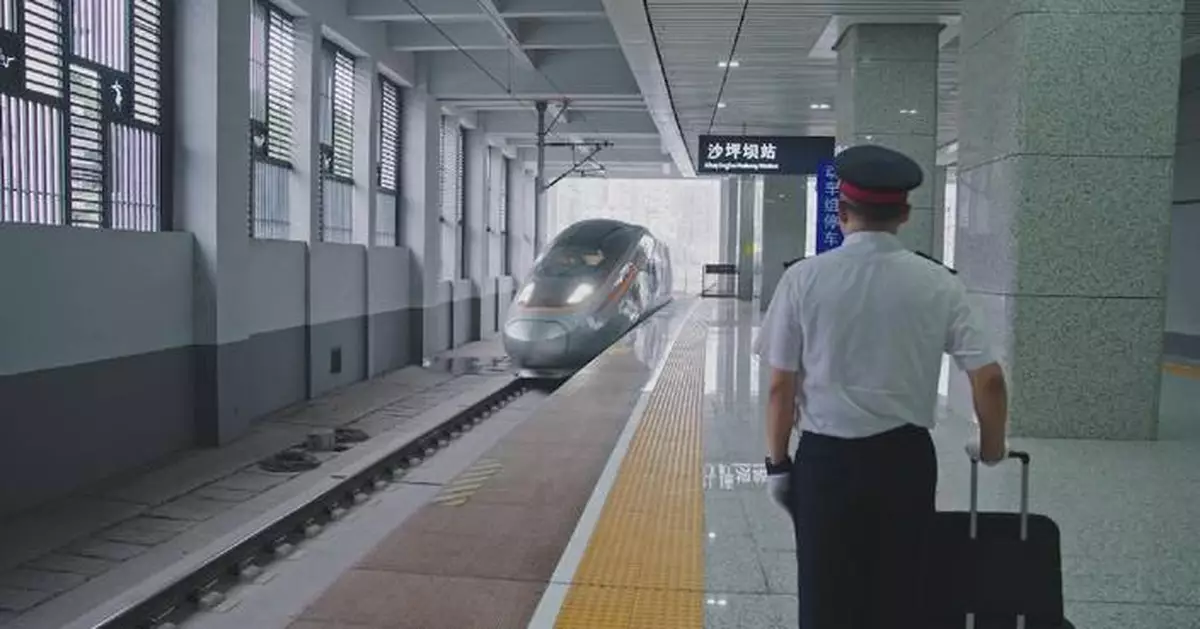
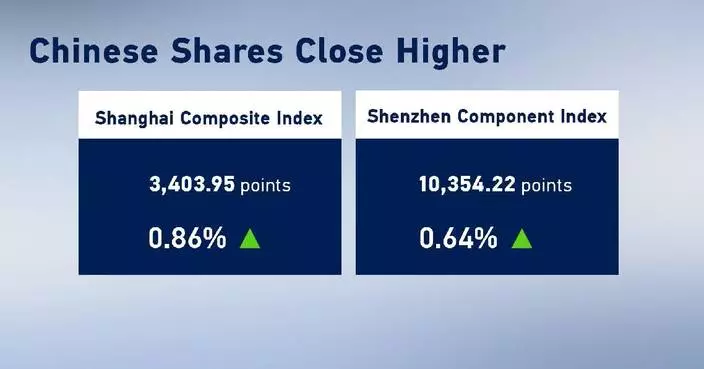
The Chengdu-Chongqing high-speed railway has facilitated closer economic integration and accelerated the development of a dual-city economic circle in southwestern China. The 308-kilometer-long high-speed railway, with a designed speed of 300 to 350 kilometers per hour, started operation in late 2015, dramatically reducing travel time between them from 13 to 2 hours. For three generations, train driver Li Zhigang and his family have been witnesses the evolution of China's rail transport from steam to high-speed trains. Li said his grandfather blew the first whistle on July 1, 1952 at the opening of the Chengdu-Chongqing railway, the first line built after the establishment of the People's Republic of China. His father Li Guofang was a retired train driver. Speed becomes a significant difference between the two generations. Li Guofang said a badge for 500,000 km of safe driving took at least a decade while Li Zhigang said now a high-speed train can make 500,000 km in a year or two. "My dad lived in the era of steam, the internal combustion engine and the electric locomotive. He's missed the era of high-speed trains," said Li Zhigang. As a Chongqing local, Li Zhigang has been a train driver for 27 years. "On December 25, 2021, the Chengdu-Chongqing line was upgraded to 350 km/h. I was the inaugural driver. I felt it was my inheritance," he said, "Now I'm driving from Chongqing to Chengdu on China's most advanced intelligent Fuxing high-speed train." Li said the high-speed railway is serving as a driving force for coordinated regional development as the two economically vibrant cities are building a dual-city economic circle with its own strengths and distinctive features as well as national impact. "Railways help to grow the local economy. The Chengdu-Chongqing dual-city economic circle, for example. Today, I might have noodles in Chongqing and then go shopping at Chengdu's Taikoo Li. Developing railways drives the surrounding economy. It's a microcosm of Chinese modernization," he said. Chongqing, the traditional industrial powerhouse in southwestern China, became China's fourth municipality in 1997 after Beijing, Shanghai and Tianjin. Covering 82,402 square kilometers and with a population of over 32 million, it is the largest of the four, even bigger in area than Ireland or the Czech Republic. Chengdu, capital of neighboring Sichuan province, boasts strong scientific research capabilities, fast economic growth and rich culture. "Chengdu and Chongqing are distinct and complementary in their industries. Chengdu leans towards soft technologies, such as communication and information technology. Chongqing excels in manufacturing, particularly smart manufacturing," said Liang Haoguang, executive director of the China Center for Modernization Research under the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The economic circle was first proposed on January 3, 2020 and its detailed guideline was released on October 21, 2021. It aims to create a new economic growth zone in the western China region. "This Chongqing-Chengdu high-speed line, which increases the connectivity of these two poles, and these two cities were identified as core drivers of western development," said Michael Dunford, emeritus professor of the University of Sussex. The Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle is another important regional development strategy, following the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, the Yangtze River Delta and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, the Yangtze River Delta and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, all in the country's east, have become the main drivers of China's economy. But the western region has lacked a national-level economic circle. The Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle is expected to drive the development of China's vast western region, and effectively solve the long-term problems of unbalanced and inadequate regional development in China. For a long time, the weak transport infrastructure of the Chengdu-Chongqing region has been one of the main stumbling blocks in its development. To solve the problem, the two cities have invested heavily in transport infrastructure in recent years. Developed transportation system is an important symbol of a world-class metropolitan area. It will also be the key to building the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle. "Creating urban clusters like the Greater Bay and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei regions groups industries and innovation zones to drive development, narrows the urban-rural gap and improves resource allocation," said Liang.
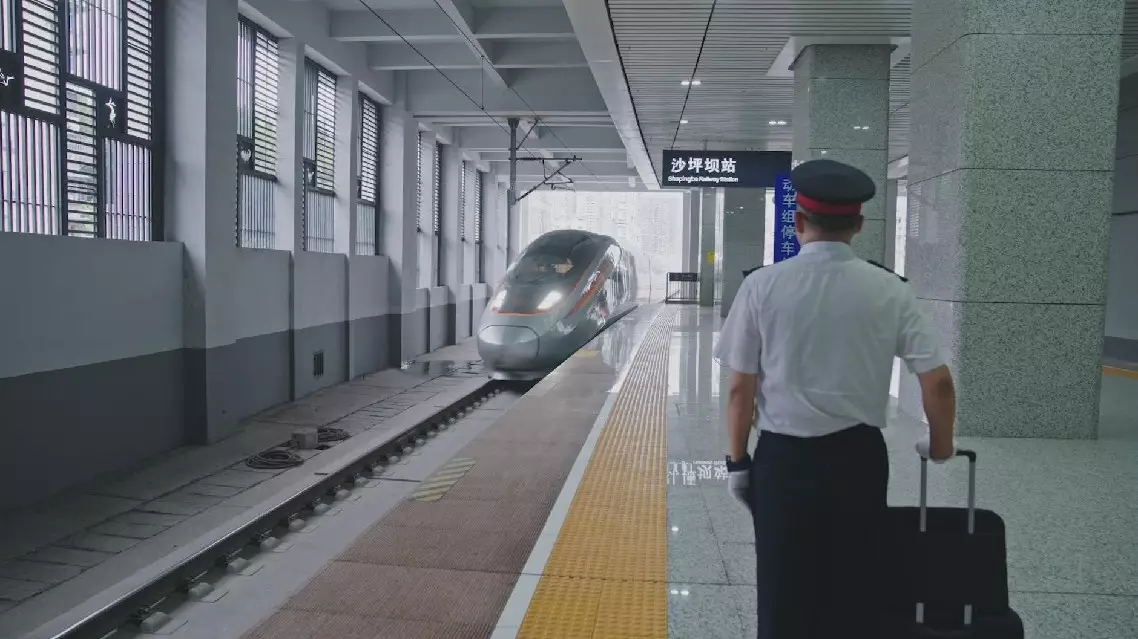

Chengdu-Chongqing high-speed railway boosts economic integration in southwest China