GENEVA (AP) — Top minds at the world's largest atom smasher have released a blueprint for a much bigger successor that could vastly improve research into the remaining enigmas of physics.
The plans for the Future Circular Collider — a nearly 91-kilometer (56.5-mile) loop along the French-Swiss border and below Lake Geneva — published late Monday put the finishing details on a project roughly a decade in the making at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research.
The FCC would carry out high-precision experiments in the mid-2040s to study “known physics” in greater detail, then enter a second phase — planned for 2070 — that would conduct high-energy collisions of protons and heavy ions that would “open the door to the unknown,” said Giorgio Chiarelli, a research director at Italy’s National Institute of Nuclear Physics.
“History of physics tells that when there is more data, the human ingenuity is able to extract more information than originally expected,” Chiarelli, who was not involved in the plans, said in an e-mail.
For roughly a decade, top minds at CERN have been making plans for a successor to the Large Hadron Collider, a network of magnets that accelerate particles through a 27-kilometer (17-mile) underground tunnel and slam them together at velocities approaching the speed of light.
The blueprint lays out the proposed path, environmental impact, scientific ambitions and project cost. Independent experts will take a look before CERN's two dozen member countries — all European except for Israel — decide in 2028 whether to go forward, starting in the mid-2040s at a cost of some 14 billion Swiss francs (about $16 billion).
CERN officials tout the promise of scientific discoveries that could drive innovation in fields like cryogenics, superconducting magnets and vacuum technologies that could benefit humankind.
Outside experts point to the promise of learning more about the Higgs boson, the elusive particle that has been controversially dubbed “the God particle,” which helped explain how matter formed after the Big Bang.
Work at the Large Hadron Collider confirmed in 2013 the existence of the Higgs boson, the central piece in a puzzle known as the standard model that helps explains some fundamental forces in the universe.
CERN Director-General Fabiola Gianotti said the future collider "could become the most extraordinary instrument ever built by humanity to study the constituents and the laws of nature at the most fundamental levels in two ways,” by improving study of the Higgs boson and paving the way to “explore the energy frontier,” and by looking for new physics that explain the structure and evolution of the universe.
One unknown is whether the Trump administration, which has been cutting foreign aid and spending in academia and research, will continue to support CERN a year after the Biden administration pledged U.S. support for the study and collaboration on the FCC's construction and “physics exploitation” if it's approved.
The United States is home to 2,000 users of CERN, making them the single largest national contingent among the 17,000 people working there, including outside experts abroad and staff on site, Gianotti said.
While an observer state and not a member, the U.S. doesn't pay into the CERN regular budget but has contributed to specific projects. Most of the CERN regular budget comes from Europe.
Costas Fountas, the CERN Council president, said he had spoken with some U.S. National Science Foundation and Department of Energy staff who relayed the message that so far “they're 'under the radar of the cuts of the Trump administration'. That’s their words.”
CERN scientists, engineers and partners behind the plans considered at least 100 scenarios for the new collider before coming up with the proposed 91-kilometer circumference at an average depth of 200 meters (656 feet). The tunnel would be about 5 meters (16 feet) in diameter, CERN said.
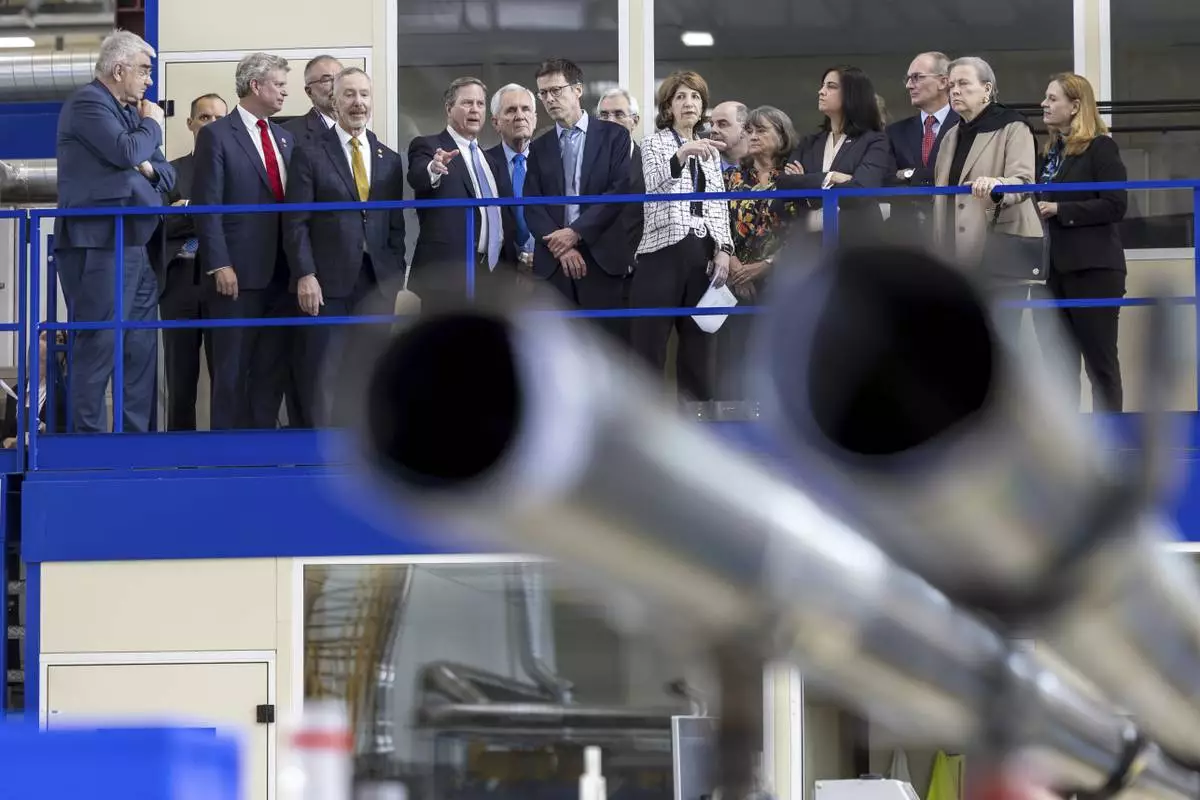

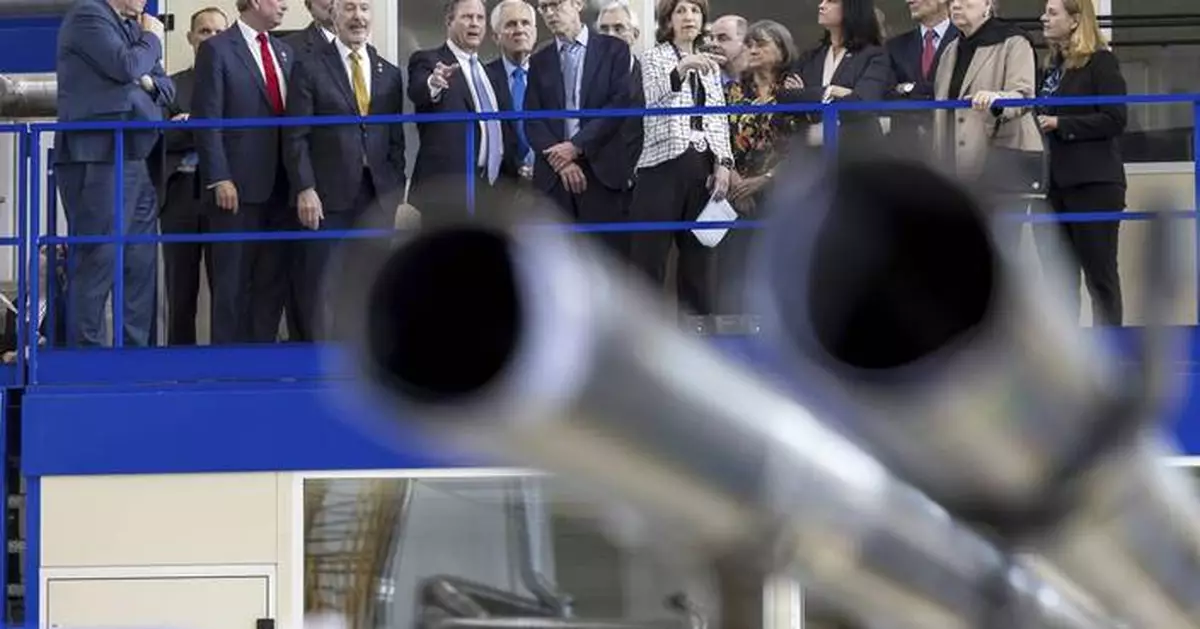
Mike Lamont, director for accelerators and technology, center left, and Fabiola Gianotti, center right, director general of the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), speak with members of the U.S. House of Representatives in the Large Magnet Facility during a visit to CERN facilities in Meyrin, near Geneva, Switzerland, Friday, March 21, 2025. (Salvatore Di Nolfi/Keystone via AP)