When a woman has a mammogram, the most important finding is whether there’s any sign of breast cancer.
The second most important finding is whether her breasts are dense.
Since early September, a new U.S. rule requires mammography centers to inform women about their breast density — information that isn’t entirely new for some women because many states already had similar requirements.
Here’s what to know about why breast density is important.
No, dense breasts are not bad. In fact, they’re quite normal. About 40% of women ages 40 and older have dense breasts.
Women of all shapes and sizes can have dense breasts. It has nothing to do with breast firmness. And it only matters in the world of breast cancer screening, said Dr. Ethan Cohen of MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
With the new rule, “there are going to be a lot of questions to a lot of doctors and there’s going to be a lot of Googling, which is OK. But we want to make sure that people don’t panic,” Cohen said.
Doctors who review mammograms have a system for classifying breast density.
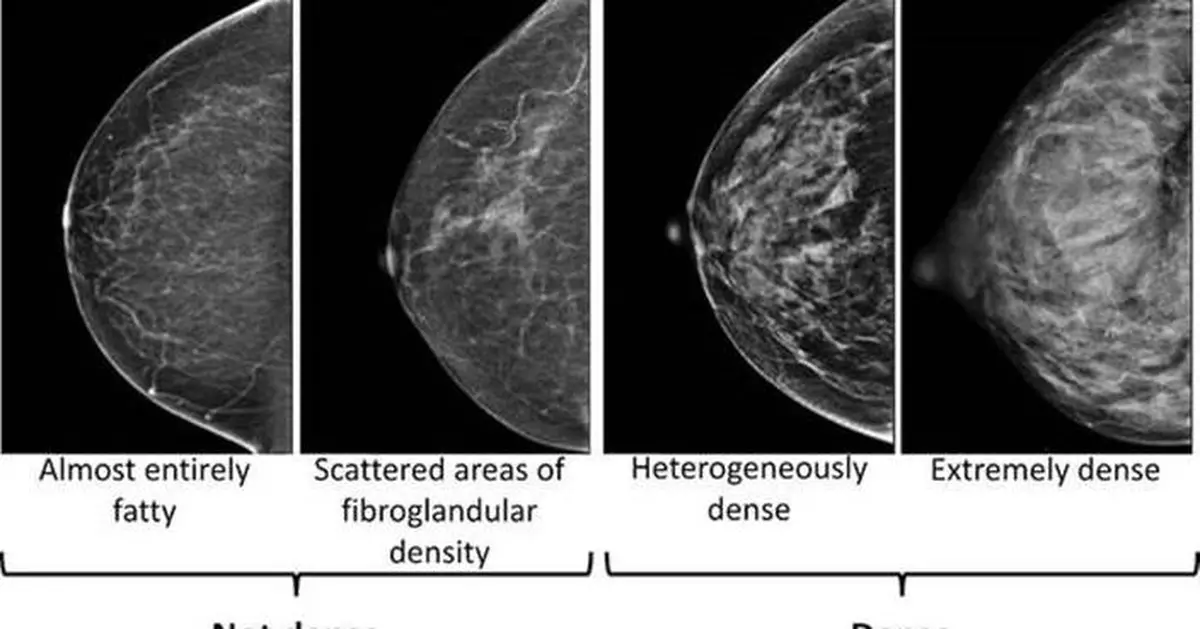
There are four categories. The least dense category means the breasts are almost all fatty tissue. The most dense category means the breasts are mostly glandular and fibrous tissue.
Breasts are considered dense in two of the four categories: “heterogeneously dense” or “extremely dense.” The other two categories are considered not dense.
Dr. Brian Dontchos of the Seattle-based Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center said the classification can vary depending on the doctor reading the mammogram "because it’s somewhat subjective.”
Two reasons: For one, dense breasts make it more difficult to see cancer on an X-ray image, which is what a mammogram is.
“The dense tissue looks white on a mammogram and cancer also looks white on a mammogram,” said Dr. Wendie Berg of the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and chief scientific adviser to DenseBreast-info.org. “It’s like trying to see a snowball in a blizzard.”
Second, women with dense breast tissue are at a slightly higher risk of developing breast cancer because cancers are more likely to arise in glandular and fibrous tissue.
Reassuringly, women with dense breasts are no more likely to die from breast cancer compared to other women.
If you find out you have dense breasts, talk to your doctor about your family history of breast cancer and whether you should have additional screening with ultrasound or MRI, said Dr. Georgia Spear of Endeavor Health/NorthShore University Health System in the Chicago area.
Researchers are studying better ways to detect cancer in women with dense breasts. So far, there’s not enough evidence for a broad recommendation for additional screening. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force called for more research in this area when it updated its breast cancer screening recommendations earlier this year.
Yes, women with dense breasts should get regular mammograms, which is still the gold standard for finding cancer early. Age 40 is when mammograms should start for women, transgender men and nonbinary people at average risk.
“We don’t want to replace the mammogram,” Spear said. “We want to add to it by adding a specific other test.”
For now, that depends on your insurance, although a bill has been introduced in Congress to require insurers to cover additional screening for women with dense breasts.
Additional screening can be expensive — from $250 to $1,000 out of pocket, so that’s a barrier for many women.
“Every woman should have equal opportunity to have their cancer found early when it’s easily treated,” Berg said. “That’s the bottom line.”
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
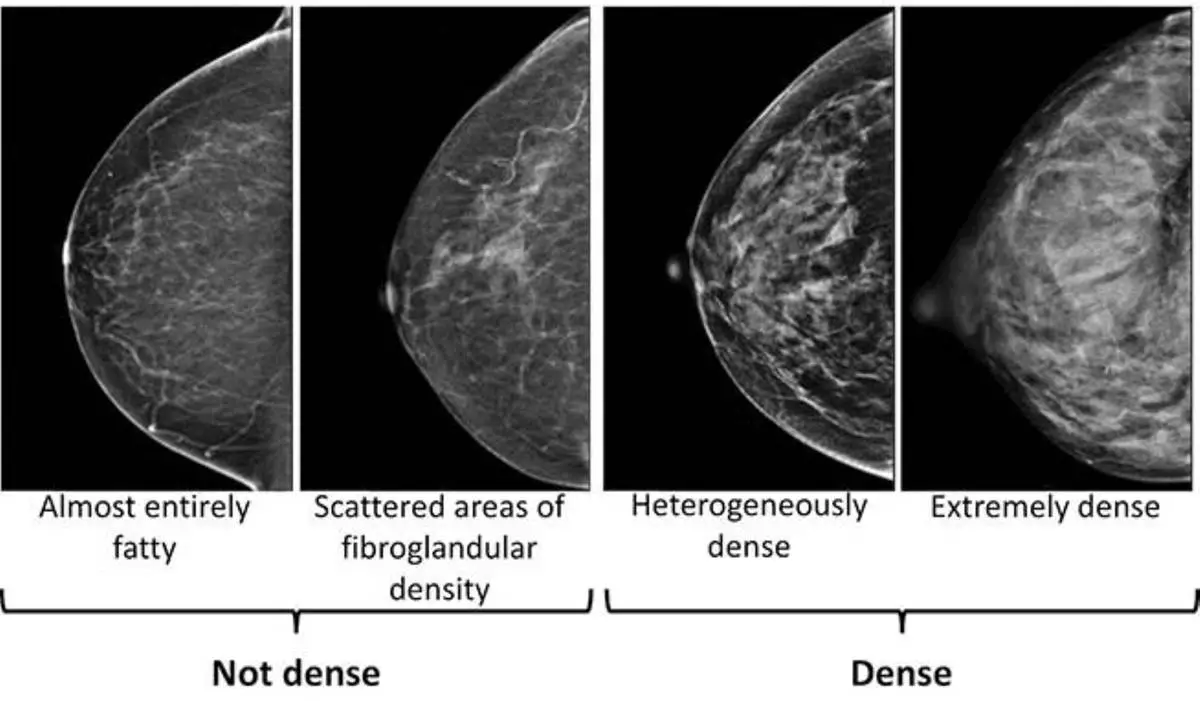
This image provided by the UW/Fred Hutch Cancer Center Breast Imaging in October 2024 shows mammogram scans with dense and not dense tissue. (UW/Fred Hutch Cancer Center Breast Imaging via AP)
The path for the NFL's Washington Commanders to return to the nation’s capital is clear after an on-again, off-again saga in Congress ended early Saturday with a postmidnight reprieve.
The U.S. Senate passed a resolution to transfer the land including old RFK Stadium from the federal government to the District of Columbia. The D.C. Robert F. Kennedy Memorial Stadium Campus Revitalization Act passed by voice vote at roughly 1:15 a.m. after more than a year of lobbying and support from Rep. James Comer, R-Ky., district Mayor Muriel Bowser, Commanders controlling owner Josh Harris and NFL Commissioner Roger Goodell.
“We are extremely grateful that our elected officials have come together on a bipartisan basis to give Washington, D.C., the opportunity to decide on the future of the RFK Stadium site," Harris said. "This bill will create an equal playing field so that all potential future locations for the home of the Washington Commanders can be fairly considered and give our franchise the opportunity to provide the best experience for all of our fans.”
The RFK Stadium land provision was part of Congress’ initial short-term spending bill Tuesday before it was torpedoed by President-elect Donald Trump and Elon Musk, the latter of whom amplified misinformation about the site on his social media platform X. Two versions of the House's slimmed-down bill, including the one that passed Friday night to avoid a government shutdown, did not include it.
Giving the local government control of the land for the next 99 years allows for the decaying husk of the old stadium to be torn down and the site redeveloped for any number of things. One of the possibilities is a football stadium and surrounding entertainment options at the franchise's former home.
Bowser called it “a win for D.C., for our region and for America.”
“Everybody loves a good comeback story — and that’s D.C.’s story,” she said.
All that awaits is President Joe Biden's signature to become law. Comer went as far as saying that Senate passage of the bill is “a historic moment for our nation's capital.”
“If Congress failed to act today, this decaying land in Washington would continue to cost taxpayers a fortune to maintain,” he said. “Revitalizing this RFK Memorial Stadium site has been a top economic priority for the city, and I am proud to have partnered with D.C. Mayor Muriel Bowser to get this bill across the finish line and to the president’s desk. This bipartisan success is a testament to the House Oversight Committee’s unwavering effort to protect taxpayers and our full commitment to ensuring a capital that is prosperous for residents and visitors for generations to come.”
Playing in Washington again is no sure thing. The Commanders are considering places in the district, Maryland and Virginia to build a stadium in the coming years.
Their lease at Northwest Stadium in Landover, Maryland, runs through 2027. Harris called 2030 a “reasonable target” for a new stadium.
The team played at RFK Stadium 2 miles (3.22 kilometers) east of the Capitol from 1961-96 before moving to Maryland. Harris and several co-owners, including Mitch Rales and Mark Ein, grew up as Washington football fans during that era, which included the glory days of three Super Bowl championships from 1982-91.
Part of the way the provision got into the bill initially involved an agreement between the team and Maryland to tear down the current stadium in a timely fashion and redevelop the site with a project of equal economic impact, a person with knowledge of the situation told The Associated Press earlier this week on condition of anonymity because the deal was not being publicized.
After the Senate greenlit the RFK Stadium land transfer, Maryland Sens. Ben Cardin and Chris Van Hollen, both Democrats, said they continued to believe their state's partnership with the team should continue long into the future.
“After working to level the financial playing field, and receiving assurances that should the team move they will redevelop the existing site in a manner that meets the needs of the community, tonight we supported the proposed land transfer legislation,” Cardin and Van Hollen said. "We have always supported the District’s effort to control its own land, and through regional discussions and cooperation, our concerns with this proposal have been addressed.”
The team has played games in Maryland since 1997 and practices in Ashburn, Virginia, not far from Dulles International Airport.
A return to the district would be another victory for Bowser, who on Thursday celebrated the start of an $800 million downtown arena renovation that is keeping the NBA's Wizards and NHL's Capitals in town. At that news conference, she took aim at Musk for sharing incorrect information on X, formerly Twitter, about taxpayers footing the bill for a new stadium.
“It was stated that the (continuing resolution) contains $3 billion for a stadium,” Bowser said. "All wrong. There are no federal dollars related to the transfer of RFK, and in fact the legislation does not require or link at all to a stadium. We’re talking about how the District can invest in removing blight.”
Musk reshared an inaccurate post saying: “Buried in the 1,547-page omnibus bill is a provision to facilitate a $3 billion NFL stadium in Washington, D.C." with the message, “This should not be funded by your tax dollars!”
The bill specifically prohibits the use of federal funds for a stadium on the site, “including training facilities, offices, and other structures necessary to support a stadium.”
AP NFL: https://apnews.com/hub/nfl

FILE - A vehicle pushes up pikes of snow after trucks dump their loads of snow in the parking lots of RFK Stadium in Washington, Monday, Jan. 25, 2016. (AP Photo/Susan Walsh, File)