Whooping cough cases are rising, and doctors are bracing for yet another tough year.
There have been 8,485 cases reported in 2025, according to preliminary data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That’s twice as many cases as this time last year, based on the CDC's final tally.
Rates of whooping cough, or pertussis, soared last year, which experts said wasn’t unexpected. The number of cases fell during COVID-19 because of masking and social distancing. Plus, experts said, the illness peaks every two to five years.
But experts say the outbreaks of vaccine-preventable illnesses, like measles and whooping cough, could be indicative of changing attitudes toward vaccines. U.S. kindergarten vaccination rates fell last year, and the number of children with vaccine exemptions hit an all-time high.
“There’s unfortunately been increasing anti-vaccine sentiment in the United States,” said Dr. Ericka Hayes at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “Our recovery is not nearly as quick as we expected it to be and we needed it to be. And again, when you fall below 95% for vaccinations, you lose that herd immunity protection.”
Whooping cough tends to peak around this time of year and in the fall. It's usually spread through respiratory droplets in the air, when people with pertussis cough, sneeze or breathe close to others. The symptoms are similar to a cold but the cough becomes increasingly severe with a distinctive sound — a “whoop” as the person tries to take in air. It is treated with antibiotics.
In the past six months, two babies in Louisiana and a 5-year-old in Washington state have died from whooping cough.
The pertussis vaccine, which also protects against diphtheria and tetanus, is given at two months, four months and six months. The CDC recommends adults get follow-up doses every 10 years.
The illness is most dangerous for infants, especially before they receive their first round of vaccinations. That’s why the vaccine is also recommended for expecting mothers — it can protect newborns. But not enough people are getting the vaccine during pregnancy, said Hayes, who is the hospital's senior medical director of infection prevention and control.
“The uptake of the vaccine for pregnant mothers is not where we need to be at all," she said.
Pennsylvania, one of the states hit hardest by the illness last year, has recorded 207 whooping cough cases in 2025.
Neil Ruhland, a state health department spokesman, said the biggest increases are in populated areas like Philadelphia and Pittsburgh and in middle and high schools and colleges. He said 94.6% of the state's kindergarteners are vaccinated.
Michigan is on track for a similar pertussis season to last year's, said Dr. Natasha Bagdasarian, the state's chief medical executive. The state has recorded 516 cases thus far, mostly among children aged 5 to 17, and saw a total of 2,081 cases in 2024.
Bagdasarian said vaccination rates vary from county to county. Some schools have rates as low as 30%, creating pockets of vulnerable communities to vaccine-preventable diseases like pertussis and measles, she said.
“We’re watching pertussis numbers very carefully, but a lot of our resources are going into contact tracing our measles cases right now,” she said. “And public health is doing much more with fewer resources in 2025 than we’ve had to do before."
AP data journalist Kasturi Pananjady contributed to this report.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
FILE - This 2016 illustration provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, based on electron microscope imagery, depicts Bordetella pertussis bacteria, which causes whooping cough. (Meredith Newlove/CDC via AP, File)
ANTALYA, Turkey (AP) — NATO foreign ministers on Thursday debated an American demand to massively ramp up defense investment to 5% of gross domestic product over the next seven years, as the U.S. focuses on security challenges outside of Europe.
At talks in Antalya, Turkey, NATO Secretary-General Mark Rutte said that more investment and military equipment are needed to deal with the threat posed by Russia and terrorism, but also by China which has become the focus of U.S. concern.
“When it comes to the core defense spending, we need to do much, much more,” Rutte told reporters. He underlined that once the war in Ukraine is over, Russia could reconstitute its armed forces within three to five years.
Secretary of State Marco Rubio underlined that “the alliance is only as strong as its weakest link.” He insisted that the U.S. investment demand is about “spending money on the capabilities that are needed for the threats of the 21st century.”
The debate on defense spending is heating up ahead of a summit of U.S. President Donald Trump and his NATO counterparts in the Netherlands on June 24-25. It's a high-level gathering that will set the course for future European security, including that of Ukraine.
In 2023, as Russia’s full-scale war on Ukraine entered its second year, NATO leaders agreed to spend at least 2% of GDP on national defense budgets. So far, 22 of the 32 member countries have done so.
The new spending plan under consideration is for all allies to aim for 3.5% of GDP on their defense budgets by 2032, plus an extra 1.5% on potentially defense-related things like infrastructure — roads, bridges, airports and seaports.
While the two figures add up to 5%, factoring in infrastructure and cybersecurity would change the basis on which NATO traditionally calculates defense spending. The seven-year time frame is also short by the alliance’s usual standards.
Rutte refused to confirm the numbers under consideration, but he acknowledged that it's important to include infrastructure in the equation, “for example to make sure that bridges, yes, are there for you and me to drive our cars but also if necessary to make sure that the bridge will hold a tank. So all these expenditures have to be taken into account.”
It’s difficult to see how many members would reach a new 3.5% goal. Belgium, Canada, Croatia, Italy, Luxembourg, Montenegro, Portugal, Slovenia and Spain are not even spending 2% yet, although Spain does expect to reach that goal in 2025, a year past the deadline.
The U.S. demand would require investment at an unprecedented scale, but Trump has cast doubt over whether the U.S. would defend allies that spend too little, and this remains an incentive to do more, even as European allies realize that they must match the threat posed by Russia.
Europe-wide, industry leaders and experts have pointed out challenges the continent must overcome to be a truly self-sufficient military power, chiefly its decades-long reliance on the U.S. as well as its fragmented defense industry.
“There is a lot at stake for us,” Lithuanian Foreign Minister Kęstutis Budrys said. He urged his NATO partners to meet the investment goals faster than the 2032 target "because we see the tempo and the speed, how Russia generates its forces now as we speak.”
British Foreign Secretary David Lammy said his country should reach 2.5% by 2027, and then 3% by the next U.K. elections planned for 2029.
“It’s hugely important that we recommit to Europe’s defense and that we step up alongside our U.S. partners in this challenging geopolitical moment where there are so many precious across the world, and particularly in the Indo-Pacific,” he said.
As an organization, NATO plays no direct security role in Asia, and it remains unclear what demands the Trump administration might make of the allies as it turns its attention to China. The last NATO security operation outside the Euro-Atlantic area, its 18-year stay in Afghanistan, ended in chaos.
Cook reported from Brussels, and Fraser from Ankara, Turkey.

NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte talks to journalists as he arrives for a NATO's informal meeting of foreign ministers in Antalya, southern Turkey, Thursday, May 15, 2025. (AP Photo/Khalil Hamra)

British Foreign Secretary David Lammy talks to journalists as he arrives for a NATO's informal meeting of foreign ministers in Antalya, southern Turkey, Thursday, May 15, 2025. (AP Photo/Khalil Hamra)

NATO foreign ministers pose for a group photo during their informal meeting in Antalya, southern Turkey, Thursday, May 15, 2025. (AP Photo/Khalil Hamra)

Turkey's Foreign Minister Hakan Fidan talks to journalists as he arrives for a NATO's informal meeting of foreign ministers in Antalya, southern Turkey, Thursday, May 15, 2025. (AP Photo/Khalil Hamra)
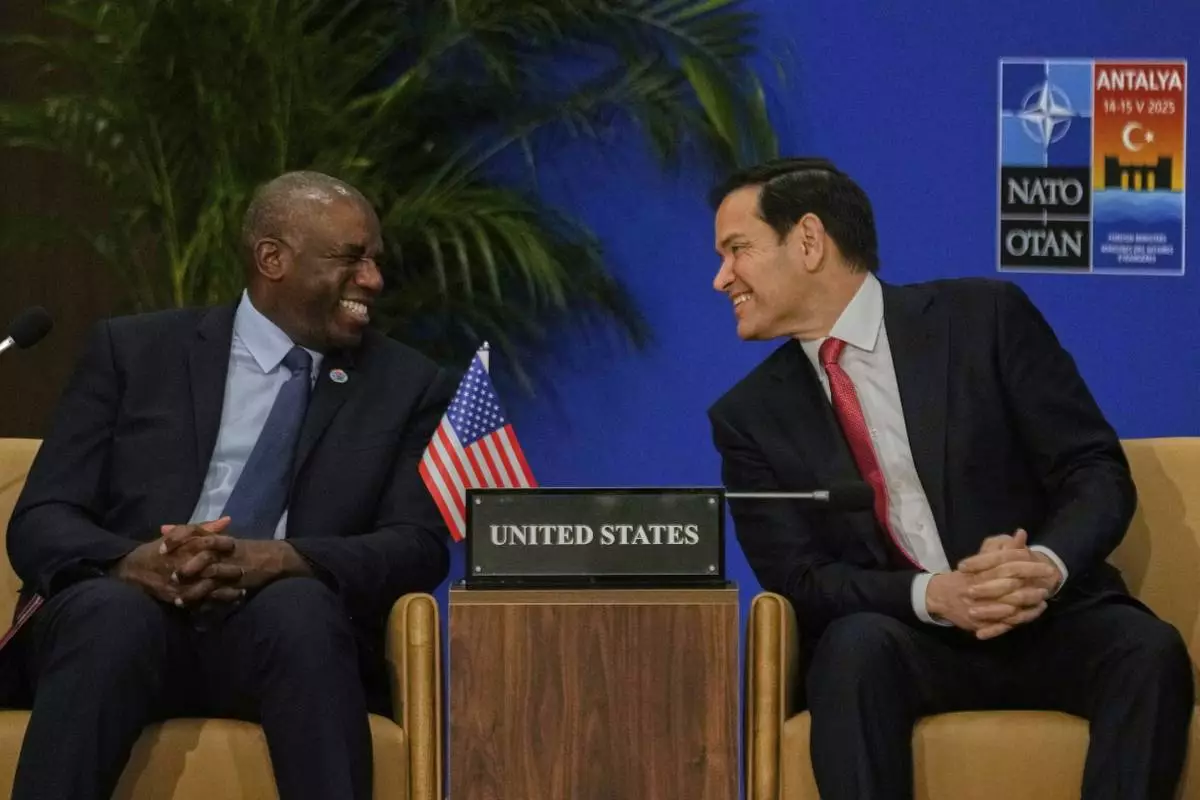

United States Secretary of State Marco Rubio, right, talks to British Foreign Secretary David Lammy during an informal meeting of NATO's foreign ministers in Antalya, southern Turkey, Thursday, May 15, 2025. (AP Photo/Khalil Hamra)
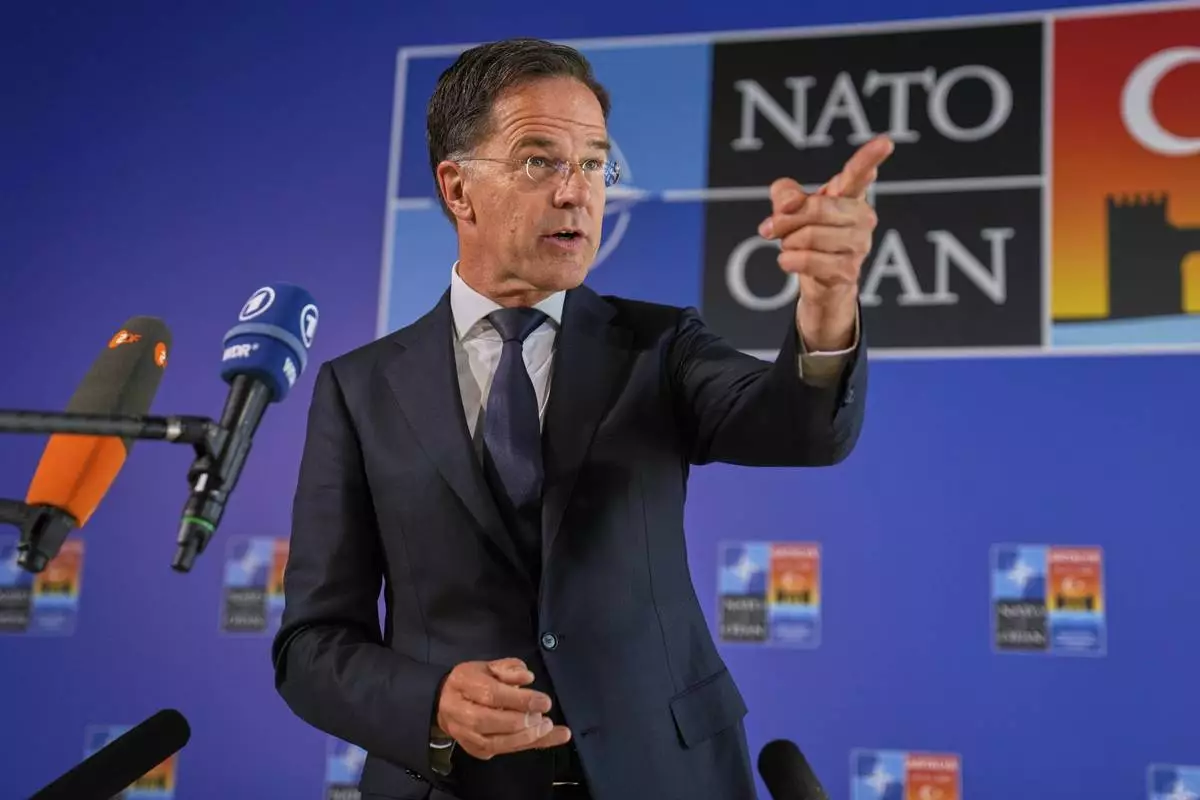

NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte talks to journalists as he arrives for NATO's informal meeting of foreign ministers in Antalya, southern Turkey, Thursday, May 15, 2025. (AP Photo/Khalil Hamra)
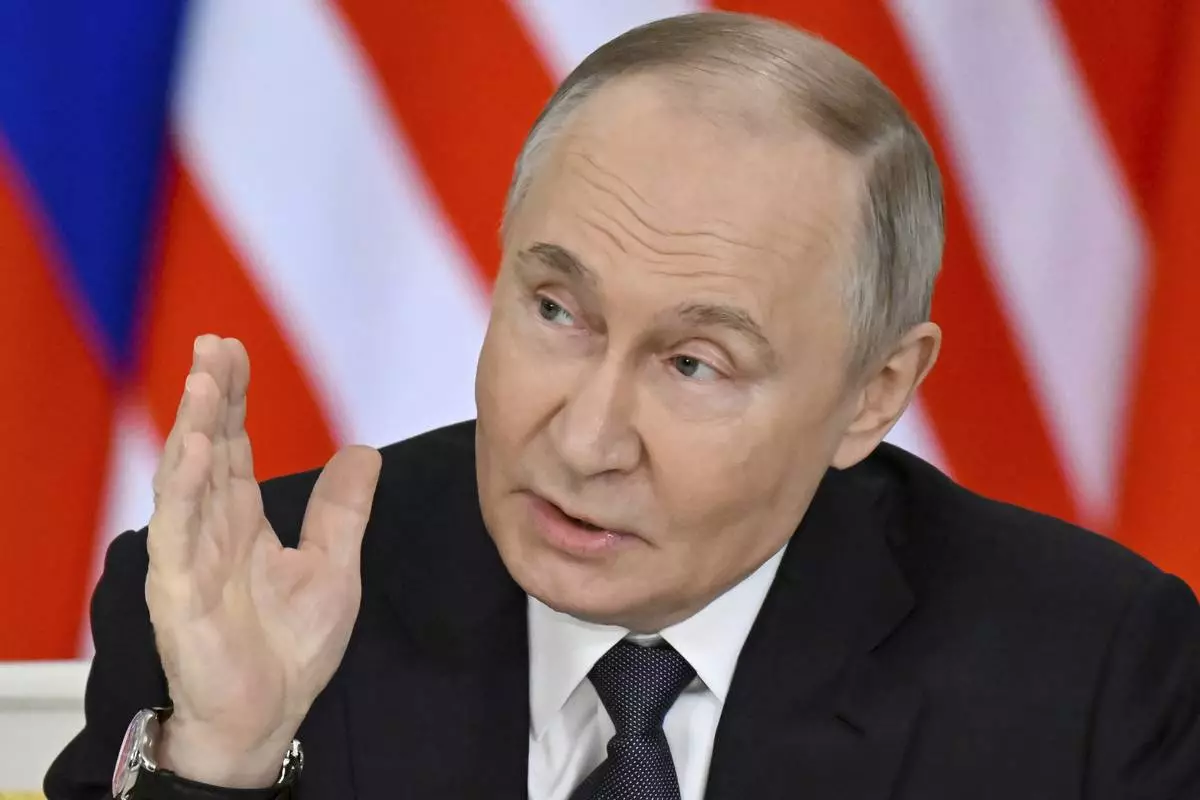

Russian President Vladimir Putin speaks during a joint press statement with Malaysian Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim at the Kremlin in Moscow, Russia, Wednesday, May 14, 2025. (Alexander Nemenov/Pool Photo via AP)
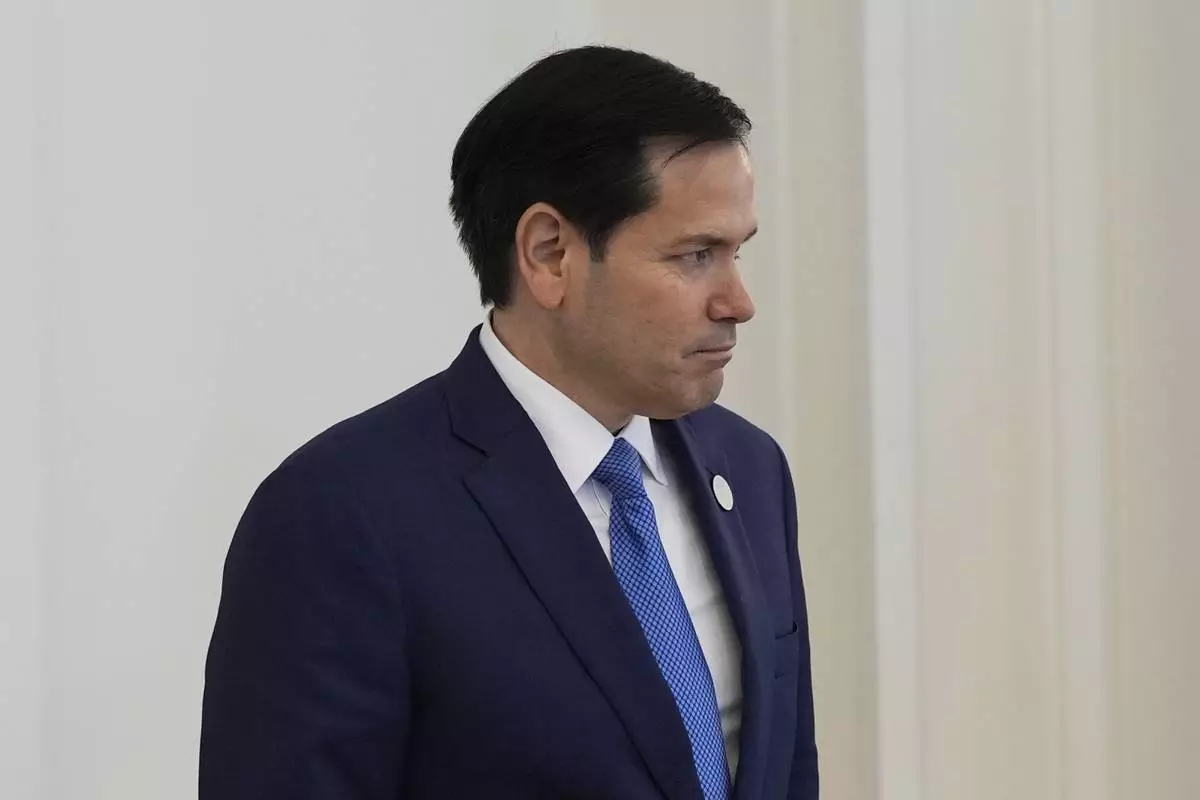

Secretary of State Marco Rubio departs a lunch between President Donald Trump and Qatar's Emir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani at the Amiri Diwan in Doha, Qatar, Wednesday, May 14, 2025. (AP Photo/Alex Brandon)