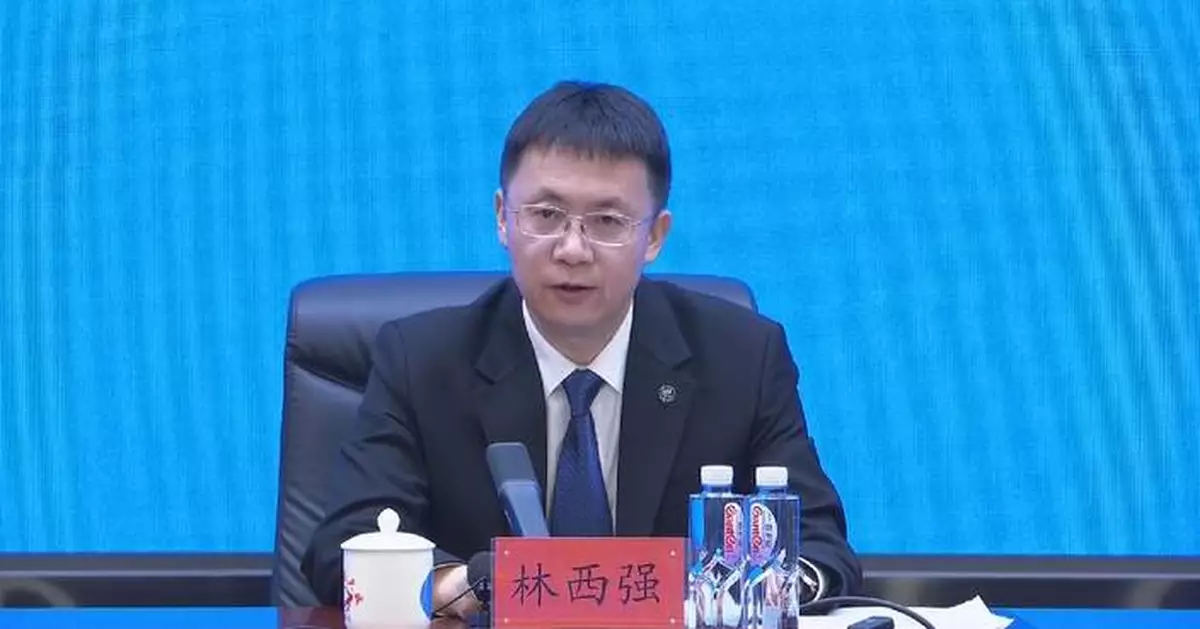
China's fourth batch of astronauts is currently undergoing training as planned and could join the candidate crew in the future, the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA) said on Wednesday.
"Since they joined the team in August 2024, the fourth batch of astronauts has undertaken the studies of basic space theory, multiple trainings on psychology and adaptability to space environment and some specialized trainings following the plan," CMSA spokesman Lin Xiqiang said at a press conference at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, ahead of the launch of the Shenzhou-20 spacecraft scheduled for Thursday.
"We are carrying out the training on the fourth batch of astronauts in an orderly and organized way as planned. After qualifying for spaceflight, they will be included in the candidate crew. We believe that they will be seen in future flight crews successively soon," Lin said.
"After they joined the team, astronauts from Hong Kong and Macao quickly adapted themselves to the working and living environment and swiftly got integrated into the astronaut crew. They have worked very hard in trainings with all the work progressing smoothly. They are currently engaged in studies and trainings on professional space technologies. As payload experts, the Hong Kong and Macao astronauts are expected to carry out their first flight mission in 2026 at the earliest," he said.
China's Shenzhou-20 crewed spaceship is scheduled to be launched at 17:17 Thursday (Beijing Time) from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the country's northwest, the CMSA announced on Wednesday.

Spokesman on training of China's fourth batch of astronauts

Spokesman on training of China's fourth batch of astronauts
A deal to give the United States exclusive access to Ukraine's mineral resources has sparked contention among Ukrainian experts, who have described earlier drafts of the agreement as "unacceptable" and "colonial."
As the war between Ukraine and Russia is showing signs of winding down, another battle is quietly unfolding beneath Ukrainian soil, with competitors eying Ukraine's vast reserves of critical minerals.
The United States and Ukraine have signed an agreement to establish the U.S.-Ukraine Reconstruction Investment Fund, the U.S. Treasury Department announced on Wednesday.
For some, the minerals deal with the United States offers a lifeline for Kiev's war-torn economy. For others, it signals the quiet start of a resource takeover, raising concerns about what Ukraine may be giving away in exchange for support.
Ukraine is rich in critical resources such as graphite, lithium, and titanium. All these are vital to electric vehicles, the aerospace industry, and the high-tech supply chain.
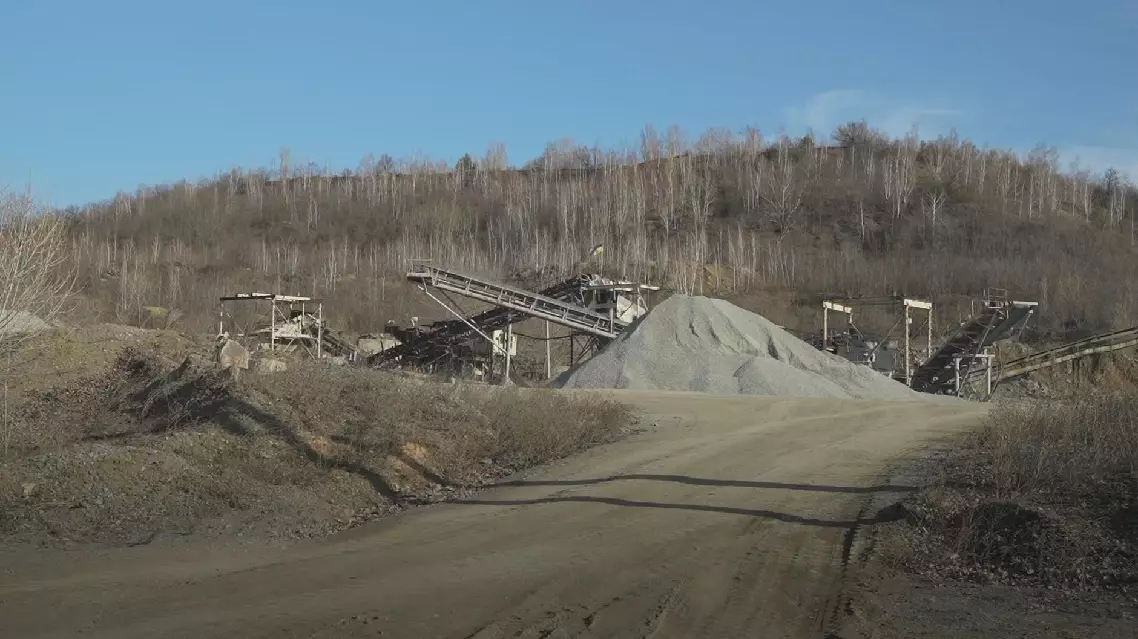
At a graphite quarry roughly 400 km south from Kiev, capital of Ukraine, the roads give way to deep ruts and scattered debris, which means the mine site falls short of normal operation in wartime.
According to Ukraine's geological survey, the country holds 22 of the 50 strategic materials identified by the U.S. as critical.
As the global race for these resources intensifies, Washington is eager to secure reliable access. Ukraine, desperate for investment for reconstruction, has opened its doors. However, according to experts, the negotiations have been tense.
"When we had the first draft of this agreement, it was absolutely awful, absolutely unacceptable for Ukraine. It was also like a colonial agreement," said Volodymyr Landa, senior economist at the Center of Economic Strategy of Ukraine.
The country's mining sector is in dire need of foreign capital. At one of Ukraine's largest graphite deposits, infrastructure is minimal, with a few dogs, a guard, and an elderly tractor driver.
A Lviv-based mine owner said water pipes freeze over in winter, bringing operations to a halt. More importantly, the war has drained both labor and funding.
"If the Ukrainian government presents it for free, for 50 years with free rent, our resources will lose from that," said Ostap Kostiuk, CEO of Zavallivskyi Graphite, located in the Kirovohrad region.
Following a tense and reportedly humiliating visit to Washington in March, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky appears to have softened his stance on a minerals deal he once said he would never sign. The move has triggered public outcry at home.
"Now they (the U.S.) say 'give me money, no, lithium' for the guarantees. It's not fair, I think," said a local resident.
"I definitely started to respect America less. He (Trump) is not interested in Ukraine actually ending the war," another added.
This graphite deposit represents only a fraction of Ukraine's untapped potential. An estimated 30 percent of its critical minerals have already been extracted. The other 70 percent, still buried across vast swathes of the country, is what many believe Washington is ultimately eying.
"Please do everything to make this peace closer to us, closer to people, closer to Ukrainians. Because every day, every hour, every minute, it costs our Ukrainian nation one to five Ukrainian best guys' lives," said Kostiuk.
In the view of Professor Valeriy Pekar, a business scholar in Kyiv and Lviv, the Trump administration is not actually interested in securing peace for Ukraine.
"To take control of our resources, it is necessary to end the war. The American leadership declares themselves great peacemakers, but what they really do is not peacemaking. It's war mongering," he said.

US interest in Ukraine's critical minerals draws public backlash