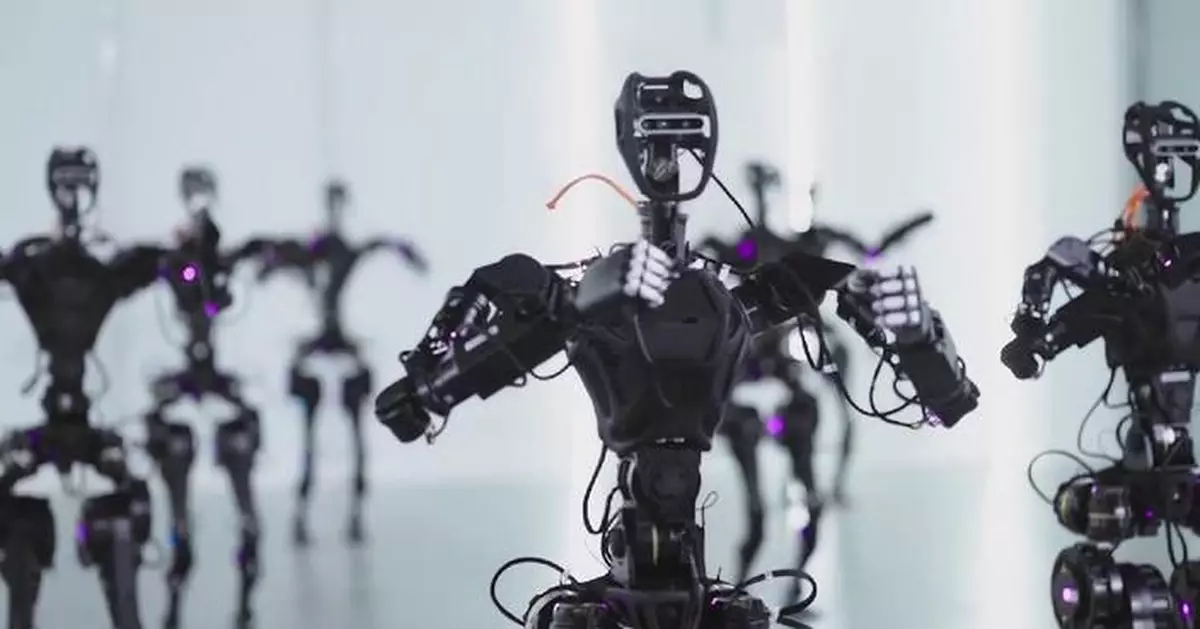
Shanghai-based robotics firm Fourier Intelligence on Monday released an open-source dataset that it hopes will allow companies and research institutions around the world to better train robots in the human-like usage of their hands.
Dubbed Fourier ActionNet, the landmark dataset was compiled by having real humans wear virtual reality headsets as they guide a humanoid robot through the use of its hands through a teleoperation system. According to Fourier, this method aims to allow robots to move away from traditional gripper-based systems and instead take advantage of the dexterity of the human hand.
The initial dataset comprises more than 30,000 high-quality training entries, featuring intricate hand movements and specialized imitation learning data for tasks involving hand dexterity. These entries span a wide range of real-world applications, including activities such as picking up and setting down tools, performing household chores, and executing various other hand-related tasks.
The release aims to foster innovation and collaboration among the global robotics community and enhance AI robot training, the company announced on Monday.
Up to now, Fourier has collaborated with over 20 top domestic and international research institutions and leading industry enterprises. The company has pledged it will continue to release more advanced data modules covering full-body motion control and multi-task coordination.

Shanghai-based robotics firm releases open-source dataset on humanoid robot hand usage
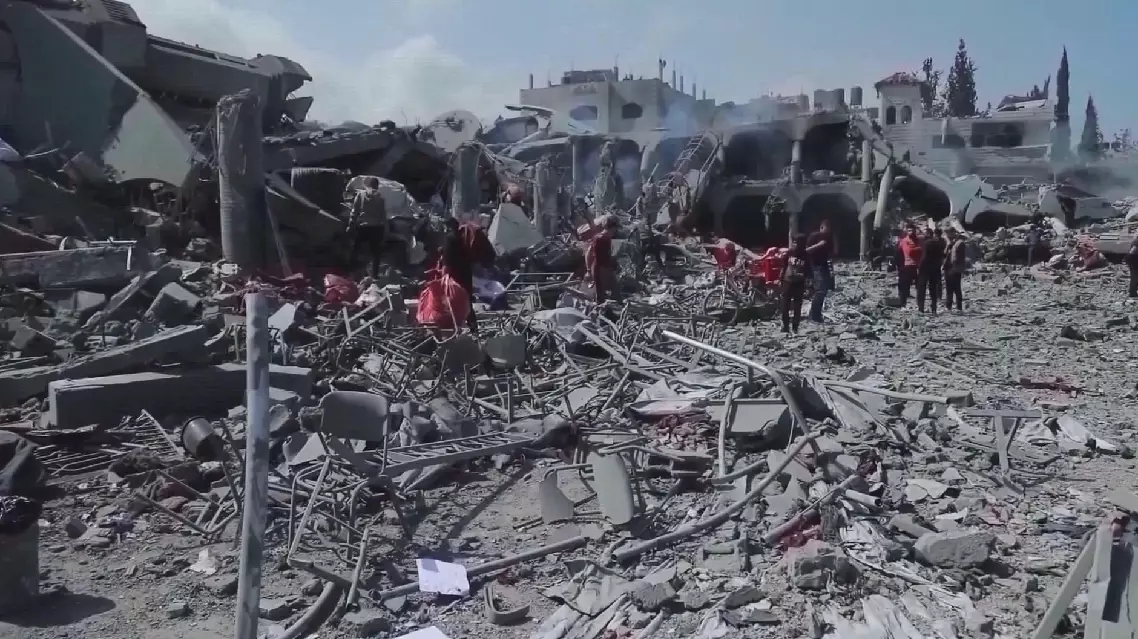
The Palestinian death toll in the Gaza Strip has risen to 52,760, with 119,264 others injured since the outbreak of the Israel-Hamas conflict in early October 2023, according to a statement released Thursday by Gaza-based health authorities.
The statement said that since Israel resumed intensive military operation on March 18, at least 2,651 Palestinians have been killed and 7,723 injured.
In the past 24 hours alone, 106 Palestinians were killed, and 367 others injured in Israeli military operations across the enclave, the statement said.
Israel halted the entry of goods and supplies into Gaza on March 2, following the expiration of the first phase of a January ceasefire agreement with Hamas.
Amid the Israeli blockade, Khalil Al-Daqran, spokesperson for Al-Aqsa Martyrs Hospital in Deir al-Balah, said Thursday in a statement that many wounded could face "a death sentence" as hospitals in Gaza "are unable to accommodate" them due to "a severe shortage of medicines" out of the blockade.
Also on Thursday, the Civil Defense in Gaza said in a press statement that 75 percent of its vehicles have stopped operating due to the depletion of fuel amid the Israeli blockade and attacks, apart from "a severe shortage of generators and oxygen devices."
The UN has already warned of an impending humanitarian catastrophe in Gaza, reporting increasing signs of acute hunger, particularly among children.
The situation is rapidly deteriorating as the U.S.-based food relief organization World Central Kitchen announced Wednesday that it would halt cooking in Gaza due to the depletion of humanitarian supplies, forcing the closure of most community kitchens in the enclave after running out of stock.

Palestinian death toll in Gaza rises to 52,760