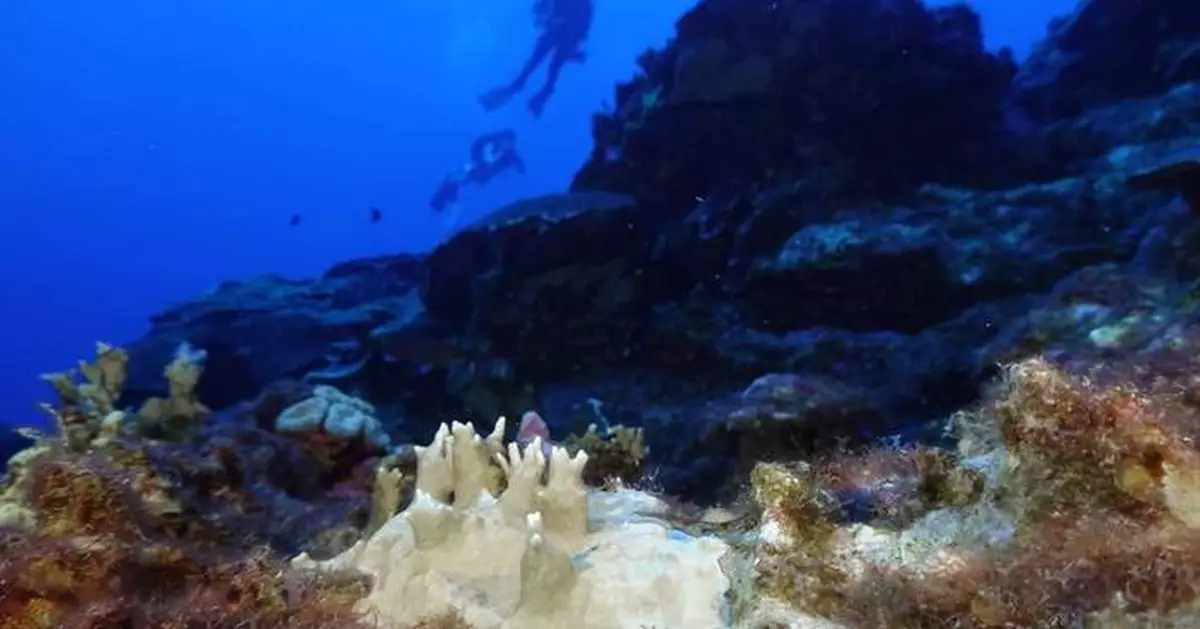
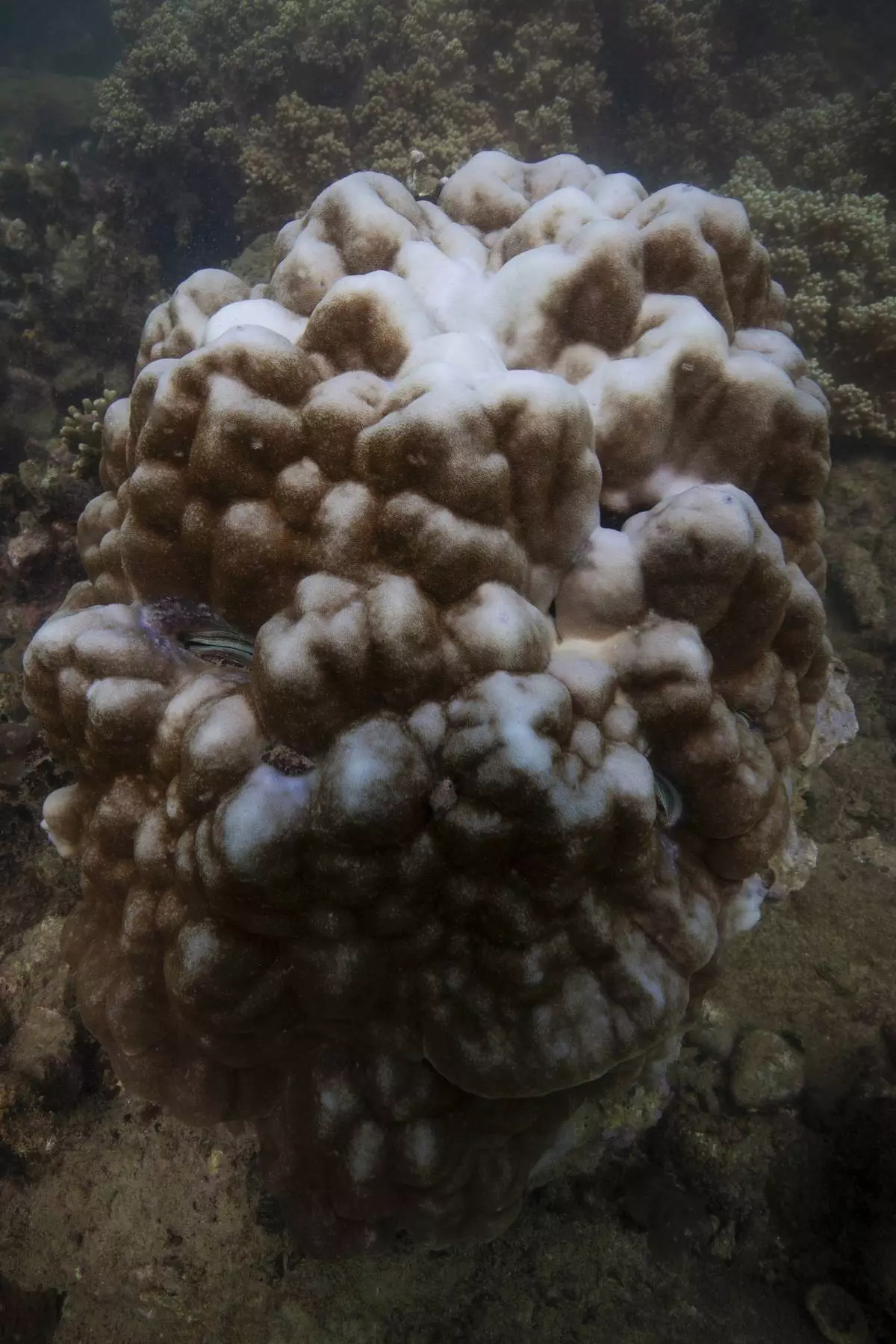
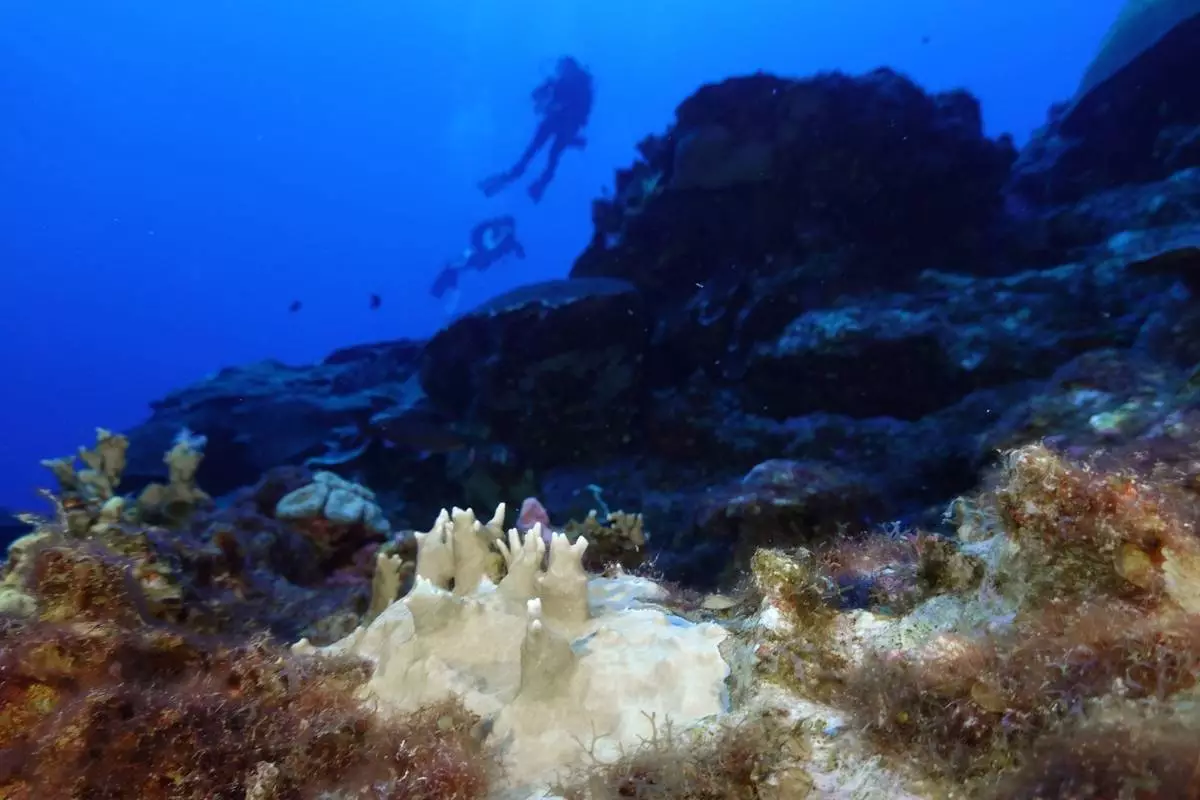
Harmful bleaching of the world's coral has grown to include 84% of the ocean's reefs in the most intense event of its kind in recorded history, the International Coral Reef Initiative announced Wednesday.
It's the fourth global bleaching event since 1998, and has now surpassed bleaching from 2014-17 that hit some two-thirds of reefs, said the ICRI, a mix of more than 100 governments, non-governmental organizations and others. And it's not clear when the current crisis, which began in 2023 and is blamed on warming oceans, will end.
“We may never see the heat stress that causes bleaching dropping below the threshold that triggers a global event,” said Mark Eakin, corresponding secretary for the International Coral Reef Society and retired chief of the Coral Reef Watch program of the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. “We’re looking at something that’s completely changing the face of our planet and the ability of our oceans to sustain lives and livelihoods,” Eakin said.
Last year was Earth’s hottest year on record, and much of that is going into oceans. The average annual sea surface temperature of oceans away from the poles was a record 20.87 degrees Celsius (69.57 degrees Fahrenheit).
That's deadly to corals, which are key to seafood production, tourism and protecting coastlines from erosion and storms. Coral reefs are sometimes dubbed “rainforests of the sea” because they support high levels of biodiversity — approximately 25% of all marine species can be found in, on and around coral reefs.
Coral get their bright colors from the colorful algae that live inside them and are a food source for the corals. Prolonged warmth causes the algae to release toxic compounds, and the coral eject them. A stark white skeleton is left behind, and the weakened coral is at heightened risk of dying.
The bleaching event has been so severe that NOAA’s Coral Reef Watch program has had to add levels to its bleaching alert scale to account for the growing risk of coral death.
Efforts are underway to conserve and restore coral. One Dutch lab has worked with coral fragments, including some taken from off the coast of the Seychelles, to propagate them in a zoo so that they might be used someday to repopulate wild coral reefs if needed. Other projects, including one off Florida, have worked to rescue corals endangered by high heat and nurse them back to health before returning them to the ocean.
But scientists say it's essential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions that warm the planet, such as carbon dioxide and methane.
“The best way to protect coral reefs is to address the root cause of climate change. And that means reducing the human emissions that are mostly from burning of fossil fuels … everything else is looking more like a Band-Aid rather than a solution,” Eakin said.
“I think people really need to recognize what they’re doing … inaction is the kiss of death for coral reefs,” said Melanie McField, co-chair of the Caribbean Steering Committee for the Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network, a network of scientists that monitors reefs throughout the world.
The group's update comes as President Donald Trump has moved aggressively in his second term to boost fossil fuels and roll back clean energy programs, which he says is necessary for economic growth.
“We’ve got a government right now that is working very hard to destroy all of these ecosystems ... removing these protections is going to have devastating consequences," Eakin said.
This story has been corrected to reflect that Mark Eakin is corresponding secretary, not executive secretary.
The Associated Press’ climate and environmental coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.

FILE - Bleaching is visible on coral reef off the coast of Nha Trang, Vietnam, Oct. 24, 2024. (AP Photo/Yannick Peterhans, File)

FILE - Bleached coral is visible at the Flower Garden Banks National Marine Sanctuary, off the coast of Galveston, Texas, in the Gulf of Mexico, Sept. 16, 2023. (AP Photo/LM Otero, File)
It was late in the afternoon and lightly snowing when four rock climbers, working their way up a steep gully between two peaks in Washington’s North Cascades Range, decided to turn around for a descent down the mountain that would claim three of their lives.
As they climbed down, the four attached their ropes to an piton — a metal spike pounded into rock cracks or ice and used to secure ropes — that had been placed by a past climber. As one of the men began rappelling off the piton, it ripped out of the mountain, sending all four falling past ice and snow and rock.
They fell some 200 feet (60 meters), landing in a more sloping ravine where they tumbled for another roughly 200 feet before coming to a stop in a tangle of rope.
Three were killed by the fall. One was knocked unconscious.
Anton Tselykh awoke in the dark. It had been hours since the fall.
Over the course of several hours, he extricated himself from the tangle of ropes, gear and debris and trekked over rough terrain of rock and snow — with help from a pick-like ice tool — to his car.
He drove for some 40 miles (64 kilometers) before finding a pay phone and calling for help in Newhalem, an unincorporated community about an hour's drive away. It was Sunday morning, eight hours since he regained consciousness.
From a Seattle hospital Wednesday morning, Tselykh, recovering from head trauma and internal bleeding, told authorities what had happened. He was in satisfactory condition at Harborview Medical Center, meaning he was not in the intensive care unit, Susan Gregg, media relations director for UW Medicine, said in an email.
Tselykh, 38, confirmed authorities' theories of what led to the deaths of his three companions, identified as Vishnu Irigireddy, 48; Tim Nguyen, 63; and Oleksander Martynenko, 36.
A three-person search and rescue team had responded to the site of the fall following Tselykh's call, said Cristina Woodworth, who led the team and spoke with the lone survivor by phone Wednesday. The team had followed coordinates from a GPS device the climbers had been carrying, which were shared by a friend of the men.
The rough terrain required a helicopter, which removed the bodies one at a time, Woodworth said.
Responders pored over the recovered equipment, trying to decipher what caused the fall. They found the piton still clipped into the climbers’ ropes, Okanogan County Coroner Dave Rodriguez said. Pitons are difficult to remove from rock, he said, and the anchor's presence on the rope was a clue to what happened.
Generally, setting up a backup anchor is a common practice among climbers, said Joshua Cole, a guide and co-owner of North Cascades Mountain Guides, who has been climbing in the area for about 20 years. It's still unclear whether the four had a backup.
The four climbers were friends, some of whom had climbed together before and appeared fairly experienced, Woodworth said, adding that Tselykh was “obviously very much affected by this.”
Irigireddy was a vice president of engineering at the Fluke Corporation, a test equipment manufacturing company, which released a statement Wednesday.
“Vishnu was an extraordinary leader, and his loss is felt profoundly across our organization,” the statement read.
Martynenko’s wife, Olga, said Tuesday in a Facebook post that her husband, whom she referred to as Alex, also left behind their son. She shared a link to a fundraiser to help “during the most devastating time of our lives.”
“I still cannot believe that you are gone, my love."
Bedayn is a corps member for The Associated Press/Report for America Statehouse News Initiative. Report for America is a nonprofit national service program that places journalists in local newsrooms to report on undercovered issues.
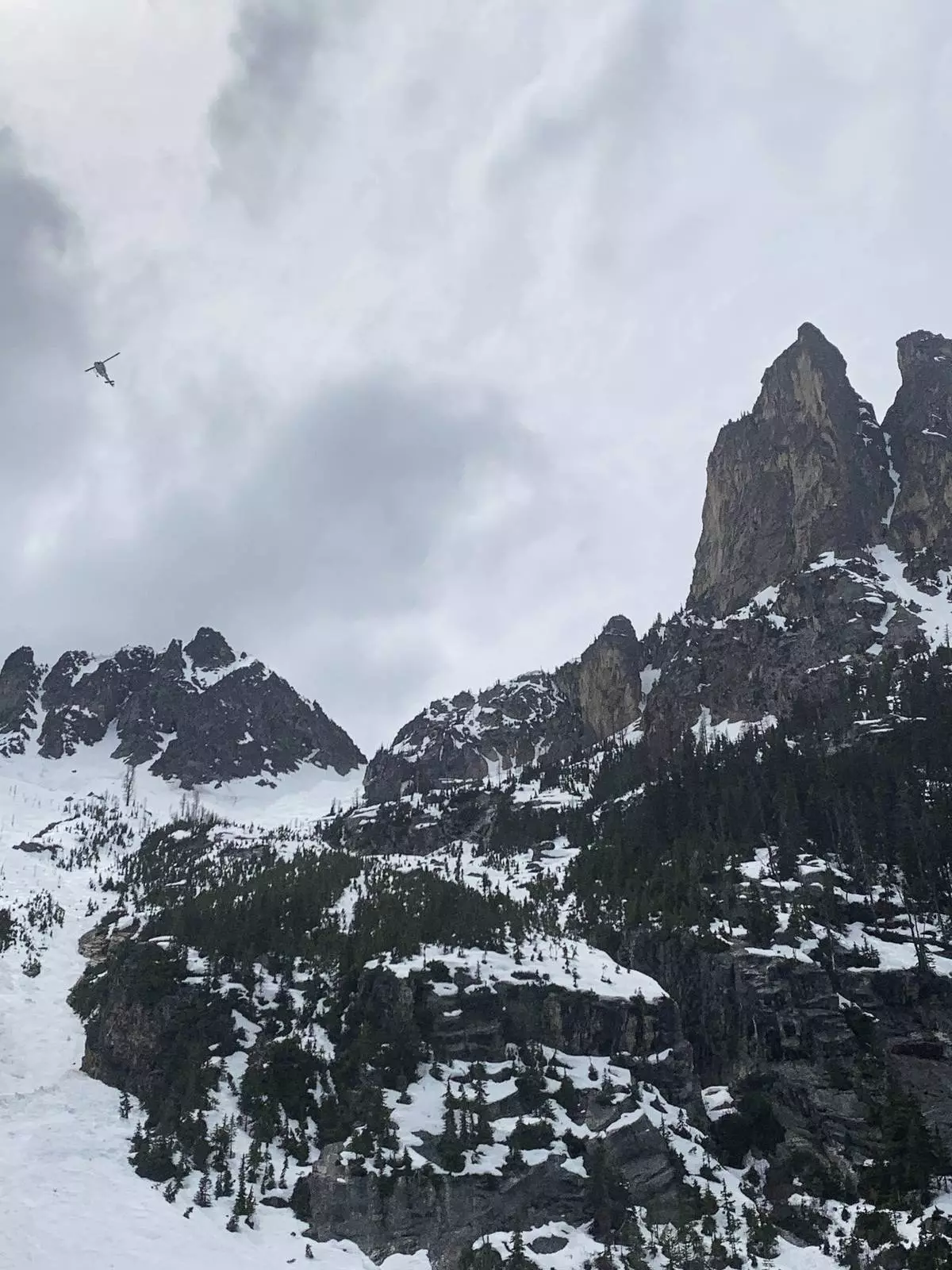

The Okanogan County Search and Rescue team responds to a climbing accident in the North Cascades mountains in Washington on Sunday, May 11, 2025. (Okanogan County Sheriff's Office via AP)
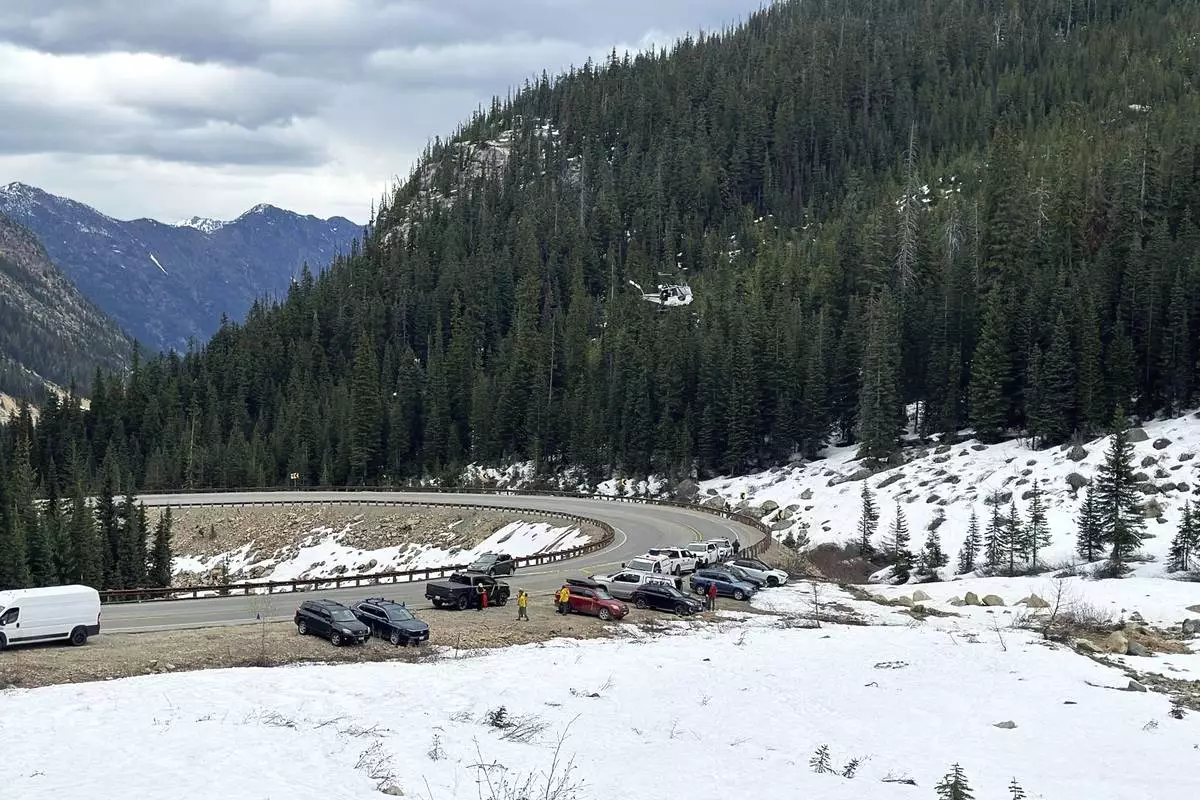

The Okanogan County Search and Rescue team responds to a climbing accident in the North Cascades mountains in Washington on Sunday, May 11, 2025. (Okanogan County Sheriff's Office via AP)
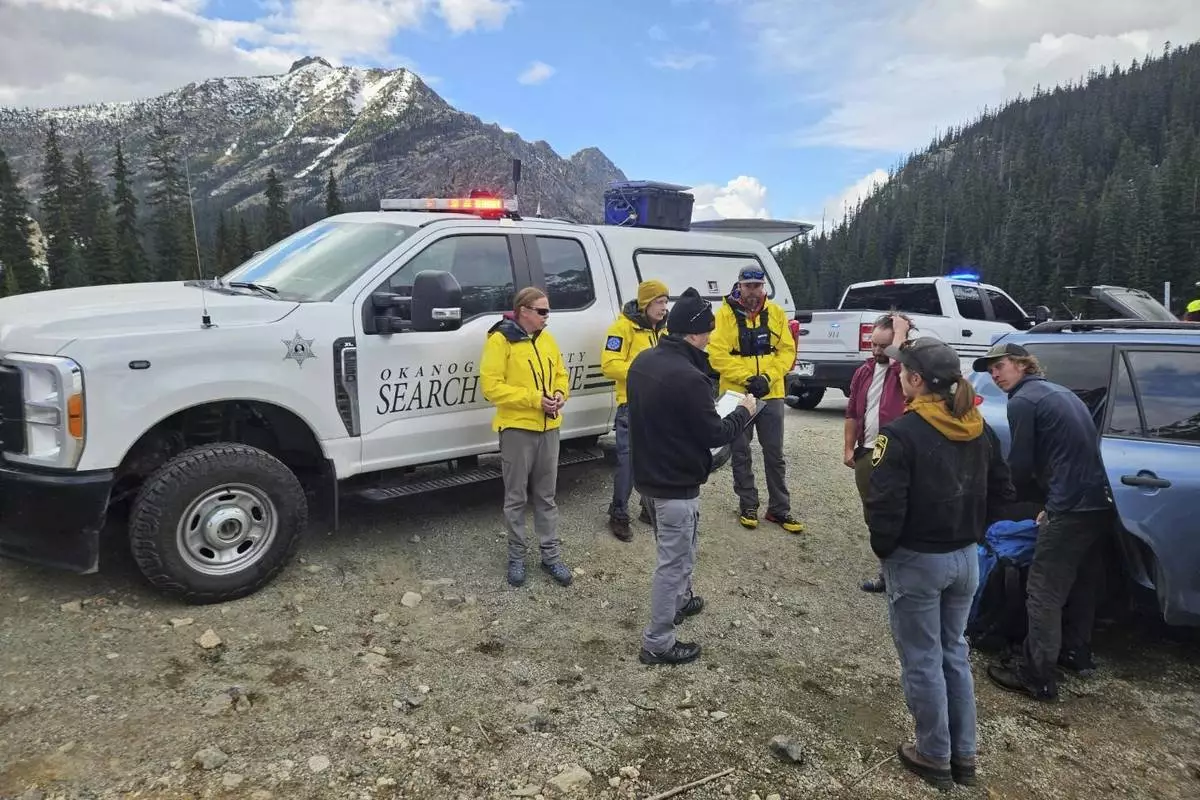

The Okanogan County Search and Rescue team responds to a climbing accident in the North Cascades mountains in Washington on Sunday, May 11, 2025. (Okanogan County Sheriff's Office via AP)