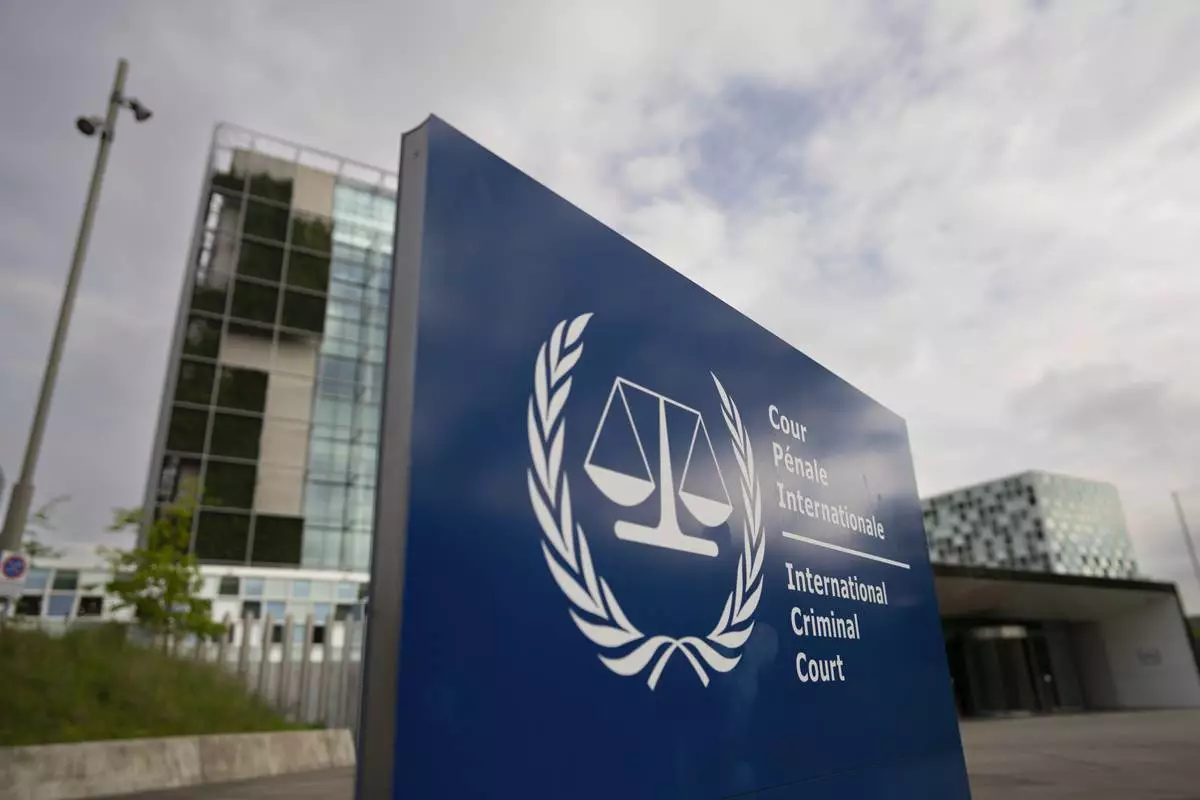

FILE - Exterior view of the International Criminal Court, or ICC, in The Hague, Netherlands, on April 30, 2024. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong, File)