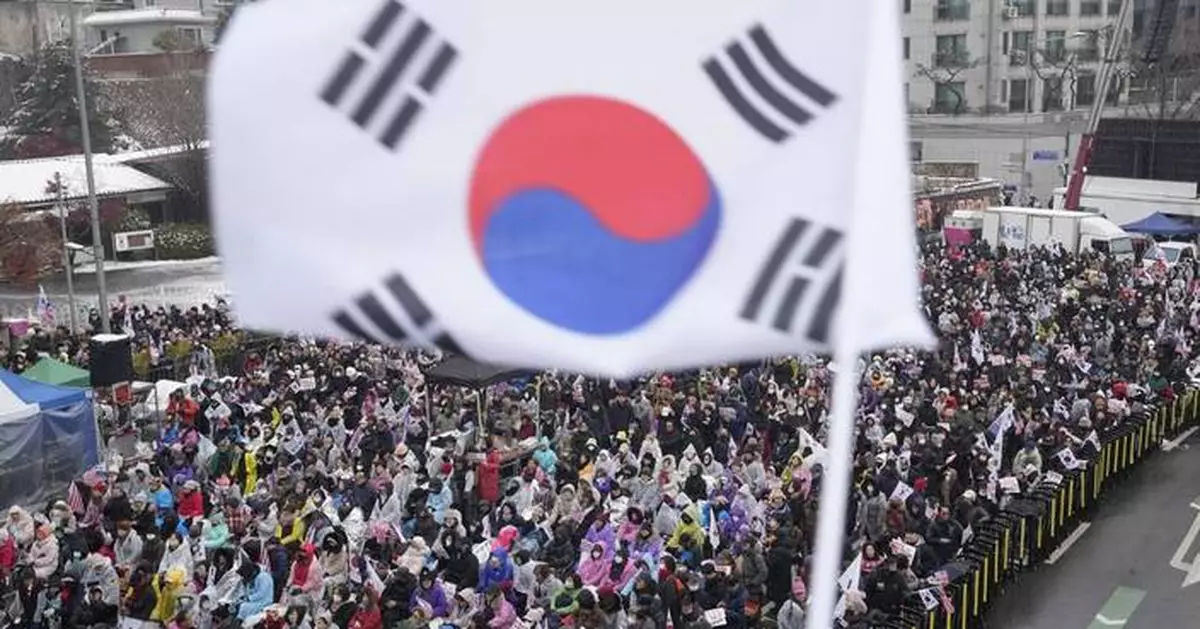
TOKYO (AP) — A standoff between rival government forces outside the presidential compound in South Korea has been startling even for those used to the country's famously rough and tumble politics.
For weeks, impeached President Yoon Suk Yeol has remained inside and refused to respond to detention and search warrants. Scuffles broke out late last week as dozens of investigators were stopped from entering the compound by hundreds of presidential security forces and a barricade.
The spectacle followed Yoon's astonishing decision last month to impose martial law during a seemingly routine impasse with the opposition, which dominates parliament.
Here's a closer view of recent events as well as South Korea's tempestuous political history, which has seen presidents toppled, arrested, jailed and shamed as millions have taken to the streets in protest.
Police and a government agency dedicated to fighting corruption are debating more forceful measures to detain Yoon. Dozens of investigators from the agency and police failed last week to bring Yoon into custody following a standoff with the presidential security service.
The initial court warrants to detain Yoon and to search his residence expired on Monday, but the anti-corruption agency obtained a new warrant on Tuesday that extended the window for Yoon’s detention. The agency didn’t immediately confirm how long the new warrant would remain valid.
Yoon has been refusing to appear for questioning over his short-lived martial law decree on Dec. 3.
He has described his power grab as a necessary act of governance against a liberal opposition that has bogged down his agenda with its legislative majority. He has vowed to “fight to the end” against efforts to oust him.
Martial law lasted only a few hours, but the country’s politics, diplomacy and financial markets have been shaken for weeks. The decree also exposed South Korea’s deeply polarized society.
Yoon’s lawyers on Monday filed complaints with public prosecutors against the anti-corruption agency’s chief prosecutor, Oh Dong-woon, and six other anti-corruption and police officers for orchestrating Friday’s detainment attempt, which they say was illegal.
Yoon's declaration of martial law unleashed a string of political aftershocks.
The anti-corruption agency, which is leading a joint investigation with police and the military, has been weighing charges of rebellion after Yoon declared martial law and dispatched troops to surround parliament. Lawmakers who managed to get past the blockade voted to lift martial law hours later.
Yoon’s presidential powers were suspended after parliament voted to impeach him on Dec. 14, accusing him of rebellion. The Constitutional Court has begun deliberations on whether to formally remove Yoon from office or reinstate him.
About 150 investigators tried to get Yoon on Friday in a tense standoff with the presidential security service that lasted more than five hours.
After getting around a military unit guarding the residence’s grounds, the agency’s investigators and police were able to approach within 200 meters (220 yards) of Yoon’s residential building but were stopped by a barricade of around 10 vehicles and approximately 200 members of the presidential security forces and troops.
In a statement, Park Jong-joon, chief of the presidential security service, hit back against criticism that his organization has become Yoon’s private army, saying it has a legal obligation to protect the incumbent president.
Yoon’s lawyers said they plan to file complaints against about 150 anti-corruption and police investigators who were involved in Friday’s detention attempt.
The why is incredibly tricky.
But a mix of history and geography have something to do with it.
The Koreas have been sandwiched between big powers for millennia, with China, Russia, Japan and the United States all playing parts of a great global game on the peninsula that extends from the east coast of Asia.
South Korea is deeply split, with the divisions reaching into many parts of life, from culture to class to gender to politics.
Much of the deep political divide can be traced to what happened at the end of World War II, when U.S. and Soviet forces met in the middle of the Korean Peninsula and agreed to divide the land into Washington and Moscow-backed spheres of influence. This solidified into independent rival Koreas in 1948 and then exploded into war and permanent division in 1950. After that, South Korea was run by a string of dictators until democracy came in the late 1980s.
Some of the passion evident in South Korean politics can be seen in the turmoil faced by recent presidents, many of whom have been jailed for corruption after leaving office.
A particularly sensational moment came in 2016 when millions protested against conservative President Park Geun-hye, who later became the first democratically elected leader to be forced from office since South Korea turned democratic.
Park, who was pardoned in late 2021 by her liberal rival and successor, had been serving a lengthy prison term for bribery and other crimes.
Associated Press writer Kim Tong-hyung in Seoul, South Korea, contributed to this report.

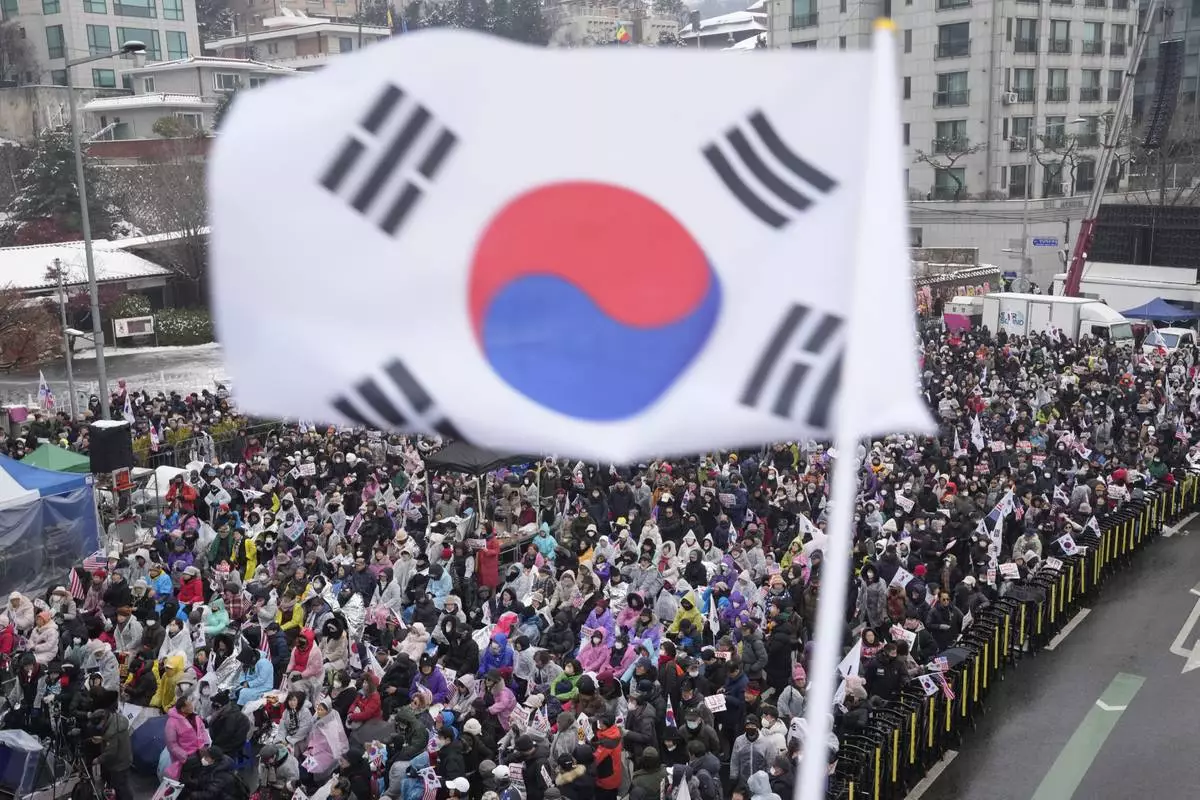
Supporters of impeached South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol stage a rally to oppose his impeachment near the presidential residence in Seoul, South Korea, Monday, Jan. 6, 2025. (AP Photo/Ahn Young-joon)

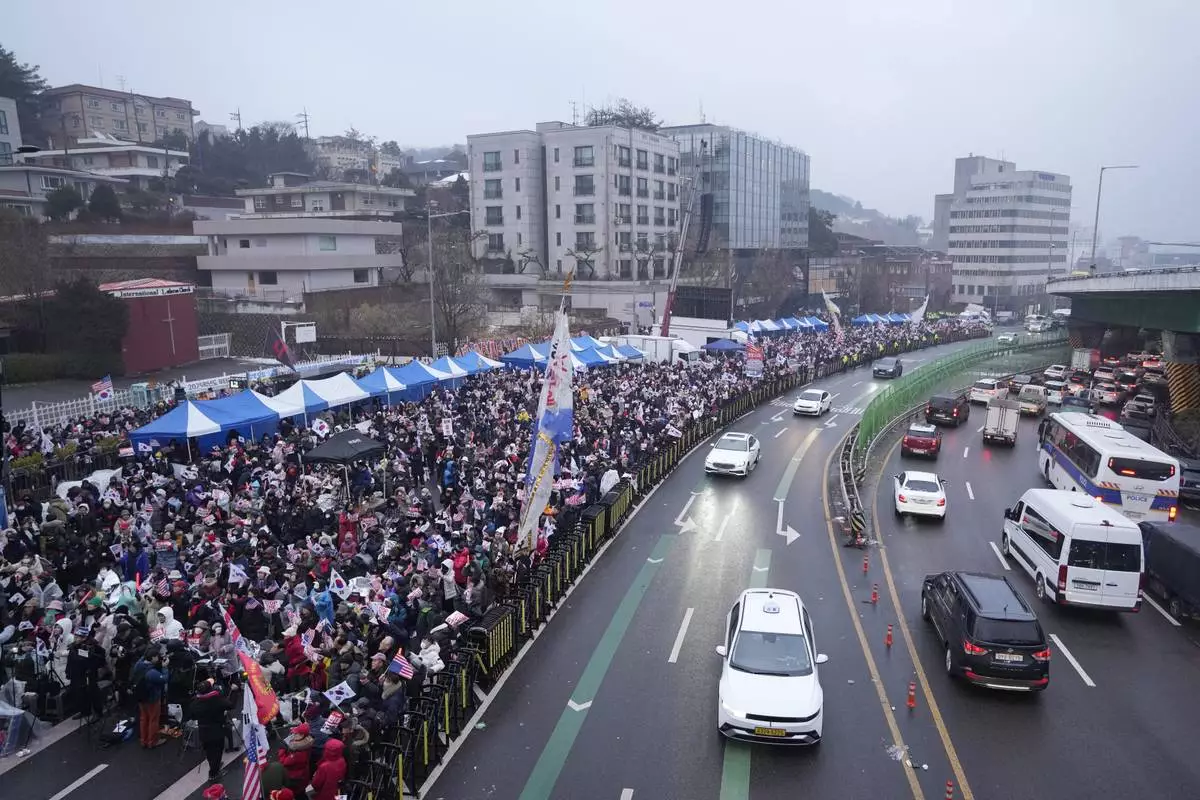
Supporters of impeached South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol stage a rally to oppose his impeachment near the presidential residence in Seoul, South Korea, Sunday, Jan. 5, 2025. (AP Photo/Ahn Young-joon)