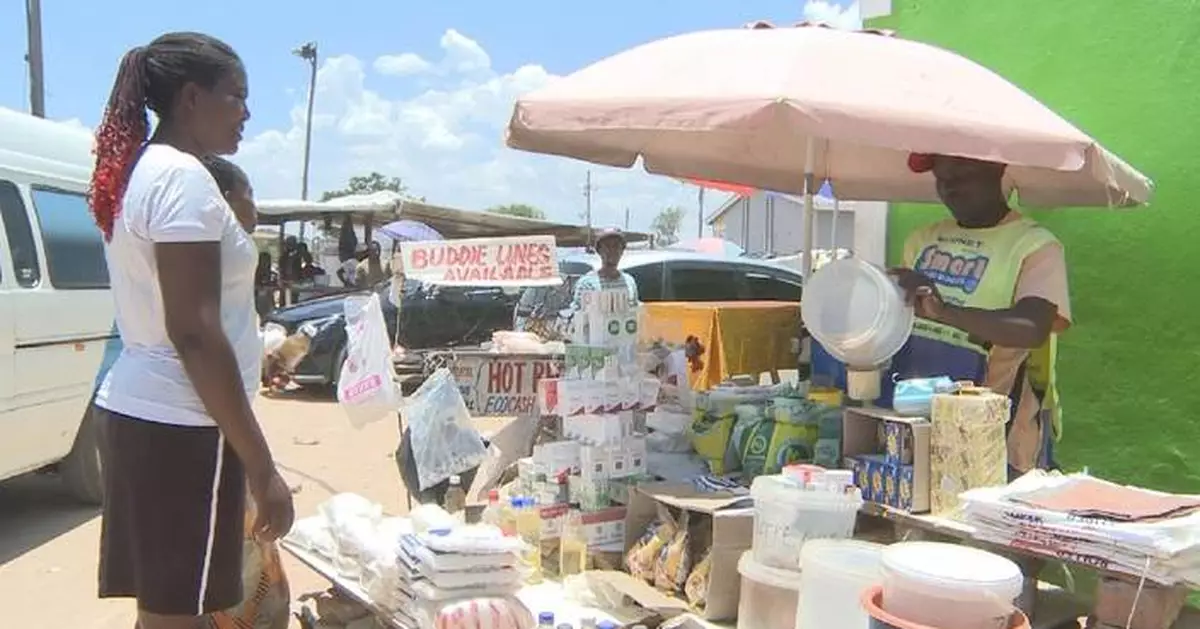
Millions of Zimbabweans continue to face food insecurity, a pressing challenge that officials blame on an El Nino-induced drought and the resulting economic slowdown.
According to the Zimbabwe Livelihoods Vulnerability Assessment released in May, about 7.7 million people in the country cannot provide enough food for themselves due to massive crop failure. The majority are in rural areas. (https://stateofthenation.co.zw/2024/05/15/drought-puts-7-7-million-zimbabweans-in-need-of-food-assistance/)
However, the hardships are not restricted to the countryside, as many families in cities are cutting back on meals and sinking into debt.
In Epworth, a high-density settlement in Harare, resident Maria Matiringe is finding it harder to get by.
"I do piece jobs as a domestic worker, but right now, no one has any extra money to pay me because things are tight due to the drought. My income has gone down when prices of most foodstuffs are going up," she said.
Matiringe has reduced the number of meals she cooks at home to one and now spends money on bare essentials, re-packed into smaller quantities.
Women and children in urban and rural areas bear the brunt of the drought.
Donors are working with authorities to sink irrigation boreholes in an effort to improve food production during dry seasons. They are also focusing on enabling communities to bounce back next season.
"People who did not harvest anything last year have no seeds to plant. They may have sold off their cattle, their goats and all, so to avoid a repeat situation next year where people did not plant enough because they didn't have seed or are not able to rely on their livestock, we need to look at ways of recovery activities. But for that harvest to happen, we need seeds, we need fertilizers, we need to work with these rural communities to enable them to restart," said Walter Mwasaa, Acting Country Director at Care International.

Continued food insecurity impacts millions of Zimbabweans

Continued food insecurity impacts millions of Zimbabweans
A 25 percent import tariff on all foreign-built vehicles entering the United States has raised serious concerns for manufacturers in South Africa.
Automotive giants like Mercedes and BMW have long used South Africa as a base for global exports -- but those plans may be shifting into reverse gear after the U.S. announced the punitive measures.
"If you take, for example, BMW, 97 percent of the X3 that we are producing in Rosslyn is exported out of the country. We only sell 3 percent in South Africa, and there's a huge number of those vehicles that also go into the U.S. So there are companies in South Africa that are purely here not because they are selling vehicles in South Africa; they are here to produce vehicles for the global market, and it's important for them to remain globally competitive," said Mike Mabasa, CEO of the National Association of Automobile Manufacturers of South Africa.
U.S. automaker Ford, which has deep roots in South Africa, is also in the crosshairs.
The company recently invested over 300 million U.S. dollars to upgrade its Silverton plant in Pretoria, South Africa, for the production of the world's only plug-in hybrid Ranger, which has just entered production but could face delays or restrictions.
"If an American citizen wants to buy specifically a Ford Ranger that is a plug-in hybrid, they can only place an order in South Africa, nowhere else in the world. So, that means, obviously, the capacity of Ford to be able to produce those vehicles in big volumes is going to be constrained, because Americans are going be looking at another Ford that is produced in another country, or even in the United States," said Mabasa.
South Africa has long enjoyed duty-free automotive exports to the U.S. under the African Growth and Opportunity Act, but that relationship now hangs in the balance.
A sharp shift in U.S. foreign policy threatens to derail an industry that employs thousands and contributes around 5 percent to the country's economy.
"We produce less than 1 percent of global automotive vehicles, so to say. So, in reality, the impact on us is likely to be more disproportionate than those of our peers that produce at the same level. And the risk is actually created -- a concentration risk -- in countries that have greater capacity and are building more; in those countries will be able to absorb some of this," said Parks Tau, South Africa's minister of trade and industry.
Amid growing concerns about overreliance on the U.S. market, Amith Singh, national manager for manufacturing at Nedbank Commercial Bank, emphasized the importance of tapping into regional trade opportunities.
"I think we need to make better use of some of our local agreements, our African continental agreements. How do we leverage that? How do we partner with the government and private sector to start benefiting the countries and the economies aside from the United States? So, those could be the catalyst to drive our localization projects; it could be what we need to drive the African economy as opposed to being completely reliant on the States (United States)," he said.
South Africa is for now standing firm in its decision not to retaliate against steep U.S. import tariffs, set to take effect in just a few days.
Officials in Pretoria acknowledge the challenges posed by the current U.S. administration but are pursuing a diplomatic approach in hopes of maintaining stable relations and preserving the African Growth and Opportunity Act.
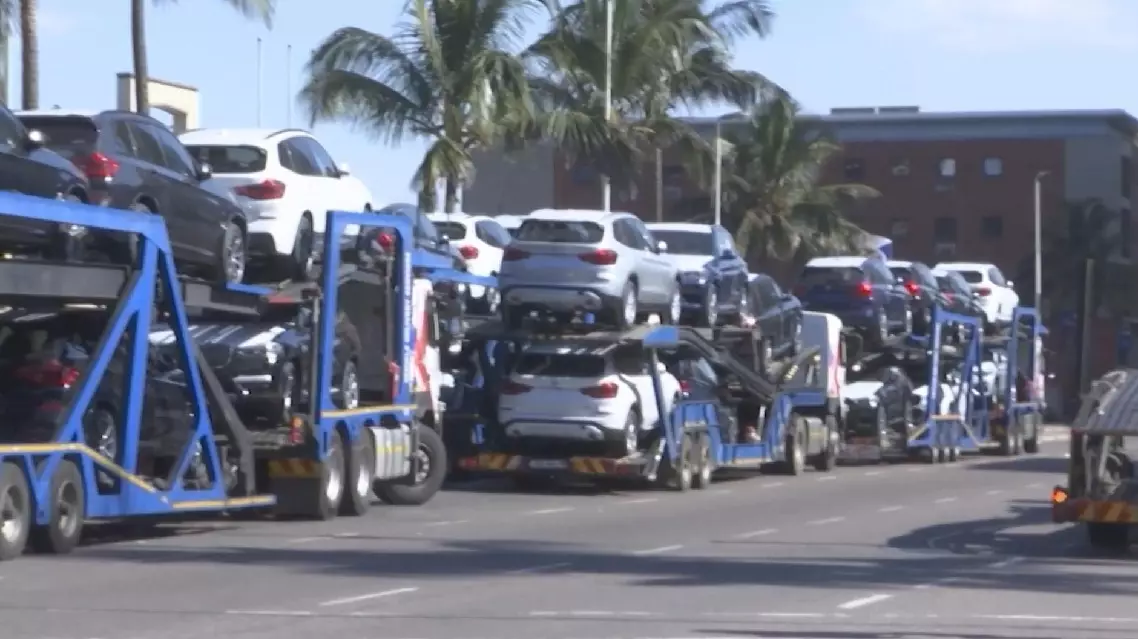

US tariffs rock South Africa’s auto industry