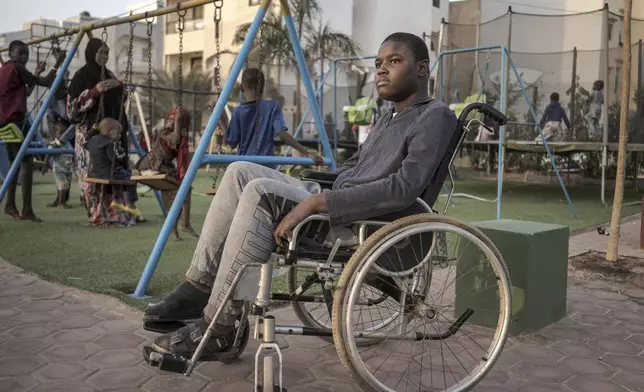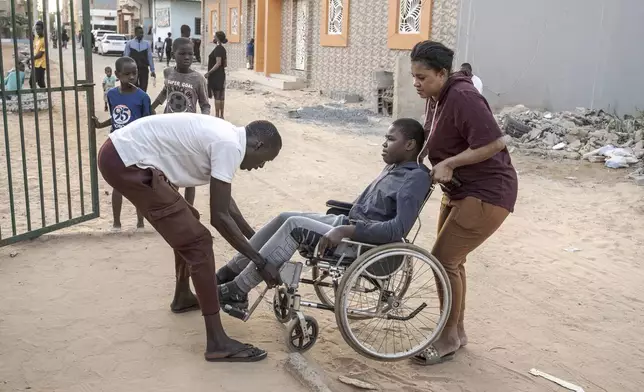DAKAR, Senegal (AP) — Ndeye Lam visits the cemetery often, praying and gently touching the seashells laid out across her daughter’s gravesite.
“Mariama will always be here,” she said, stepping away from the grave and onto a path that winds through rows of monuments outlined with white tile, stone and sand.
At home, Lam and her husband Pathé smiled over an old video clip of their daughter beaming as she celebrated her 13th birthday with cake and sparklers. When the girl was little, she loved to play. By 13, her muscles had weakened, her spine had curved and stiffened and in her last months, she struggled increasingly to breathe.
She visited Fann hospital in Dakar, where neurologist Dr. Pedro Rodriguez Cruz measured her lung capacity. He suspects Mariama had SELENON-related myopathy, a muscular dystrophy that causes severe respiratory compromise. A new BiPAP machine might have helped to ease her breathing, but it was too late.
Globally, more than 350 million people live with rare diseases, most of them caused by a misstep hidden within their genes. Some conditions can be caught early and treated—but in parts of Africa where population data and resources are scarce, many people go undiagnosed. Rodriguez is trying to change that by connecting patients with genetic testing and medical support, while gathering key data from those patients and their families.
“Most rare disease data has been collected from people of European ancestry, so we have very little knowledge about what’s happening in other parts of the world, mainly in Africa,” Rodriguez said.
His research is funded by organizations including the La Caixa Foundation in Spain and the National Ataxia Foundation in the United States. And he has consulted with scientists in China, France, Boston, and elsewhere around the world, documenting rare diseases and novel disease-causing gene variants.
That research is creating a library of genetic data for scientists and clinicians. Patients in Senegal are benefiting, too, with a path to diagnosis.
In Guediawaye, Fatoumata Binta Sané’s daughter Aissata has glutaric acidemia type I, an inherited disorder in which the body can’t process certain proteins properly. Her arms and legs are tightly drawn up toward her chest. She can’t walk or reach for things, speak, sit on her own or hold her head up. Sané cradles Aissata in her arms constantly, and the 8-year-old smiles at the sound of her mother’s voice.
In the U.S., newborns are screened for treatable genetic conditions. In Senegal, newborn screening is not routine. Infants who appear healthy at birth might go undiagnosed and experience irreversible decline. Glutaric acidemia type I, for example, can cause brain damage, seizures, coma and early death.
Sané is waiting for genetic testing results for Aissata’s one-year-old sister Aminata. Patients can live long, healthy lives if they start treatment before the onset of symptoms. That includes following a strict diet, avoiding protein-rich foods like nuts, fish and meat and taking the supplement L-carnitine. Though consultation with Rodriguez was free, lifelong treatment is not. If Aminata shares her sister’s disease, Sané will need government assistance to buy medication.
Prof. Moustapha Ndiaye, head of the neurology department at Fann, hopes young physicians will graduate prepared to assist rare disease patients not just in Senegal but in other African countries.
“Students travel from across Africa to study here,” Ndiaye said.
At the start of her career, Dr. Henriette Senghor saw patients who were hospitalized for months. Some died, and no one knew why.
“There was this problem—there was this void,” said Senghor, who’s now training with Rodriguez.
In 2021, Rodriguez established a partnership between the Cheikh Anta Diop University of Dakar and CNAG, the National Center for Genomic Analysis in Barcelona. Rodriguez collects patients’ blood samples and delivers the extracted DNA to Barcelona, where scientists sequence it, storing the answers it holds in a large database. Almost 1,300 participants—patients and families—have enrolled in his study of rare disease in West Africa.
In the Gambia, Fatou Samba’s sons Adama, 8, and Gibriel, 4, like to play soccer and feed the sheep in their backyard. On a recent afternoon, they took turns playing with a toy airplane and a globe. Adama, who hopes to be a pilot, pointed to where he wanted to go: the U.S. Outside, he started to climb a pile of bicycles propped up against the wall, and Gibriel followed.
“We’re climbing Mount Everest,” Adama said.
Standing on a bicycle wheel, Adama hesitated. Samba reached for him, setting him down on solid ground. There is a tiny scar on his forehead where broken skin has been stitched back together. Last year, Samba couldn’t explain his frequent falling, so she sought answers in Dakar. Rodriguez confirmed Adama had Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Gibriel's genetic test results are pending. Children often lose the ability to run or climb stairs first, and later can’t walk or raise their arms. In adulthood, they develop heart and breathing problems.
Both boys are taking corticosteroids, which can slow disease progression for patients diagnosed early.
“Without the medication, it would have been terrible. Once we started, after a few weeks we saw improvement,” Samba said. “Doctors are destined to investigate (the disease) and find a cure … I pray doctors will find a cure.”
Back at Fann Hospital, Rodriguez and Senghor consult with Woly Diene, 25, and her mother and brother. When Diene was 15, she started falling at school. Soon, she felt pain throughout her body. She couldn’t move. She lost her hearing, the strength in her hands and control of the muscles in her face.
Diene, who comes from a rural village in Senegal, has riboflavin transporter deficiency. High doses of vitamin B2—a supplement available on Amazon—can slow, stop and even reverse damage from this condition that is fatal without treatment.
Diene took her first dose when she was diagnosed in August 2023. She still has some difficulty hearing, but Diene is walking again. She has regained the strength in her face and hands. Diene’s brother Thierno said vitamin B2 is expensive, but he knows his sister needs it for the rest of her life.
“I am happy,” Diene said, smiling. “I hope to keep improving.”
While efforts like these help patients, they also allow doctors to collect data—and that’s vital for rare disease research, policy and drug development, said Lauren Moore, chief scientific officer at the National Ataxia Foundation.
“The most prevalent diseases get the most attention and the most funding,” she said. “Data … really is the first step.”
A $50,000 grant from the foundation allows Rodriguez and colleagues to enroll study participants in Senegal and Nigeria with inherited ataxias—which can lead to muscle weakness, loss of mobility, hearing and vision difficulties and life-shortening heart problems.
The USAID cuts have not affected his research, but grant awards are limited. Rodriguez, Senghor and Rokhaya Ndiaye, professor of human genetics at the University of Dakar, are making plans to ensure genetic testing continues in Senegal.
Global collaboration is essential, said Ndiaye—and strengthening local infrastructure is just as important.
“The need is there,” she said. “And we have a lot of hope.”
For more on Africa and development: https://apnews.com/hub/africa-pulse
The Associated Press receives financial support for global health and development coverage in Africa from the Gates Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.
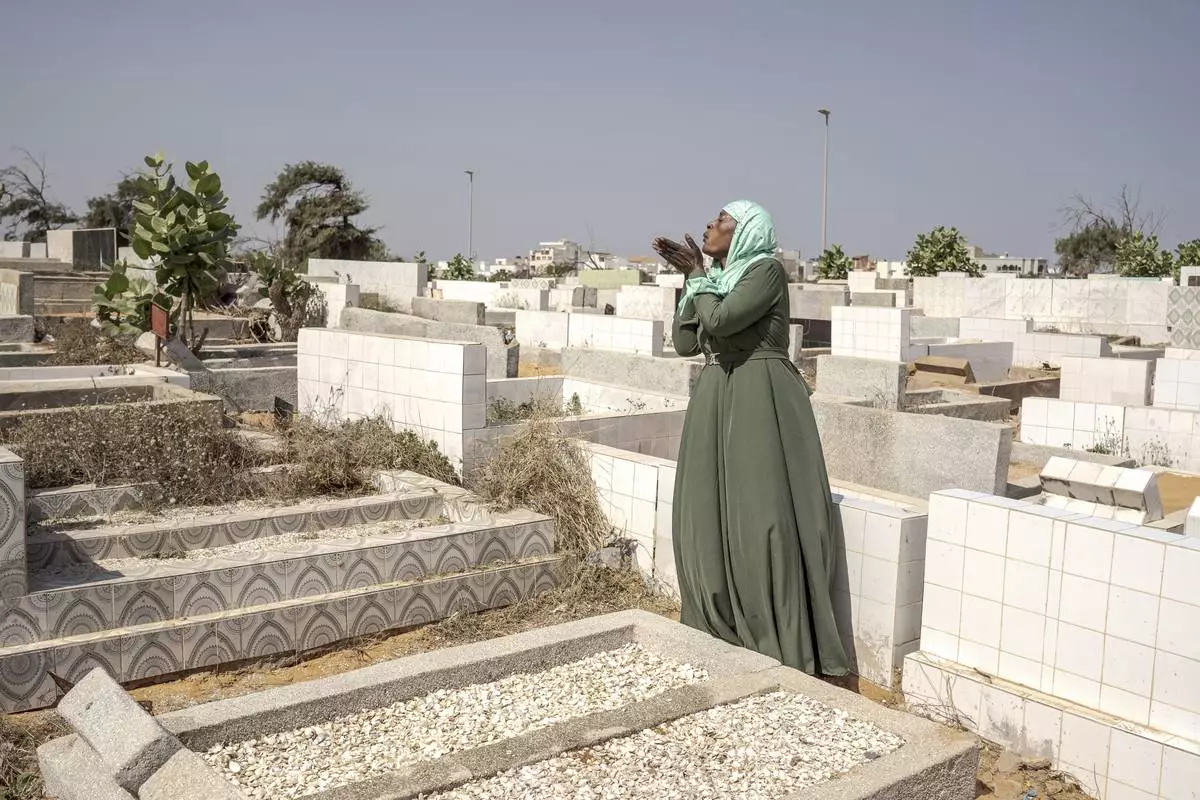

Ndeye Lam sends a prayer at the foot of her daughter Mariama's grave in Dakar, Senegal, Saturday, Jan. 11, 2025. (AP Photo/Annika Hammerschlag)
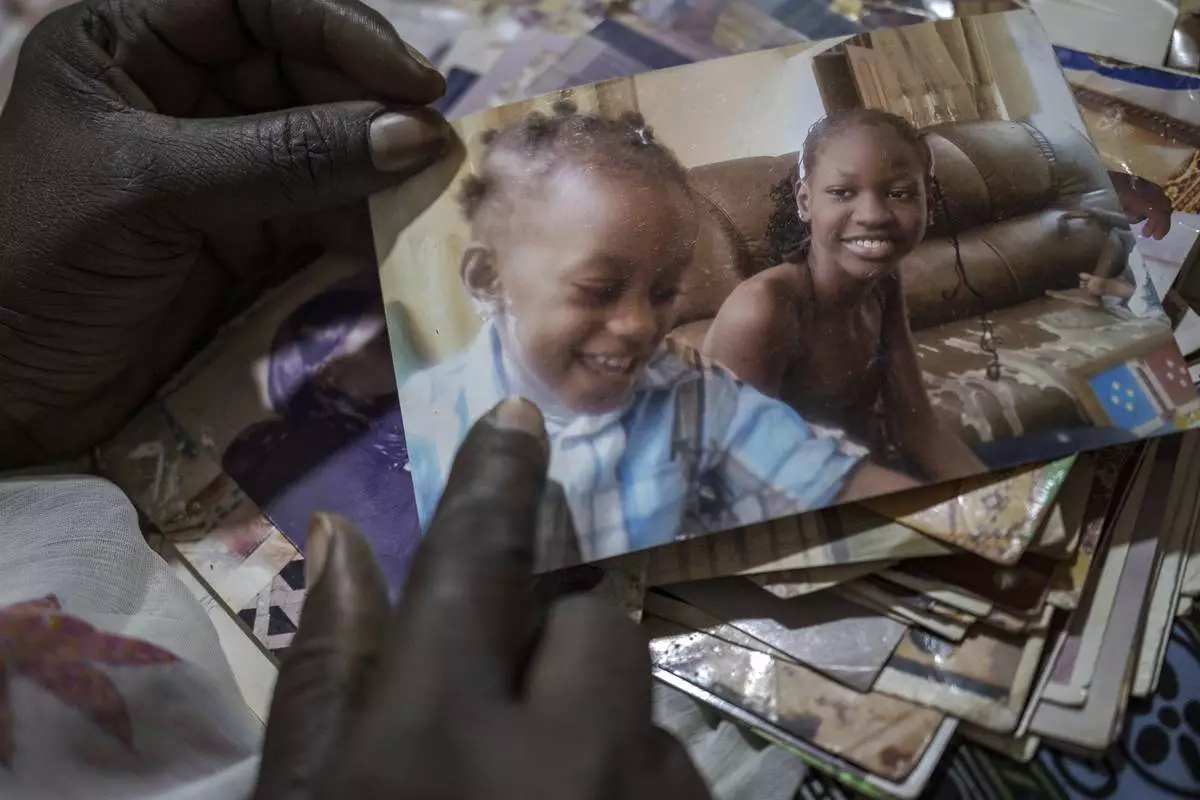

Ndeye Lam looks at photos of her deceased daughter Mariama who died at age 13 of a rare genetic disease, in Dakar, Senegal, Saturday, Jan. 11, 2025. (AP Photo/Annika Hammerschlag)
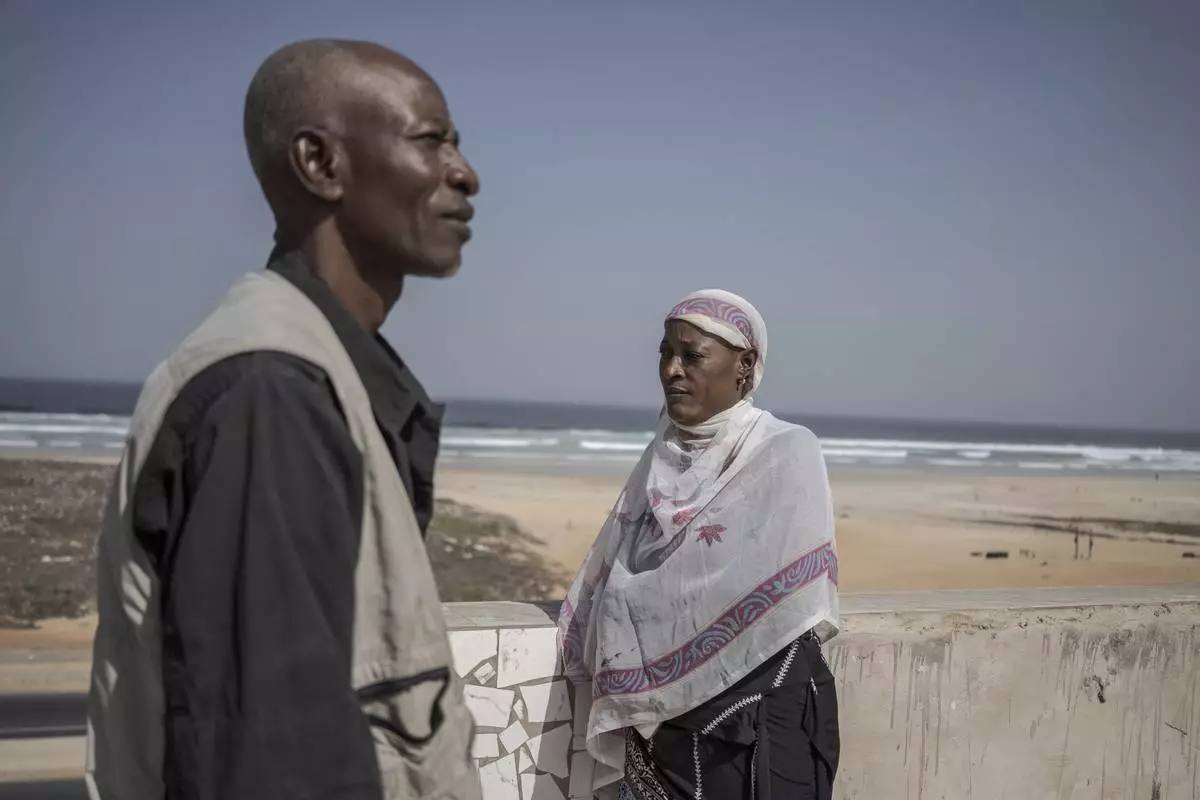

Pathe Gueye, left, and Ndeye Lam, right, stand on their roof in Dakar, Senegal Saturday, Jan. 11, 2025. Their daughter Mariama died at age 13 of a rare genetic disease. (AP Photo/Annika Hammerschlag)
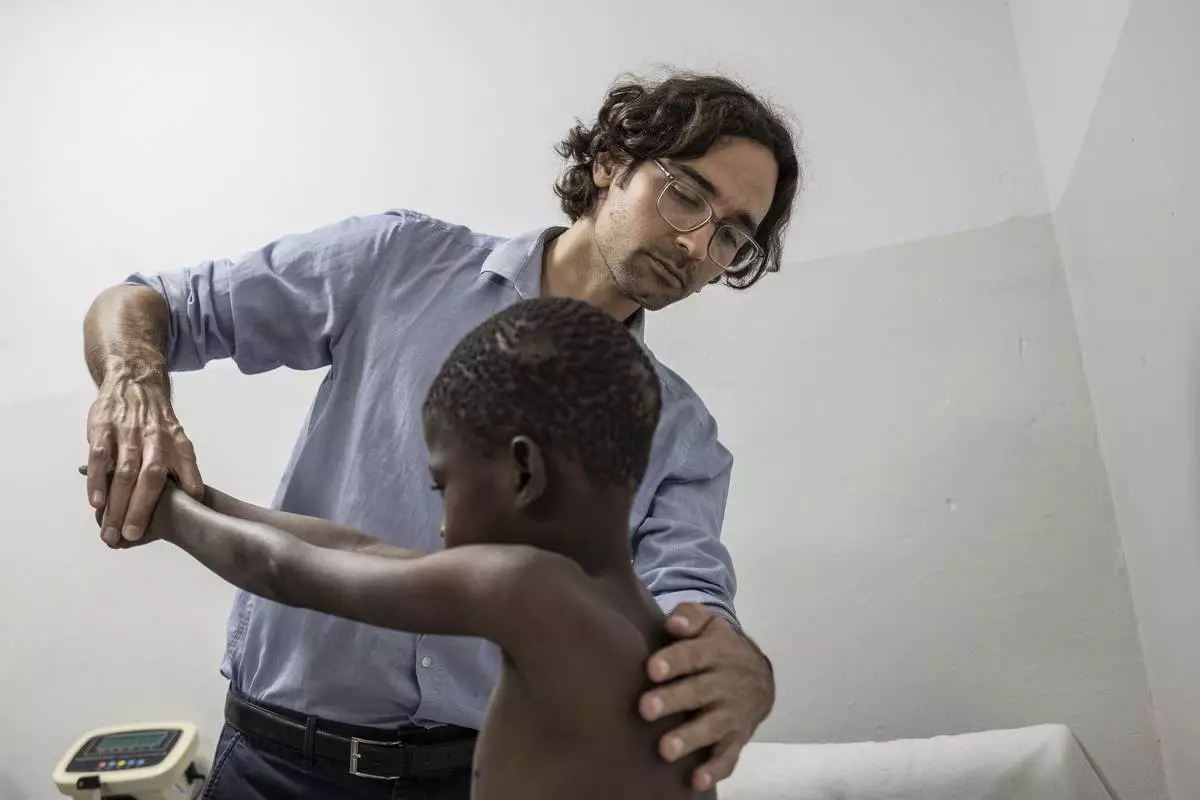

Rare disease researcher Pedro Rodriguez, left, examines Ibrahima Ndiaye, 8, in Dakar, Senegal, Friday, Jan. 10, 2025. (AP Photo/Annika Hammerschlag)
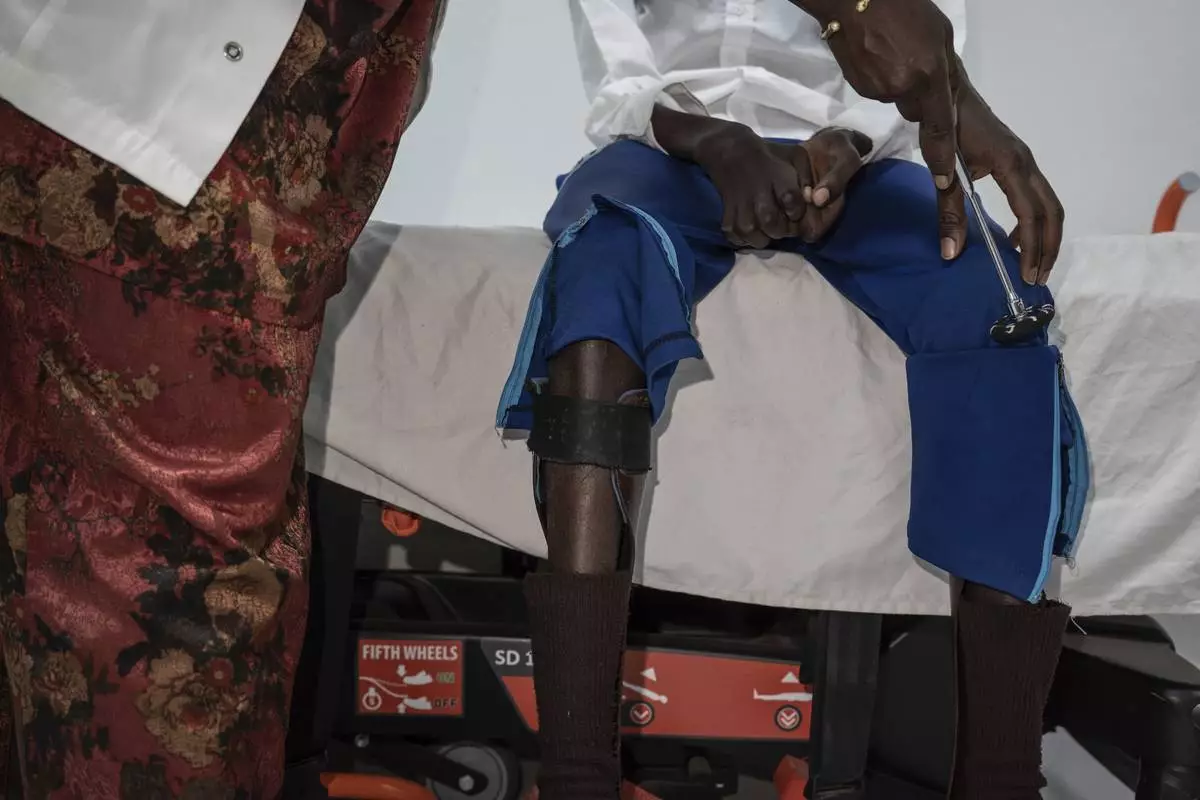
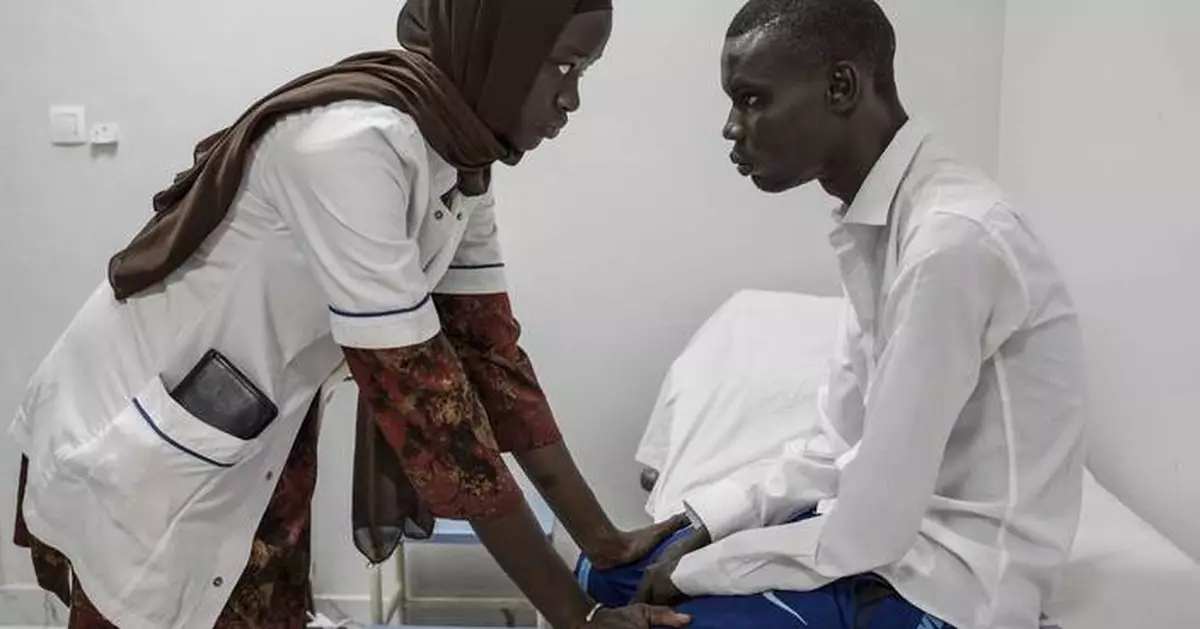
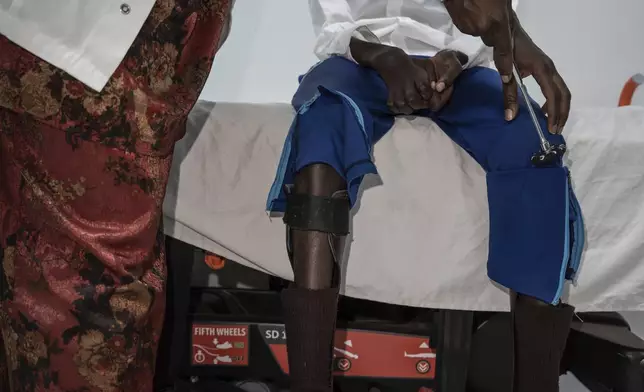
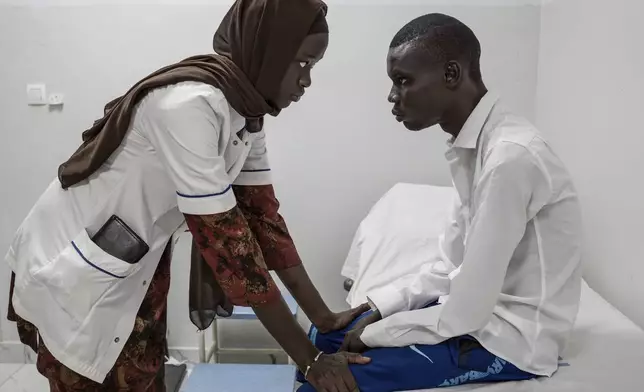
Neurology student Henriette Dieng examines Abdou Diop, a patient with genetic neuropathy at Pedro Rodriguez's clinic in Dakar, Senegal, Friday, Jan. 10, 2025. (AP Photo/Annika Hammerschlag)
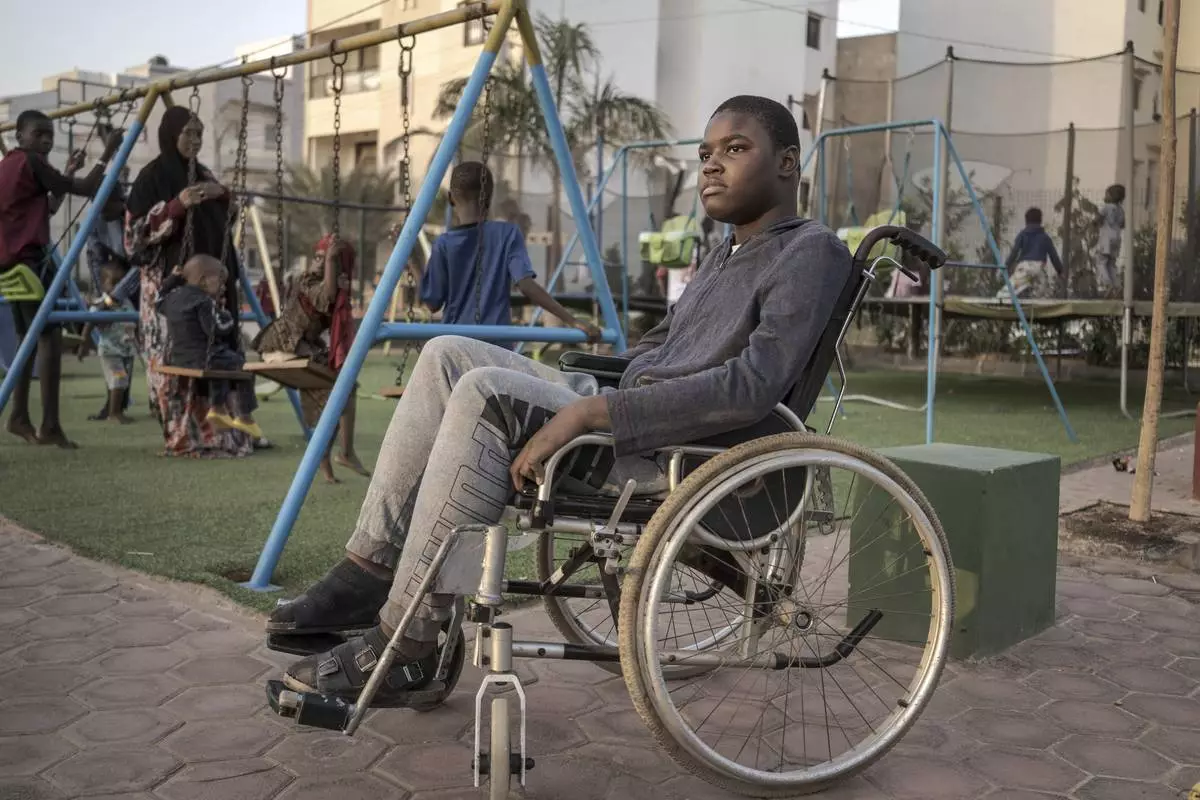

Mamadou, 13, watches children play in Dakar, Senegal, Saturday January 11, 2025. (AP Photo/Annika Hammerschlag)
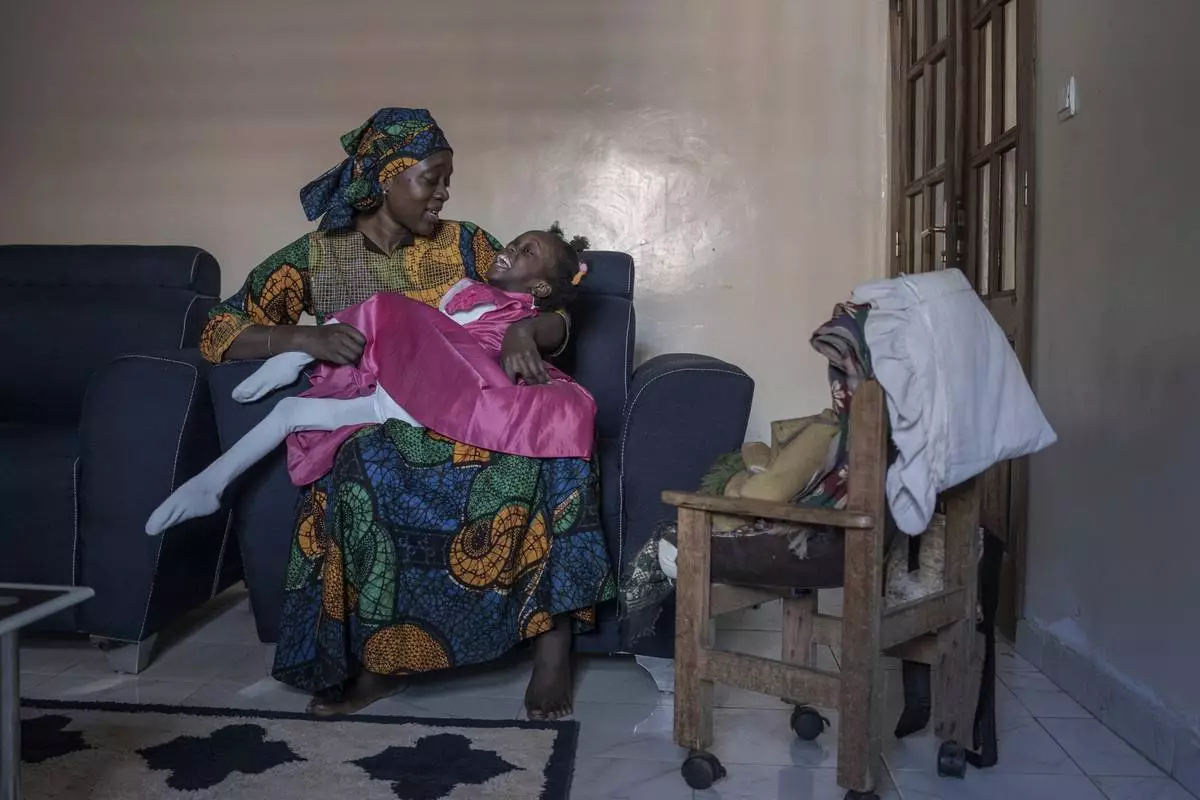

Fatoumata Sané holds her daughter Aissata, 8, who suffers from a rare genetic disease, at their home in Dakar, Senegal, Saturday, Jan. 11, 2025. (AP Photo/Annika Hammerschlag)
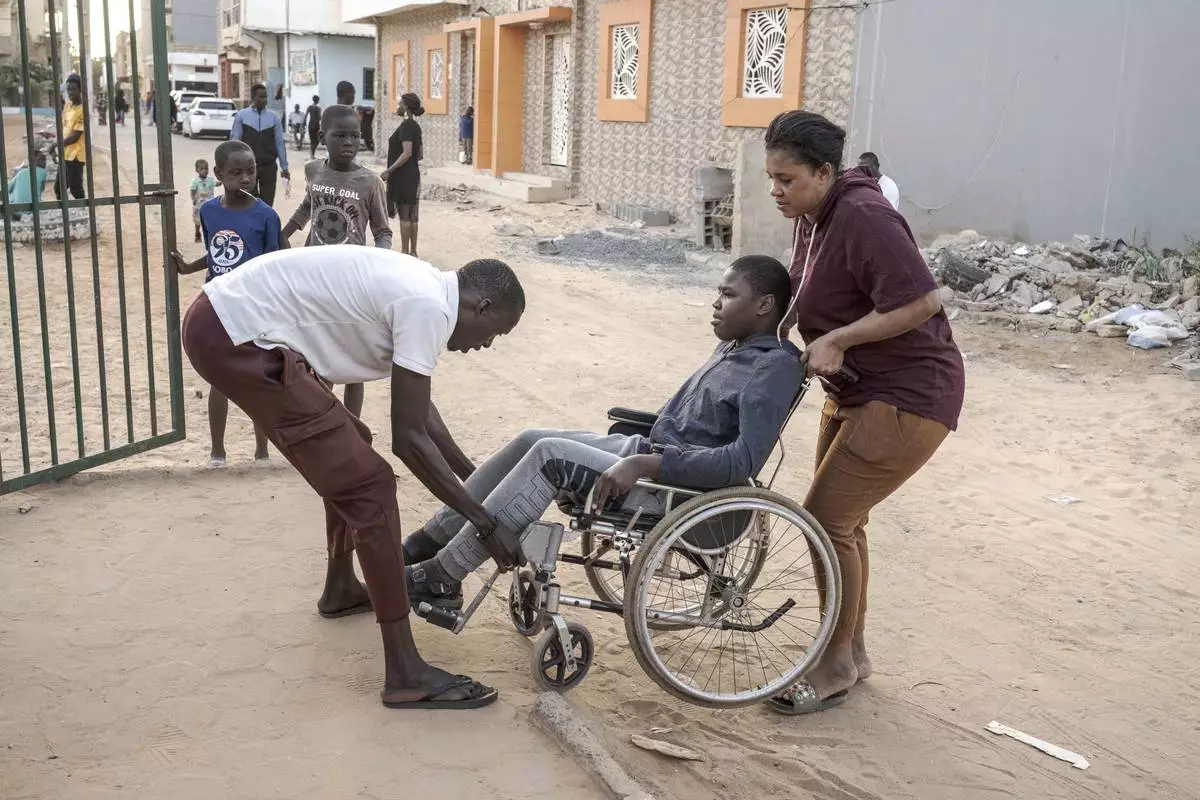

A man helps Adiaratou Ba, right, lift her son Mamadou, 13, suffering from a rare genetic disease, onto the curb in Dakar, Senegal, Saturday Jan. 11, 2025. (AP Photo/Annika Hammerschlag)
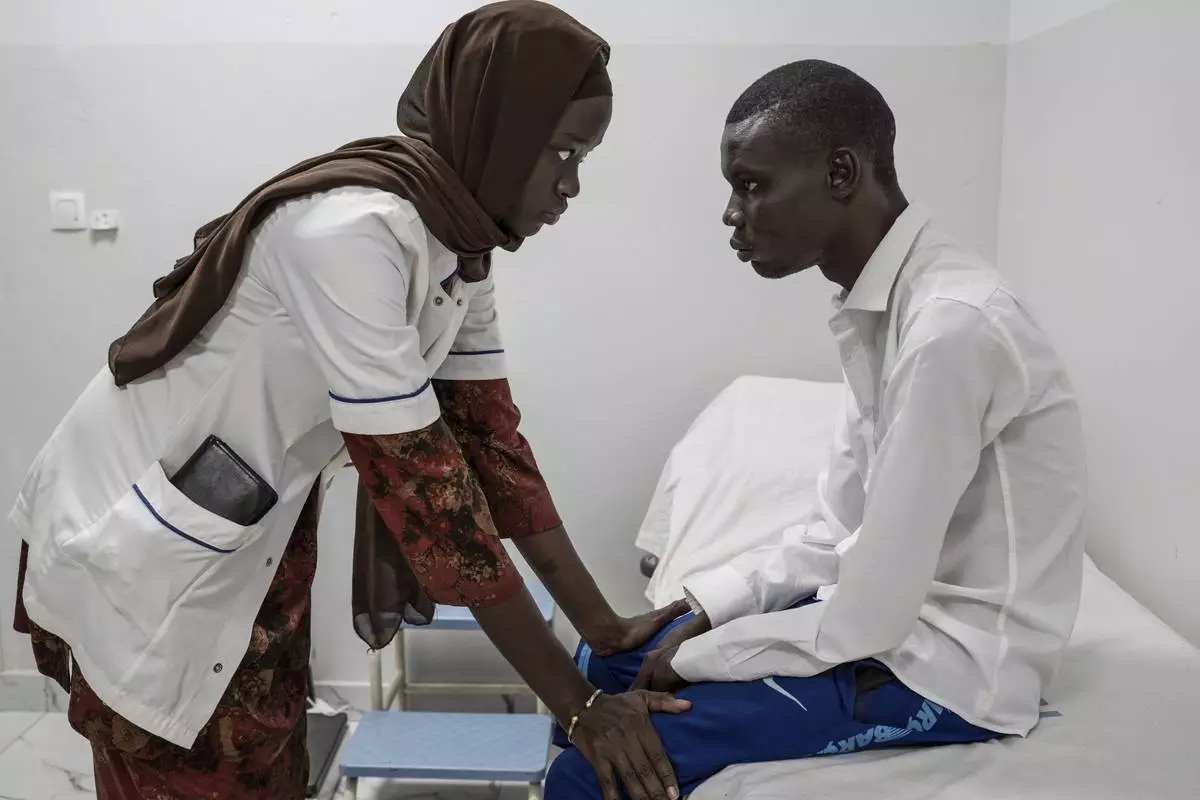

Neurology student Henriette Dieng examines Abdou Diop, a patient with genetic neuropathy at Pedro Rodriguez's clinic in Dakar, Senegal, Friday, Jan. 10, 2025. (AP Photo/Annika Hammerschlag)