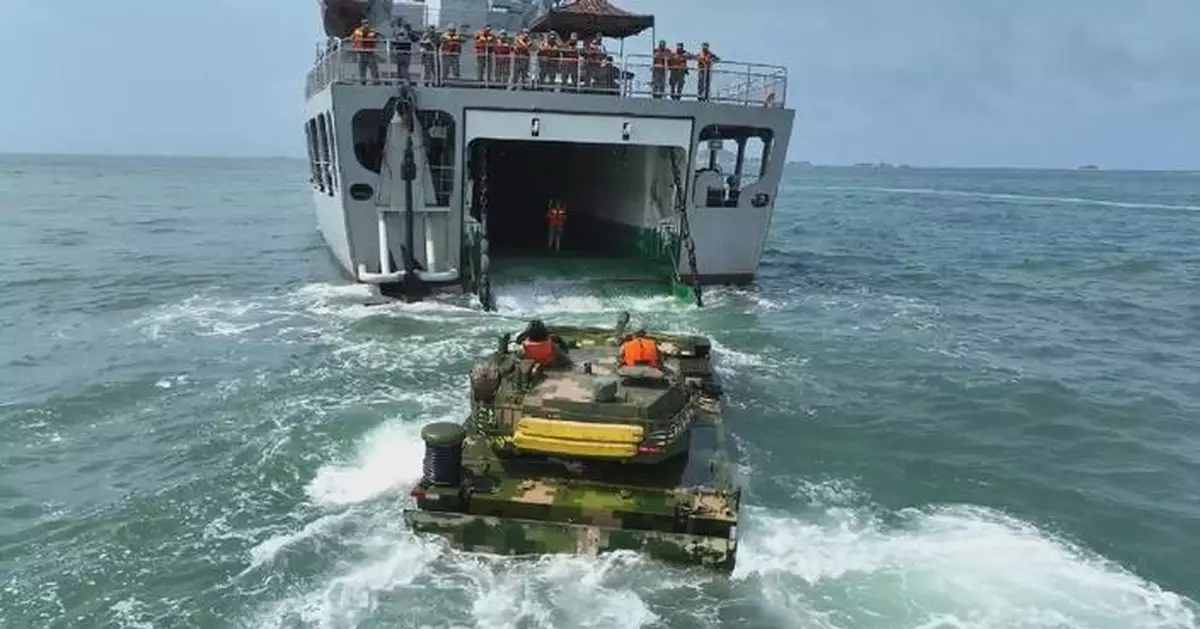
An amphibious armored detachment of China's 74th Army Group, together with a navy landing ship of the Chinese People's Liberation Army (PLA), has conducted a day-and-night multi-course training in unfamiliar waters to enhance the force's at-sea combat capability.
Various types of military cars, including amphibious armored assault vehicles and infantry combat vehicles, formed a tactical formation during the voyage and maneuvered to the target sea area several kilometers away.
Upon arrival in the exercise waters, the soldiers immediately started daytime and nighttime training on embarking and disembarking the landing ship.
Getting on and off the landing ship is an important link for an amphibious force to deliver troops and materials between ship and shore under combat conditions, which is difficult and challenging due to the winds and wave undulations on the sea. With the close cooperation of the instructors and crew members, the soldiers successfully drove the amphibious vehicle quickly into the landing ship and fixed them in the cabin.
The nighttime training was more complicated for the armored vehicle drivers because of reduced visibility. They constantly adjusted and corrected the course of the vehicles according to instructions, and managed to complete the task under the complex sea conditions.
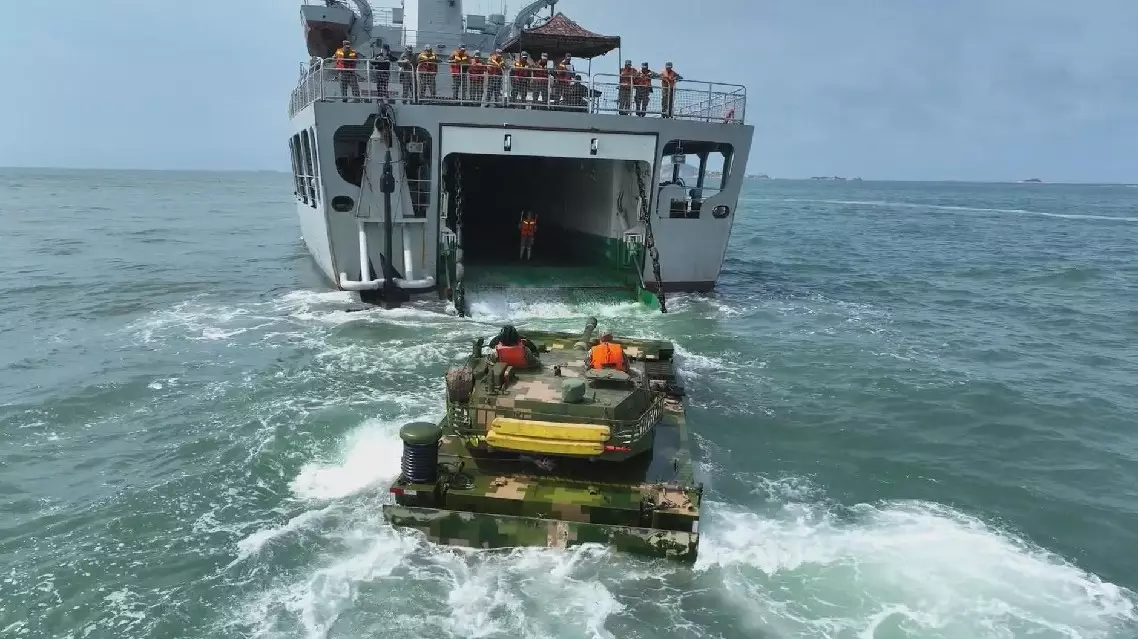

PLA amphibious armored force, landing ship conduct day-and-night maritime training

PLA amphibious armored force, landing ship conduct day-and-night maritime training
China's first commercial spacecraft launch site marked its dual-pad readiness for future missions on Wednesday, with a group of 18 low Earth orbit satellites being launched aboard the Long March-8 Y6 carrier rocket.
The satellite group was launched from the Hainan commercial spacecraft launch site in south China's Hainan Province at 00:38 Wednesday.
The satellites, the fifth group of its kind, have entered the preset orbit successfully, according to the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC). They will constitute China's commercial internet constellation Spacesail.
This mission marks the inaugural launch from the site's No. 1 launch pad, which, following the inaugural launch from the No. 2 pad on Nov. 30, 2024, signifies the dual-pad readiness of China's first commercial spaceport for future missions.
The No. 1 launch pad, standing 83 meters tall, is tailored for the Long March-8 rocket. It features a modular steel structure design and employs a dual-direction flame deflection cone for cooling and noise reduction for the first time, enhancing rapid reuse capabilities.
The launch pad now supports a seven-day launch and seven-day reset cycle, crucial for meeting surging launch demands.
The construction of the Hainan commercial spacecraft launch site commenced in July 2022. It completed its first launch mission in November 2024.
Now it is advancing the construction of the phase II project.
The Long March-8 rocket, developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology under the CASC, is a medium-lift liquid-fueled rocket optimized for cost-effective, multi-satellite launches to low- and medium-Earth orbits.
The mission marks the 563rd flight of the Long March rocket family, the pillar of China's space transport system.

China's first commercial spacecraft launch site marks dual-pad readiness with launch of 18 satellites