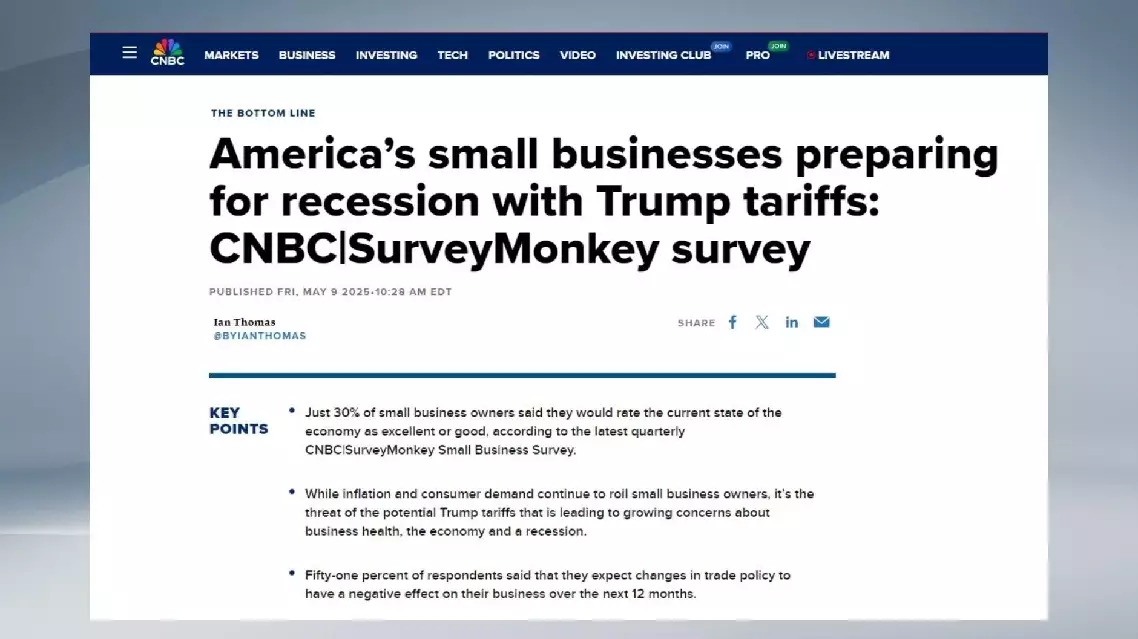
Chinese robotic developers unveiled the country's first training dataset for embodied intelligent robots in recent days, advancing the robots' abilities to learn from various environments and perform complex tasks.
The training dataset was jointly released by the National-Local Co-built Humanoid Robot Innovation Center and the School of Computer Science at Peking University.
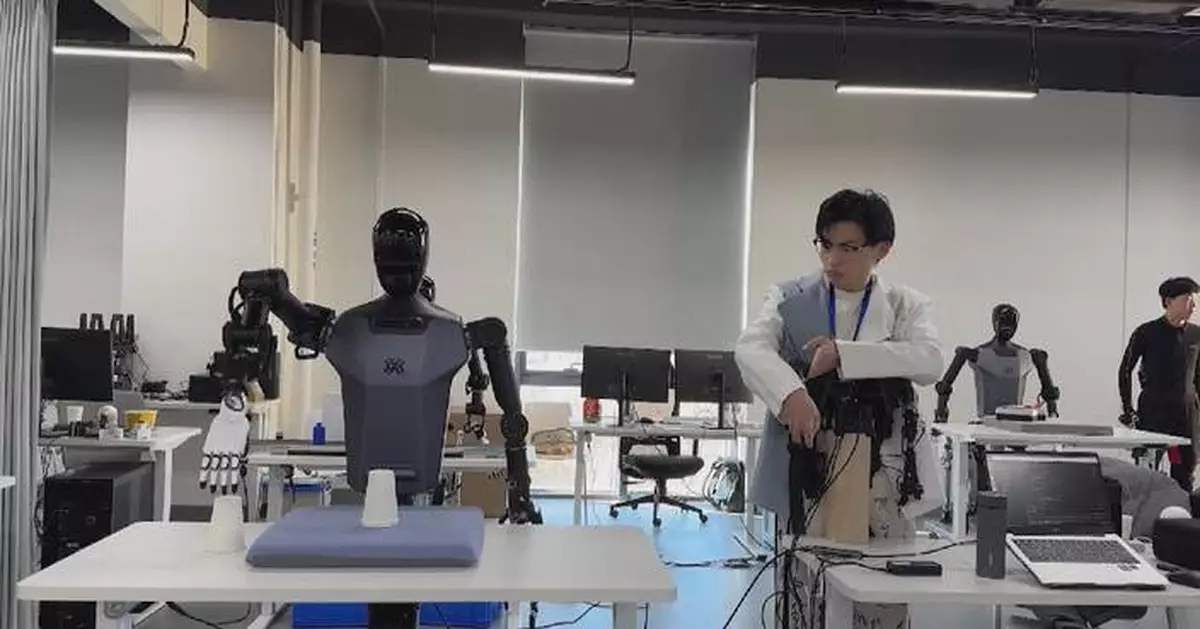
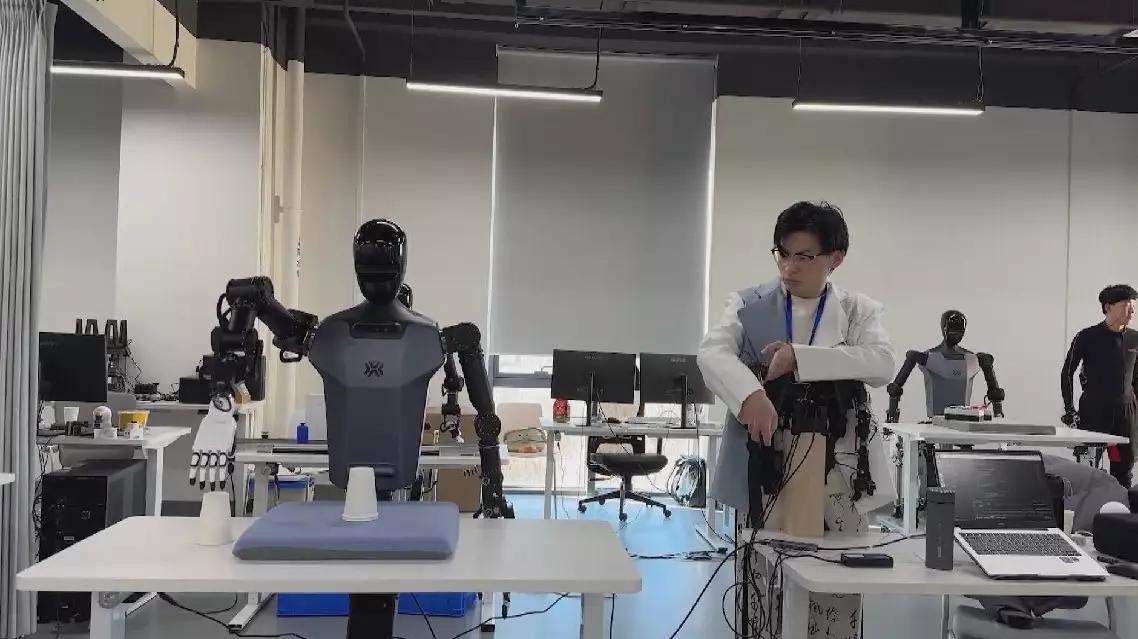
At Beijing's innovation center, robotic engineers use a hands-on approach to train embodied AI robots, employing remote control devices and motion-capture suits to teach them human-like movements and actions through interactive sessions.
The related data is then collected in real-time and used for further improvement and research.
Additionally, the center has built simulated environments that mimic real-world settings, such as retail stores, factories, and homes, to provide the robots with realistic training experiences.
The dataset contains data from 279 different task scenarios, involving different types of robots, like single-arm, two-arm, and humanoid robots. The dataset also records various robotic skills that can be applied widely.
It is the first universal dataset for embodied intelligent robots in China, and has been validated through model testing.
"The innovation center keeps collecting data on complex, long-term tasks. So far, we have hundreds of thousands of high-quality data records, mostly from real robot testing, along with some data from simulations and remote operations. In the future, the center plans to gradually release the dataset, covering more robots and the tasks they perform," said Wei Jiaxing, a staff member at the innovation center.
The quality of the dataset and its scale of application are key to training smarter robots, according to experts. Along with the dataset, evaluation standards have also been released, providing clearer guidelines on the requirements and quality of the robotic data.

China unveils groundbreaking training dataset for embodied AI robots