ASILOMAR, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Apr 7, 2025--
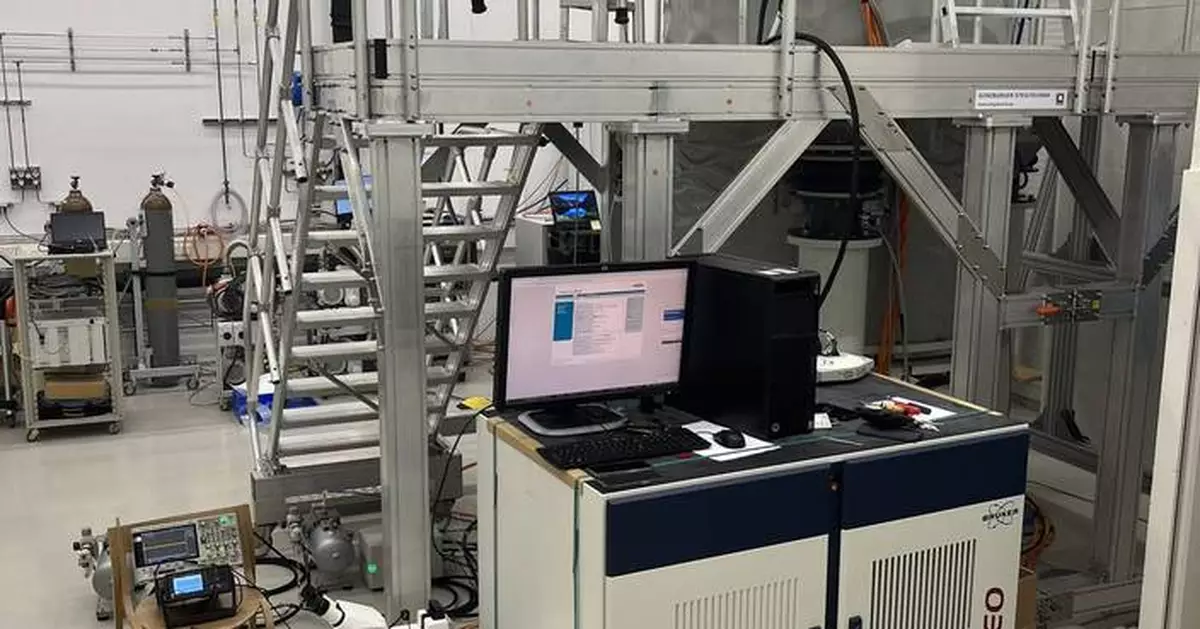
At the Joint ENC-ISMAR Conference 2025, Bruker Corporation, the leading provider of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy solutions, announced the successful development and testing of the world’s first high-resolution 1.3 GHz NMR spectrometer with a stable, standard-bore 54 mm superconducting magnet. This first-of-a-kind ultra-high field magnet and spectrometer pushes the boundaries of what is possible in the field of NMR research and opens a new chapter of ultra-high field NMR with even higher dispersion and resolution.
This press release features multimedia. View the full release here: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20250407030056/en/
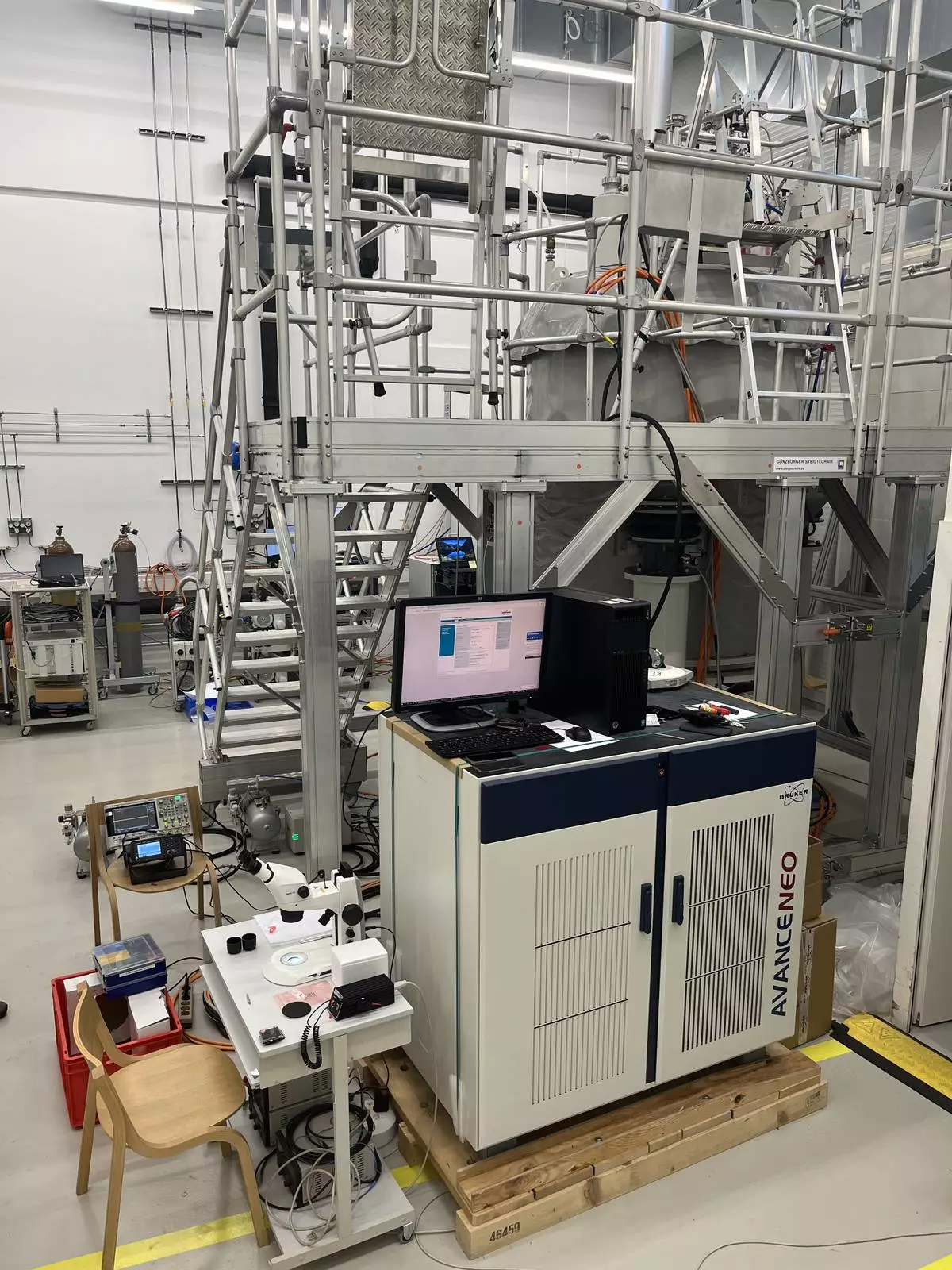
Building on the success of its 1.0-1.2 GHz systems, Bruker's 1.3 GHz NMR spectrometer offers unprecedented resolution and sensitivity, enabling scientists to study complex biomolecular systems and advanced materials in greater detail. The first-of-a-kind superconducting and persistent standard-bore NMR magnet has a field strength of 30.5 Tesla (T) and incorporates a novel ReBCO high-temperature superconductor (HTS) insert, generating even higher magnetic fields. The novel 1.3 GHz magnet extends Bruker’s innovative LTS-HTS hybrid magnet architecture. Despite higher field, the 1.3 GHz magnet maintains the same physical dimensions and cryogen consumption as Bruker’s 1.2 GHz magnets, with a slightly increased stray field radius.
Applications testing at 1.3 GHz proton frequency was conducted using five different NMR probe configurations: a 3 mm TXI liquids room-temperature probe, a 5 mm TXO liquids CryoProbe, a 111 kHz (0.7 mm) HCN solid-state magic-angle spinning (MAS) probe, a 42 kHz (1.9 mm) solid-state MAS probe optimized for materials research, and the new ultra-fast spinning 160 kHz (0.4 mm) HCN solid-state MAS probe, the latest innovations in solid-state NMR for the study of biological systems. These tests confirmed the applicability of the 1.3 GHz NMR first-of-a-kind spectrometer, yielding high-resolution liquids and solids NMR spectra at 1.3 GHz. The results demonstrated increased resolution and sensitivity, highlighting the potential for groundbreaking biomolecular and materials research.
The increased magnet field strength particularly benefits spectroscopy of bio-macromolecules lacking dispersion, such as carbohydrates, glycoproteins, RNA, and intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) without secondary and tertiary structures. Direct 13 C and 15 N detection of IDPs shows the gain of 1.3 GHz sensitivity, offering new strategies to obtain atomic resolution with respect to dynamics and function. In solid state, UHF NMR is crucial for studying quadrupolar nuclei, where the increased field leads to narrower spectral lines due to the inverse relationship between the breadth of the quadrupolar pattern and the field strength. Additionally, the chemical shift interaction grows linearly with the field, enhancing the ability to measure chemical shift tensors using UHF systems. These technological advancements are driving exciting breakthroughs in both material science and biological science.
"Achieving 1.3 GHz is yet another testament to Bruker's commitment to innovation," said Dr. Falko Busse, President of the Bruker BioSpin Group. "We are confident that our high-resolution GHz-class NMRs enable researchers to advance their scientific understanding of complex biomolecular systems, and also provide substantial benefits for advanced materials science research, particularly in molecules and materials incorporating chemical elements with quadrupolar and low-gamma nuclei."
"We are thrilled to be among the first scientists to experiment with the 1.3 GHz NMR spectrometer," said Dr. Takanori Kigawa from the Center for Integrative Medical Sciences of the RIKEN Yokohama Institute, Japan, a leading researcher in structural biology. "The gain in resolution and sensitivity is truly remarkable. We were blown away by the level of detail we observe in our protein and nucleic acid samples, which opens up new opportunities for our research in biological systems.”
Dr. Pierre Florian, materials science researcher at CEMHTI-CNRS Orléans, France, who ran solid-state samples for characterization, stated: "I am very impressed with the first experiments carried out on the 1.3 GHz spectrometer. This technology dramatically improves our ability to resolve different types of atomic environments in complex materials and also offers unprecedented sensitivity."
About Bruker Corporation – Leader of the Post-Genomic Era (Nasdaq: BRKR)
Bruker is enabling scientists and engineers to make breakthrough post-genomic discoveries and develop new applications that improve the quality of human life. Bruker’s high performance scientific instruments and high value analytical and diagnostic solutions enable scientists to explore life and materials at molecular, cellular, and microscopic levels. In close cooperation with our customers, Bruker is enabling innovation, improved productivity, and customer success in post-genomic life science molecular and cell biology research, in applied and biopharma applications, in microscopy and nanoanalysis, as well as in industrial and cleantech research, and next-gen semiconductor metrology in support of AI. Bruker offers differentiated, high-value life science and diagnostics systems and solutions in preclinical imaging, clinical phenomics research, proteomics and multiomics, spatial and single-cell biology, functional structural and condensate biology, as well as in clinical microbiology and molecular diagnostics. For more information, please visit www.bruker.com.

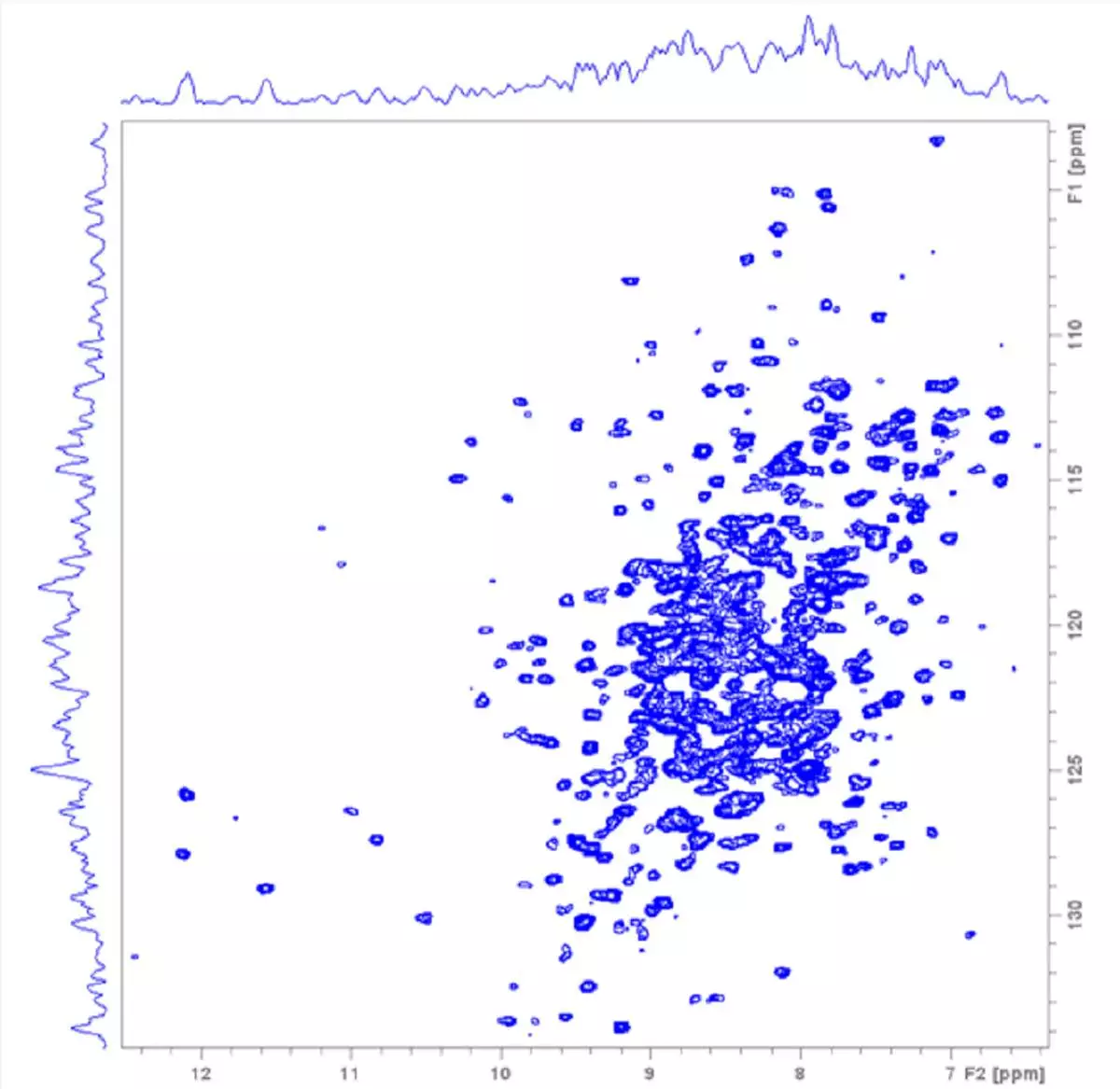
1.3 GHz 2D solids NMR: Ultra-Fast MAS 160 kHz solid-state NMR of tryptophan synthase (2 x 72 kDa), one of the largest enzymes studied by solid-state NMR. This 1.3 GHz spectrum was achieved with the integration of two groundbreaking technologies, namely ultra-high field NMR at 1.3 GHz, combined with ultra-fast magic angle spinning (MAS) at 160 kHz.
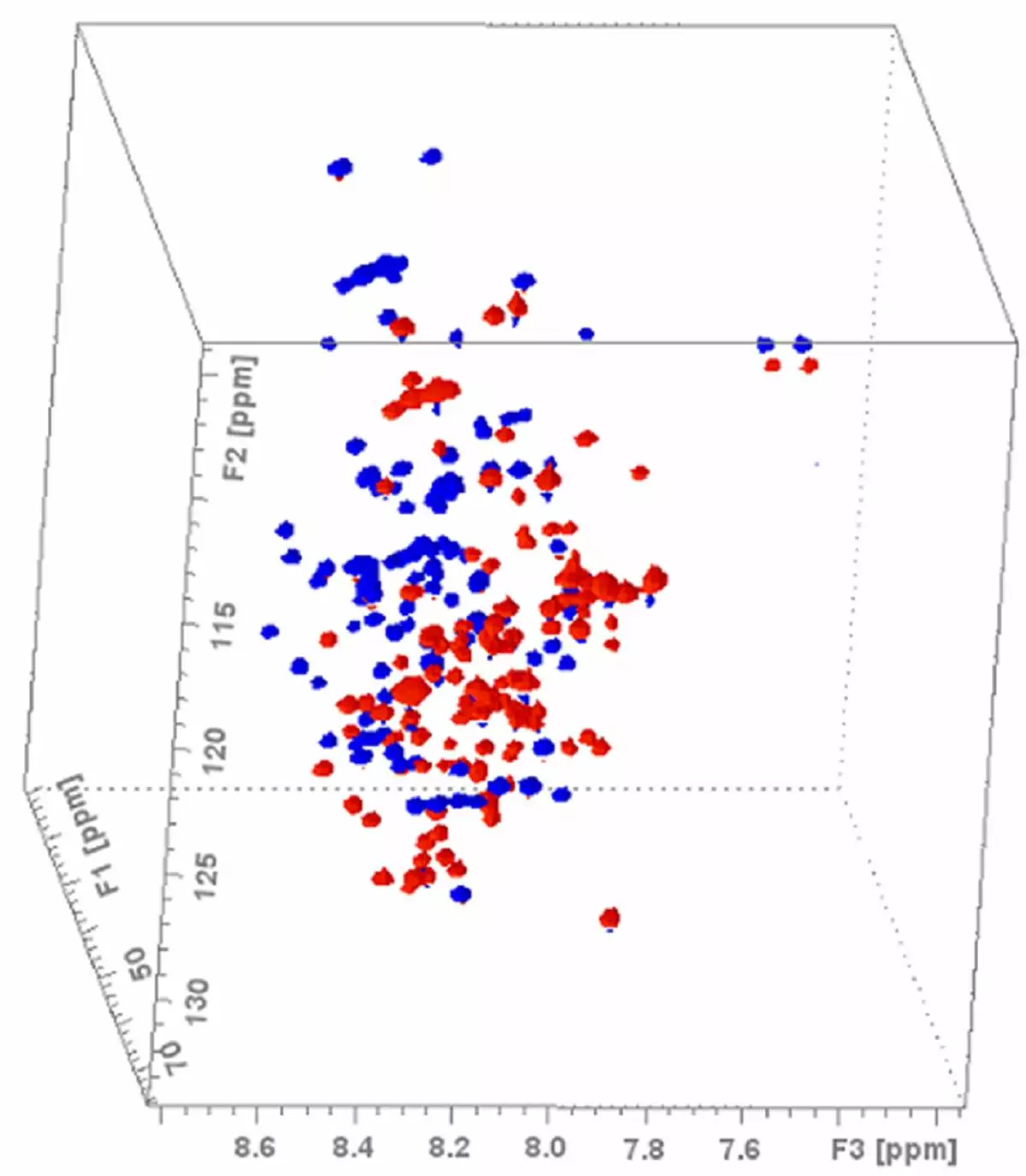
1.3 GHz 3D liquids NMR: BEST TROSY HN(CO)CaCb correlation of a-synuclein recorded with a 1.3 GHz 5mm TXO liquids CryoProbe. Sample courtesy of CERM, Florence, Italy.

The 1.3 GHz first-of-a-kind high-resolution UHF NMR spectrometer in Bruker’s UHF facility in Fällanden, Switzerland