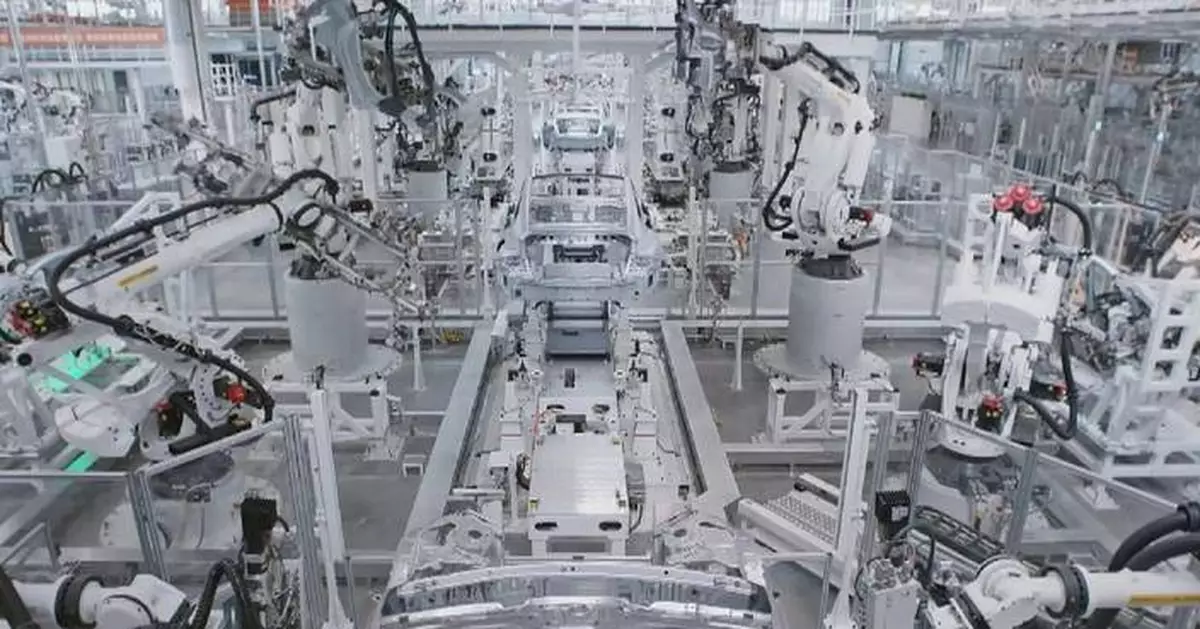
The deepening integration of sci-tech innovation and industrial innovation emerged as a key focus for potential cooperation among global business leaders at the China Development Forum 2025 held in Beijing on Sunday and Monday.
Speaking at the forum, Li Lecheng, Party secretary of the Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, highlighted China's steadfast implementation of the innovation-driven development strategy.
Currently, the number of foreign-invested enterprises established in China has surpassed 1.2 million, with foreign investments spanning 31 major categories and 548 subcategories within the country's manufacturing sector.
"Promoting the deep integration of scientific and technological innovation and industrial innovation is not a solo performance by China, but a chorus by the world. China has a complete industrial system, rich application scenarios, a super-large-scale market and a large number of talents, which provides a broad cooperation space for international industrial scientific and technological innovation," Li said.
Notably, beyond production, establishing research and development centers in China to collaborate with domestic enterprises on tackling key technical challenges has increasingly become a growing trend among foreign investors.
British pharmaceutical giant AstraZeneca signed a landmark agreement on Friday to invest 2.5 billion U.S. dollars in Beijing over the next five years. Under the agreement, AstraZeneca will establish a global strategic research and development center in Beijing, its sixth worldwide and second in China after one in Shanghai. The new center, equipped with an advanced artificial intelligence and data science laboratory, will accelerate early-stage drug research and clinical development.
"The reason we want to invest in China is because of the explosion of innovation that is happening in the country. As we work with those companies, we invest, of course, but we also invest in bringing our own capabilities, our own skills. We are investing in the life science physical ecosystem in Beijing, for instance, where we are actually going to help smaller startup companies come up with new products, training people who will actually be able to create economic growth," said AstraZeneca CEO Pascal Soriot.
The economic transformation led by innovation has also brought new opportunities for foreign-funded enterprises.
"We invest in high quality growth, we invest in innovating, and we invest in cooperating with our good Chinese partners. It's a journey that has just started right now, but it also is an area where we need to work close together," said Kim Fausing, president and CEO of Danfoss, a global market leader in heating and cooling.
China integrating innovation with industrial progress resonates with global business leaders
It's impossible to build a system of governance that ensures artificial intelligence (AI) systems always operate and police themselves in alignment with both human and machine well-being without the participation of China, American columnist Thomas L. Friedman said in an article on Tuesday.
Friedman, a three-time Pulitzer Prize winner and the author of "The World Is Flat: A Brief History of the Twenty-First Century," attended the China Development Forum 2025 held on March 23 and 24 in Beijing.
Based on what he saw and heard during the event, Friedman published an article in the New York Times titled "What I'm Hearing in China This Week About Our Shared Future" on Tuesday.
"There is an earthshaking event coming — the birth of artificial general intelligence (AGI). The United States and China are the two superpowers closing in on AGI — systems that will be as smart or smarter than the smartest human and able to learn and act on their own," the article reads.
Friedman cited an M.I.T. Technology Review report on the "16 humanoid robots" that danced on stage during China's televised Spring Festival gala this year which read: "Clad in vibrant floral print jackets, they took part in a signature ... dance, twirling red handkerchiefs in unison with human dancers."
Friedman wrote in his column that "In their day job, these robots work assembling electric vehicles. Dancing was just their hobby."
"The advances that China has made on AI in just the past year have made it absolutely clear that Beijing and Washington are now the world's two AI superpowers," Friedman wrote.
He mentioned a recent report by Morgan Stanley describing China's dominance over the West in the humanoid robot industry, saying the country is home to a majority of the top-listed companies in this sector.
Noting AI systems and humanoid robots offer so much potential benefit to humanity, Friedman warned they could also be hugely destructive and destabilizing if not embedded with the right values and controls.
He repeatedly stressed the importance of collaboration between the U.S. and China in AI.
"Because what Soviet-American nuclear arms control was to world stability since the 1970s, U.S.-Chinese AI collaboration to make sure we effectively control these rapidly advancing AI systems will be for the stability of tomorrow's world," Friedman wrote.
"China has greatly narrowed the gap with us and surpassed the other democracies. This can't be done without Beijing. So guess who's coming to dinner. It's a table for two now," he said.
Friedman wrote in the article that "Once AGI arrives, if we are not assured that these systems will be embedded with common trust standards, the United States and China will not be able to do anything together."
He pointed out that in this case, neither side will trust anything they trade with the other, because AI will be in everything that is digital and connected, including cars, watches, toasters, chairs, implants, and notepads.
"So if there is no trust between the U.S. and China and each of the two countries has their own AI systems, it will be the TikTok problem on steroids. A lot of trade will just grind to a halt, with only soybeans for soy sauce sold to each other," Friedman wrote, saying "It will be a world of high-tech feudalism."
Friedman said he was taken with a speech by Israeli historian Yuval Noah Harari during the conference, who said that "We should build more trust between humans before we develop truly superintelligent AI agents. But we are now doing exactly the opposite. All over the world, trust between humans is collapsing. Too many countries think that to be strong is to trust no one and be completely separated from others. If we forget our shared human legacies and lose trust with everyone outside us, that will leave us easy prey for an out-of-control AI."

Global AI governance cannot happen without China: American columnist