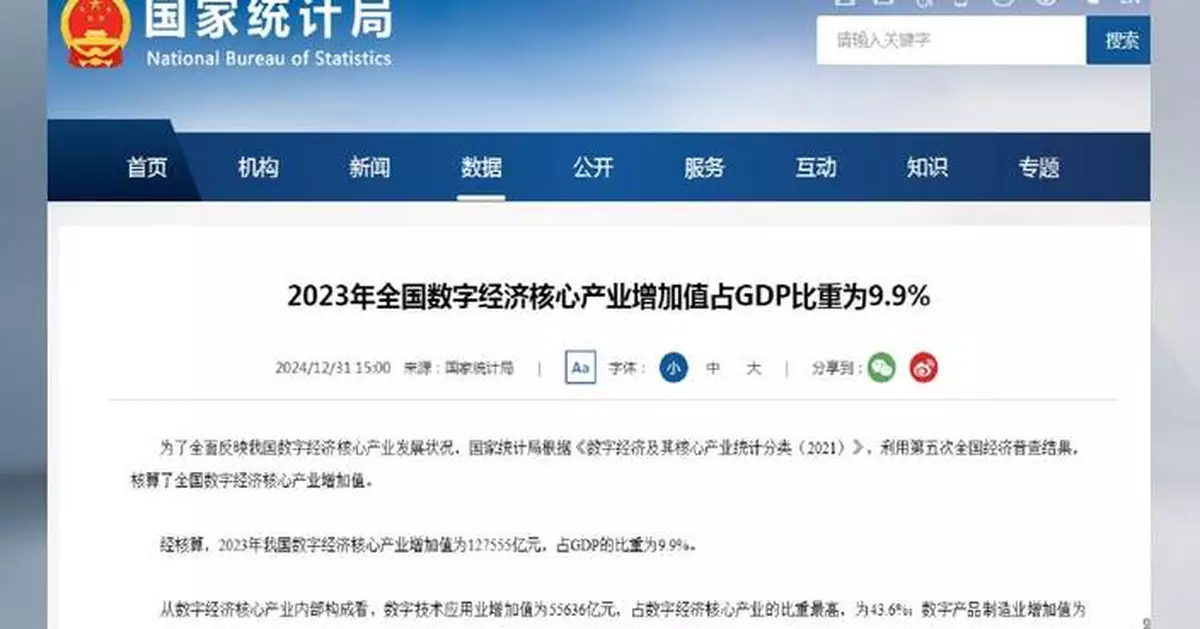
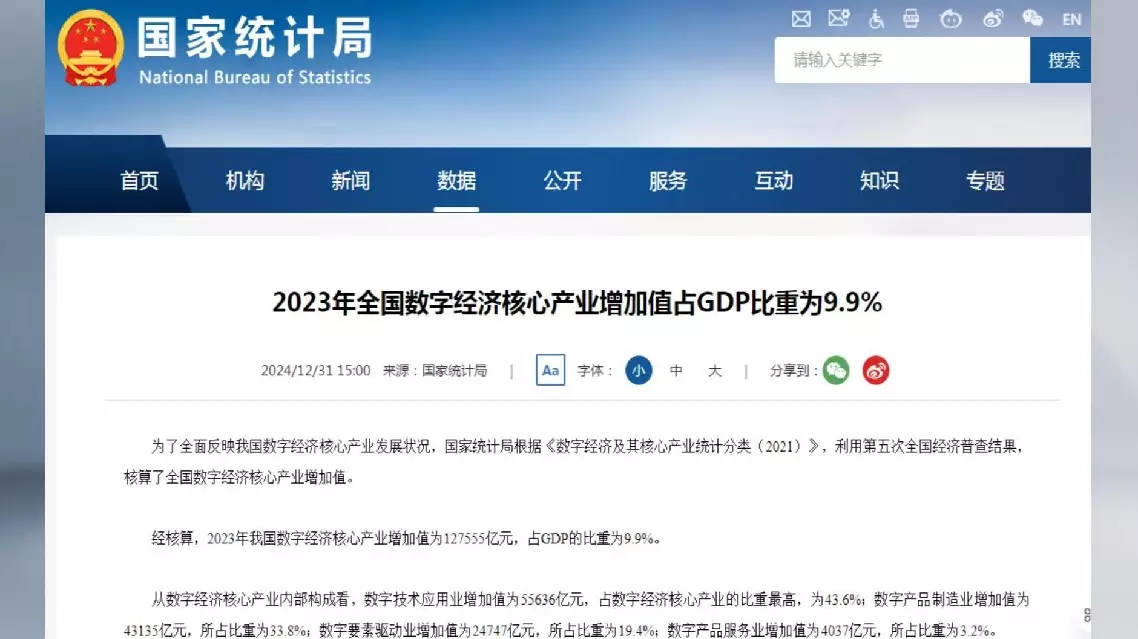
In 2023, the value-added output of core industries in the digital economy reached 12.75 trillion yuan (about 1.74 trillion U.S. dollars), 9.9 percent of China's total gross domestic product (GDP), according to data released by the National Bureau of Statistics of China on Tuesday. The data, calculated on the basis of China's fifth national economic census, is expected to comprehensively reflect the development status of core industries of the country's digital economy.
From the internal structure of the core industries of the digital economy, the added value of the digital technology application industry was 5.56 trillion yuan (about 761.71 billion U.S. dollars), accounting for the highest proportion of the core industries of the digital economy, at 43.6 percent.
The added value of the digital product manufacturing industry was 4.31 trillion yuan (about 590.46 billion U.S. dollars), accounting for 33.8 percent; the added value of the digital-factor-driven industry was 2.47 trillion yuan (about 338.38 billion U.S. dollars), accounting for 19.4 percent.
The added value of the digital product service industry was 403.7 billion yuan (about 55.30 billion U.S. dollars), accounting for 3.2 percent.
Value-added output of core industries in digital economy accounts for 9.9 percent of China's GDP