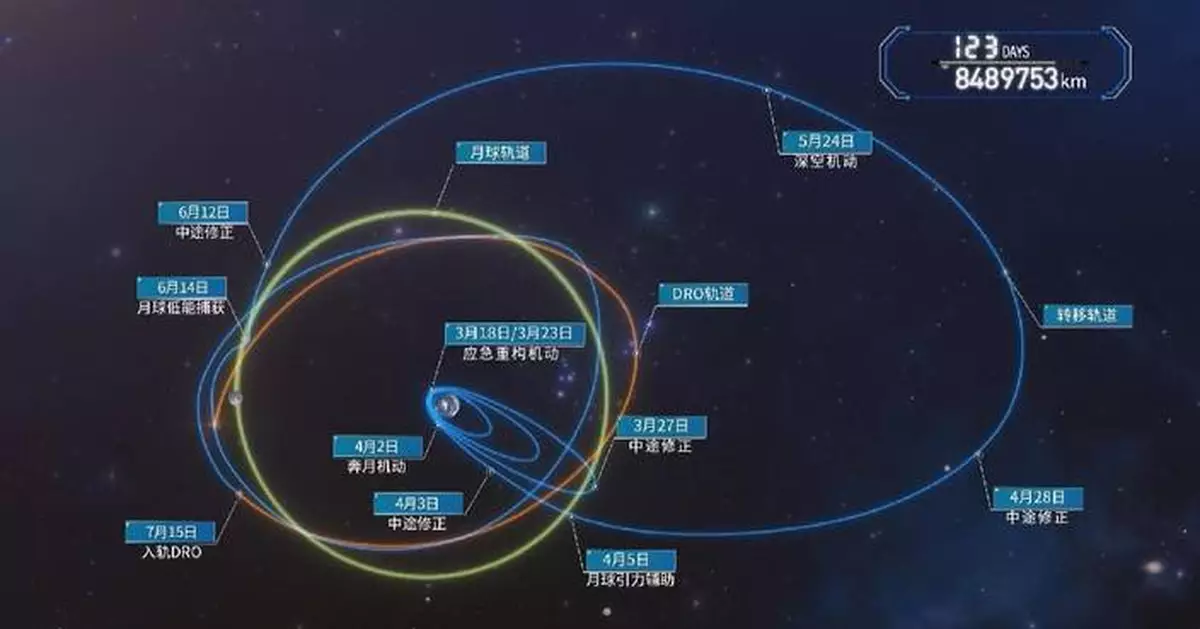
China has established the world's first three-satellite constellation based on the Distant Retrograde Orbit (DRO) in Earth-moon space, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in scientific research and space exploration across multiple fields.
The Earth-moon space, spanning up to 2 million kilometers from Earth, serves as a strategic zone for lunar resource development and deep-space exploration. China's efforts in this area began in 2017 with preliminary research and technological advancements, culminating in the successful launch and networking of three satellites in 2024, including DRO-A and DRO-B entering the DRO.
"DRO is one of the most stable types of orbits in Earth-moon space. Its stability makes it an ideal 'laboratory' or 'lighthouse' in space, allowing satellites to remain in position for extended periods," said Zhang Hao, a researcher at the Chinese Academy of Sciences' (CAS) Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization.
Currently, the constellation has achieved several breakthroughs, including a low-energy transfer to DRO using only one-fifth of the fuel required by traditional methods.
"These satellites can help these spacecraft accurately determine their positions in the vast ocean of the Earth-moon space. This way, they can better carry out their missions," said Mao Xinyuan, an associate researcher at the center.
It has also established the world's first 1.17 million-kilometer K-band inter-satellite microwave measurement and communication link.
Additionally, the satellites have validated a new satellite-tracking-satellite orbit determination system, reducing the cost of orbit determination for spacecraft in Earth-moon space.
Wang Wenbin, a researcher at the center, highlighted the significance of these achievements.
"This is the first time we have used satellite-to-satellite tracking instead of ground-based tracking. It transforms traditional ground stations into low-orbit satellites, providing a new technical pathway for future Earth-moon and deep-space exploration. This will support various orbit determination, navigation, and timing needs in Earth-moon space and offer efficient solutions for large-scale commercial activities in Earth-moon space in the future for our country," said Wang.
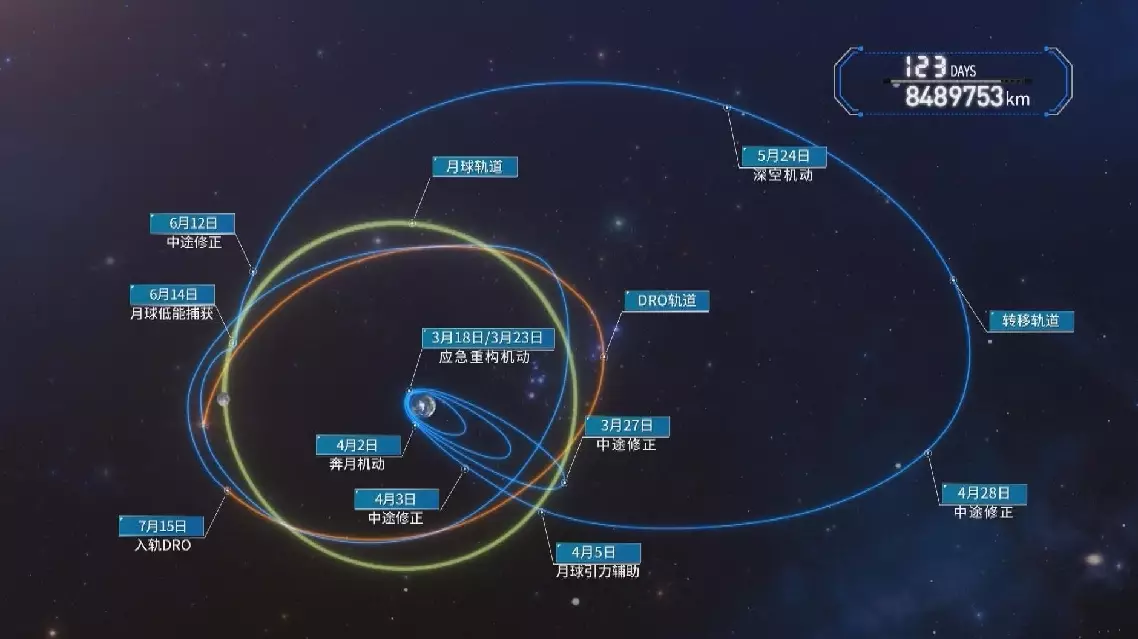
China's Earth-moon space constellation pioneers multidisciplinary research