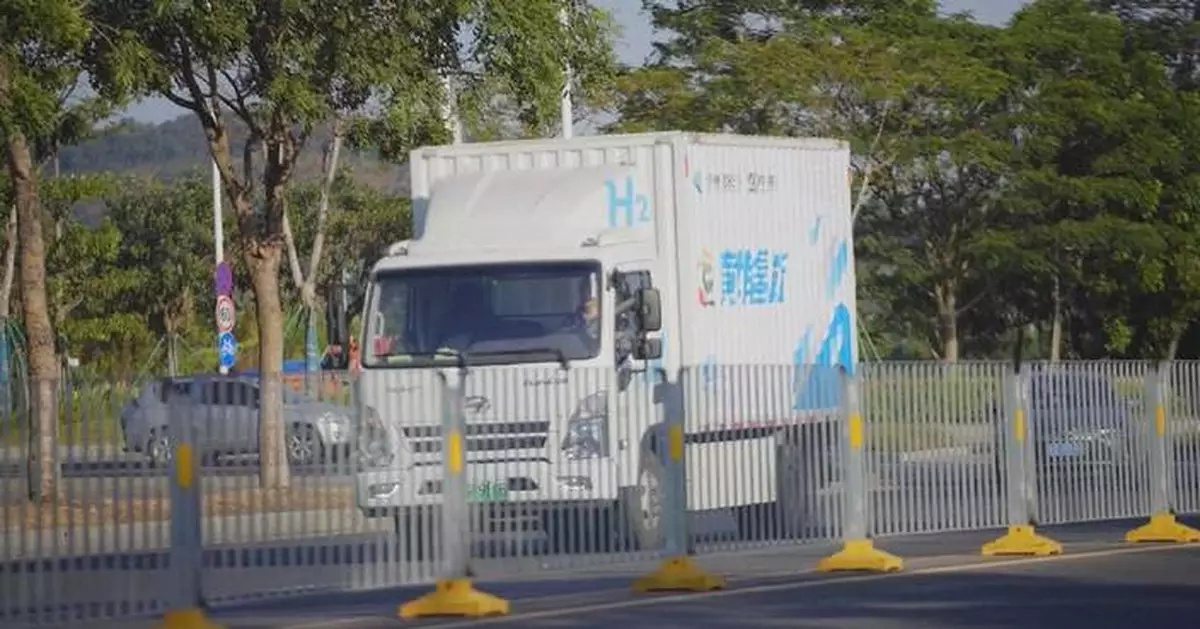
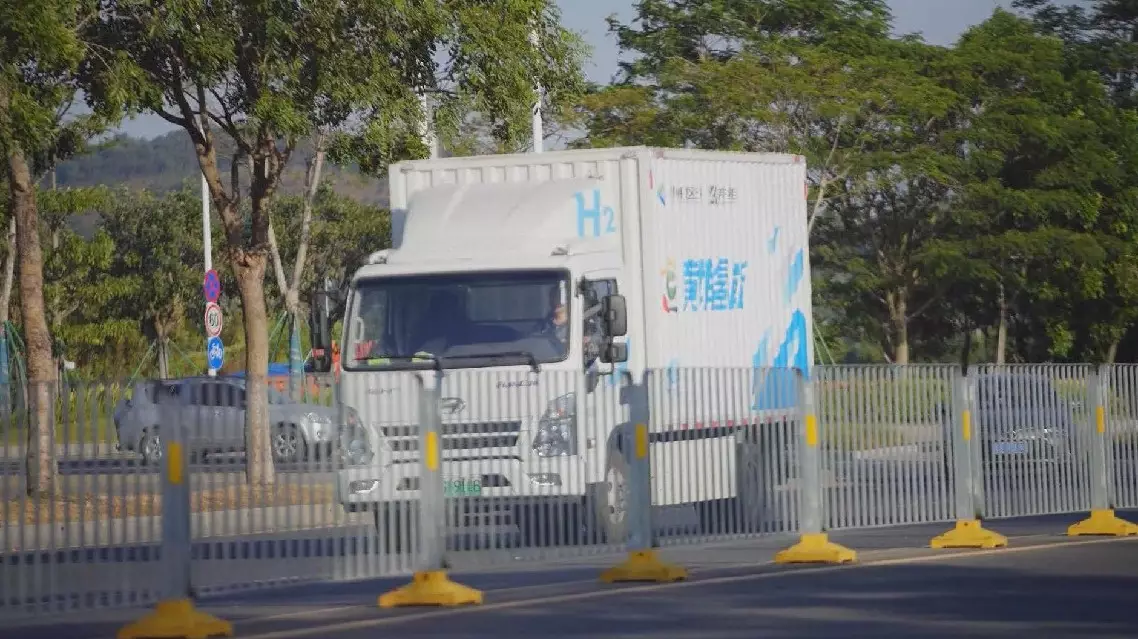
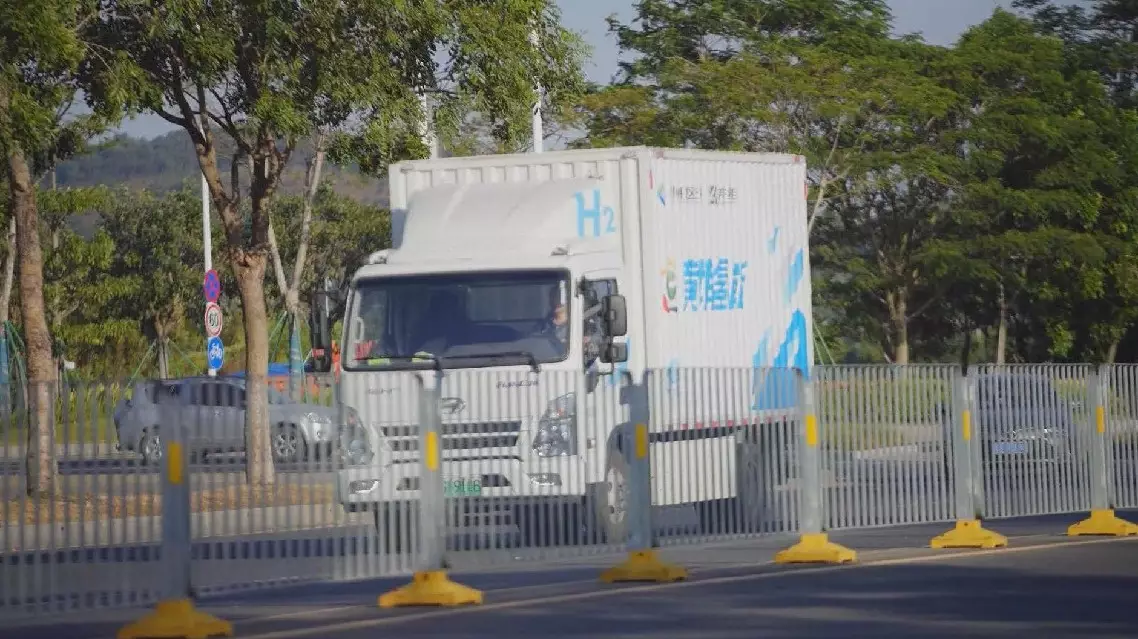
China's fuel-cell vehicle fleet is expected to grow to 1 million by 2035 as the country is setting sight on wider commercial use of the green means of transportation.
The growth should be boosted by more stable and more expansive hydrogen supply as well as wider use of hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles in various business models, said industry insiders.
China should have more hydrogen fueling stations and their utilization rate should be higher, analysts said, adding that companies should also be encouraged to deploy more hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles in their businesses, like those for ride-hailing and taxi services.
The growth in the green means of transportation can in turn encourage an eco-friendlier lifestyle and improve the country's transportation system, said Zhang Yanyi, director of the fuel cell division of the new energy test center under the China Automotive Technology and Research Center.
"This (the increase in hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles) means that the strategic emerging industry of hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles obtains a milestone achievement, which is conducive to promoting green travel models and building a low-carbon transportation system," Zhang said.
China has already taken concrete steps to expand the commercial use of hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles over the past few years.
Over 140 such vehicles have already been deployed in Guangzhou, the capital of south China's Guangdong Province, for sanitary and logistic use.
In Shanghai, auto giant SAIC Motor has been piloting large-scale hydrogen fuel-cell vehicle use since 2022.
Similar pilot programs are also taking place in north China.
A mine in Xilingol League of north China's Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region is testing a heavy-duty loader powered by 36 hydrogen tanks.
The vehicle, driven by both hydrogen and electricity, can help cut more than 1,000 metric tonnes of carbon emissions a year. "The transporter can work better in open mines in north China, where winter is longer and extreme cold conditions are more frequent. Hydrogen fuel cells can work stably in cold, windy and snowy days to ensure consistent supply of energy. A hydrogen fuel-cell vehicle emits only water vapor while running and it is capable of working intensely for 20 hours non-stop a day," said Liu Xi, director of the Shengli Energy Electromechanical Information Center of the China Energy Group.

China's hydrogen fuel-cell vehicle fleet expected to grow to 1 miln by 2035

China's hydrogen fuel-cell vehicle fleet expected to grow to 1 miln by 2035