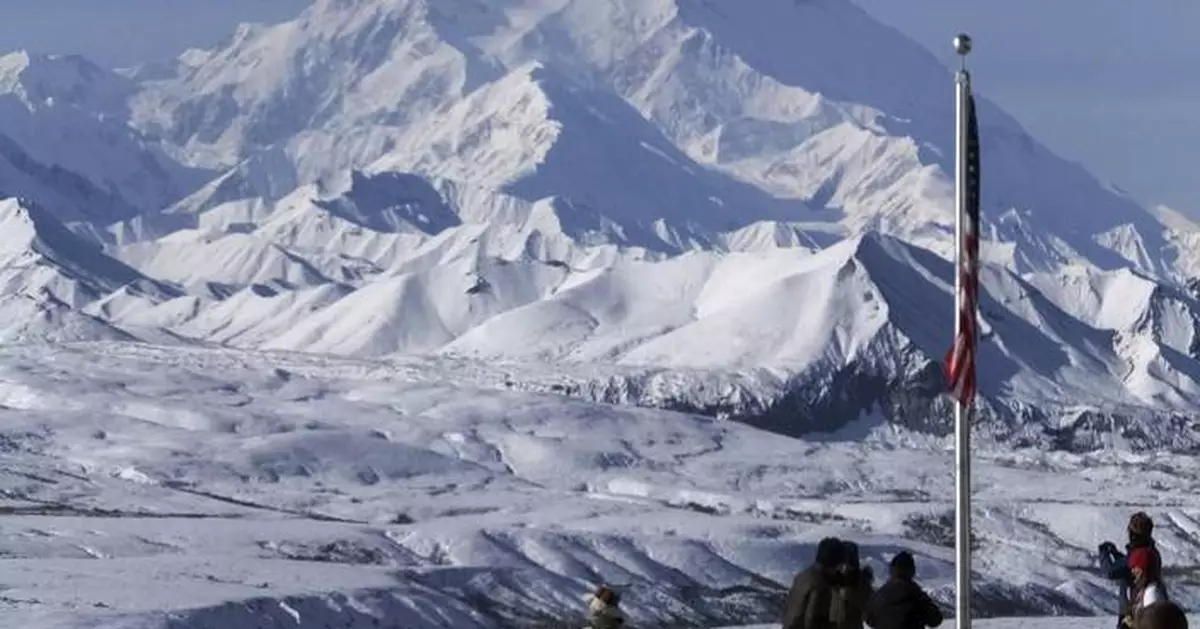
JUNEAU, Alaska (AP) — President Donald Trump issued an executive order Monday calling for North America’s tallest peak — Denali in Alaska — to be renamed Mount McKinley, reviving an idea he’d floated years ago and drawing a rebuke from Alaska’s Republican senior senator.
The order came hours after Trump, who took office for a second time Monday, said he planned to “restore the name of a great president, William McKinley, to Mount McKinley, where it should be and where it belongs. President McKinley made our country very rich through tariffs and through talent.”
U.S. Sen. Lisa Murkowski in a statement said she disagrees strongly with Trump wanting to change Denali's name.
“Our nation’s tallest mountain, which has been called Denali for thousands of years, must continue to be known by the rightful name bestowed by Alaska’s Koyukon Athabascans, who have stewarded the land since time immemorial," she said.
According to the National Park Service, a prospector in 1896 dubbed the peak “Mount McKinley” for William McKinley, who was elected president that year. McKinley had never been to Alaska. The name was formally recognized by the U.S. government until it was changed in 2015 by the Obama administration to Denali, to reflect the traditions of Alaska Natives and preference of many Alaskans. The move drew opposition from lawmakers in McKinley’s home state of Ohio.
Denali is an Athabascan word meaning “the high one” or “the great one.” The iconic 20,310-foot (6,190-meter) mountain, snow-capped and dotted with glaciers, is in Denali National Park and Preserve. The Tanana Chiefs Conference, a consortium of Athabascan tribes in Interior Alaska, spent years advocating for the peak to be recognized as Denali.
Trump's executive order celebrates McKinley, saying the 25th president “championed tariffs to protect U.S. manufacturing, boost domestic production, and drive U.S. industrialization and global reach to new heights.” McKinley, a Republican, was assassinated early in his second term in 1901.
"This order honors President McKinley for giving his life for our great Nation and dutifully recognizes his historic legacy of protecting America’s interests and generating enormous wealth for all Americans," the document states.
Messages seeking comment about the name change also were left for the other members of Alaska’s congressional delegation and Republican Gov. Mike Dunleavy. Alaska's U.S. senators in 2017 vehemently opposed a prior suggestion by Trump that the name Denali revert back to Mount McKinley.
Trump revisited the topic during a rally late last year, following his election.
“McKinley was a very good, maybe a great president,” Trump said in December. “They took his name off Mount McKinley, right? That’s what they do to people.”
Alaska and Ohio had been at odds over the name for decades. Alaska had a standing request to change the name since 1975, when the legislature passed a resolution and then-Gov. Jay Hammond appealed to the federal government.
In the same executive order Monday, Trump also called for changing the name of the Gulf of Mexico to the Gulf of America.
Among other executive actions, Trump rescinded a 2023 decision by then-President Joe Biden barring drilling on nearly 3 million acres of the Beaufort Sea off the northern coast of Alaska. The U.S. Department of Interior at that time said there had not been a federal oil and gas lease sale in the Arctic Ocean since 2007.
The 2023 decision came around the same time the Biden administration approved a large oil project, known as Willow, in the National Petroleum Reserve-Alaska, angering environmentalists. Litigation around the approval of Willow is still pending.
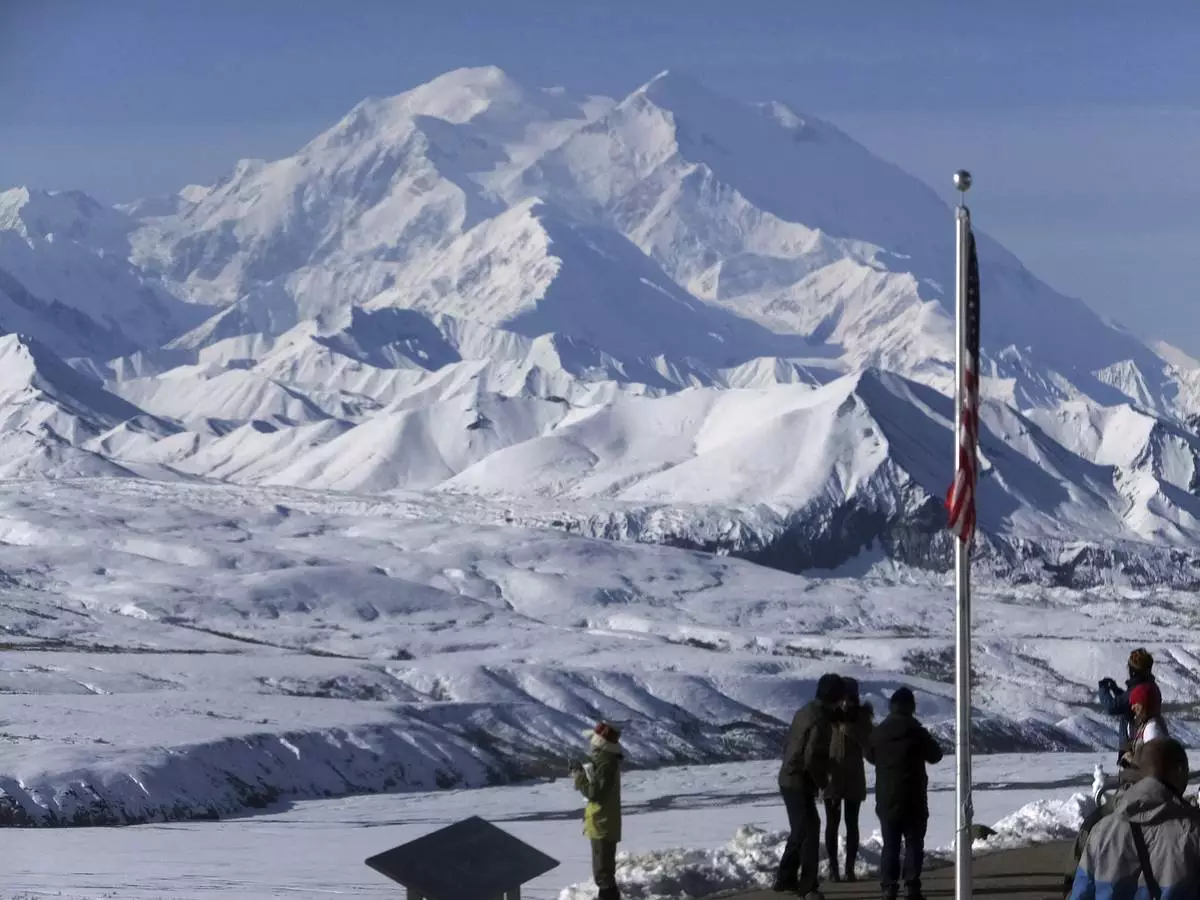

FILE - People stand at the Eielson Visitor Center with a view of North America's tallest peak, Denali, in the background, Sept. 2, 2015, in Denali National Park and Preserve, Alaska. (AP Photo/Becky Bohrer, file)
ATLANTA (AP) — A pregnant woman in Georgia was declared brain-dead after a medical emergency and doctors have kept her on life support for three months to allow enough time for the baby to be born and comply with Georgia’s strict anti-abortion law, family members say.
The case is the latest consequence of abortion bans introduced in some states since the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade three years ago.
Adriana Smith, a 30-year-old mother and nurse, was declared brain-dead — meaning she is legally dead — in February, her mother, April Newkirk, told Atlanta TV station WXIA.
Newkirk said her daughter had intense headaches more than three months ago and went to Atlanta's Northside Hospital, where she received medication and was released. The next morning, her boyfriend woke to her gasping for air and called 911. Emory University Hospital determined she had blood clots in her brain and she was later declared brain-dead.
Newkirk said Smith is now 21 weeks pregnant. Removing breathing tubes and other life-saving devices would likely kill the fetus.
Northside did not respond to a request for comment Thursday. Emory Healthcare said it could not comment on an individual case because of privacy rules, but released a statement saying it “uses consensus from clinical experts, medical literature, and legal guidance to support our providers as they make individualized treatment recommendations in compliance with Georgia’s abortion laws and all other applicable laws. Our top priorities continue to be the safety and wellbeing of the patients we serve.”
Smith's family says Emory doctors have told them they are not allowed to stop or remove the devices that are keeping her breathing because state law bans abortion after cardiac activity can be detected — generally around six weeks into pregnancy.
The law was adopted in 2019 but not enforced until after Roe v. Wade was overturned in 2022, opening the door to state abortion bans. Georgia's ban includes an exception if an abortion is necessary to maintain the life of the woman.
Smith's family, including her five-year-old son, still visit her in the hospital.
Newkirk said doctors told the family that the fetus has fluid on the brain and that they're concerned about his health.
“She’s pregnant with my grandson. But he may be blind, may not be able to walk, may not survive once he’s born,” Newkirk said. She has not commented on whether the family wants Smith removed from life support.
Monica Simpson, executive director of SisterSong, the lead plaintiff in a lawsuit challenging Georgia’s abortion law, said the situation is problematic.
"Her family deserved the right to have decision-making power about her medical decisions,” Simpson said in a statement. “Instead, they have endured over 90 days of retraumatization, expensive medical costs, and the cruelty of being unable to resolve and move toward healing.”
Lois Shepherd, a bioethicist and law professor at the University of Virginia, said she does not believe Georgia's law requires life support in this case.
But she said whether a state could insist Smith remains on the breathing and other devices is uncertain since the 2022 ruling in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization, which overturned Roe including that fetuses do not have the rights of people.
“Pre-Dobbs, a fetus didn’t have any rights,” Shepherd said. “And the state’s interest in fetal life could not be so strong as to overcome other important rights, but now we don’t know.”
Brain death in pregnancy is rare. Even rarer still are cases in which doctors aim to prolong the pregnancy after a woman is declared brain-dead.
“It’s a very complex situation, obviously, not only ethically but also medically,” said Dr. Vincenzo Berghella, director of maternal fetal medicine at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.
A 2021 review that Berghella co-authored scoured medical literature going back decades for cases in which doctors declared a woman brain-dead and aimed to prolong her pregnancy. It found 35.
Of those, 27 resulted in a live birth, the majority either immediately declared healthy or with normal follow-up tests. But Berghella also cautioned that the Georgia case was much more difficult because the pregnancy was less far along when the woman was declared brain dead. In the 35 cases he studied, doctors were able to prolong the pregnancy by an average of just seven weeks before complications forced them to intervene.
“It’ s just hard to keep the mother out of infection, out of cardiac failure,” he said.
Berghella also found a case from Germany that resulted in a live birth when the woman was declared brain dead at nine weeks of pregnancy.
Georgia's law confers personhood on a fetus. Those who favor personhood say fertilized eggs, embryos and fetuses should be considered people with the same rights as those already born.
Georgia state Sen. Ed Setzler, a Republican who sponsored the 2019 law, said he supported Emory’s interpretation.
“I think it is completely appropriate that the hospital do what they can to save the life of the child,” Setzler said. “I think this is an unusual circumstance, but I think it highlights the value of innocent human life. I think the hospital is acting appropriately.”
Setzler said he believes it is sometimes acceptable to remove life support from someone who is brain dead, but that the law is “an appropriate check” because the mother is pregnant. He said Smith's relatives have “good choices,” including keeping the child or offering it for adoption.
Georgia’s abortion ban has been in the spotlight before.
Last year, ProPublica reported that two Georgia women died after they did not get proper medical treatment for complications from taking abortion pills. The stories of Amber Thurman and Candi Miller entered into the presidential race, with Democrat Kamala Harris saying the deaths were the result of the abortion bans that went into effect in Georgia and elsewhere after Dobbs.
The situation echoes a case in Texas more than a decade ago when a brain-dead woman was kept on maintenance measures for about two months because she was pregnant. A judge eventually ruled that the hospital keeping her alive against her family’s wishes was misapplying state law, and life support was removed.
Twelve states are enforcing abortion bans at all stages of pregnancy, with limited exceptions. Georgia is one of four with a ban that kicks in at or around six weeks into pregnancy — often before women realize they’re pregnant.
Last year, the Texas Supreme Court ruled unanimously against a group of women who challenged that state’s abortion ban, saying the exceptions were being interpreted so narrowly that they were denied abortion access as they dealt with serious pregnancy complications. This year, the state Senate has passed a bill that seeks to clarify when abortions are allowed.
South Dakota produced a video to inform doctors about when exceptions should apply. Abortion rights groups have blasted it.
The U.S. Supreme Court heard arguments in December over whether the federal law that requires hospitals to provide abortion in emergency medical situations should apply. A ruling is expected in coming months.
Mulvihill reported from Cherry Hill, New Jersey. Associated Press journalists Kate Brumback, Sudhin Thanawala, Sharon Johnson and Charlotte Kramon contributed.

Emory University Hospital Midtown is seen on Thursday, May 15, 2025, in Atlanta. (AP Photo/Brynn Anderson)

Emory University Hospital Midtown is seen on Thursday, May 15, 2025, in Atlanta. (AP Photo/Brynn Anderson)

Emory University Hospital Midtown is seen on Thursday, May 15, 2025, in Atlanta. (AP Photo/Brynn Anderson)

Emory University Hospital Midtown is seen on Thursday, May 15, 2025, in Atlanta. (AP Photo/Brynn Anderson)

FILE - The Georgia State Capitol is seen from Liberty Plaza in downtown Atlanta, April 6, 2020. (Alyssa Pointer/Atlanta Journal-Constitution via AP, File)