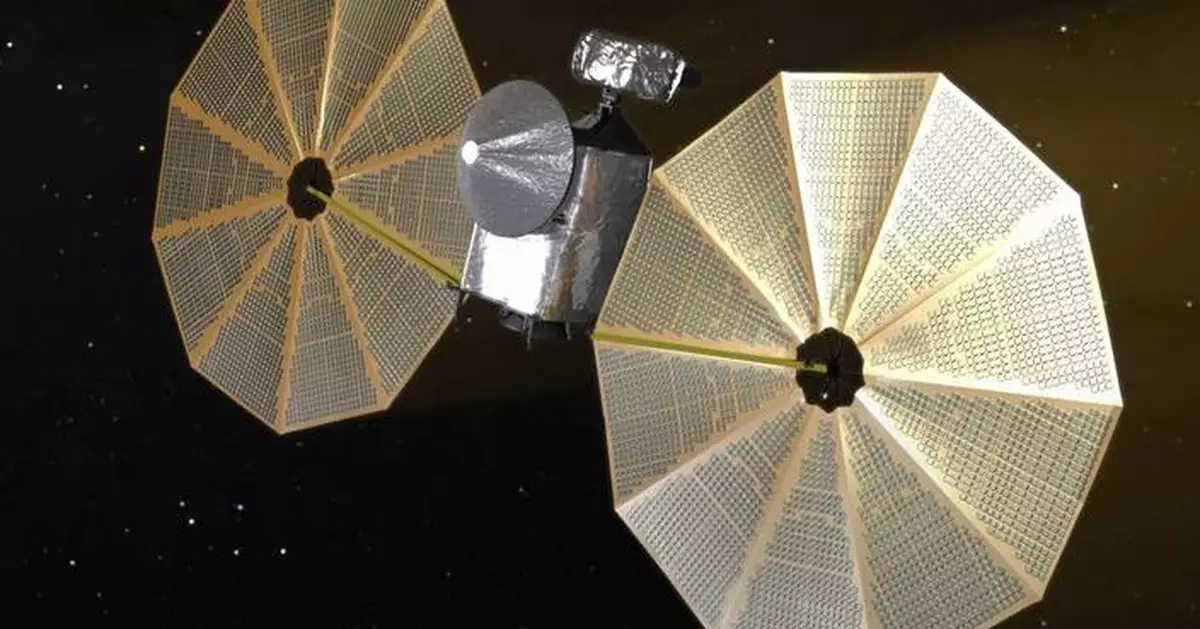
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — NASA’s Lucy spacecraft will swoop past a small asteroid this weekend as it makes its way to an even bigger prize: the unexplored swarms of asteroids out near Jupiter.
It will be the second asteroid encounter for Lucy, launched in 2021 on a quest that will take it to 11 space rocks. The close approaches should help scientists better understand our early solar system when planets were forming; asteroids are the ancient leftovers.
The upcoming flyby is a dress rehearsal for 2027 when Lucy reaches its first so-called Trojan asteroid near Jupiter.
Cranking up its three science instruments, the spacecraft on Sunday will observe the harmless asteroid known as Donaldjohanson. The encounter will take place 139 million miles (223 million kilometers) from Earth in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, so far away it will take 12 minutes for each bit of data to reach flight controllers in Colorado.
The paleontologist for whom the asteroid is named plans to be at spacecraft builder and operator Lockheed Martin’s Mission Control for all the action. He discovered the fossil Lucy in Ethiopia 50 years ago; the spacecraft is named after the famous human ancestor.
NASA’s Lucy will venture as close as 596 miles (960 kilometers) to this asteroid, an estimated 2 ½ miles (4 kilometers) in length but much shorter in width. Scientists should have a better idea of its size and shape following the brief visit. The spacecraft will zoom by at more than 30,000 mph (48,000 kph).
The asteroid is among countless fragments believed to have resulted from a major collision 150 million years ago.
“It's not going to be a basic potato. We already know that,” said lead scientist Hal Levison of Southwest Research Institute.
Rather, Levison said the asteroid may resemble a bowling pin or even a snowman like Arrokoth, the Kuiper Belt object visited by NASA's New Horizon spacecraft in 2019. The other possibility is that there are two elongated but separate asteroids far apart.
“We don’t know what to expect. That’s what makes this so cool,” he said.
There will be no communications with Lucy during the flyby as the spacecraft turns its antenna away from Earth in order to track the asteroid. Levison expects to have most of the science data within a day.
Lucy’s next stop — “the main event,” as Levison calls it — will be the Trojan asteroids that share Jupiter’s orbit around the sun. Swarms of Trojans precede and follow the solar system’s largest planet as it circles the sun. Lucy will visit eight of them from 2027 through 2033, some of them in pairs of two.
Lucy’s first asteroid flyby was in 2023 when it swept past little Dinkinesh, also in the main asteroid belt. The spacecraft discovered a mini moon around it.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
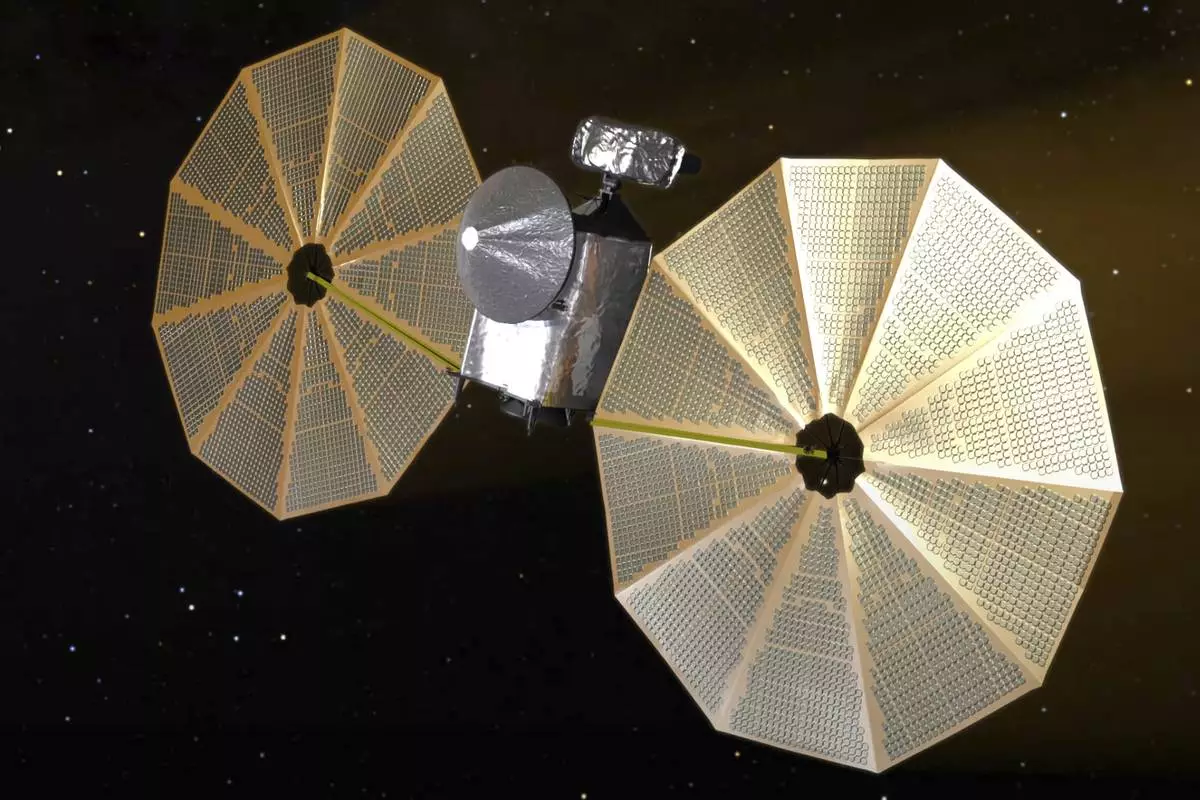

This image from video animation provided by NASA in October 2022 depicts the Lucy spacecraft. (NASA via AP)
VATICAN CITY (AP) — “Conclave,” the movie, may have introduced movie-goers to the spectacular ritual and drama of a modern conclave, but the periodic voting to elect a new pope has been going on for centuries and created a whole genre of historical trivia.
Here are some fun facts about conclaves past, derived from historical studies including Miles Pattenden's “Electing the Pope in Early Modern Italy, 1450–1700” and interviews with experts including Elena Cangiano, an archeologist at Viterbo's Palazzo dei Papi (Palace of the Popes).
In the 13th century, it took almost three years — 1,006 days to be exact — to choose Pope Clement IV's successor, making it the longest conclave in the Catholic Church’s history. It's also where the term conclave comes from — "under lock and key," because the cardinals who were meeting in Viterbo, north of Rome, took so long the town's frustrated citizens locked them in the room.
The secret vote that elected Pope Gregory X lasted from November 1268 to September 1271. It was the first example of a papal election by “compromise,” after a long struggle between supporters of two main geopolitical medieval factions — those faithful to the papacy and those supporting the Holy Roman Empire.
Gregory X was elected only after Viterbo residents tore the roof off the building where the prelates were staying and restricted their meals to bread and water to pressure them to come to a conclusion. Hoping to avoid a repeat, Gregory X decreed in 1274 that cardinals would only get “one meal a day” if the conclave stretched beyond three days, and only “bread, water and wine” if it went beyond eight. That restriction has been dropped.
Before 1274, there were times when a pope was elected the same day as the death of his predecessor. After that, however, the church decided to wait at least 10 days before the first vote. Later that was extended to 15 days to give all cardinals time to get to Rome. The quickest conclave observing the 10-day wait rule appears to have been the 1503 election of Pope Julius II, who was elected in just a few hours, according to Vatican historian Ambrogio Piazzoni. In more recent times, Pope Francis was elected in 2013 on the fifth ballot, Benedict XVI won in 2005 on the fourth and Pope Pius XII won on the third in 1939.
The first conclave held under Michelangelo's frescoed ceiling in the Sistine Chapel was in 1492. Since 1878, the world-renowned chapel has become the venue of all conclaves. “Everything is conducive to an awareness of the presence of God, in whose sight each person will one day be judged,” St. John Paul II wrote in his 1996 document regulating the conclave, “Universi Dominici Gregis.” The cardinals sleep a short distance away in the nearby Domus Santa Marta hotel or a nearby residence.
Most conclaves were held in Rome, with some taking place outside the Vatican walls. Four were held in the Pauline Chapel of the papal residence at the Quirinale Palace, while some 30 others were held in St. John Lateran Basilica, Santa Maria Sopra Minerva or other places in Rome. On 15 occasions they took place outside Rome and the Vatican altogether, including in Viterbo, Perugia, Arezzo and Venice in Italy, and Konstanz, Germany, and Lyon, France.
Between 1378-1417, referred to by historians as the Western Schism, there were rival claimants to the title of pope. The schism produced multiple papal contenders, the so-called antipopes, splitting the Catholic Church for nearly 40 years. The most prominent antipopes during the Western Schism were Clement VII, Benedict XIII, Alexander V, and John XXIII. The schism was ultimately resolved by the Council of Constance in 1417, which led to the election of Martin V, a universally accepted pontiff.
The cloistered nature of the conclave posed another challenge for cardinals: staying healthy. Before the Domus Santa Marta guest house was built in 1996, cardinal electors slept on cots in rooms connected to the Sistine Chapel. Conclaves in the 16th and 17th centuries were described as “disgusting” and “badly smelling,” with concern about disease outbreaks, particularly in summer, according to historian Miles Pattenden. “The cardinals simply had to have a more regular and comfortable way of living because they were old men, many of them with quite advanced disease,” Pattenden wrote. The enclosed space and lack of ventilation further aggravated these issues. Some of the electors left the conclave sick, often seriously.
Initially, papal elections weren’t as secretive, but concerns about political interference soared during the longest conclave in Viterbo. Gregory X decreed that cardinal electors should be locked in seclusion, “cum clave” (with a key), until a new pope was chosen. The purpose was to create a totally secluded environment where the cardinals could focus on their task, guided by God’s will, without any political interference or distractions. Over the centuries, various popes have modified and reinforced the rules surrounding the conclave, emphasizing the importance of secrecy.
Pope John XII was just 18 when he was elected in 955. The oldest popes were Pope Celestine III (elected in 1191) and Celestine V (elected in 1294) who were both nearly 85. Benedict XVI was 78 when he was elected in 2005.
There is no requirement that a pope be a cardinal, but that has been the case for centuries. The last time a pope was elected who wasn’t a cardinal was Urban VI in 1378. He was a monk and archbishop of Bari. While the Italians have had a stranglehold on the papacy over centuries, there have been many exceptions aside from John Paul II (Polish in 1978) and Benedict XVI (German in 2005) and Francis (Argentine in 2013). Alexander VI, elected in 1492, was Spanish; Gregory III, elected in 731, was Syrian; Adrian VI, elected in 1522, was from the Netherlands.
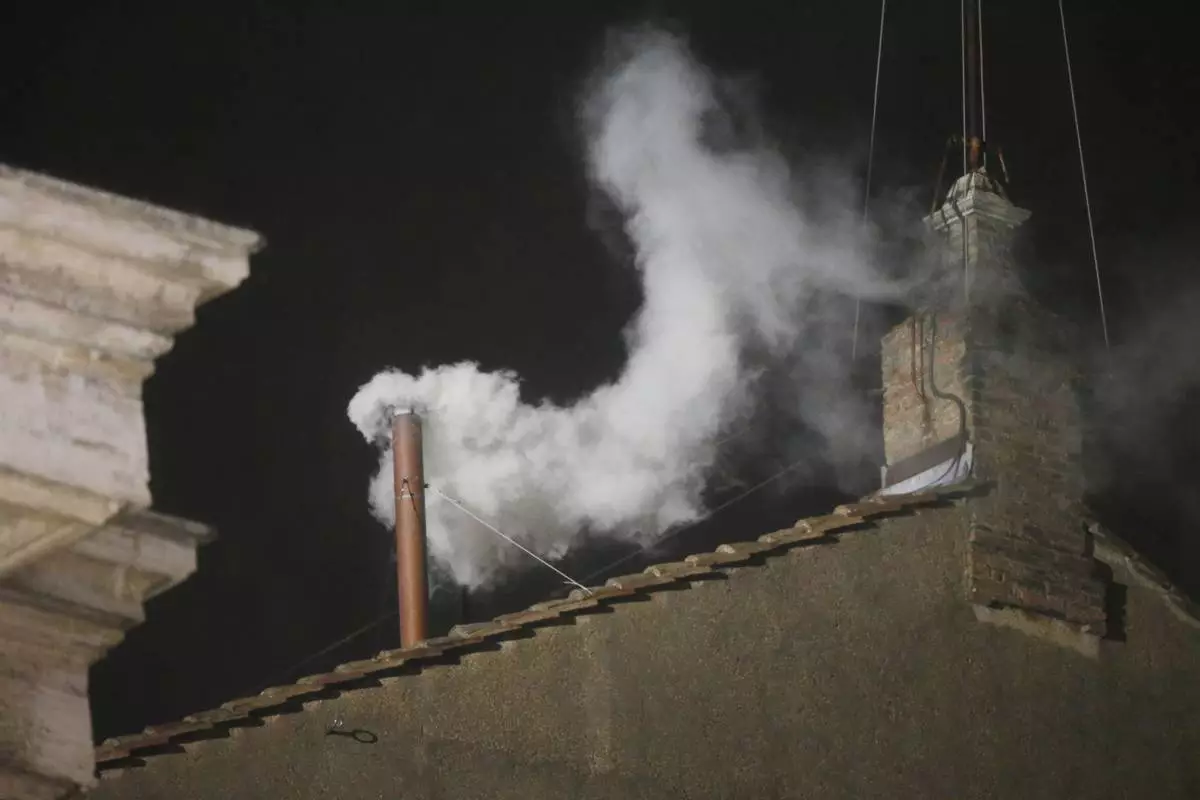

FILE - White smoke is seen billowing out from the chimney of the Sistine Chapel and announcing that a new pope has been elected on Wednesday, March 13, 2013. (AP Photo/Gregorio Borgia, File)
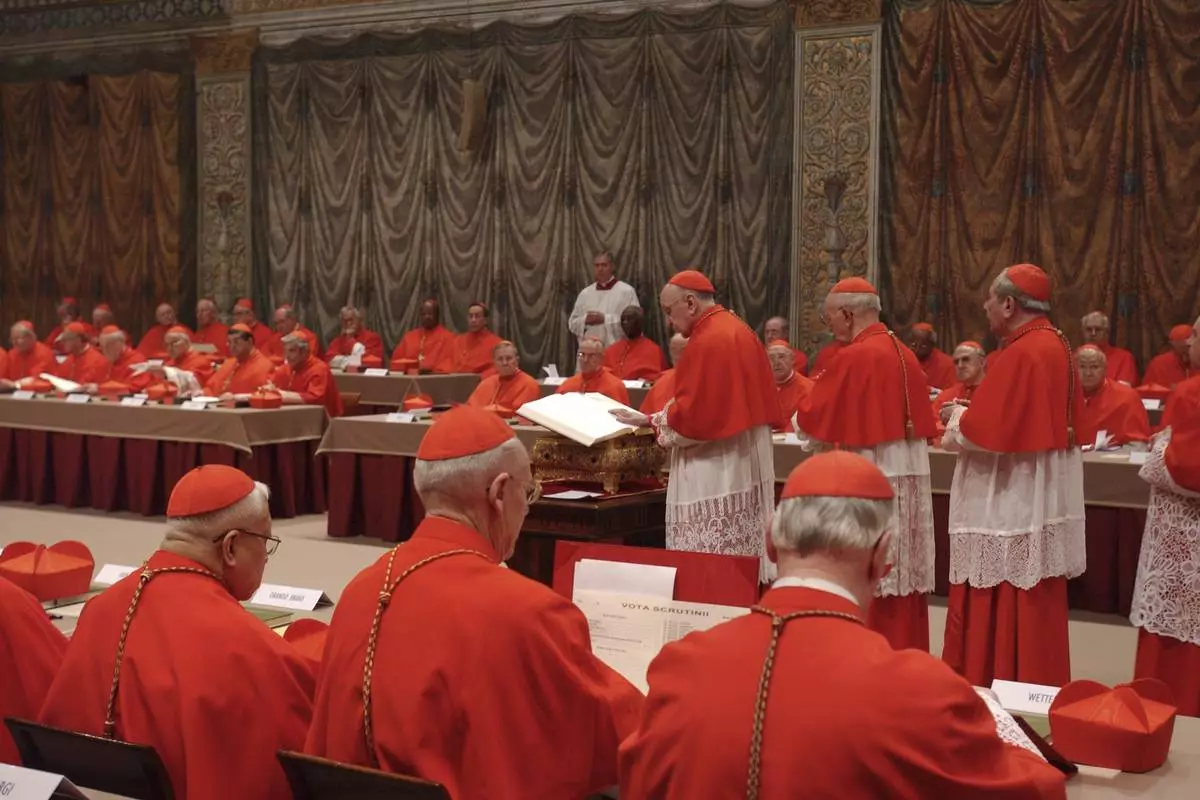

FILE - Italian Cardinal Giacomo Biffi, center, takes an oath at the beginning of the conclave to elect the next pope in the Sistine Chapel at the Vatican, Monday, April 18, 2005. (AP Photo/Osservatore Romano via AP, File)
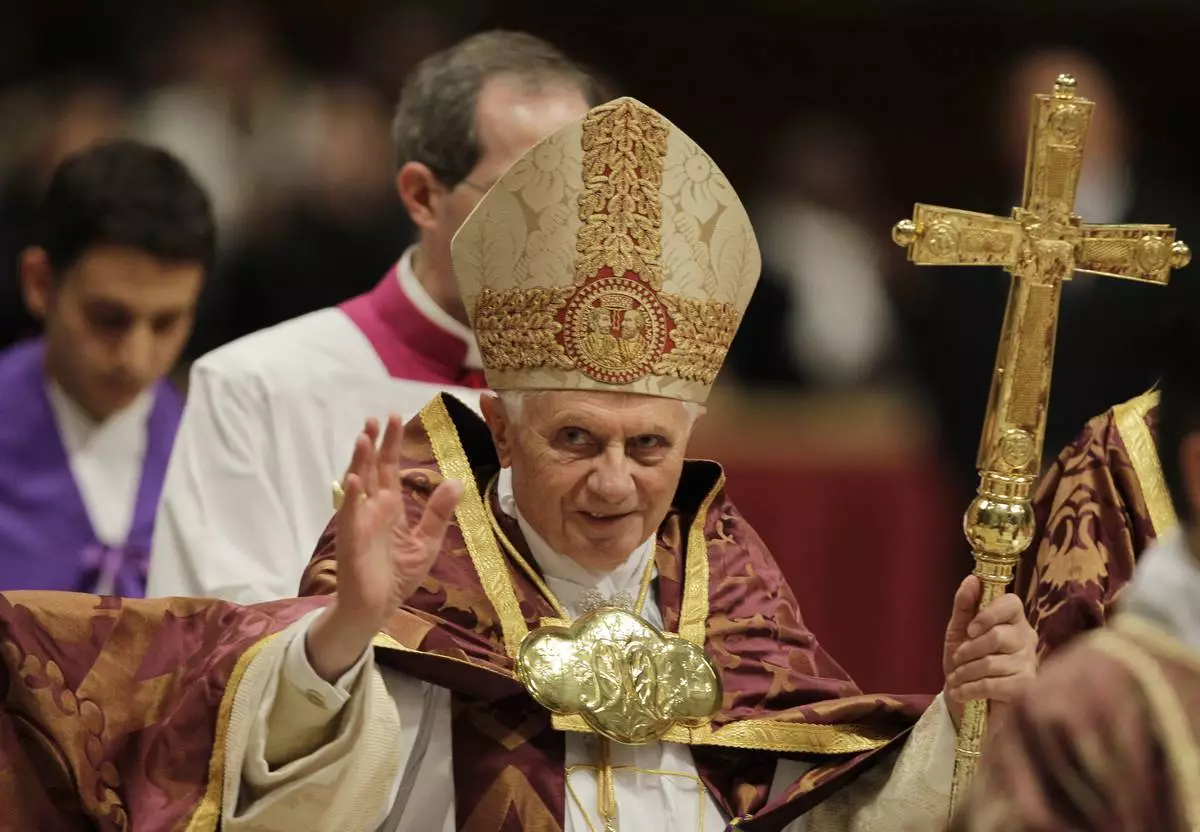

FILE - Pope Benedict XVI blesses the faithful as he arrives at St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican, Dec. 16, 2010. (AP Photo/Alessandra Tarantino, File)
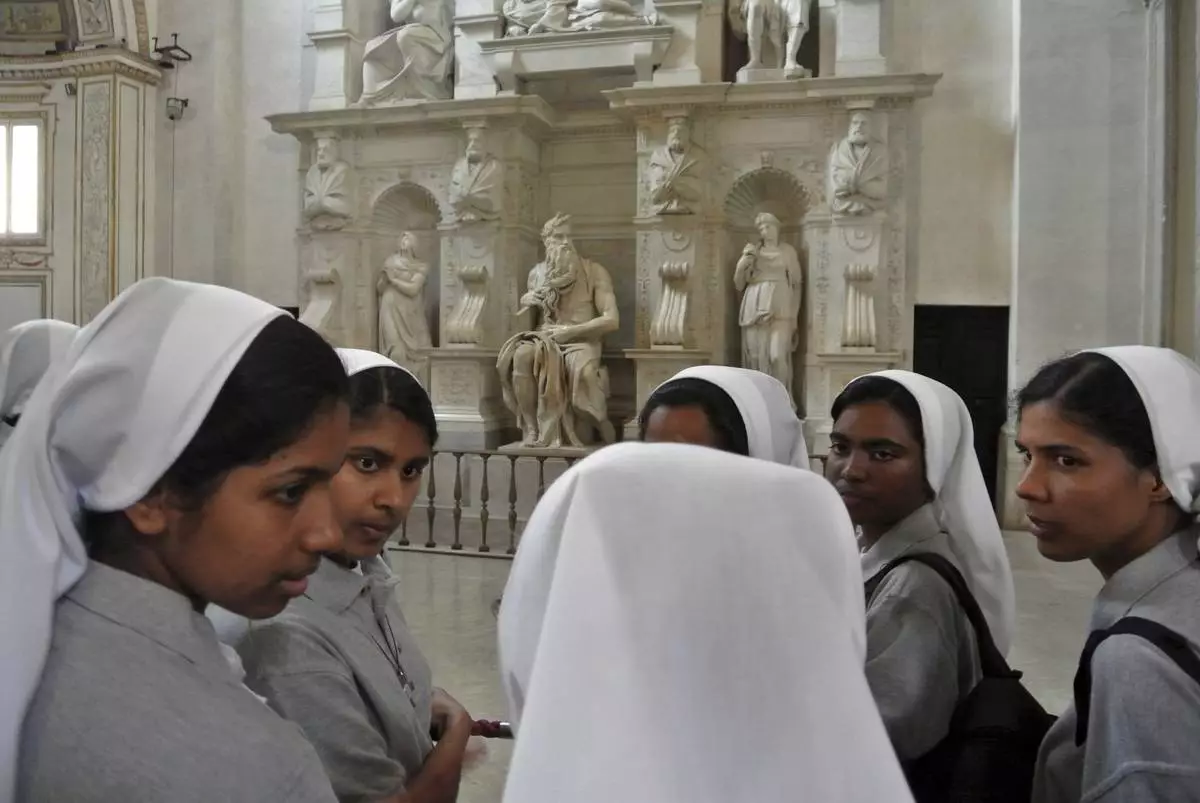

FILE - Nuns talk in front of Italian Renaissance artist Michelangelo Buonarroti's Moses statue, part of a funerary monument he designed for Pope Julius II inside San Pietro in Vincoli Basilica in Rome, July 2, 2013. (AP Photo/Gregorio Borgia, File)
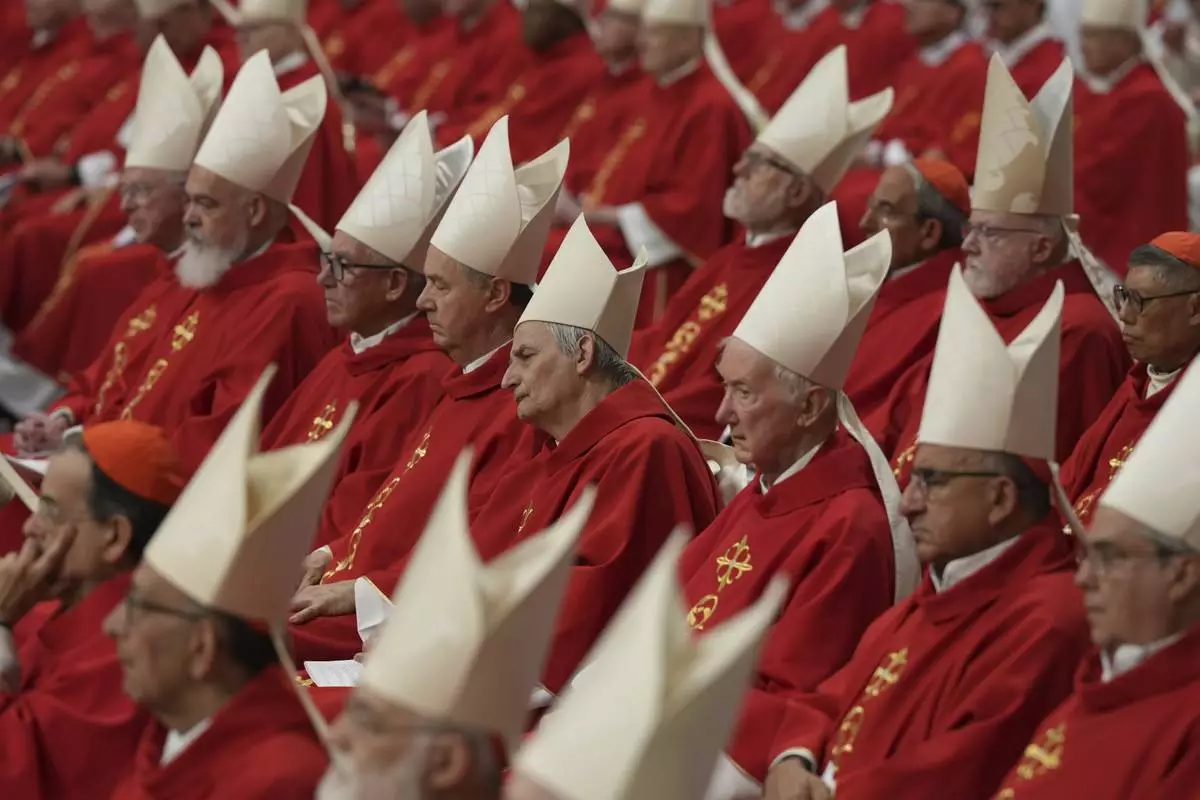

Cardinal Matteo Zuppi, centre, attends a mass on the third of nine days of mourning for late Pope Francis, in St. Peter's Basilica at the Vatican, Monday, April 28, 2025. (AP Photo/Andrew Medichini)
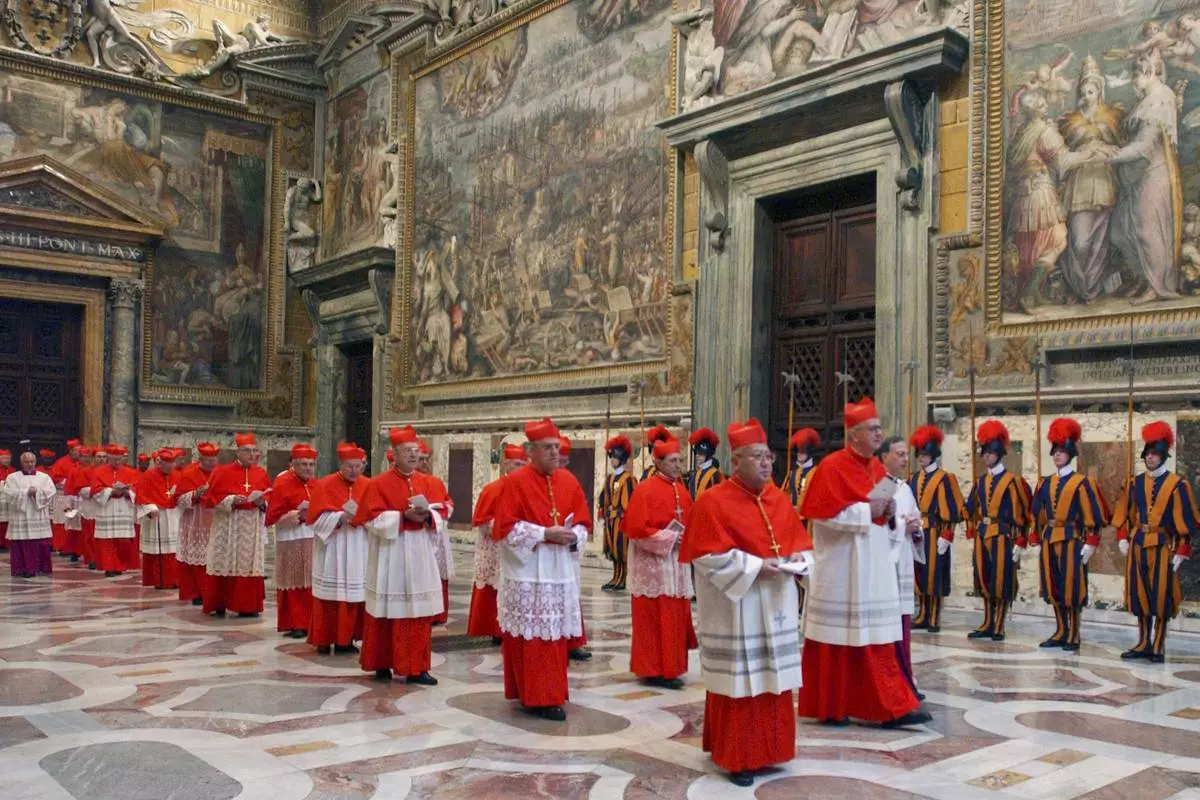

FILE - Cardinals walk in procession to the Sistine Chapel at the Vatican, at the beginning of the conclave, April 18, 2005. (Osservatore Romano via AP, File)