RALEIGH, N.C. (AP) — North Carolina's Supreme Court temporarily halted enforcement on Monday of an appeals court decision that favored a Republican candidate in a close and unresolved November election for a seat on the state's highest court.
In a pair of one-sentence statements without objections, the Supreme Court issued a temporary stay of Friday's order by a Court of Appeals panel that in part directed election workers to identify and contact potentially tens of thousands of voters whose ballots were challenged by Republican candidate Jefferson Griffin.
The stay, which was sought in part by Justice Allison Riggs — the Democratic incumbent in the race — is in place while the Supreme Court determines whether it wants to formally review the Court of Appeals decision and or decide if it was correct.
Two of three judges on the panel declared that the State Board of Elections wrongly dismissed in December protests filed by Griffin challenging over 65,000 ballots counted in the race. Riggs leads Griffin by 734 votes after two recounts of the over 5.5 million ballots cast in the election.
Friday's decision, if ultimately upheld, could flip to Griffin the outcome of the election — the nation’s only 2024 race that is still undecided.
Griffin is currently a Court of Appeals judge but recused himself from any deliberations in his election case. Riggs also has recused herself from deliberations in the case at the Supreme Court, including on Monday's orders.
In the prevailing opinion backed by the two Republican judges on the panel, the Court of Appeals found that ballots within three categories contained in Griffin’s protests were wrongly allowed in the tally. But the judges said election officials must give voters who cast ballots in the race that fall within two of the categories a three-week period to provide additional information. Their ballots would count if the information is provided in time and verified.
Without Monday's temporary stay, election workers would have had to start the vote “curing” process on Tuesday.
Lawyers for the state elections board and Riggs opposed Friday's ruling, saying the votes were lawfully cast based on the rules in place for the November election and should remain in the tally.
Riggs attorney Ray Bennett wrote in a motion seeking the stay that it's "impossible to predict the full scope of confusion” of carrying out an unprecedented curing process before the Supreme Court rules on the case, especially since it ”will be inadequate to prevent the disenfranchisement of thousands of North Carolina voters."
Five of the six remaining justices on the Supreme Court are registered Republicans. Lawyers for Riggs and the board have signaled they will take the matter to federal court if necessary.
One category of ballots that would be subject to the curing process involves those cast by individuals whose voter registration records lacked a driver’s license number or last four digits of a Social Security number. The other category covers military or overseas voters who did not provide copies of photo identification or ID exception forms.
However, the prevailing Court of Appeals opinion said people within the third category — potentially hundreds of overseas voters who have never lived in the U.S. — were ineligible based on state residency laws to cast ballots and their choices could not count.
Griffin did not oppose the temporary stay issued Monday but is against efforts to halt enforcement of the Court of Appeals decision while the Supreme Court reviews the case and the appeal is resolved, according to motions filed by Riggs and the board.
Griffin's protests “have been vindicated and the people of our state deserve to see this important election finalized with every legal vote counted,” state Republican Party Chairman Jason Simmons said in a press release before Monday’s stay was issued.

FILE - Judge Jefferson Griffin, the Republican candidate for the N.C. Supreme Court listens to testimony in Wake County Superior Court on Friday, February 7, 2025 in Raleigh, N.C. (Robert Willett/The News & Observer via AP, File)

FILE - North Carolina Gov. Roy Cooper, right, appoints State Court of Appeals Judge Allison Riggs, left, to the North Carolina Supreme Court to fill a vacancy, Monday, Sept. 11, 2023, at the Executive Mansion in Raleigh, N.C. (AP Photo/Hannah Schoenbaum, File)
ATLANTA (AP) — The U.S. House on Thursday approved legislation requiring documentary proof of U.S. citizenship for anyone registering to vote, something voting rights group have warned could disenfranchise millions of Americans.
The requirement has been a top election-related priority for President Donald Trump and House Republicans, who argue it's needed to eliminate instances of noncitizen voting, which is already rare and, as numerous state cases have shown, is typically a mistake rather than part of a coordinated attempt to subvert an election. It's already illegal under federal law for people who are not U.S. citizens to cast ballots and can lead to felony charges and deportation.
The bill, known as the Safeguard American Voter Eligibility Act, or the SAVE Act, now heads to the Senate, where its fate is uncertain because Republicans don't have a large enough majority to avoid a filibuster.
Here’s a look at key issues in the debate over a proof of citizenship requirement for voting:
If it eventually becomes the law, the SAVE Act would take effect immediately and apply to all voter registration applications.
“This has no impact on individuals that are currently registered to vote,” said Rep. Bryan Steil, a Wisconsin Republican who has been advocating for the bill.
Voting rights groups say there is more to the story. The law would affect voters who already are registered if they move, change their name or otherwise need to update their registration. That was acknowledged to some extent by the bill’s author, Republican Rep. Chip Roy of Texas, during a recent hearing on the legislation.
“The idea here is that for individuals to be able to continue to vote if they are registered,” Roy said. “If they have an intervening event or if the states want to clean the rolls, people would come forward to register to demonstrate their citizenship so we could convert our system over some reasonable time to a citizenship-based registration system.”
The SAVE Act compels states to reject any voter registration application in which the applicant has not presented “documentary proof of United States citizenship."
Among the acceptable documents for demonstrating proof of citizenship are:
— A REAL ID-compliant driver’s license that “indicates the applicant is a citizen.”
— A valid U.S. passport.
— A military ID card with a military record of service that lists the applicant’s birthplace as in the U.S.
— A valid government-issued photo ID that shows the applicant’s birthplace was in the U.S.
— A valid government-issued photo ID presented with a document such as a certified birth certificate that shows the birthplace was in the U.S.
In general, driver’s licenses do not list a birthplace or indicate that the card holder is a citizen – even many that are REAL ID-compliant.
REAL ID was passed by Congress in 2005 to set minimum standards for IDs such as driver’s licenses and requires applicants to provide a Social Security number and demonstrate lawful status either as a citizen or legal resident.
After years of delays, any driver’s license used for identification to pass through airport security will have to be REAL ID-compliant beginning May 7. U.S. passports will still be acceptable.
Although states designate REAL ID compliance on driver’s licenses with a marking such as a gold or black star, that alone would not indicate U.S. citizenship. People who are legal residents but not citizens also can obtain a REAL ID.
States are currently not required to label IDs with a “citizen” mark, although a handful of states (Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Vermont and Washington) offer a citizen-only REAL ID alternative that might meet SAVE Act requirements. Republicans say they hope more states will move in the direction of IDs that indicate citizenship.
“The structure is put in place now to -- I think there’s at least five states that do have the citizenship status as part of the REAL ID -- encourage more states to do so,” Roy said. “That would be part of the goal here.”
Adoption of REAL ID has been slow. As of January 2024, about 56% of driver’s licenses and IDs in the U.S. were REAL ID-compliant, according to data collected by the Department of Homeland Security.
Voting rights group say the list of documents doesn’t consider the realities facing millions of Americans who do not have easy access to their birth certificates and the roughly half who do not have a U.S. passport.
They also worry about additional hurdles for women whose birth certificates don’t match their current IDs because they changed their name after getting married. There were examples of this during local elections last month in New Hampshire, which recently implemented a proof of citizenship requirement for voting.
Republicans say there is a provision in the SAVE Act that directs states to develop a process for accepting supplemental documents such as a marriage certificate, which could establish the connection between a birth certificate and a government-issued ID.
They argue the process is similar to obtaining a U.S. passport or REAL ID-compliant driver’s license.
“We have mechanisms giving the state fairly significant deference to make determinations as to how to structure the situation where an individual does have a name change,” Roy said. “The process is specifically contemplated in this legislation.”
Democrats counter that the bill should have specified how this was to be done, rather than creating the potential to have 50 different rules.
The legislation says applicants who submit the federal voter registration form by mail must present documentary proof of U.S. citizenship in person to their local election office under a deadline set by their state.
Voting rights groups have noted this would be a huge barrier for people who live in more rural parts of the country, where the nearest election office might be hours away by car.
The SAVE Act directs states, in consultation with the U.S. Election Assistance Commission, to ensure that “reasonable accommodations” are made to allow individuals with disabilities who submit the form to provide proof of citizenship to their election official.
The legislation also considers that some states permit same-day voter registration and says, in those cases, voters must present proof of citizenship at their polling location “not later than the date of the election.”
That would mean that people who do not have such proof with them would have to return with their documents before polls close to be registered and have their ballot counted.
It’s less clear what this means for those states that have online voter registration systems or automatic voter registration set up through their state’s motor vehicle agency. Democratic state election officials have raised concerns that the legislation means these processes would no longer be operational under the proposal.
The legislation says anyone registering through a state motor vehicle agency also is required to provide proof of citizenship. It directs the Election Assistance Commission to issue guidance to state election officials about implementing the law’s requirements.
Republicans say any instance of voting by noncitizens, no matter how rare, is unacceptable and undermines confidence in U.S. elections.
Democrats respond by saying that voting by noncitizens is already illegal in federal elections —those for president and Congress — and penalties can result in fines and deportation. They say Congress should be more focused on helping states improve their ability to identify and remove any noncitizens who might end up on voter lists instead of forcing everyone to prove citizenship beforehand.
A recent review in Michigan identified 15 people who appear to be noncitizens who voted in the 2024 general election, out of more than 5.7 million ballots cast in the state. Of those, 13 were referred to the attorney general for potential criminal charges. One involved a voter who has since died, and the final case remains under investigation.
“Our careful review confirms what we already knew – that this illegal activity is very rare,” Michigan Secretary of State Jocelyn Benson said in a statement. “While we take all violations of election law very seriously, this tiny fraction of potential cases in Michigan and at the national level do not justify recent efforts to pass laws we know would block tens of thousands of Michigan citizens from voting in future elections."
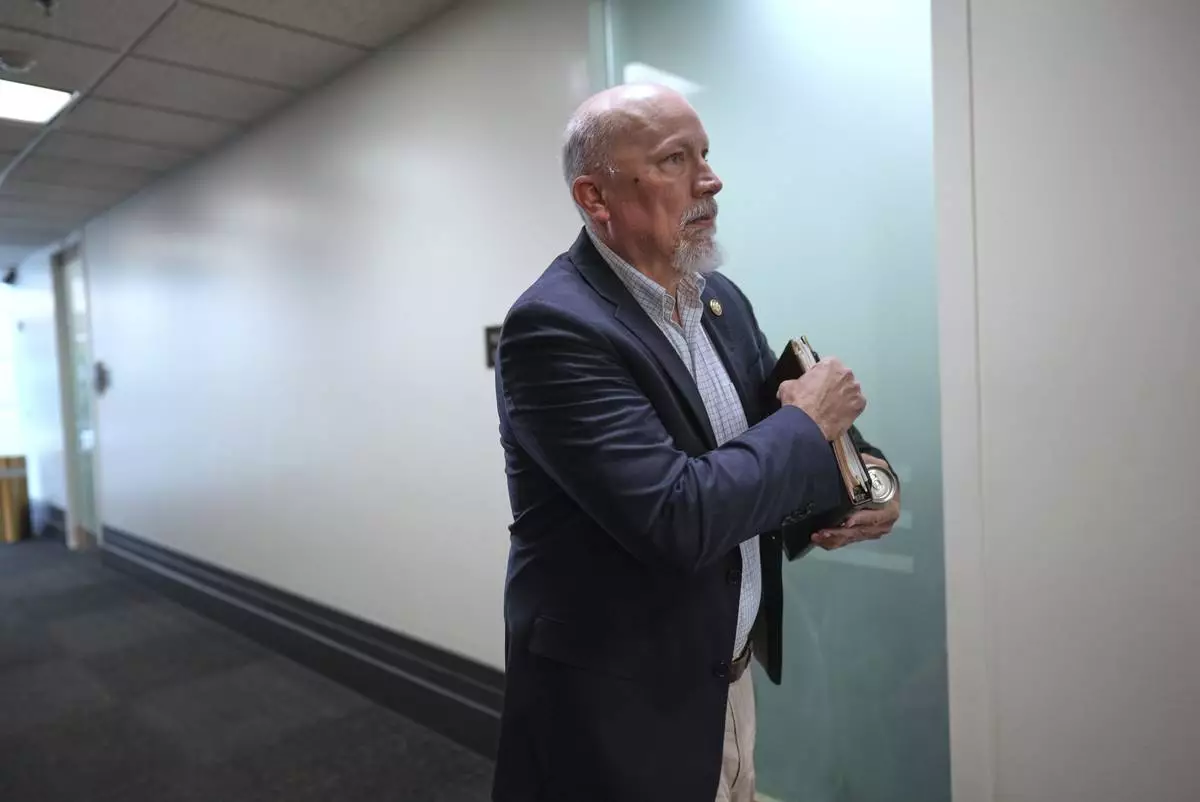

Rep. Chip Roy, R-Texas, a member of the conservative House Freedom Caucus, walks outside of the closed-door House Republican Conference as Speaker of the House Mike Johnson, R-La., talks to fellow Republicans to push for a House-Senate compromise budget resolution to advance President Donald Trump's agenda, at the Capitol in Washington, Tuesday, April 8, 2025. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)